Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
This is a division of copending, commonly assigned
Canadian Patent Application Serial No. 488, 861 filed on August
16, 1985.
BACKGlROUND OF THE INVENTION
FILED OF THE INVENTION
This invention relates to an apparatus for assembling
two-part connectors. In particular, the invention relates to
a bandolier assembly Eor use with an apparatus for connecting
two-part multiple plug and socket connectors to a multiple core
strip cable.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PRIOR ART
It is known to provide a cable in the form of a flat
strip or ribbon in which a plurality of insulated conductors
are arranged in side by side configuration. A wide variety of
multiple plug and socket connectors are known for use with such
cable. Generally the connectors have a plurality of contacts,
one positioned to correspond with each of the conductors in a
strip cable, and connection to the strip is made by causing the
contacts to move into connection with a respective conductor
of the cable by displacing the insulating material surrounding
15335/LCM:sks
~"
12947~6
the conductor. Such connectors are known as insulation
displacement contact connectors or IDC connectors. Typically,
IDC connectors have a lower body portion that may, for example,
form a plug for cooperation with a socket, and an upper cap
portion. In the assembly of such connectors with a ribbon
cable, the cable is appropriately positioned between the upper
and lower connector portions which are subsequently brought
towards one another, this movement causing the contacts to make
connection with the conductors of the cable, by displacing
insulating material and, in a final position, to grip the cable
firmly within the connector.
Assembly of such a connector/cable arrangement is
typically an essentially manual operation which is time
consuming and unreliable. Apparatus has been proposed to
mechanise the final clamping of the connector to a cable, for
example using a pneumatic press. The use of such presses still
requires manual assembly of the connector in relation to a
cable.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
Z0 The invention according to the parent application
provides generally speaking an apparatus for assembling a pre-
assembled two-part connector with an interposed cable, which
apparatus comprises a pair of opposing, relatively movable
press elements, storage means for containing a plurality of
the connectors, means for moving a connector from the storage
means to an operative position between the pair of press
15335/LCM:sks 2
~2~'7~6
elements, means for actuating at least one of the press
elements to achieve crimping of the connector and the
interposed cable when the connector is in the operative
position and means for individually holding the respective
parts of the two-part connector and movably separating the
parts away from each other so as to facilitate entry of the
cable therebetween for subsequent crimping.
On the other hand, the present invention may be
considered as providing a bandolier assembly for use in an
apparatus for assembling a two-part electrical connector with
: an interposed cable, comprising: a plurality of electrical
connectors, each having a base and a cover, the base and the
cover being pre-assembled in a manner defining a spacing
therebetween for .interposition of an electrical cable; an
elongate bandolier supporting the plurality of pre-assembled
connectors in longitudinally spaced locations, the bandolier
comprising two longitudinally extending films, each film having
transversely spaced, longitudinal extending marginal edges, the
films at least at the location where each pre-assembled
connector is supported being transversely spaced and defining
therebetween an envelope containing each-preassembled
connector, each envelope having openings at the marginal edges
: of the film for disposing the connectors therethrough, there
being in registry with each envelope a projection extending
inwardly of one of the films into the envelope and into the
spacing between the cover and the base to maintain the spacing
until the connector is assembled with the cable.
15335/LCM:sks 3
.
7~i6
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF T~IE DRAWINGS
In order that the invention may be more readily
understood, and so that further features thereof may be
appreciated, an embodiment of an apparatus of the invention
will now be described, by way of example, with reference to the
accompanying dra~ings, in which:
Figure 1 is a perspective view of an apparatus of the
invention;
Figure 2 is a side elevation of the apparatus of Figure
10 1;
Figure 3 is an end elevation of the apparatus of Figure
2;
Figures 4a, b and c illustrate various stages in the
assembly of the connector;
Figures 5A to L illustrates schematically the operating
: faces of the apparatus;
Figures 6A to L illustrates one preferred operation and
control means for the invention, and
Figures 7 to 10 illustrate a variety of alternative
connector supply arran~ement for use with the apparatus of the
invention.
DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
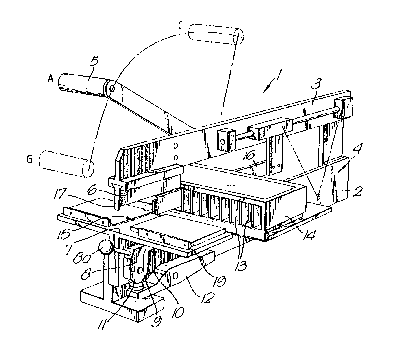
Referring to Figure 1 an apparatus embodying the
invention is generally indicated at 1. The apparatus 1
comprises a lower support member 2 and an upper press member
15335/LCM:sks
66
3. The press member 3 is held in a fixed position relative to
the support member 2. Operation of the apparatus is achieved
by actuation of a control means generally indicated 4, one form
of which will be described in detail hereinbelow. The control
means 4 includes an operating handle 5.
At a forward end, the apparatus 1 has upper and lower
press elements 6, 7 respectively. The upper press element 6
is fixedly connected to, the member 3 and projects downwardly
towards the support member 2. The lower press element 7 is
positioned at an outer upper end region of the support member
2 and defines an upwardly facing anvil Eor cooperation with the
press element 6. The lower press element 7 cooperates with
the support member 2 but is movable in a substantially vertical
direction with respect thereto from an operation position, as
shown in Figure 1, to an upper crimping position, best seen in
Figure 6G, and to a lower clearance position best seen in
Figure 6L. The relation position of the press element 7 is
controlled by a pivoting element 8 having a projection 9 that
cooperates with a support pin 10 connected to the element 7.
In its lower region, the pivoting element 8 presents a cam
surface 11 that cooperates with an arm 12 of the control means
4. The element 8 is normally maintained in an upright
position, as shown in Figure 1. The arm 12 is pivotable so
that, on appropriate movement of the control means 4, the end
of the arm 12 that cooperates with the lower region of the
element 8 is moved upwardly, causing the element 8 and thus the
press element 7 to move from the operative position to the
crimping position. The element 8 may be pivoted, using a
15335/LCM:sks 5
7~i6
handle 8a, to a second, inclined, position the cooperation
between the cam surface 11 and the arm 12 allowing the element
7 to mo~e in a downward direction to the clearance position.
A connector storage and feed mechanism is positioned
between the member~ 2 and 3 and is operative to feed connectors
13 from a magazine 14 to the ope:rative position, indicated 15,
between the press elements 6 and 7.
The connectors 13 are held within the magazine 14 in a
connected but spaced-apart arrangement that enables a ribbon
cable to be fed between the spaced apart elements before these
are clamped to achieve the desired connection. A sliding ram
16, that is operated by the control means 4, is operative to
move a selected connector 13 out from the magazine 14 into the
operative position 15. As best seen in Figure 2, a stop plate
17 projects downwardly from an outer end face of the press
element 6 to limit movement of the connector 13 and thus to
position the connector 13 for clamping in the operating region
15. When the sliding ram 16 urges a connector 13 towards and
into engagement with the end plate 17 the connector is locked
in position by cooperation between the end plates 17 and the
ram 16.
As best shown in Figure 3, the lower press element 7
compris~s support plates 18, that extend outwardly to form a
substantially T-section element. The plates 18 provide support
and guidance for a ribbon cable to be inserted between the
upper and lower parts of a connector 13 when this is in the
operative position 15, and, additionally, edge guides 19
(Figure 1) project upwardly from an upper surface of the plates
15335/LCM:sks 6
~Z94~
18 to ~acilitate correct positioning of the cable. It will be
appreciated that by appropriate positioning of the edge guides
19 and the end plate 17 correct alignment of the ribbon cable
with a connector 13 can be achieved, irrespective of the width
of the connector and cable.
Referring again to Figure 3, a lower retaining means
comprising a fixed side stop 21 and a spring biassed clamp 22,
acts to retain the lower connector body in fixed relation to
the upper cap part. Spring biassed plates 23, 24 are
positioned on the upper surface of the plates la, on either
side of the operative position 15. Wh~n a cable is in position
and the lower press element 7 is moved towards the upper press
element 6 the plates 23, 24, cooperate with depending
projections 25, 26 of the press element 6 to flatten and hold
the cable in the correct orientation.
Referring to Figures 2, 4, ~a and 4b operation of the
apparatus will be described briefly. As described in detail
later, the operation of the handle 5, causes the sliding ram
16 to move a connector 13 from the magazine 14 to the operative
position 15, where it is held by cooperation with the forward
end of the ram 16 and the depending end plate 17. This
position is indicated in the dotted lines in Figure 2. A flat
ribbon cable is then fed between the spaced apart upper and
lower portions of the connector and when this has been
appropriately positioned, the handle 5 is operated to cause the
press element 7 to move towards the press element 6 and thus
to move the upper part of the connector 13 from its insertion
level, as shown in Figure 4b, to the crimping position as shown
15335/LCM:sks 7
lZg~76~
in Figure 4a. Further operation of the handle 5 releases the
crimped connector 13 following which the press element 7 is
lowered allowing the crimped connector and cable to be removed
easily from the apparatus.
In situations where the ends of the ribbon cable are
obstructed, for example by another previously positioned
connector, and thus the cable cannot be fed through the
connector 13 in its spaced apart but connected arrangement, the
apparatus provides a further operating step to allow the two
parts of the connector t~ be separated to permit a cable to be
inserted between the respective connector parts in a transverse
direction. To achieve this operation a connector is moved into
the operative position 15 as in the previously described
operation. In this position the upper part of the connector
is held fixed by the ram 16 and the plate 17 whilst the lower
part is firmly held by the side plate 21 and spring retaining
means 2~. Prior to the crimping operation, and with the two
parts fixed as described, operation of the pivot element 8 to
move the press element 7 downwardly causes a separation o~ the
connector parts allowing insertion of the ribbon cable. When
the cable is appropriately positioned the element 8 is again
actuated to move the press element 7 back to its operative
position. It should be appreciated that as the upper and lower
parts of the connector 13 are gripped separately and the
apparatus parts are constrained to move in fixed directions,
correct alignment of the upper and lower parts will be
maintained during the separation and re-connection phases. The
15335/LCM:sks 8
lZ~'~7~
cable can be correctly aligned using the edge guides 19 and the
connector and cable can be crimped together as described above.
Figure 5 shows schematically various stages in the
operation. In position A the apparatus is in a rest position
with the sliding ram positioned between the press element 6 and
7 but with no connector in position. The various stages A to
L correspond to different movements of the handle 5 of the
control means to achieve relative movements of various elements
of the apparatus.
At B the sliding ram is moved out from between the press
elements and this is followed by indexing the connector
magazine 14 to bring a connector 13 into alignment with the
ram 16 so that forward movement of the ram, as indicated by
the arrow A, will move the ram into cooperation with a
connector 13 to move this out of the magazine and towards the
operative position 15 between the press element 6, 7. As shown
at E the ram 16 is held in its forward position to clamp the
upper part of the connector 13 in the operative position~
Continuing to F, a ribbon cable 27 is then fed between the
upper and lower parts of the connector 13. Alternatively, if
; the cable 27 (step I.) is to be fed transversely into the
connector 13 the lower press element 7 is moved downwardly, as
described above, to separate the connector elements and allow
insertion of the cable 27. The handle t S then moved towards
position G in which the connector parts are crimped together
to form the connector/cable assembly. As indicated at G1,
movement of the press elements towards each other causes the
plates 23, 24 to engage with shoulders Z5, 26 of the element
15335/LCM:sks g
129~7~6
6 thus flattening the cable before crimping occurs. This
ensures correct alignment oE respective conductors with a
corresponding contact. The lower press element 7 is then moved
downwardly whilst the assembled connector is held in position
by the cooperation of the ram 16 and the front plate 17 (step
H) and subsequent rearward movement of the ram 16 allows the
assembled connector/cable to be removed from the apparatus.
Figure 6A and 6B shows in detail one convenient form of
control means 4. Referring firstly to Figure 6A, the control
means 4 comprises the handle element 5 that is connected to a
crank 28 by a suitable slipping friction clutch. Connected to
a crank 28, to control movement thereof, is a spring biassed
lever 29, that is connected at its outer end to the upper
member 3 by a spring 30. The connecting rod 31 connects the
crank 28 with one end of the pivoting rod 12, the other end of
which cooperates with the element 8, to achieve the desired
movement of the press element 7. The rod 12 is pivotally
connected with the lower support member 2 by a pivot 32.
A swivel plate 33, that is substantially triangular in
shape, is rotatably mounted towards the rear of the support
member 2, a pin 34 being provided to limit the carrier movement
of the plate 33. The drive element 35 connects the plate 33
with the sliding ram 16, the drive element 35 being pivotally
connected to the plate 33 at one end, and having at its other
end a slot that receives a pin projecting downwardly of the
sliding ram 16. A spring pawl 36 cooperates with the lower end
of the drive element 35 to control movement thereof. For this
purpose, the lower end of the drive element is profiled to
15335/LCM:sks 10
76~
present a cam surface 37 that cooperates with the spring pawl
36 to achieve control movement of the sliding ram 16 upon
rotation of the plate 33. The plate 33 is connected to the
handle element 5 by a connecting rod 38. The connecting rod
38 is pivotally connected at one end ko the plate 33 and has
a slot 39 towards its other end that receives a pin that
projects it from an extension of the handle element 5, the pin
40 being urged towards the top of the stop 39 by a spring 41.
Connec~ing means (not shown) are also provided between
the control means 4 and an indexing mechanism for the magazine
14 so that appropriate movement of the handle 5 causes first
a magazine pawl 42 to retract followed by indexing of the
magazine 14. Relative movements of the elements of the control
means is controlled by appropriately positioned stops, as
illustrated in the Figures.
Operation of the control means will be best appreciated
by consideration of Figures 6A to L, the reference letter
corresponding to movement positions of the handle 5,
illustrated in Figure 6A. The reference letters used in Figure
6 correspond to those used when describing the general
operation of the apparatus with reference to Figure 5.
When the handle is in position A the apparatus is in its
; rest position. Movement of the handle to position ~ causes the
sliding ram 16 to move away from its rest position and clear
of the magazine 14. As soon as the ram 16 is clear of the
magazine 14 the magazine pawl 42 begins to retract and the
press element 7 moves to its lower clearance level. Movement
of handle to position C causes full retraction of the magazine
15335/LCM:sks 11
76~
pawl and subsequent movement of the handle to position D causes
indexing of the magazine to bring a connector into alignment
with the ram 16. At this time the press element 7 is returned
to its upward position and the crank 2~ is restrained from
further movement by a stop pin on the crank pin lever 29.
Movemsnt of the handle 5 to position E causes the
sliding ram 16 to move a connector 13 into the operative
position to abut the end plate 17 and the spring pawl 36, o~
the plate 33, is caused to move up the cam face 37 thus urging
the sliding ram against the connector 13 to hold this in the
desired position. As the handle is moved to position F (the
rest position) the action of the spring pawl 36 against the cam
face 37 acts to retain pressure on the sliding ram 16 and thus
to retain the connector 13 in the desired position. In this
position a ribbon cable (not shown) is fed into the gap between
the connector parts. Subsequent movement of the handle to
position G causes the rod 12 to pivot, moving its outer end
upwardly and thus causing the lower press element 7 to be
- raised towards the press element 6 and thus to achieve crimping
of the connector and cable.
Return movement of the handle to position H moves the
press element 7 towards its clearance position whilst
maintaining pressure on the ram 16 to retain the crimped
connector 13 in position between the ram 16 and the end plate
17. Further movement of the handle to position l causes
retraction of the sliding ram 6 allowing removal of the
assembled cable and connector from the apparatus.
15335/LCM:sks 12
~ - .~, . ,, ., .. ... ,. - ..
ll25~7~6
As explained, the apparatus is also useful for
transverse, or mid-span, assembly of a connector and a cable.
To achieve such assembly the above described steps are
conducted up to handle position F, at which time, with the
upper connector part held firmly between the ram 16 and end
plate 17, the element 8 is rotated, cooperation between the
rod 12 and the cam face of the element 8 allowing the element
8, and the press element 7, to move downwards to the clearance
position. ~s the lower cable part is held firmly in position
on the lower press element 7, the connector parts are moved
apart allowing transverse insertion of the cable~ This is
illustrated in Figure 6L. When the element 8 is returned to
its original position the crimping steps achieve to L are
carried out.
Any other convenient control means may be used. For
example, a pneumatic arrangement for achieving the desired
movement o~ the press elements and indexing of the connector
magazine could be used. Operation may be manual or automaticO
Figures 7 to 10 illustrates the variety of forms of
suitable magazines for retaining a store in connectors. As
shown in Figures 7a and b the connectors may be contained in
a flexible bandolier or, as shown in Figure 8, the connectors
may be positioned in a magazine rack.
- Whilst the embodiment illustrated in Figures 1 to 6
shows an arrangement of the apparatus suitable for use with a
magazine rack containing connectors 13 it will be appreciated
that only minor modifications to the described arrangement ar~
required to enable the use of a flexible bandolier, such as
1533~/LCM:sks 13
~2~47~6
that illustrated in Figure 7. In order that the connectors are
presented in the desired upright configuration appropriate
access apertures may be provided in the members 2 and 3 to
allow substantially vertical feed o~ the bandolier through the
apparatus.
Considering the bandolier arrangement of Figure 7, it
will be seen that connectors 13 are spaced from each other in
a semi-rigid plastics film, each connector being held in a
distinct-envelope part 40 of the bandolier. The ends of each
envelope part 40 are open to allow the connector 13 to be moved
from the bandolier to the operative position of the apparatus
by the sliding ram 16. A dimpled area 41 projects inwardly
from each side of each envelope part and acts to retain the
, desired separation between the connector parts. The bandolier
may conveniently be provided in short strips or in longer
lengths, for example in a roll. Any suitable indexing means,
associated with the control means 4 may be used to sequentially
bring connectors into alignment with the ram 16.
Whilst suitable for use alone, apparatus of the
invention may advantageously be used in combination with an
automatic cable cutting machine. For example, in one
particularly preferred arrangement a cable cutter ,and clamp
means are associated with the apparatus for cutting
predetermined lengths of cable. In such an arrangement (not
shown) a cable cutter is positioned on one side of the press
elements and a cable clamp is positioned on the opposite side
of the press elements.
15335/LCM:sks 14
~2S~7~i
In operation a length of cable is fed se~uentially
through the cable clamp, between the upper and lower press
element and the cutter means. The cable is locked in position,
by operation of the clamp and is cut by operation of the cutter
means. The cable may then be moved rearwardly so that the cut
end is positioned between the press elements. The apparatus
is then operated as above to crimp a connector adjacent the cut
end of the cable.
Desirably, operation of the cutter means and clamp is
lo controlled by the same control means as the apparatus so that
sequential automatic operation can be achieved.
In another arrangement a cutter means may be provided
in parallel between a pair of cooperating press elements, cable
clamp being provided on the opposite side of each pair of press
elements. The cutter operates as above allowing the
simultaneous crimping of connectors adjacent each cut end.
From the foregoing it will be appreciated that many
possible embodiments may be made of this invention without
departing from the scope thereof. It is to be understood that
all matter herein set forth or shown in the accompanying
drawings is to be interpreted as illustrative and not in a
limiting sense.
15335/LCM:sks 15