Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
~ 1 3 1 0456
~ 7~-165
EXTRUD[N~ APPARAT~S F~
EXTRUDING SYNTHETIC RESIN
The present invention relates to an extruding
apparatus for ex-truding a synthetic resin and, more
partieularly, to an extrudiny appara-tus for extruding a
synthetic resin, comprising two extruders, a supply port
of one of whieh is connected to a diseharge por-t of the
other and a vent hole for exhaus-ting by-produet gas.
The present appliea-tion is divided from Canadian
Patent Applieation Serial No. 528,808 filed February 3,
1987, the parent application.
A eonventional extruding appara-tus is disclosed in
Japanese Patent Disclosure ~Kokai~ No. 48-79864. This
extruding apparatus ineludes first and second extruders
eaeh having a eylinder whieh has a screw shaft -therein.
The second extruder, located at a front portion, has a
single supply port connected to a discharge port of the
first extruder, located at a rear portion. The supply
port has a sectional area corresponding to the amount of a
molding material supplied to the cylinder of the second
extruder.
Accordingly, the molding material is softened by the
first extruder, at the rear portion, into a semimolten
~5 state, and is supplied into a space between the cylinder
and the screw shaft of the second extruder, -through the
supply port thereof. However, when the space becomes
filled with semimolten resin, a problem occurs at the
outer surface of a screw shaft except helical blades or
flight of the screw shaft. More specifically, no axial
feed effect oeeurs at the outer surfaee of -the shaft, and
the semimolten resin beeomes attached to the outer surface
of the shaft. The semimolten resin gradually aeeumula-tes
on the already attaehed resin, and the seetional area of
the spaee between the eylinder and the screw shaft becomes
~31~5~
-- 2
significantly reduced. In addition, the resin -that has been
attached for a long time is removed from the screw shaft and
tran~erred to a discharge port. So that a discharge amount
of the re~in i~ unstabilized and quality of the extruded resin
is degraded.
The second extruder disclosed in Japanese Patent
Disclosure (Kokai) No. 48-79864 is provided with a vent hole
for exhausting a gas generated when the molding material is
melted. This conventional vent hole is situated adjacent to a
position in a cylinder where pellet~ used as a molding
material are heated and begin to melt, and passes through the
cylinder perpendicular thereto. In addition, the vent hole is
normally connected directly to a vacuum pump.
However, ~ome of the resin melted near the vent hole is
extruded outwardly therefrom, and is drawn by the vacuum pump
thereby disturbing the operation of the pump. When the vacuum
pump is unable to operate properly, it must then be cleaned by
temporarily stopping the operation of the extruder, or else
the extruder must be driven by ~witching the vacuum pump to an
auxiliary pump which is located in advance during cleaning of
the pump, Such a process effectively prevents an extruding
operation, and inevitably results in higher operating costs.
The pre~ent invention provides an extruding apparatus for
extruding a synthetic resin, that can be continuously driven
without the need for it to be periodically stopped.
Continuous operation i~s pos~ible due to the presence of a
venting arrangement.
Accordingly, the present invention provides an extruding
apparatus comprising a cylinder, a supply port provided at a
proximal end of ~aid cylinder, and supplying a re~in molding
material into ~aid cylinder, a di.scharge port provided at a
distal end of said cylinder, and
1 3 1 0456
3 --
discharging -the resin moldiny material contained in said
cylinder, a screw shaf-t arranged inside said cylinder, and
having a helical blade, a motor connected to and driving
said screw shaft, a vent hole formed in a side wall
portion of said cylinder which a distal end of the helical
blade of said screw sha~t opposes when said helical blade
moves downward by rotation of said screw shaft, an axis of
said vent hole having a predetermined angle wi-th respect
to a vertical line, so that an outer end of said vent hole
is situated at a higher level than its inner end and
wherein the axis of said vent hole is inclined, with
respect to a normal line of said screw shaft, at an angle
within the range of from 30 to 90 in a direction
opposite to a direction of rotation of said screw shaft:
an airtight vacuum chamber connected to said vent hole and
mounted on the side wall portion of the cylinder of the
extruder including a bottom cover, a top cover and side
walls, wherein the vacuum chamber allows gas which is
evolved from the semimolten resin molding material to
readily be released under a reduced pressure prevalen-t
within that chamber, while allowing that resin which
enters a vent hole at the time of gas removal and is cured
there to be collected within the chamber; and a vacuum
pump connected to said airtight vacuum chamber.
This invention can be more fully understood from the
following detailed description when taken in conjunction
with the accompanying drawings, in which:
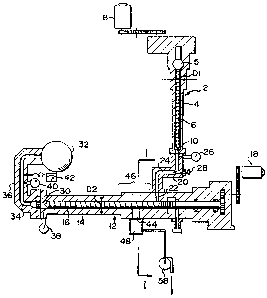
Fig. 1 is a plan view, partially in cross section, of
a complete extruding apparatus according to the present
invention;
Fig. 2 is a vertical sectional view of a second
extruder, taken along the line I - I of Fig. 1;
An embodiment of the,present invention will now be
described in detail, with re~erence to the accompanying
drawings.
. -` t 3 1 0456
-- 4
As is shown in Fig. 1, an extru~ing apparatus
according to the present invention includes first extruder
2 and second extruder 12. First cylinder 4 is provided
for extruder 2. First supply port 5 for supplying a
molding material into c~linder 4, is provided at the
proximal end of cylinder 4. First screw shaft 6 for
transferring the molding material supplied from port 5, is
arranged inside cylinder 4, and first motor ~ for driving
shaft 6 is mounted at the proximal end of extruder 2.
Discharge port 10 is provided a-t the dis-tal end of
extruder 2. Extruder 2 includes second cylinder 14, and
second supply port 22 for supplying the material into
cylinder 14 is provided to the proximal end thereof~
Second screw shaft 16 is arranged inside cylinder 14, and
second motor 18 for driving shaft 16 is mounted at the
proximal end of extruder 12. Coupling member 20 has first
communication passage ~4 for connecting discharge port 10
of cylinder 4 and supply port 22 of cylinder 140 First
pressure gage 26 for measuring resin pressure in passage
24 and pressure control valve 28 for controlling the resin
pressure to be supplied to extruder 2, are mounted to
member 20.
Inner diameter Dl of cylinder 4 of extruder 2 and
inner diameter D2 of cylinder 14 of extruder 12 are
designed in accordance with the following relationship;
Dl/D2 < 1
and more preferably, in accordance with the following
equation;
Dl/D2 = 0.9 to 0.65
For example, when Dl = 100 mm, D2 = about 130 mm.
Extruding port 30 of extruder 12 is coupled to
extruding die 32 by connecting member 36 having passage
3~. Second and third pressure gages 33 and 40 ~or
measuring the internal resin pressure are provided near
port 30, and are in the middle of second connecting member
.
~ . i'
~310~5~
-- 5
36. Thermometer 42 for measuring mol-ten resin temperature
inside passage 34 is provided on mernber 36.
Vent hole 44 for exhausting a gas generate~ when the
resin is mel-ted is provided in suppl~ por-tion 46 of
extruder 12. More specifically, it is provided in a
cylinder side wall, which the distal end of blade or
flight 72 of shaft 16 opposes when b:lade 72 moves down~
ward, by way of rotation of shaft 16, in an arrow direc-
tion, as is shown in Fig. 2. In this embodiment, hole 44
is provided such that its axis is inclined -to the
horizontal or vertical, at about 45, and at the same
time, is inclined with reæpect to a normal line of shaft
16, at an angle of 45, in a direction opposite to the
direction of rotation of shaf-t 16. However, inclina-tion
angle ~, with respect to the normal line of shaf-t 16,
may be arbitrarily selected, as long as it falls within
30 to 90.
As is shown in Fig. 2, airtight vacuum chamber 48 is
connected to the outer end of hole 44. Chamber 48 is
constituted by side wall 52, bottom cover 50, and top
cover 62, and has a space 49 which is shielded from the
ambient atmosphere. Space 49 is normally set in a vacuum.
Opening 56 of hole 44 is provided in a side wall portion
at an upper level, rather than in a middle portion, of
chamber 48. Bottom cover 50 is mounted on a bottom
portion of side wall 52, to be opened and closed by a
suitable fastener 78, such as a bolt. Cooling coils 54
and 55 are attached to the outer surfaces of side wall 52
and bottom cover 50, respectively, and their inner
surfaces serve as heat-exchange surfaces for cooling the
resin overflowing from hole 44. The heat-exchange
surfaces are provided at a predetermined distance below
opening 56 of hole 44. On the other hand, pump-
connecting port 60, cowpled -to vacuum pump 58, is provided
in a side wall portion, at a level above that of opening
56. Top cover 62 for closing an upper opening of chamber
I ~ ~ 0456
- 6 --
48 is formed partially of a -transparent material, -this
transparent portion serving as a window for external
observa-tion of the interior of the airtight vacuum
chamber.
The operation of the extruding apparatus will now be
described below.
Firs-t, a thermoplas-tic synthetic resin or a mix-ture
25 of this resin and a powder of a filler ma-terial is
supplied as a raw material from supply port 5 of first
extruder 2. Yirst and second screw shafts 6 and 16 are
rotated by motors 8 and 18, respectively, and selectecl
portions of cylinders 4 and 14 are heated to a prede-
termined temperature, by a conven-tional method. As a
result, the resin in a semimolten state, prepared by
extruder 2, is discharged from discharge por-t 10, and is
supplied, through communica-tion passage 24, to supply port
22 of second extruder 12~ The semimolten resin supplied
into the cylinder of extruder 12 is transferred toward the
distal end by second screw shaft 16, and is further heated
during transfer. ~ gas generated while the resin is
passing through cylinder 14 is drawn and exhausted by
vacuum pump 58, through vent hole 44 formed to sllpply
portion 46, and through airtight vacuum chamber 48.
On the other hand, the molten resin minus the gas, is
further mixed by shaft 16. The resultant resin is then
supplied -to die 32 from extruding port 30, through passage
34. Upon supply to die 32, the molten synthetic resin is
molded into a desired shape.
When the molten resin passes near the inner end of
hole 44, a part thereof is extruded into hole 44.
However, since hole 44 is inclined by a predetermined
angle, as is shown in Fig. 2, most of the extruded resin
returns by its own weight, into cylinder 14, and is then
milled again by shaft 16, and mixed with ano-ther portion
1 31 0456
-- 7 --
of resin. Thereafter, the resin is mixed uniformly and
supplied -to die 32.
In the apparatus of this embodiment, the amount of
resin supplied to die 32 is controlled by the rotational
frequency of shaft 16, and the rotational frequency of
shaft 6 of extruder 2 is controlled so that the pressure
indicated by second pressure gage 38 will be always
maintained substantially constant. In addition, pressure
control valve 2~ is controlled when needed, to s-tabilize
the pressure indicated by gage 38. This control may be
manually executed by an operator, while observing the
pressure of gage 38 and the amount of molten resin
supplied from hole 44 and extruded into the airtight
vacuum chamber. Alternatively, an automatic control
device provided with a plurality of sensors may be mounted
to automatically control the rotational frequency of shaft
6.
Furthermore, in the extruding apparatus according to
the present invention, since inner diameter Dl of the
cylinder of first extruder 2 is smaller than inner
diameter D2 of the cylinder of second extruder 12,
extruder 12 is less adversely affected by variations in
: the amount of resin extruded from extruder 2. Since the
rotational speeds of the respective shafts can be easily
and finely controlled, the rotational frequency of the
screw sha~t of extruder 2 may be selected to stabilize the
pressure, so that the amount of resin extruded from the
vent hole can be reduced.
In addition, since the cylinders of the first and
second extruders have different diameters, the rotational
speed of the screw shaft of the first extruder can be
relatively increased. For this reason, the plasticising
efficiency and melting efficiency of -the pellets are
increased.
''
1310~5~
On the other hand, the inner diameter of the cylinder
of the second extruder is formed larger, and the screw
shaft of the second ex-truder is rota-ted more slowly, by
about 10 to 50% of that of the screw shaft of the first
extruder. Accordingly, the resin transferred inside the
cylinder is heated sufficiently by a heater, but is not
overheated because of the low rotational speed of the
second screw shaft, resulting in less degradation of the
resin.
However, when the ratio of the inner diameters of
cylinders of two extruders is smaller than that describecl
above, almost no above-mentioned effects can be obtained
by cylinders having different inner diameters. When the
ratio is larger than that described above, the ro-tati.onal
frequency of -the screw shaft of the first extruder becomes
faster than is needed, thereby adversely affecting the
resin.
In this extruding apparatus, when the entire
apparatus is operating, the semimolten pelle-ts and the
filler material are transferred axially with respect to
cylinder 14 and shaft 16, and the gas, produced when the
resin is melted, is exhausted through hole 44 during
transfer. A part of resin 66 in a molten or semimolten
state is extruded into hole 44 as described above, but the
resin or the filler material in hole 44 is :orced to
return into cylinder 14, by force of gravi-ty, due to hole
44 being inclined aæ shown in Fig. 2. In addition, since
hole 44 is inclined, with respect to the normal line of
the screw shaft, at a predetermined angle, in a direction
opposite to the direction of rotation of the screw shaft,
the resin emerging from hole 44 is scraped by blade 72, as
shaft 16 rota-tes, thereby most of the remaining resin then
returning into cylinder 14.
However, the molten or semimolten resin t.rapped in
hole 44 and attached to its inner wall surface gradually
-` t 31 045~
g
expands, pushes an~ opens normally closed valve 76, and
then is extruded into airtigh-t vacuum chamber ~8.
The resin extruded into chamber 48 flows downward,
and is stored thereinO At the same time, the gas and the
resin are separated, the gas being drawn GUt and removed
by pump 5~.
When the resin stored in chamber 48 approaches
connecting port 56 of the ven-t hole, pump 58 is tem-
porarily stopped to equalize the pressure inside chamber
l() 48 with an ambient atmosphere, fastener 78 is loosened to
open bottom cover 50, and the solidified resin is removed
from chamber 48. Thereafter, cover 50 is closed and
fastened by fastener 78, and pump 58 is restarted.
As is described above, in the extruding apparatus of
the present invention, the resin extruded from the vent
hole is solidified in chamber 48. For this reason, the
resin can be easily removed, and the resin extruded into
the airtight vacuum chamber can be re-used, because it is
almost uncontaminated by a polluted ambient atmosphere.
In addition, the interior of chamber 48 can be easily
observed, since top cover 62 includes a transparent
portion. Moreover, top and bottom covers 62 and 50 can be
opened to facilitate cleaning of the interior of chamber
48.
When inclination angle A of hole 44 is se-t within the
range described above, with respect to the normal line of
cylinder 14, -the resin supplied into hole 44 can be easily
returned to the cylinder. When angle A is set outside the
above range, the amount of resin supplied into hole 44 is
increased.
When the angle of inclination of hole 44, with
respect -to the horizontal, is set to about 45, chamber 48
- lo -- 1 3 1 04 5 6
can be easily mounted thereon, ancl the supplied amount of
-the molten resin can be reduced.
As a modification of this embodiment, two such
airtight vacuum chamberæ 48 may be provided and moun-ted -to
be alternately slid to opening 56 of hole 44. When one of
the airti.ght vacuum chambers becomes full of resin, and
the resin is to be removed, another airtight vacuum
chamber may then be connected to opening 56, replacing the
first chamber. Thus, the efficiency of the extruding
apparatus can be further increased.
In addition, since a vent hole for exhausting by -
produced gas is provided at a portion near the supply
port, the surface a.rea of the pelletized semimolten resin
is increased near the vent hole, with the result that the
gas included therein is completely exhausted out.