Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
TRANMIS5ION SYSTEM
WO90/03082 describes a transmission system for a
temporal and spatial high definition picture signal with a
large band width being transmitted over two transmission
channels with a smaller band width whereby a first transmission
channel transmits picture signals of a first standard with
lower spatial and higher temporal definition and a second
transmission channel transmits a spatial high definition but
temporal low definition picture signal.
The invention specifies a transmission system as
well as a receiver for a high definition television signal
which also renders possible the reconstruction of picture
information when only one channel is received using existing
limited band transmission channels on the receiver side.
A HDTV signal with higher spatial and temporal
definition is split into two signals on the transmitter side.
The first signal exhibits a small spatial but high temporal
definition and can be converted, through corresponding coding,
into a standard TV signal, for example, PAL, Secam, NTSC or
D2-MAC or digital with or
A 27779-22
i
2Q~8719
-- 2 --
without data reduction, and transmitted over a first limited
band channel.
The second signal exhibits a high spatial but small
temporal definition. This can be attained, for example,
through the omission of frames, preferably every second
frame. The signal can be converted through a corresponding
coder, for example, into a HD-MAC signal, or also be
directly transmitted in digital form with or without data
reduction over a second limited band channel.
On the receiver side, a complete picture signal with
low spatial and high temporal definition can be received
with the aid of the first channel.
A complete picture signal with low temporal and high
spatial definition can be received via the second channel
from which an adequate picture signal with high spatial
definition, hereinafter called HD signal, can be
reconstructed through suitable decoding and measures for the
picture regeneration.
The regeneration measures serve for the reconstruction
of lost information which is lost on the receiver side
through the omission of frames particularly with moving
sequences.
When a complete HDTV signal is to be regenerated both
channels must be evaluated on the receiver side. For that
purpose, the temporal high definition frame information from
the first channel is utilized for the reconstruction of the
HD picture, in particular with dynamic picture contents.
Thus, a HDTV transmission system compatible with the
conventional transmission systems ensues whereby the first
channel supplies a picture signal with a definition
H 89/097 REPLACEMENT SHEET
- 3 ~ 7 ~ ~
corresponding with the present television standard and the
second channel supplies a complete picture signal with a high
spatial definition.
It is the object of this present invention to create
the possibility for a transmission similar to HDTV, with at
least the high spatial resolution of the HDTV picture, also via
the second transmission channel.
In accordance with the present invention, there is
provided method for the transmission of a picture signal of
high temporal and spatial definition and of large band width
over two transmission channels each having a smaller band
width, wherein the first transmission channel transfers a
complete standard picture signal with low spatial and high
temporal definition which can be decoded and reproduced by a
standard receiver, and wherein the second transmission channel
transfers an auxiliary signal which can be combined with the
standard picture signal by an improved receiver in order to
form a picture signal having high spatial and high temporal
definition, characterized in that the auxiliary signal is a
complete picture signal with high spatial and low temporal
definition which can be decoded by an improved receiver, and
in that: motion vectors are transmitted over at least the
second transmission channel; additional information concerning
the other channel, which can be used for automatic tuning to
that channel, is transmitted in at least one of the two trans-
mission channels; one transmission channel transfers amplitude
and phase position reference signals for the purpose of match-
ing the amplitude and phase position of the picture signal of
the other transmission channel.
A 27779-22
.,
- 3a - ~ 7 ~ ~
In accordance with another aspect of the invention,
there is provided method for the transmission of a picture
signal of high temporal and spatial definition and of large
band width over two transmission channels each having a smaller
band width, wherein the first transmission channel transfers a
complete picture signal with low temporal definition and the
second transmission channel transfers an auxiliary signal which
can be combined with the low definition picture signal in an
improved receiver in order to form a picture signal having high
spatial and high temporal definition, characterized in that the
first transmission channel transfers in digitally coded form
from a source picture signal every second picture with low
temporal and high spatial definition and the second trans-
mission channel transfers in digitally coded form the other
pictures of the source picture signal with low temporal and
high spatial definition as the auxiliary signal, and in that:
motion vectors are transmitted over at least the second trans-
mission channel; additional information concerning the other
channel, which can be used for automatic tuning to that
channel, is transmitted in at least one of the two transmission
channels; one transmission channel transfers amplitude and
phase position reference signals for the purpose of matching
the amplitude and phase position of the picture signal of the
other transmission channel.
From WO90/03082 it is known that motion vectors are
determined in the coder and transmitted. However, because the
channel capacity is limited the motion vectors cannot be
transmitted with the desired precision, rather, only with a
27779-22
A
~,
- 3b ~
limited value. Ho~ever, more accurate motion vectors can be
formed in an improved receiver, preferably by utilizing the
transmitted motion vectors.
If the receiver combines the signals from the first
transmission channel with the signals from the second trans-
mission channel, the signals must fit together. In particular,
the level and phase situation of the signals must be adapted
if the signals are transmitted over two different channels.
For this purpose, one channel contains reference signals for
level ~d phase.
For the user to economize on the input, or rather,
the programming of each of the two channels for the reproduction
of a HDTV broadcast, either the first channel or the second
channel or both channels can contain additional information
and by means of which the receiver automatically determines
and receives the other required channel.
27779-22
A
7 ~ ~
-- 4 --
If, in a corresponding future television system, both
channels are used as digital channels for transmitting HDTV
signals and with the temporal position of the pictures from the
first channel being between the pictures from the second
channel, a better use of the picture memories, or rather, a
reduction in the number of picture memories can be achieved, in
a corresponding receiver which necessarily contains picture
memories, through the loss of a picture regeneration circuit
and a frame-wise changeover between picture memories.
Two embodiment examples are subsequently illustrated
by means of the following drawings. They show:
Fig. 1 -- block circuit diagram in a HD-decoder with
improved motion vector calculation,
Fig. 2 -- known two-channel HDTV transmission system
with an analog and a digital channel each,
Fig. 3 -- block circuit diagram of a known picture
regenerator, and
Fig. 4 -- two-channel HDTV transmission system with
two digital channels according to the invention.
Fig. 1 shows an improved HD-decoder 7 with a buffer
memory and video multiplexer 15. Always one of the outputs of
the buffer memory 15 leads to a decoder 16 and another to a
motion vector decoder 21. One output of the decoder 16 leads
to a block reconstruction circuit 20 via an inverse weighting
17, an inverse scanner 18 and an inverse discrete cosine
transformer 19. The output of the block
27779-22
A
2U68719
reconstruction circuit 20 leads to a picture regeneration
circuit, which is not shown here, as well as a first input
of a picture memory 22. The output of the motion vector
decoder 21 leads firstly to a motion vector corrector 211
and then to a second input of the picture memory 22.
Transmitted addresses and coefficients are decoded into
their original form prior to transmission in the decoder 16.
Likewise, the motion vector decoder 21 carries this out for
the motion vectors. However, because only a limited data
rate is available for the transmission of the motion vectors
they also only exhibit a limited accuracy, or rather, a
limited value. Whether the motion vectors have a correct
value can be examined through a comparison of the newly
calculated picture elements with the already existing
surrounding picture points in a receiver with an improved
HD-decoder 7. If this is not the case they are adjusted
accordingly in the motion vector corrector 211 by means of
already calculated picture elements from the picture memory
22.
Fig. 2 shows the two-channel HDTV transmission system
proposed in WO 90/03082. A HDTV signal generated by a
source ïs fed to a first transmission path consisting of a
transcoder 1 and a TV-encoder 2 in the transmitter and a TV-
decoder 3 and a transcoder 4 in the receiver and to a second
transmission path consisting of a picture suppression
circuit 5 and a HD-encoder 6 in the transmitter and a HD-
decoder 7 and a picture regeneration circuit 8 in the
receiver.
The transcoder 1 of the first transmission path reduces
the horizontal definition of the picture in the ratio 2:1
and the vertical definition in the ratio 3:2 through
suitable filtering. Besides, the present, progressivly-
scanned HDTV signal is converted into a signal afflicted
H 89/097 REPLACEMENT SHEET
20~87~9
with line interlacing whereby the received temporal
definition remains. The output signal of the transcoder 1
is fed to the TV-encoder 2 which generates a standard TV
signal, for example, in PAL, Secam, NTSC or D2-MAC, and the
output of which is connected with a first transmission
channel.
The incoming standard TV signal is decoded in the TV-
decoder 3 in the receiver section for the first transmission
channel. The standard TY signal is then available at the
output of the TV-decoder 3.
The HDTV signal which is fed over the second
transmission path is subjected to an omission of pictures
for the adaptation to a second transmission channel with a
limited band. For example, by means of the picture
suppression circuit 5 only every second frame is
transmitted. The output signal of the picture suppression
circuit 5 arrives at a second transmission channel via the
HD-encoder 6. The HD-encoder generates, for e~ample, a
digital signal which is transmitted over the channel after
data reduction.
The incoming signal is fed to the HD-decoder 7 in the
receiver section for the second transmission channel. The
output of the HD-decoder 7 is connected to the picture
regeneration circuit 8 which carries out a reconstruction of
the frames omitted on the receiver side by using motion
vectors transmitted with the signal. A HD signal with high
spatial definition and the original temporal definition is
then available at the output of the picture regeneration
circuit 8 with, however, possible errors in the area of
moving picture contents.
In order to minimize these errors in the area of moving
picture contents and therewith attain the original high
H 89/097
2Q5~7i9
-- 7 --
temporal definition of the source HDTV signal an inversion
of the function of the transcoder 1 is undertaken in the
transcoder 4 with the standard TV input signal. The output
signals of the transcoder 4 and the picture regeneration
circuit 8 are fed to a combination filter 9 which supplies a
HDTV output signal with high temporal and spatial definition
by suitable weighting.
Fig. 3 represents the picture regenerator 8 described
in WO 90/03082. The output signal of the HD-decoder 7 is
fed to a first picture memory 38. One output of the first
picture memory 38 leads to a picture interpolation circuit
37; a further output leads to a second picture memory 39
and a multiplexer 40. Further inputs of the picture
interpolation circuit 37 receive further data from the HD-
decoder 7, for example, the motion vectors 53 and the code
mode information 54, i.e. information concerning inter-, or
rather, intra-frame coding. One output of the picture
interpolation circuit 37 leads to the multiplexer 40. A HD
signal with 1440 * 864 picture elements, 50Hz, 1:1 is
available at the output of the multiplexer 40.
Now, if in a future HDTV transmission system digital
information is also transmitted over the analog channel then
the result can be a saving of picture memories in suitable
HDTV receivers.
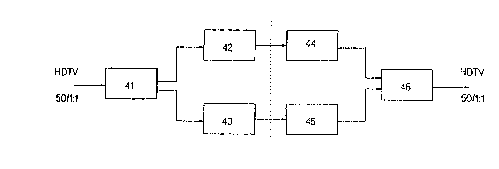
Fig. 4 shows a corresponding HDTV transmission system
for two digital channels. A HDTV signal generated from a
source with, for example, 50Hz frame repetition rate and
progressive scanning, is split into odd- and even- numbered
frames in a separation circuit 41. The odd-numbered frames
are coded in a first HD-encoder 42 and the even-numbered
frames in a second HD-encoder 93. Therewith, the motion
vectors can also be calculated and transmitted to the
respective HD-decoder together with the coded HD picture
H 89/097 REPLACEMENT SHEET
20~8~9
- 8 -
signals. The data for the odd-numbered frames are, for
example, transmitted over the first channel and decoded in a
first HD-decoder 94. Accordingly, the data for the even-
numbered frames are transmitted over the second channel and
decoded in a second HD-decoder 45. The streams of output
data from both HD-decoders are combined in a combination
circuit g6 and a HDTV-signal is generated with, for example,
a standard corresponding with the source signal.
A transmission system according to WO 90/03082 contains
three picture memories (22, 38, 399). However, the
transmission system according to Fig. 4 only contains two
picture memories (22 in HD-decoder 44 and 22 in HD-decoder
45). The first HD-decoder 44 and the second 45 each
contain, for example, a HD-decoder according to Fig. 1. A
picture regeneration circuit 8 according to Fig. 3 can be
cancelled with the picture memories 38 and 39 because
alternating, completely coded HDTV pictures are transmitted
in both channels.
.
The picture memories 38 and 39 are cancelled but
because the first HD-decoder 44 and the second HD-decoder 45
each require one picture memory 22 the net result with the
two-channel HDTV transmission system with two digital
channels in contrast to the two-channel HDTV transmission
system according to WO 90/03082 is at least a saving of one
picture memory.
H 89/097 REPLACEMENT SHEET