Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02898976 2015-07-30
BELOW SLAB GAS REMOVAL AND SUMP SYSTEM
TECHNICAL FIELD
[0001] Building construction.
BACKGROUND
[0002] Radon gas has been identified as a hazardous material that occurs
naturally
within the ground and that may enter buildings through their foundations due
to buildup of
radon gas pressure. Some building codes, such as the National Building Code of
Canada,
require that in new building construction measures be taken to prevent radon
from entering
the envelope of a building. When constructing a new home, builders may use a
range of
approaches, including installing an air barrier under the foundation slab and
an air tight cover
for the sump pit to prevent the entry of radon, and a rough-in for a possible
future subfloor
depressurization system, should radon problems emerge. To reduce radon gas
pressure
under a foundation slab, a published recommendation suggests a vent extending
upward
through the centre of the slab from below to above the slab, such a vent being
connected to a
pipe that extends laterally below the slab, or a pipe that extends from the
centre of the slab
underneath the slab to a vent elsewhere. In each case, radon gas pressure is
thereby reduced
under the slab.
SUMMARY
[0003] In an embodiment, there is provided a radon removal system for a
building,
where the building has a slab forming part of a foundation of the building.
The system
includes a perforated pipe, for example that is perforated, the pipe extending
under the slab,
the perforated pipe being connected to a vent through a sealed system with a
blower for
generating a negative pressure in the pipe. The blower may be situated within
a pipe that
provides the vent.
[0004] In an embodiment, there is provided a radon removal system
comprising a
pipe connected to a vent through a sealed system having a blower for
generating a negative
CA 02898976 2015-07-30
pressure in the pipe, the sealed system comprising a sump having an inlet for
water and a
sump pump connected to a water outlet
[0005] In various embodiments, there may be included any one or more of
the
following features: the pipe being perforated, the pipe extends under the
foundation to a
central area of the foundation; the sealed system comprises a sump; the sump
comprising a
water inlet, sump pump and water outlet; the sump having an interior and
window for
allowing viewing of the interior of the sump; the sump comprising a neck that
may be
embedded in concrete with a gasket around the neck between the neck and the
concrete; the
pipe comprising weeping tile; and the pipe comprising hard plastic.
[0006] These and other aspects of the device and method are set out in the
claims,
which are incorporated here by reference.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FIGURES
[0007] Embodiments will now be described with reference to the figures, in
which
like reference characters denote like elements, by way of example, and in
which:
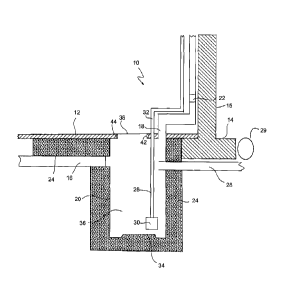
[0008] Fig. I is a section through a radon removal system showing a sump
with
pump and vent system, wherein the sump provides a sealed unit for evacuating
radon from
underneath a slab and venting the gas to atmosphere; and
[0009] Fig. 2 is a top view of the sump with the ground broken away to
show an inlet
perforated pipe for drawing radon gas from under the foundation, as well as
the inlet water
pipe for drawing water into the sump from the weeping tile normally found
around a
foundation.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
[0010] Immaterial modifications may be made to the embodiments described
here
without departing from what is covered by the claims. In the claims, the word
"comprising"
is used in its inclusive sense and does not exclude other elements being
present. The
indefinite articles "a" and "an" before a claim feature do not exclude more
than one of the
feature being present. Each one of the individual features described here may
be used in one
2
CA 02898976 2015-07-30
or more embodiments and is not, by virtue only of being described here, to be
construed as
essential to all embodiments as defined by the claims.
[0011] As shown in Fig. 1, a radon removal system 10 is provided and
works in
conjunction with a slab 12 forming part of a foundation of a building that
includes a footing
14 and wall 15. The slab 12, footing 14 and wall 15 are all conventional and
may have
various configurations depending on the building structure. in an embodiment,
a pipe 16,
such as a perforated PVC pipe, extends under the slab 12, to the center of the
slab 12, or such
other location as permitted by local building regulations. A sealed container
20 is provided
under the slab 12 or in another suitable location. For example, the sealed
container 20 may
be provided outside of the foundation or within the building. The pipe 16 is
connected via a
sealed connection to the container 20. A vent or vent line 18 is provided for
the sealed
container 20 that extends to the roof of the building or other suitable
location for the disposal
of radon gas. A blower or fan 22 is piovided inline in the vent line 18 to
provide a negative
pressure on the interior of the container 20. Operation of the blower or fan
22 draws gas
from the pipe 16 into the sealed container 20 and up into the vent 18.
Depending on the
strength of the blower 22, the container 20 and the related system components
need only be
sufficiently sealed to allow the system to function, and this is what is meant
by sealed. A
functioning system draws gas from under the slab and vents to a safe place,
such as to the
exterior of the building from a roof of the building. The blower or fan 22 may
be any of
various commercially available fans.
[0012] The perforated pipe 16 thus connects to the vent 18 through a
sealed system
to the blower 22 for generating a negative pressure in the perforated pipe 16.
The vent 18
may be a pipe such as a PVC pipe. Radon gas may be collected in the perforated
pipe 16 and
be pulled by the negative pressure from the blower 22 through the sealed
system 2 to the
vent 18, to release the radon gas outside the building. The radon gas may be
released through
= the roof of the building.
[0013] The perforated pipe 16 may extend under the foundation 14 to a
central area
of the foundation 14 for the collection of radon gas. Permeable material 24,
for example
washed rock of a type and thickness depending on local code requirements, may
underlay the
slab 12 and provide a path for radon gas to reach the pipe 16. Permeable
material 24 may
3
CA 02898976 2015-07-30
also surround the sealed system 20 and lie beneath the entire floor of the
building. The
perforated pipe 16 may comprise for example weeping tile or hard plastic, such
as PVC.
Hard here means sufficiently hard that in normal use the plastic retains its
shape, for example
when the pipe is made of PVC. In another embodiment, the pipe 16 is not
perforated, but is
sealed and extends to underneath the center of the slab.
[0014] The container or sealed system 20 may comprise a sump 26, provided
under
or above the slab 12. The sump may comprise a water inlet 28 connected to a
suitable fitting
on the sump, sump pump 30 and water outlet 32. The water inlet 28 may be for
example a
tee pipe 28 which leads out to weeping tile 29, or other water collection
material permitted
by local code requirements. Water collecting around the foundation flows into
weeping tile
29, and then flows into the tee 28 and into the container 20, where it
collects on the bottom
of the sump 26. The water outlet 32 may be a pipe which extends from the sump
pump 30
through the floor of the building. Depending on the local code requirements,
the outlet 32
may dispose of water outside onto or into ground surrounding the building or
into a
municipal water disposal system. The container 20 may have a raised bottom 34.
The sump
26 may operate in the normal manner of a sump, such that the pump 30
periodically turns on
to pump water out of the sump 26, for example when a high water level is
reached.
Conventional sump pumps may be used for the pump.
[0015] The sump 26 may be provided with a clear lid 38 forming a window
for
viewing the interior 36 of the sump. As shown in Fig. 2, the vent 18 for
releasing radon may
extend from the sealed system 20, and similarly the water outlet 32 for the
sump 26 may
extend from the sealed system 20, in close proximity to the viewing window 38.
An
electrical connection 40 for the pump 30 and blower 22 may also extend from
the sealed
system 20 near the window 38. The pump 30 and blower 22 may be connected via
the
electrical connection to a power source (not shown) for example the
conventional electrical
supply for the building through a conventional plug in. The fan 22 may be
allowed to run
continuously.
[0016] As shown in Fig. 1, when the container 20, here sump 26, is
provided
underneath the slab 12, the container 20 or sump 26 may comprise a neck 42
embedded in
concrete, such as for example the floor of the building, with a gasket 44
around the neck 42
4
CA 02898976 2015-07-30
and the concrete to maintain a seal between the sump 26 and slab 12 and
prevent gas from
entering the building around the container 20. If the slab 12 is made of
concrete, the neck 42
may be embedded in the slab 12. The gasket 44 may be made of rubber. Various
sizes of
components may be used. In some embodiments, the washed rock may be 100 mm
washed
rock, the pipe 16 may be 4" pipe, the tee 28 may be 4" pipe, and the vent 18
may be made
from 4" pipe, such as PVC plastic.