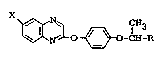Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
13(~30~1
The present invention relates to quinoxaline derivatives
and herbicidal compositions containing the same.
Various compounds have been used as herbicides. These
herbicides have been proposed and used to eliminate agricultural
labo~r and to improve the productivities of agricultural and
horticultural crops.
Herbicides having superior herbicidal characteristics
are always in demand. Herbicides for agricultural and horticul-
tural purposes are preferably compounds which selectively control
the particular weeds in a small dose without toxicity to the crop
plants. Known herbicides do not always have optimum herbicidal
characteristics.
The present invention provides useful herbicides espec-
ially heterocyclic compounds with herbicidal characteristics.
Substituted pyridyloxyphenoxy fatty acid herbicides
are disclosed as heterocyclic ether type phenoxy fatty acid
derivatives in Japan Unexamined Patent Publication No. 106735/
1976. Benzimidazole, benzthiazole, and benzoxazole derivatives
and herbicidal effect of these compounds are disclosed in Japanese
2Q Unexamined Patent Publication No. 40767/1978.
The present invention provides quinoxaline derivatives.
The present invention also provides a herbicidal compo-
sition which has excellent æelective herbicidal activity to
various weeds, especially gramineous weeds, but substantially no
phytotoxicity to broad leaf crop plants.
According to the present invention there is
provided a quinoxaline derivative of general formula:
~k
~
~3~3C1 41
o ~ -CH-R (I)
wherein:
X represents a halogen atom; and 9~N ~N~ CH3
R represents a group selected from -C ~ ~ -C ~O ~ C~3,
-CH=CH-C00-Cl_4 alkyl and -CORl, wherein Rl represents a
~roup selected from -O-(CH2)2- ~ o, -o-(cH2)2scH3
-O(CH2)2-N(CH3)2 and -NHR4, wherein R4 represents a group
selected from Cl_4 alkoxy carbonylalkyl, hydroxy alkyl, Cl_4
alkoxy alkyl and di-C1_4 alkyl amino.
The present invention provides also herbicidal compo-
sitions comprising the quinoxaline derivative as an active
ingredient.
The quinoxaline derivatives having the formula (I) of
the present invention are the novel compounds and are signifi-
cantly unique compounds which are effective for controlling
gramineous weeds without any phytotoxicity to broad leaf crop
plants as well as broad leaf weeds, especially in the post-
emergence treatment.
Typical compounds of the present invention having the
$ormula (I) are shown in Table (1) together with the physical
properties.
'F
13~3~1
Table l-l
~ O ~ CH3
Comp,No. _~g__ R Physical Property
1 F -coo(cH2)2- ~ ~D2=1.4666 Colorless ~q
2 - -Coo(cH2)2-N(cH3)2 mp 69-71C W.C.
-CONHCH2CCX~C2Hs mp 143-145C W.C.
_ .
.' -CONHCH2CH20H W. C .
_ c~N ~ mp 159-161C W.C.
6 ,l . -C~O ~ CH3 mp 95-970C W.C.
7 ll -CH=CH-COOCH3 mp 92-940C W.C.
8 C~ -COO(CH2)2SCH3 Colorless liq
9ll -CONHCH2CH2C~CH3 mp 134-135C W.C;
10_ -CONH N(CH3)2 mp 182-183C W.C.
F
i3~?30d~1
Table 1-2
5Comp. No. X _ R Physical Property `
11 C~ c~N~ mp 173-174C W.C.
12 .. -CH=CHCOOCH3 ND0=1.5421 Colorless llq. .
- 13 .- -CH=CHCOOC2H5 N2D =1.5630 Colorle liq.
14 Br -CH-CHCOOCH3 NDO=1.5468 Colorless liq.
" -C_O~ mp 143-145C W.C.
Note: W.C.: white crystal
~3l~3C1~1
The compound (I) of the present invention may be pro-
duced by the following processes:
A) condensation of a compound having the formula
N ~ (II)
Hal
wherein X and Haldesignate a halogen atom; with 4-hydroxyphenoxy
derivative havingtheformula
CH3
10 HO - ~ OCH-R (III)
wherein R is defined above, in the presence of an inorganic or
organic base, such as sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide or
potassium carbonate, at a suitable temperature. The reaction
can be carried out in an inert solvent, such as dimethylforma-
rnide, dimethylsulfoxide, or acetonitrile;
B) condensation of a compound having the formula (II)
with a hydroquinone monobenzyl ether having the formula
HO - ~ O-CH2 ~ (IV)
in the presence of an inorganic or organic base to produce a com-
pound having the formula
N ~ O ~ OCH2- ~ (V)
and then hydrogenation of the product with a catalyst, such as
palladium-carbon catalyst to cause debenzylation and to yield a
compound having the formula
1.3~3041
~ N ~ O - ~ ~H (VI)
and then condensation of the product with a haloalkyl derivative
having the formula
Hal-CH-R (VII)
CH3
in the presence of an inorganic or organic base, such as potas-
sium carbonate in a polar organic solvent, such as methyl ethyl
ketone, acetonitrile or dimethyl-formamide or
C) The product obtained by the process A) or B) is
converted into the other compounds of the present invention by
hydrolysis, esterification, ester interchange, salt or amidation.
In the esterification, it is possible to use conven-
tional coupling agents as well as unique coupling agents, such
as imido coupling agents, especially dicyclohexyl carboimide.
The concentrations of the reagents and the temperatures in the
reactions and types of the inert solvents can be selected as
~ desired.
:~ In the process A), the reaction is preferably carried
out at 50 to 200C, especially at 80 to 100C, at a molar ratio
-~ of the compound (II): 4-hydroxyphenoxy derivative (III) of 1:0.2
to 5.0, preferably 1:0.5 to 2.0, especially 1:0.8 to 1.5. The
inorganic or organic bases may be any base which is useful for
: the condensation of thè compound (II) and the compound (III).
The concentration of the starting materials in the inert solvent
may be in the range of 5 to 50 wt. ~, preferably 10 to 30 wt. %.
~: 30 In the process B), the reaction is preferably carried
out at 50 to 200C especially at 100 to 150C at a molar ratio
of the compound (II): The hydroquinone monobenzyl ether (IV)
s 6 -
13~3(~1
of 1:0.2 to 5.0, preferably 1:0.5 to 2.0, especially 1:0.8 to
1.5. The inorganic or organic base may be any base which is
useful for the condensation of the compound (II) and the compound
(IV). The reaction is preferably carried out in an inert solvent
S at a concentration of the starting material of 5 to 50 wt. ~,
preferably 10 to 30 wt. %.
The hydrogenation of the resulting intermediate (V) is
carried out under conditions for the debenzylation to yield the
compound (VI). The hydrogen pressure is preferably in the range
of 1 to 5 atm. preferably 1 to 2 atm.
The reaction of the compound (VI) with the compound
(VII) is preferably carried out at 80 to 100C at a molar ratio
of the compound (VI): the compound (VII) of 1:0.2 to 5.0,
preferably l:O.S to 2.0, especialiy 1:0.8 to 1.5. The inorganic
..
or organic base may be the same as above. The concentration of
the starting materials in the inert solvent may be in the range
of 5 to 50 wt. %, preferably 10 to 30 wt. %.
In the process C), the conditions of the hydrolysis,
the esterification, the ester interchange, the neutralization
and the amidation can be selected as desired.
The present invention will be described with reference
to the following Examples.
Preparation 1:
2-tl-{4-(6-fluoro-2-quinoxalyoxy)phenoxy}-ethyl]-4,4-
dimethyl-2-oxazoline:
(Compound 6)
In 20 ml of dimethyl-formamide, 2.0 g (0.0070 mol) of
6-fluoro-2-(4-hydroxyphenoxy)-quinoxaline, 1.8 g (0.0087 mol) of
`E~
~3~3041
2~ bromoethyl~-4~4-dimethyl-2-oxazoline and 1.3 g (0.0094 mol)
of potassium carbonate were dissolved and the mixture was heated
at 90C for 8 hours. After cooling, the reaction mixture was-
poured into water and the product was extracted with benzene and
the benzene layer was washed with 2% aqueous solution of sodium
hydroxide and then with water and the benzene layer was dehydrated
o~er sodium sulfate. The solvent was distilled off. The result-
ing crude crystals were washed with n-hexane to obtain 0.8 g
~yield 27~) of the object compound.
Preparation 2:
Methyl y-methyl-y-t4-(6-fluoro2-quinoxalyloxy)phenyoxy]
crotonate:
(Compound 7)
In 150 ml of methyl ethyl ketone, 2.6 g (0.01 mol) of
6-fluoro-2-(4'-hydroxyphenoxy)quinoxaline, 2.0 g (0.01 mol) of
methyl r-bromo- ~methyl crotonate and 2.0 g (0.014 mol) of potas-
sium carbonate were dissolved and the mixture was refluxed for 8
hours.
After the reaction, the precipitate was separated by
filtration and the filtrate was concentrated and dried. The
residue was dissolved in chloroform and the chloroform solution
was washed with 5% aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide and then
with water and, dehydrated, condensed and dried. The residual
solid product was purified by column chromatography with silica
gel and chloroform to obtain 3.0 g of white crystals of Compound
No. 22 having a melting point of 92.0-94.0C (yield of 82~).
3o
-- 8
F
~,
13~3C~41
The compound of the present invention can be used as a
herbicidal composition.
In the preparation of the herbicidal compositions, the
compound of the present invention can be uniformly mixed with or
dissolved in suitable adjuvants, such as a solid carrier such as
clay, talc, bentonite, diatomaceous earth; a liquid carrier such
as water,-alcohols (e.g. methanol or ethanol), aromatic hydro-
carbons (e.g. benzene, toluene or xylene) chlorinated hydrocarbons
F g
iL3~3~4~
etherSr ketones, esters (e.g. ethyl acetate), acid amides ~e.g.dimethylformamide) if desired, with an emulsifier, a dispersing
agent, a suspending agent, a wetting agent, a spreader, or a
stabilizer to form a solution, an emulsifiable concentrate, a
wettable powder, a dust, a granule or a flowable suspension which
is applied if desired, by diluting it with suitable diluent.
It is possible to combine the compound of the present
invention with another herbicide, or an insecticide, a fungicide,
a plant growth regulator, a synergism agent.
Examples of the herbicidal compositions of the present
in~ention will be illustrated. In the Examples, the part means
part by weight.
Solution:
Active ingredient: 5 to 75 wt. %, preferably 10 to
50 wt. ~, especially 15 to 40
wt. %
Solvent: 95 to 25 wt. %, preferably 88 to
30 wt. %, especially 82 to 40
wt. %
Surfactant: l to 30 wt. %, preferably 2 to
20 wt. %
Emulsifiable concentrate:
Active ingredient: 2.5 to 50 wt. %, preferably 5
to 45 wt. %, especially lO to
40 wt. %
Surfactar.t: l to 30 wt. ~, preferably 2 to
25 wt. %, especially 3 to 20
wt. %
Liquid carrier: 20 to 95 wt. %, preferably 30
to 93 wt. %, especially 57 to
85 wt. %
Dust:
Active ingredient: 0.5 to lO wt. %
Solid carrier: 99.5 to 90 wt. %
Flowable suspension:
Active ingredient: 5 to 75 wt. %, preferably lO to
50 wt. %
Water: 94 to 25 wt. %, preferably 90 to
30 wt. %
-- 10 --
~3~`3~1
Surfactant: 1 to 30 wt. %, preferably 2 to
20 wt. %
Wettabl_ powder:
Active ingredient: 2.5 to 90 wt. %, preferably 10
to 80 wt. %, especially 20 to
75 wt. %
Surfactant: 0.5 to 20 wt. %, preferably 1 to
15 wt. %, especially 2 to 10 wt.
Solid carrier: 5 to 90 wt. %, pref~rably 7.5 to
88 wt. %, especially 16 to 56
wt. %
Granule:
Active ingredient: 0.5 to 30 wt. %
Solid carrier: 99.5 to 70 wt. %
The emulsifiable concentrate is prepared by dissolving
the active ingredient in the liquid carrier with the surfactant.
The wettable powder'is prepared by admixing the active ingredient
with the solid carrier and the surfactant and the mixture is pul-
verized.
The flowable suspension is prepared by suspending to
disperse the pulverized active ingredient into an aqueous solution
of the surfactant. The dust, the solution, the granule, etc. are
prepared by mixing the active ingredient with the adjuvant.
In the following compositions, the following adjuvants
are used.
~ 13~3041
Sorpol- 2 6 8 0 ( a trademark)
POE- h ormylnonylphenolether 50 wt. parts
POE-nonylphenolether 20 "
POE-sorbitan alkyl ester 10 "
Ca- alkylbenzenesulfonate 20 "
Sorpo~ 5039 (a trademark)
POE-alkylarylether sulfate50 "
Silica hydrate 50
C arplex ( a trademark)
Silica hydrate 100 "
Zeeklite (a trademark)
Clay 100 "
Sorpol W-150 (a trademark)
POE-nonylphenolether 100 wt.parts
15 Composition 1: Wettable powder:
Active ingredient 50 wt.parts
Zeeklite A (a trademark) 46 "
Sorpol 5039 (Toho Chem. ) (matk)a e2 "
Carplex (a trademark) Z "
These components were uniformly mixed and pulverized
to prepare a wettable powder. The wettable powder was diluted with
water 50 to 1, 000 times and the diluted solution was sprayed at a
dose of 5 to 1,000 g, of the active ingredient per 10 ares.
Composition 2: Emulsifiable concentrate:
Active ingredient 20 wt.parts
Xylene 7 5 "
Sorpol 2680 (Toho Chem )maarkt)rad~5
13(~3C~
The components were uniformly mixed to prepare an emul-
sifiable concentrate. The emulsifiable concentrate was diluted with
water 50 to 1, 000 times and the diluted solution was sprayed at a
dose of 5 to 1000 g. of the active ingredient per 10 ares.
Composition 4: Wettable powder:
A ctive ingredient 30 wt . parts
Other herbicide 20 "
Zeeklite A (a trademark) 46 "
Sorpol 5039 (Toho Chem. )(aatrrka)de~ "
Carplex (a trademark) 2 "
~ ,
- 13 --
~3~3~1
As the other herbicide, the following known herbicides
were re spectively used 2- (2, 4- dichlorophenoxy)propionic acid,
2, 4 - dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, 3 - ( 3 - trifluoromethylphenyl) - 1, 1-
dimethylurea,3-(4-methylphenethyloxyphenyl)- 1-methyl- 1-methoxy urea,
3-(methoxycarbonylamino~phenyl-N-(3-methylphenyl) carbamate,
3-(ethoxycarbonylamino)-phenyl-N-phenylcarbamate, 3-isopropyl- lH-
2, l, 3-benzo thiadiazine-(4)-3H- one-2, 2-dioxide, 5-amino-4-chloro-
2 - phenylpyridazine- 3-one, 3 - cyclohexyl- 5, 6- trimethyleneuracil,
2-chloro-4-ethylamino-6-isopropylamino-1, 3, 5-triazine, 2-chloro-
4, 6-di(ethylamino)-1, 3, 5-triazine, 2-rnethylthio-4, 6-bis(isopropyl-
amino) - 1, 3, 5 - triazine, 4 - amino- 4, 5- dihydro- 3 - methyl- 6- phenyl-
1, 2, 4-triazine- 5-one, 4-amino-6-t-butyl-4, 5-dihydro- 3-methylthio-
1, 2, 4-triazine-5-one, 2-chloro-4-trifluoromethylphenyl-3~-ethoxy-4'-nit-
rophenyl ether or sodium-5-[2-chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl) phenoxy~-2-
nitro benzoate.
It is also possible to combine the compound of the present
invention with other herbicidal compounds which are described in
"Weed Control Handbook" (Vol. I 6th edition 1977; Vol. II 8th edition
1978) issued by the British Crop Protection Council edited by J.D.
Fryer I\IA & R.J. Makepeace BSc . Blackweli Scientific Publication.
-- 14 --
~3~3~41
The quinoxaline derivatives of the present invention
impart excellent herbicidal effect to various weeds, especially
gramineous weeds in soil trea~ment or in foliaye treatment, with-
out any phytotoxicity to broad leaf crop plants, such as cotton,
soybean, radish, cabbage, eggplant, tomato, sugar beet, ground
nut, peas, beans, lin seed, sun flower, safflower, potato,
tabacco, alfalfa and onion. Therefore,thequinoxaline derivatives
of the present invention are suitable for selective control of
gramineous weeds in a culture of a broad leaf crop plant as
herbicide for agricultural and horticultural fiel~s especially
up-lands.
The quinoxaline derivatives of the present invention
are also effective as herbicides for controlling various weeds
in the agricultural and horticultural fields such as up-lands,
paddy fields and orchards as well as non-cultivated lands, such
as playgrounds, vacant land, and railway sidings.
The herbicidal composition usually contains 0.5 to 95
wt. ~ of the compound of the present invention as the active
ingredient and the remainder of the adjuvants in the concentrated
form. The dose of the compound of the present invention depends
upon the weather condition, the soil condition, the form of a
composition, the season of an application and the type of crop
plant and weeds and is usually in the range of 1 to 5000 g, pre-
ferably 5 to 1000 g of the compound of the invention per 10 ares.
The herbicidal activities of the quinoxaline derivatives
of the present invention will be illustrated in the following
Tests.
In the following Tests, the herbicidal effects of the
compounds of tne present invention to gramineous weeds including
rice are shown together with non-phytotoxicity of the same com-
pound to broad leaf crop plants as well as broad leaf weeds
especially, non-phytotoxicity of the same compounds to broad leaf
13~`3041
weeds in post-emergence. These remarkable selectivities have not
been found by the other compounds.
Test 1: Tests for herbicidal effect in soil treatment:
Each of a number of plastic boxes having a length of
15 cm, a width of 22 cm and a depth of 6 cm was filled with a
sterilized diluvium soil and seeds of rice (Oryza sativa), barn-
yard grass (Echinochloa crus-galli), large crab-grass (Digitaria
aascendens), lambsquarters (Chenopodium ficifolium), common purs-
lane (Postuloca oleracea), hairy galinsoga (Galinsoga ciliata),
yellow cress (Rorippa atrovirens) were sown at a depth of about
1.5 cm. Each solution of each herbicidal composition was uni-
formly sprayed on the surface of the soil to give the specific
dose of the active ingredient.
- 16 -
~3(?30~1
The solution was prepared by diluting, with water, a
wettable powder, an emulsifiable concentrate or a solution described
in examples of the composition except varying the active ingredient.
The solution was sprayed by a small spray. Three weeks after the
treatment, the herbicidal effects to rice and various weeds were
observed and rated by the following standard. The results are snown
in Table 2.
Standard rating:
5: Growth control of more than 90%
(substantial suppression)
4: Growth control of 70 to 90%
3: Growth control of 40 to 70%
2: Growth control of 20 to 40%
1: Growth control of 5 to 20%
0: Growth control of less than 5%
(non-herbicidal effect)
Note: Ri: Rice
- Ba.: Barnyard grass
L, C.: Large crab grass
La.: Lambsquarters
C. P.: Common purslane
H. G.: Hairy galinsoga
Y. C.: Yellow cress
:;
.
-- 17 --
~3~3~1
Table 2-1
Comp .Do se of _
No.Comp. Ri Ba L.C. La.C.P. H.C. Y.C .
(g/a) _
100 5 S 5 2 2 2 2
1 50 5 5 5 1 1 1
S 0 0 0 0
100 S 5 5 3 3 3 3
2 50 5 5 5 2 1 1 2
S 5 5 0 0 0 0
100 5 5 5 2 2 2 2
3 50 5 5 5 0 1 1
S 5 5 0 0 0 0
100 5 S 5 2 2 2 2
4 50 5 5 S 1 1 1
0 0 0 0
100 5 5 5 2 2 2 2
1 1 1
; 25 5 5 5 0 0 0 0
100 5 5 5 2 2 2 2
6 50 5 5 5 1 1 1
S 5 5 0 0 0 0
7 1050 5 1 5 1 5S 23 2 2
! 5 1 5
~ - 18 -
~
13(~3041
Table 2 - 2
Comp. ¦ Dose of .
No .¦ Compj RiBaL . C . La. C . P . H .G . Y. C: .
_
100 5 5 5 2 1 2 2
8 S0 5 S 5 1 0 1 1
. 25 5 S S 0 0 o 0
100 S 5 5 2 1 2 2
9 50 5 5 5 1 O ' 1
2~ 5 S 5 0 0 0 0
100 5 S S 2 2 1 2
1 1 O
S S 0 0 0 0
100 5 S S 2 2 2 2
11 50 5 5 5 1 1 1
S S S 0 0 0 0
- F 19
~3U3041
Table 2-3
Comp. ¦ Dose of . .
NoComp RiBa L. C. La.C. P .H. G . Y . C .
100 S S 5 2 1 2 2
12.50 5 S 5 1 0 1 1
S S 0 0 0 0
100 S S S 2 2 2 3
13 S0 S S S 1 1 1 2
. 25 S S S 0 0 0 0
100 S S S 2 2 2 2
14 S0 S S S 1 1 1
lo 25 S 5 S 0 0 0 0 ___
100 S 5 5 2 2 2 2
15 S0 S S S 1 1 1 1
S 5 S 0 0 0 0
; 20
- 20 -
.
.
.
.,
13~3041
Test 2: Tests for herbicidal effect in foliage treatment:
.. . .
Each of a plurality of plastic boxes having a length
of 15 cm, a width of 22 cm, a depth of 6 cm was filled with a
sterilized diluvium soil and seeds of rice, barnyward grass,
large crab-grass, lambsquarters, common purslane, hairy galinsoga,
- yellow cress and tomato were sown in a form of spots in a depth
of about 1.5 cm. When the weeds were grown to 2 to 3 leaf
stage, each solution of each herbicidal composition was uniformly
sprayed to foliages at each dose of each active ingredient shown
in Table 3. The solution was prepared by diluting, with water,
a wettable powder, an emulsifiable concentrate or a solution
described in examples of the composition except varying the
active ingredient and the solution was uniformly sprayed by a
small spray on all of foliages of the plants.
Two weeks after the spray treatment, the herbidical
: effects to the weeds and tomato were observed and rated by the
standard shown in Test 1. The results are shown in Table 3.
.
.
;,'
.~
- 21 -
` 13~3Q41
Table 3-l
Comp.TDose of . _ .
No . Comp . Ri Ba L . C . La . C . P . H . G . Y . C .
__ (g/a) _
100 5 5 5 2 2 2 3
1 S0 S 5 S 1 1 0 2
0 0 0 0
100 5 5 S 3 2 2 2
2 50 5 S 5 1 1 l
S S 0 0 ` 0
100 5 5 5 2 3 2 2
3 50 ` 5 5 5 1 2 1
2S S S S O û 0 O
100 S 5 5 2 2 2 2
4 255 55 5 55 1 l 1
100 5 5 5 2 1 1 2
25 55 5 5 l l 0
100 5 5 5 2 1 1
6 50 5 5 5 1 0 0
S 5 5 0 0 0 0
100 5 S S 2 2 1 2
7 S0 S 5 5 0 1 0
. 25 5 5 S 0 0 0 0
2s
-- 22 --
F
. .
`` 13~3Q9~1
Table 3 - 2
Comp.Dose of _ _
No . Comp; Ri Ba L . C . La .C . P . H . G .Y . C .
100 5 5 5 2 3 2 2
8 50 5 5 5 1 2 1
I 25 5 5 5 0 0 0 0
100 5 5 5 2 2 2 2
9 50 5 5 5 1 1 O
. 25 5 5 5 0 0 0 0
.
100 5 5 5 2 l 2 2
S 1 O O
lo 25 5 5 S 0 0 0 0
.
100 S 5 5 2 1 1
11 SO S S S 1 O O O
S 5 0 0 0 0 .
-- 23 --
F
~3~30~1
Table 3- 3
Colap.Dose of ¦ _ _ ~ .
No . Comp; I Ri Ba L. C . La, C. P . H . G . Y . C .
100 5 5 5 2 3 2 2 .
S0 S 5 5 1 2 1
12 25 S S S 0 0 0 0
. _
_ 100 5 5 5 2 2 2
13 S0 5 5 5 1 1 1 0
S 5 S 0 0 0 0
100 S S 5 2 2 2
14 50 5 5 5 1 1 1 0
S 0 0 0 0
100 S S 5 2 2 2
S0 5 5 S 1 1 . 1 0
. 25 5 5 S 0 0 0 0
- 24 -
! ~
_ 13~?3041
Test 3: Tests for phytotoxicity to crop plants (foliage
treatment ):
Each of a plurality of plastic boxes having a length of 15 cm
a width of 22 cm, and a depth of 6 cm was filled with a sterilized
diluvium soil and seeds of cotton, soybean, ~adish, cabbage and
eggplant were sown in a form of spots in a depth of about 1. 5 cm.
When the plants were grown to leaf-emergence stage, each solution
of each herbicidal composition was uniformly spraye~ to foliages
at each dose of active ingredient shown in Table 4. The solution
was prepared by diluting, with water, a wettable powder, an emul-
sifiable concentrate or a solution described in examples of the
composition except varying the active ingredient of the solution
was uniformly sprayed by a small spray on all of foliages of the
plants .
Two weeks after the spray treatment, the phytotoxicities
~o the plants were observed and rated by the following standard.
The results are shown in Table 4.
Standard ratin~-
5: Complete death of plant
` 20
4: Serious phytotoxicity to plant
3: Fair phyt otoxicity to plant
2: Slight phytotoxicity to plant
1: Only slight phytotoxicity to plant
0: Non phytotoxicity
Note: Cot.: Cotton
Soy.: Soybean
Rad.: Radish
Cab.: Cabbage
Egg.: Eggplant
-- 25 --
13~3041
Table 4-1
Co~ ~ d Co ~ound ¦ Cot- ¦ Soy- ¦ Rad- ¦ Cab- ¦ Egg-
O O I O O O
1 25 0 0 1 0 0 0
. 50 O O O O O
2 25 0 0 0 0 0
.
O O O O O
3 25 0 0 0 0 0
4 52S 0 _ 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
50 O O O O O
6 25 0 0 0 0 0
lS 7 S0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
O O O O O
8 25 0 0 0 0 0
.
`:
.
~:~ 30
F - 26 -
13i~304i
Table 4-2
C~oun~ Do of Cot.Soy ~ Egg.
O O O O O
9 25 0 0 0 0 0
O O O O O
2S 0 0 0 0 0
O O O O O
11 25 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 - 0 0
12 25 0 0 0 0 0
13 S0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
O O O O O
14 25 0 0 0 0 0
O O O O O
0 0 0 0 0
.
-- 27 --
F