Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
--1--
The invention relates to a funnel type measuring
device. Measuring devices for measuring air flow
rates are indispensable, e.g., for instantly and
exactly fixing in situ at an air terminal device or
an air intake device or the like, as part of an air
treatment appliance, an air fan appliance, an air
heating installation or such like installations, the
air flow rate which is blown out or which is
suctioned per unit of time. The invention has as an
object to provide for a measuring device which is
easy to handle, promptly operating and also
portable, which fully and reliably satisfies all
requirements.
According to the invention, this is obtained by a
measuring device, more particularly a portable
measuring device for automatically measuring in situ
and over an air passage opening through which a gas
flow passes, the rate of volume of such a gas flow
per unit of time - hereinafter called gas flow
delivery - which measuring device is provided with a
pressure difference gauge allowing the measurement
of a pressure difference between the inside and the
outside of the funnel mouth connected to said device
after the latter is placed for measuring purposes
over said opening, the value of the pressure
difference thereafter being transferred into an
electronic signal which controls the intensity of
power supply to and, also if desired, its running
direction, of a control fan which is located in the
throat cross section of the measuring device, one
and the other in such a way, that after placing the
funnel mouth over said opening while operating said
device for measuring the gas delivery, each measured
pressure difference is reduced down to zero at a fan
.~
13~1483
--2--
speed and fan running direction which corresponds to
the relevant gas delivery and its relevant direction
of gas flow which flow rate values become instantly
readable from a reading window which is connected to
the measuring device.
The operation of the pressure difference gauge which
is built in the measuring device is such like, that
the fan speed is measured by an electronic speed
measuring device and is transferred by calibration
into a value indicating the extent of gas delivery
(air flow rate) which becomes instantly readable
from the said reading window.
The relationship between the fan speed and the air
flow rate is fixed by calibration. By means of a
revolutions counter the speed of revolutions of the
fan is measured and transferred in the corresponding
air flow rate, which is instantly made readable in
analogous or digitals from a reading window which is
provided at the measuring device. The measuring
range of the measuring device can, e.g., vary from
lO m3/h till 500 m3/h. This large measuring range
area is obtained by using measuring areas
overlapping each other, and this is effected by
mounting to the underside of the measuring device a
flow resistance disc. This flow resistance disc is
provided by a disc having one or more holes.
Also, the temperature of the air flowing through the
measuring device is measured and made readable from
a reading window, which is provided to the measuring
device. By means of the measuring device the most
._,. . ~ !,~
'.
13(1~ 33
3--
relevant values for air flow rate through a passage
opening can so exactly be measured, e.g., the air
flow rate and temperature of the flowing air or gas.
The measuring device can be fitted with an adapted
mounting piece for use with terminal devices and air
intake passages of various dimensions. For
operational purposes the measuring device is
provided with a pair of handles. The most important
operating means are mounted and located in such a
way so that they can be easily operated when the
user holds the handles. The manipulation and the
simplicity of use of the measuring device, as well
as the speed for measuring with the measuring device
under practical circumstances, are highly furthered
by providing the power supply to the fan and to the
entire electronic measuring / and control system by
means of a preferably rechargeable battery, all
located in a portable bag and connected to the
measuring device by means of a connection cable. It
will be clear that where the measurement would
relate to the suctioning or the blowing of gas or
air respectively, the difference will become
readable and visible upon the reading window.
The measuring device offers the following measuring
possibilities:
1. Signals generated by the pressure difference
gauge automatically select for the direction of
turning and the number of revolutions of the fan in
such a way, that the static pressure difference
inside and outside the funnel mouth / mounting piece
is reduced to zero (0). In the event of
fluctuations in the air flow rate, automatic control
of the number of revolutions is effected so that the
13~1~83
point of zero is again obtained and retained
respectively. Air flow rates which are generated
during this operation, appear on the reading window
of the measuring device. An optical signal is shown
when the point of zero is again reached. The
measuring procedure starts by pushing a knob nearby
the handle and the process is stopped by pushing
that knob again;
2. Since gas flow rates passing through passage
openings do often and sometimes fluctuate to a
relative strong extent, the air flow rate is defined
in such event by the measured average value during a
certain defined period of time. The measuring
device enables this by retaining the measuring
procedure under 1 during a period which is long
enough and then it defines an average value of all
such air flow rates which are measured in the said
period. The last average value is shown and
retained in the reading window. This automatic
procedure is finished by pushing the knob nearby the
handle. By again pushing said knob, the reading
window becomes empty again and a next measurement
can be effected;
3. In the event that the differential width of the
fluctuations is larger than the preset differential
width at the measuring device, than this procedure
as described under 2 will not result into a readable
rate value and alternately the differential for
fluctuations on the measuring device must be set at
a greater value, or the procedure under 1 must be
followed;
4. The procedure as described under 2 can also be
finished without showing intermediate air flow
rates;
13~ 33
5. The measuring device offers the possiblity to
preset the direction of turning and the number of
speed revolutions of the fan by hand. The measuring
time is thereby shortened because proceeding this
way, the fan will quickly start and reach its
desired number of revolutions in the desired
direction of turning;
6. The temperature of the air or gas is measured
and can be read analogous or digital;
7. The measuring device offers possibilities for
simplifications, such as:
7.1 Switching of the automatic pressure difference
= 0 searching system, enabling to measure air flow
rates totally by hand;
7.2 No measurement of temperature;
7.3 Permanent mounting of the pressure difference
gauge upon the mouth of the measuring device, in
which case, while using a mounting piece, the
pressure difference gauge need not be mounted to the
mounting piece, causing, however, a slight measuring
error, which can be corrected later on and if
desired, by means of a calibration graph, or
automatically (e.g., by means of a microprocessor).
In the drawing a preferred embodiment of the
invention will be explained hereinafter:
Fig. 1 is a perspective view of the portable
measuring device;
Fig. 2 schematically shows an axial cross section
through the measuring device;
Fig. 3 is a circuit diagram of the pressure
difference gauge;
Fig. 4 is a circuit diagram of the measuring- and
control system for the measuring device;
13~14E~3
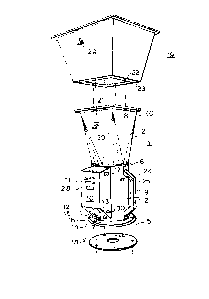
The measuring device 1 in Figs. 1 and 2 consists of
a funnel housing 2 which is composed of a
cylindrical part and a reducing piece going from a
round shape to a square shape. In the cylindrical
part, a fan 3 is mounted in an axial direction by
means of radial supporting means, as well as by a
parallel flow passage director 4, and it is provided
with a ring shaped lower flange 5. By means of a
ring shaped folded edge 6, the reducing piece
running from a round shape to a square shape, is
connected and fixed to the cylindrical part. At its
upper and lower side the funnel housing is provided
with both holes 7 and 8 respectively. At the
outside of the funnel housing are provided
diametrically two handles 9 and between these
handles 9 there is located a box 10 having a reading
window 11, two position switches 12 ("automatic" and
"continuous") and 13 ("hand operation switch"), a
connection 14 for battery power supply, an indicator
15 for pressure differences ( + or 0 or - ) and a
gauge 16 for the calibration of the funnel measuring
device. Upon the box 10 there is an optional switch
17 for handsetting the calibration scale which
corresponds to the measuring range ~including or not
the use of a flow resistance disc 18) and an adapted
mounting piece 19. A mounting piece 19, provided in
various dimensions and shapes can be fixed upon the
measuring device 1 by means of bolting to be set via
holes 8 in the square flange 20 at the upper side of
the funnel mouth 21 and holes 22 in the connectable
square flange 23 of the mounting piece 19. For
quick mounting and removal respectively of a
mounting piece 19, it will be clear that use can be
made of quick closing means instead of the bolting
described before. Integrated in or nearby the
:
c'~,
~ `- : ' ' . .
~ .
~:
'
'
13-01483
--7--
handle 9 there is provided an on/off switch 24 and
an operating knob 25 for hand control/presetting of
the fan 3. For connection against the lower flange
5 of the measuring device 1, a flow resistance disc
18 can be provided by means of via bolt holes 17 or
in a similar way.
Mounting piece 19 can be rigid or of foldable shape.
If the latter applies, the flexible wall 26
consists, e.g., of impregnated nylon or rubber cloth
that is stretched by means of a number of cloth
stretching means 27, each of which is located in a
corner of the mounting piece. Such a stretched
structure, which is per se known for other purposes,
will not be further described here.
The temperature of the flowing air or gas is now
measured and the measured value is readable from
window 11, or from a separate window 28. The art by
which temperatures of gasses are measured and are
being made readable in an analogous or digital
scanner, is already known from other applications
and will not be further described herein. The
pressure difference gauge of measuring device 1 or
mounting piece 19 is further shown by reference
number 29.
Fig. 3 schematically shows the principle of the
measurement for the static pressure difference. In
fact, it is based upon measurement of an air flow.
If the static pressure pl in space I is greater then
the static pressure p2 in space II, then a gas flow
is generated from 01 to 02, which touches NTC
thermistor A, however it does not touch NTC
thermistor B. This will cause electrical voltage
13~1483
differences between A and B and these indicate the
magnitude and direction (pl is greater than p2) of
the static pressure difference. In the event of a
reversed direction of flow, where pl is smaller than
p2, and if there is no flow at all, pl = p2(zero).
A recorder connector 30 provided on the measuring
device makes registration of the measurement
possible.
Fig. 4 shows the principle of the measuring - and
control system of the measuring device. The battery
in the portable bag 31 provides for the power supply
to the entire system. Preferably battery 31 will be
rechargable and thereto it can be coupled to a
battery charger 32.
For carrying out the measurements, battery 31 is
connected to the supply main 33. Supply main 33
generates from the power supply a number of
different voltages which are desired in the system.
Via a central control unit 34, the system can be
started by means of an on/off switch 24. By
actuating this switch for the second time, the
system can be stopped. In operation, after the
measuring device 1, whether or not provided with a
mounting piece 19, is placed over a gas passage
opening, the measuring system is started up by means
of switch 24. The central control unit 34 generates
a. o. a signal to the power supply main 33, in order
to bring other parts of the system also under
voltage. Furthermore, the central control unit 34
generates a signal to the reading window 11 for
showing the measured values and also, by means of
*~
13~148;~
a + or - sign to show the direction of turning of
the fan 3. The direction of turning indicates the
direction of flow of the gas through the device and
thus provides for an indicator to show if the air or
gas flow is blown into or suctioned from
respectively the gas flow passage. The central
control unit 34 activates also the calibration of
the air flow rate 35. Correct calibration must be
handset by means of the selecting switch 17. Each
calibration position of the selecting switch 17
corresponds to two circuits, one for each direction
of turning of the fan 3. The direction of turning
is switched on in the control signal converter 36
and except that it is being passed on to the band
width controller 37, it is also passed on to the
central control unit 34 and via the latter on to the
air flow calibrating means 35.
Calibration may take place by using the measuring
device, with or without flow resistances 18 and also
the combinations of the measuring device with the
flow resistances 18 and mounting pieces 19, with an
exact air flow rate measuring instrument, e.g., a
measuring range with a measuring flange, measurable
in both directions of turning of the fan. The air
flow rate is proportional with the number of
revolutions of the fan. With the aid of the
potentiometer or a microprocessor (which allows a
very great exactness) for each combination and
direction of turning, the correct relationship
between the number of revolutions of the fan and the
air flow rate can be set. The manner in which the
setting of the potentiometer or the microprocessor
takes place is already known from other applications
and it will therefore not be described here further.
., . }
13Q1483
--10-- .
Pressure difference gauge 29 measures the static
pressure difference between the pressure inside and
outside the measuring device 1 or the mountiny piece
19 and also if this pressure difference is of a
positive or negative value. The system itself will
try to render this pressure difference as small as
possible. Pressure difference gauge 29 sends the
measuring signal to the pressure difference
indicator/switch 38. The latter controls indicator
15, consisting of three LED's (LED = Light Emitting
Diode). By means of the indicator 15 the user can
check if the pressure difference is positive, zero
or negative and thereby know in which operational
state of control the system actually is.
Now the operation will be described whereby switch
13 is in the position "switch on". Pressure
difference indicator/switch 38 emits also four
switching signals. Three signals are received by
the zero control means 39. All these three switch
signals are related to so called signal windows, a
very small window and symmetrically surrounding it a
larger window. In this way, the range of signals is
divided into five different areas. The outgoing
signal of the pressure difference gauge 19 may be
located in one of these areas. Depending on the
position of the signal, there will be carried out a
quick or a very slow control activity. In the event
that the outgoing signal is located within the small
signal window, the pressure difference
indicator/switch 38 will not carry out a control
activity and there will be only a memory function.
In the last event, the outgoing voltage of the zero
control means 39 will remain constant; this
situation corresponds to a static pressure
.
13~ 3
--11--
difference of zero. The output of zero control
means 39 serves as a variable setpoint for a second
control loop. This signal reaches control signal
converter 36. This second control loop is
constituted by fan 3, counter measurement 40,
control signal converter 36 and signal width control
means 37. This second control loop follows the
setpoint. The control loop may follow the setpoint
only by changing the direction of turning and the
number of revolutions of the fan 3. Corresponding
to a defined setpoint, there is only one number of
revolutions and corresponding direction of turning
of the fan 3 and this is just the combination of
number of revolutions and the direction of turning
which, at the output of the measurement for the
revolutions 40, will generate a voltage which is
fully equal to that of the setpoint. The output at
the control signal converter 36 controls band width
control means 37, which in its turn controls the fan
3.
Once the setpoint has obtained a value by which the
measuring system indicates a static pressure
difference of zero value, then by means of the
fourth switch signal, derived from the pressure
difference indicator/switch 38, the zero point
detector 41 is activated. Zero point detector 41
then generates a switch signal which is sent to the
central control unit 34 via switch 12. In the
position "automatic" of switch 12, a certain period
of time will lapse after the zero point detector 41
has issued a switch signal to the central control
unit 34, whereafter the measurement is automatically
stopped. During this time, there is carried out an
averaging of the measured values which have been
130~3
-12-
offered during this period. It is this average
value which, after the average time has gone by, is
shown on the reading window 11. By retaining this
average value, it can be read also after the
measurement has been finished. In the event that
switch 12 is in the position "continuous", the
switch signal, derived from the zero point detector
41, is blocked and then the user himself must finish
the measurement by pushing in the on/off switch 24.
The positon "continuous" of switch 12 is necessary,
in the event that the air flow rate demonstrates
such large fluctuations, that the setpoint will
never be stable enough to arrive to automatic
switching off.
If switch 13 is set in the position of "hand
operation", then switch 12 is also set in its
position "continuous". In this position of "hand
operation" of switch 13, the automatic control of
the fan to a value, in which the pressure difference
inside and outside the measuring device/the mounting
piece is zero, is blocked and by means of a
potentiometer 25 any given setpoint and so any given
number of revolutions of the fan and its direction
of turning can be chosen. Potentiometer 25 is hand
operated. In the position "hand operation" of
switch 13, it will thus be possible to carry out a
measurement entirely by hand, based upon the signals
which appear upon the indicator 15. A much more
important application, however, is the following: by
hand the direction of turning and the number of
revolutions of the fan is selected, lying closely to
the expected air flow rate to be measured
(presetting). If, thereafter, measurement is made
in which the switch 13 is in its operating position
13~ 83
"switch on", then fan 3 is given a number of
revolutions for starting up, which is equal to the
presetting, so that the fan very quickly reaches
nearly the desired number of revolutions.
Thereafter, the automatic control system comes into
operation again. The time for measurement is
thereby very much shortened, because the fan is
reaching its number of revolutions very fast.
The value of the measurement, which is shown on the
reading window 11 corresponds to the calibration of
air flow rates 35. Indicator 42 shows the warning
"low batt" upon the reading window 12, when the
voltage of the battery will arrive under a
predefined value.
. .
., ~
'