Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
PATEN~ APPLICATION OF
RONALD LINGEMANN AND HOWARD W. SELBY III
FO~
ADAPTIVE ELECTRICAL POWER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
Background of the Invention
Field of Invention
Thi~ invention relates generally to electrical
power sy3tems in battery-operated electronic devices, and
more particularly to an electrical power management system
that controls power consumption of various components
within an electronic devica so as to conserve power use
and prolong battery operation.
De~cr:lption o~ Prior Art
Numerous electronic devices today can be operated
on battery power. Due to electrical demands within the
such d~vices, e.g., portable computers, to power
components such as diso drivas, display screens, back
light elements, etc., operation of such devices on battery
power alonQ is limited.
Prior art in computer technology allows the user
to manually turn off various elements within the computer
which ara not needed ( Q . g ., modems can be deactivated by
the user in most portabl~ computers) and some computers
` allow the display screen to b~ powered down after a
specified tim~ period during which the computer receives
no user input (this is called a tim~-out procedure).
It would bQ desirable to have an electrical power
management system that automatically powers components of
an electronic device on and of~, or reduce~3 power
~ ~OO~
-2-
consumption o~ such componenks based on the operational
requirements of the device and the need~ of the user.
Summary of the Invention
~he invention provides a means to conserve power
consumption in a battery operated electronic device by
determ~ning when a component within the device i~ not
required to be fully powered, a determination that i~
based on the operation of the electronic device. The
invention involves monitoring operation of the electronic
device and analyzing the power consumption of components
within the device. The invention uses algorithms to
recognize information which indicates that a given
component or group of components i8 not opQrationally
requlred and can be powered down. The power supply to the
component or group of components is partitioned so that
the component or group of component~ can be powered down
without affecting the power consumption of other
components within the electronic device.
As us~d in this specification, powered down
includes turning power completely off or any other power
conser~ation state that ls less than full power on (such
as reducing the clock speed in a computer which affects
the power consumption o~ components interrelated to the
clock speed).
The algorithms employed in the invention can
analyses a broad variety of softwarQ instructions without
any prior Xnowledge or experience with such software
permitting the power managemant system to automatically
operate while running mo~t software that is used today.
In addition, the invention may employ adaptive --
techniques which allow the user to instruct the power
manayement ~ystem when it ha~ made an error in a power
management decision; once instructed, the power management
system adapts itself so that the proper power management
decision is made the next time.
~3()S~3~L
--3
Components within the electronic device are
power~d on or down as needed during operation of the
device. This yield~ prolonga~d operation o~ the electronic
device on battery powPr.
Brief Description of the Drawl~@
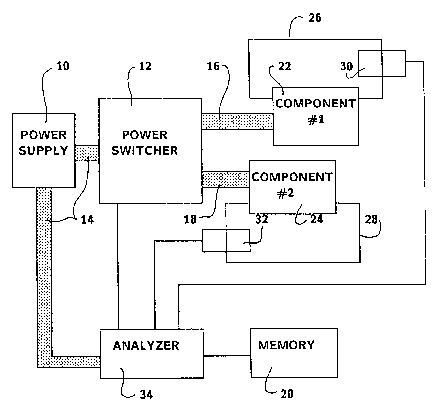
FIG. 1 is a block diagram o~ a partitioned power
circuit showing two partition~ed power buse6 controlled by
an analyzer and power switcher, and two CompOnentB~ one
connected to each o~ the two partitioned power buses.
FIG. 2 is a flow chart of the operation of the
adaptive electrical power management sy~tem.
Detailed Description of the Preferred EmbodimentA
Referring now to the drawings, therein like
numerals represent like or corresponding elements
throughout the several views, there is shown in FIG. 1 the
elements o~ an elactronic device which incorporate~ the
invention, showing a main pow~r supply 10, a main pOWQr
bus 14, a power ~witcher 12 which contxols power to two
partition~d power buses 16 and 18, each partitioned power
bu~ being connected to a component 22 and 24 respectively,
and the analyzer 34 which controls the power switcher.
Main power to the electronic device i9 supplied
by the main power supply 10 which con3titutes a battery
operated type power supply. The main power supply 10
feed~ electrical power to the main power bus 14 which
supplies ~lectrical power to the power switcher 12 and the
analyzer 3~.
Hardware implementations of the analyze~ 34 could ~
include a processor, an auxiliary microproces~or (such as ~:
a Motorolla 68HCll); a logic cell array ~such as a
conventional Xylink M2018 logic cell array); a macro cell
array (such as a conventional LSI Logic Corporation LL3020
macro cell array); an application-specific integrated
circuit; a yate array; or other forms o~ mask programmable
logic. The analyzer controls power consumption o~ the
,.; ' '~:
~oo~o~ :
-4-
component~. A shown in FIG. 1 the control of power
con~umption of the component~ i~ a function o~ controlling
the partitioned power buses. Thi~ method of control i5
the ba is ~or the descxiptioll that follows. However, the
analyzer 34 could control other elements such as a switch
on the component itself, or an element such as the clock
in a computer, that would control the rate of power
consumption of a component a~a a means of managing power
consumption.
Components or eleme,nts of the electronic device
22 and 24 are connected to the partitioned power buses, 16
and 18 re~pectivaly, and are independently powered by such
buses .
The path of instruation flow for each component
is shown on FIG. 1 as 26 and 28 respectively. Each path
is monitored by tha analyzer 34 through instruction
detectors 30 and 32.
The analyzer 34 monitors all ~ystams within the
devlce to determina whethQr components are needed or not
~or operation of the device. FIG. 1 shows ~ust two
components within the devicQ. TherQ could ba many more
compon~nts or groups of component3 that are monitored.
A memory element 20 is also controlled by the
analyz0r 34. The memory stores the state o~ a component
prior to that component being powered down 50 that that
state can be reinstalled in the component prior to its
being powered up. The memory function is only used if the
state of a component needs to be saved and restored during
a power down cycle.
FIG. 2 is a flow chart showing the operation of
the adaptive power management system. At step 100 a given
component within the device is powered on. At step 101
the analyzer monitors information related to the operation
o~ the device. The analyzer looks for a pattern that
indicates that a component is not being used. The
analyæer's ability to recognize such a pattern is based on
algorithms. Recognition of such a pattern answers the
i~O~)Sll~
-5-
question of whether the component i8 needed or not, step
102.
I~ the component i5 needed, step 103, the
analyzer continues to monitor operation of the device to
determine i~ the component continue~ to be needed, step
101. I~ the component is not needed, ~tep 104, the
component power down saquence commences, step 105.
I~ the component 1 8 state i5 needed once the
component is powered on again, the state of the component
is saved in memory be~ore the component is powered down so
that that ~tate can be relnstalled prior to re-
establishing power to tha component, st~p 105. Once the
component ~tate i~ saved, t~e component is powered down
either through the pow~r bus that serves the component or
at the component itself. Components on the main power bu3
and other partitioned power buse~ are not affected.
In step 106, the analyzer continues to monitor
operation a~ the device for in~ormation indicating that
the component i9 needed agaln. The analyzer continually
checks to see whether the component is needed, step 107.
I~ the component is not n~eded, the analyzer continues its
monitoring function, step 106.
I~ the ¢omponent is needed, step 108, the
component power up sequence commenceR, step 109. If the
state of the component had been stored in memory, that
StatQ i9 reinstalled in the component and the power to the
partitioned bus serving th~ component is re-established.
The component returns to a powered on status, step 111.
The process of monitoring and analyzing operation
information and powering components up and down continues
during operation o~ the electronic devica. Components are
only powered down when thay are inactive or nok neaded.
The result is less power consumption by tha electron~c
de~ice. ~-
`
.'.`'~.,"
';:`: -" ''
:~ '~',''' ''
- :''.