Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
~034065
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Field of the-Invention
The present invention relates to an industrial robot
and more particularly to an industrial robot having at least
three articulated pivotal joints. The present invention can
most suitably be applied to a welding robot for carrying out
spot welding in a motor vehicle body assembling line but the
invention is not limited to such an application.
Description of the Prior Art
In the motor vehicle industry, there is an increasing
trend of manufacturing the vehicle body by welding thin steel
sheets for decreasing the body weight and providing the body
with a required rigidity. Spot welding is commonly adopted
for the purpose. Recent tendency is that the spot welding is
made with finer spacings than used to be so that number of
spot welding is substantially increased. As an example,
approximately 5000 spot weldings are made in each one of
vehicle bodies. It is therefore unavoidably required in a
vehicle body assembling line to provide a spot welding line
of a substantial distance. From the viewpoint of effective
utilization of the factory space, however, it is advisable to
make the spot welding line as short as possible.
A typical example of spot welding robots adopted in
vehicle body manufacturing lines is shown in Figures 10 and
11. As shown, the robot includes a stationary base 1
supporting a swivel body 2 for swivel movements about a
vertical axis 3. On the swivel body 2, there is mounted a
vertical swing arm 5 for fore-and-aft swinging movements
2034065
about a horizontal axis 6. On the upper end portion of the
arm 5, there is mounted a horizontal swing arm 8 for vertical
swing movements about a horizontal axis 7. The horizontal
arm 8 carries a hand 9 having welding electrodes at a tip
end. A link 11 is provided to extend in parallel with the
arm 5 and connected at an upper end with a rearward end
portion of the horizontal arm 8. The link 11 has a lower end
which is connected with a horizontal link lla which extends
rearwardly from the axis 6 in parallel with the arm 8.
As shown in Figure 11, the swivel body 2 is provided
with a driving motor 4 for driving the arm 5 about the axis
6. the arm 5 is swingable in the fore-and-aft direction
through an angular range 02. The swivel body 2 is further
provided with a driving motor 10 which is arranged to drive
the link lla so that the link 11 is moved in a vertical
direction to thereby make the horizontal arm 8 swing in the
vertical direction through an angular range 03. Appropriate
operations of the motors 4 and 10 cause swinging movements of
the arms 5 and 8 so that the robot hand 9 can be moved in the
region designated by the reference numeral 13.
This type of welding robot is considered as being
advantageous in that the robot hand can be moved in a wide
range with a relatively small robot body. It should however
be noted that the welding robot of this type still has a
disadvantage which will be described below. In Figure 10,
the rearward end portion of the arm 8 is shown by the
reference numeral 12 when the arm 8 is in the horizontal
2034065
position and by the reference numeral 14 when the arm 8 is in
the fully upwardly swung position. It will therefore be
understood that the rearward end portion 14 of the arm 8
projects by a distance R1 from the vertical axis 3 around
which the swivel body 2 is rotated.
It will be noted that in this structure the rear end
portion 14 of the arm 8 moves along a circular path of a
radius R1 with a center at the axis 3 when the robot is
rotated about the axis 3. In a typical vehicle body welding
line, a plurality of robots 16 are arranged side by side with
relatively small spacings between each adjacent two robots as
shown in Figure 12 at each side of a conveyor along which
vehicle bodies 15 are moved. The aforementioned movement of
the rear end portion 14 of the arm 8 may then cause an
interference with the adjacent robot so that a larger spacing
between each two adjacent robots must be provided for
avoiding such possible interference.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is therefore an object of the present invention to
provide an industrial robot which requires a smaller space
than a conventional robot does.
Another object of the present invention is to provide
an industrial robot in which possibility of interference with
a robot which is located to the first-mentioned robot can
significantly be decreased.
According to the present invention, the above and other
objects can be accomplished by an industrial robot including
an arm assembly having at least a first arm and a second arm,
20~065
each having a longitudinal axis, said first arm being mounted
at a lower end portion on a base for a swingable movement in
a substantially vertical plane about a substantially
horizontal first axis, said second arm being provided
adjacent to an upper end portion of said first arm to extend
in a direction crossing the longitudinal axis of said first
arm, pivot means provided between said first and second arms
for allowing swingable movements of said second arm with
respect to said first arm about a second axis which is
perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of said first arm and
a third axis which is in a plane cont~in;ng the longitudinal
axis of said first arm, driving means for selectively
effecting said swingable movements of said first and second
arms.
According to the features of the present invention, the
pivot means is provided for allowing a swingable movement
about the third axis which is in a plane containing the
longitudinal axis of the first arm and the pivot means is
located above the first axis which is provided for the
swingable movement of the first arm in a substantially
vertical plane. It will therefore be understood that the
rearward end portion of the second arm will be moved under
the swingable movement about the third axis along a circular
path of a radius corresponding to a horizontal distance
between the pivot means and the rear end of the second arm
and this radius does not increase even when the first arm is
fully inclined rearward. Thus, the possibility of
2034065
interference between the rear end of the second arm and
an adjacent robot will significantly be decreased.
According to one aspect of the present invention, the
second axis is located below the third axis. For the
purpose, a swingable member may be connected to the upper end
portion of the for the swingable movement about the second
axis. The second arm is- connected to the swingable member
for the swingable movement about the third axis. In this
arrangement, the swingable member is swingable in a
substantially vertical plane and the third axis lies in this
plane. In another aspect of the present invention, the third
axis is located below the second axis. In this arrangement,
a rotatable member may be provided in axial alignment with
the longitudinal axis of the first arm for a rotational
movement about the third axis which is in an axial alignment
with the longitudinal axis of the first arm. The second arm
may then be connected with the rotatable member for the
swingable movement about the second axis in a sideward
direction.
The above and other objects and features of the present
invention will become apparent from the following description
of preferred embodiments taking reference to the accompanying
drawings.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Figure 1 is a side view of a spot welding robot in
accordance with one embodiment of the present invention;
Figure 2 is a plan view of the robot shown in Figure 1;
Figure 3 is a sectional view taken substantially along
2034065
the line A-B-C-D in Figure 1;
Figure 4 is a partially cut-away front view of a lower
portion of the robot;
Figure 5 is a partially cut-away side view of an upper
portion of the robot;
Figure 6 is a partially cut-away front view of the
upper portion of the robot; .
Figure 7 is a plan view of the robot with the upper arm
in a forwardly shifted position;
Figure 8 is a plan view of a vehicle body welding line
showing an example of arrangement of the spot welding robot
shown in Figures 1 through 7;
Figure 9 is a schematical illustration of a spot
welding robot in accordance with another embodiment of the
present invention;
Figure 10 is a side view similar to Figure 1 but
showing a conventional spot welding robot;
Figure 11 is a perspective view of the conventional
robot shown in Figure 10; and,
Figure 12 is a plan view of a vehicle body welding line
showing interference between two adjacent robots.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
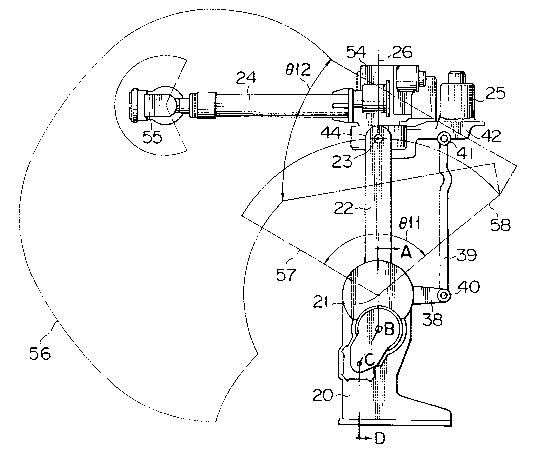
Referring to the drawings, particularly to Figures 1
and 2, there is shown a spot welding robot including a
stationary base 20 supporting a lower arm 22 for a swingable
movement about a horizontal axis 21. The lower arm 22
extends upwards from the base 20 and has an upper end on
20~065
which an upper-arm 24 is mounted. For mounting the upper arm
24 on the lower arm 22, there in provided a swingable member
or a mounting bracket 42. Referring to Figure 6, it will be
noted that the swingable member 42 has a pair of stub shafts
42a provided at diametrically opposite positions and is
mounted at the stub shafts 42a on the upper end portion of
the lower arm 22 for swingable movement about a horizontal
axis 23.
As shown in Figure 1, a link 39 is provided in parallel
with the lower arm 22. Referring to Figure 4, it will be
noted that the lower end of the lower arm 22 is mounted on
the base 20 through a horizontal shaft 20a which has an axis
coaxial with the aforementioned axis 21. A horizontal link
38 is integrally connected at one end with the horizontal
shaft 20a. The other end of the horizontal link 38 is
pivotally connected through a pin 40 with the lower end of
the link 39. The upper end of the link 39 is pivotally
connected through a pin 41 with the swingable member 42 as
shown in Figure 1.
Referring to Figures 5 and 6, it will be noted that the
upper arm 24 is formed at a rear end portion 54 with a stub
shaft 54a which is extending vertically downward and mounted
through a bearing 54b on the upper end of the lower arm 22
for swingable movement about an axis 26 which is
perpendicular to the axis 23. As shown in Figure 1, the
upper-arm 24 is provided at a front or tip end with a hand 55
which has welding electrodes.
In order to drive the lower arm 22 for effecting the
203~065
swingable movement, the arm is provided at the lower end
portion with a gear 43 as shown in Figure 3. The gear 43 is
in meshing engagement with a gear 80. A driving motor 81 is
provided and has an output shaft 81a which is drivingly
connected through a gear mechanism 82 with the gear 80. A
selective operation of the driving motor 81 will therefore
produce a swingable movement of the lower arm 22 throughout
an angular range 011 shown in Figure 1.
Referring to Figures 3 and 4, it will be noted that the
shaft 20a is provided with a gear 36 which is rigidly secured
to the shaft 20a. A motor 27 is provided and has an output
shaft 28 to which a driving gear 29 is secured. an
intermediate gear is provided on an intermediate shaft 31 and
is in meshing engagement with the driving gear 29. The
i5 intermediate shaft 31 further has a gear 32 secured thereto.
The gear 32 on the intermediate shaft 31 is in meshing
engagement with a gear 33 provided on a second intermediate
shaft 34. The second intermediate shaft 34 has a gear 35
which is in meshing engagement with the driving gear 36 on
the shaft 20a. It will be understood that the lower arm 22,
the links 38 and 39 and the swingable member 42 provide a
parallelogram so that a selective operation of the driving
motor 27 causes a swinging movement of the link 38 and a
swinging movement of the member 42. Thus, the upper arm 24
is swingably moved through an angular range ~12 as shown in
Figure 1.
Referring now to Figures 5 and 6, it will be noted that
2034065
a driving motor 25 is provided on a rear end portion of the
swingable member 42. The motor 25 has an output shaft 46
which is provided with a pulley 46a. On the swingable member
42, there is further provided a pulley 48 which is drivingly
connected with the pulley 46a through a belt 47. An
intermediate pulley 49 is provided coaxially with the pulley
48 and connected with this pulley 48 to rotate together. A
driven pulley 51 is provided at the lower end portion of the
stub shaft 54a on the rear end portion 54 of the upper arm 24
and connected with the pulley 49 through a belt 50. It will
therefore be understood that by a selective operation of the
motor 25 the upper arm can be swingably moved about the axis
26 through an angular range ~13 as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 7 shows the upper arm 24 in a position swung leftward
about the axis 26.
In the structure described above, the hand 55 on the
tip end of the upper arm 24 can be moved throughout the range
56 as shown in Figures 1 and 2 by selective operation of the
driving motors 25, 27 and 81. By an operation of the motor
81, the lower arm is moved to swing between a forwardly
inclined position 57 and a rearwardly inclined position 58.
In the rearwardly inclined position 58 of the lower arm 22,
the swing axis 26 is shifted rearwards to a position shown by
a reference 26a in Figure 2. The rear end portion of the
swingable member 42 is also shifted rearwards to a position
shown-by a reference 42b. When the motor 25 is operated with
the lower arm 22 located in this rearwardly inclined position
58, the rear end portion 54 of the upper arm 24 will be moved
203406~
along a circular path having a center of the circle at the
point 26a as shown by a reference 54b in Figure 2.
In a conventional design, the horizontal swinging
movement is produced about a vertical axis which will not be
shifted rearward even when the lower arm is inclined
rearwards. Therefore, the upper arm 24 will be swingably
moved about the axis 26 even when the lower arm is fully
inclined rearwards. Thus, the rear end portion 54 of the
upper arm 24 will be moved along a circular path 54c having a
center of circle at the point 26 as shown in Figure 2. The
arrangement of the present invention is advantageous over the
conventional design in that the path of the rear end portion
54 of the upper arm 24 is much smaller than in the
conventional design.
The illustrated structure is further advantageous in
that the motor 25 for driving the upper arm 24 is provided on
the swingable member 42 which is formed separately from the
upper arm 24. In Figure 2, it will be noted that the
swingable member 42 will be shifted rearwards to the position
shown by 42b when the lower arm 2 is fully inclined
rearwards. However, since the swingable member 42 is made
separately from the upper arm 24, the rear end portion of the
member 42 does not move when the upper arm 24 is swung about
the axis 26a. According to the conventional design, the
upper arm is mounted on the upper end portion of the lower
arm and had a rearward extension to provide the
aforementioned parallelogram. The rear end portion of the
2034065
upper arm will therefore be moved along a circular path 59
having a center of circle at the point 26 shown in Figure 2.
The -structure of the illustrated arrangement is therefore
significantly advantageous over the conventional design in
decreasing the space required for locating the robot.
In Figure 8, there is shown a typical example of
arranging the robots in accordance with the present
invention. As shown, vehicle bodies 60 to be welded are
transported along a conveyor 62. A plurality of robots 61
are arranged along the opposite sides of the conveyor 62.
According to the present invention, it becomes possible to
locate the robots with close spacings.
Referring now to Figure 9, there is shown another
embodiment of the present invention. The robot shown in
Figure 9 includes a stationary base 63 supporting a lower arm
65 through a horizontal shaft 64 for a swingable movement.
An intermediate arm 67 is connected with the lower arm 65
through a swivel joint 66 so that the arm 67 is rotatable
about a longitudinal axis of the lower arm 65. An upper arm
68 is connected to an upper end of the intermediate arm 67
for a swingable movement about an axis 71 which is
perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the lower arm 65.
The upper arm 68 is connected at a tip end with a second
upper arm 70 through a swivel joint 69 for rotation about a
longitudinal axis of the first upper axis 68.
The invention has thus been shown and described with
reference to specific structures, however, it should be noted
that the invention is in no way limited to the details of the
203~06S
illustrated structures but changes and modification may be
made without departing from the scope of the appended claims.