Note : Les revendications sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
THE EMBODIMENTS OF THE INVENTION IN WHICH AN EXCLUSIVE
PROPERTY OR PRIVILEGE IS CLAIMED ARE DEFINED AS FOLLOWS:
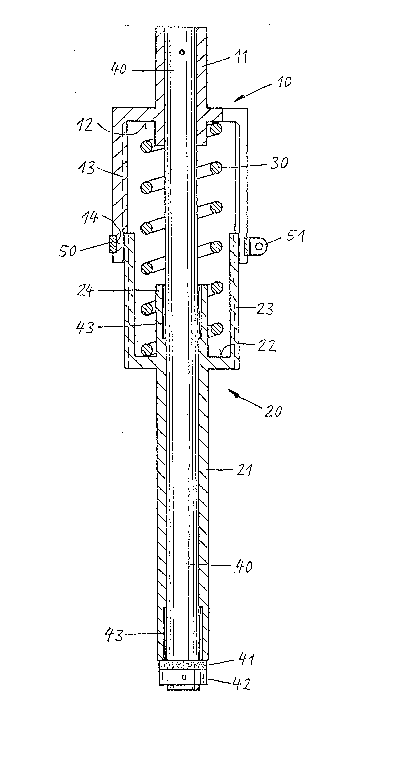
1. Spring-cushioned saddle support for bicycles, characterised
by:
- a top part (10) which has at the top a saddle carrier
spigot (11), and a bottom part (20), which at the bottom
has a tube extension (21) which can be inserted into the
saddle support tube of a bicycle frame,
- a helical compression spring (30), which is provided
between a spring rest (12) of the top part which spring
rest is in the vicinity of the saddle carrier spigot and a
spring rest (22) of the bottom part which spring rest is
in the vicinity of the tube extension,
- telescoping tube members (13, 23) formed on the top part
(10) and the bottom part (20), which originate roughly
from the respective spring rests and which telescope into
each other,
- outer splines provided on the inside telescoping tube
member (23) and corresponding inner splines formed on the
outer telescoping tube member (13),
- a central guide rod (40) which is fastened in the top
part, extends centrally through the telescoping tube
members and is axially displaceably guided (43) in the
bottom part, and
- a dampened (41) stop (42) which is fastened to the bottom
end of the guide rod (40) which protrudes from the tube
extension (21) of the bottom part, which stop interacts
with the bottom face of the tube extension to limit the
possible expansion of the spring.
2. Spring-cushioned saddle support according to claim 1,
characterised in that the guide rod (4) is axially
displaceably guided in guide bushes (43), which are mounted
in the region of the top and bottom ends, respectively, of
the bottom part (20).
3. Spring-cushioned saddle support according to claim 1 or 2,
characterised in that the telescopic tube members (13, 23)
are provided inside of the spring (30).
4. Spring-cushioned saddle support according to claim 3,
characterised in that the inner telescoping tube member
(23) is provided on the bottom part and one of the guide
bushes (43) is mounted in the upper region of this inner
telescopic tube member.
5. Spring-cushioned saddle support according to claim 1 or 2,
characterised in that the telescopic tube members (13, 23)
surround the spring (30).
6. Spring-cushioned saddle support according to claim 5,
characterised in that the outer telescopic tube member (13)
is assigned to the top part.
7. Spring-cushioned saddle support according to claim 5 or 6,
characterised in that the bottom part (20) has a projection
(24) which extends radially inside of the spring, in which
projection the top guide bush (43) is mounted.
8. Spring-cushioned saddle support according to any one of the
claims 5 to 7, characterised in that the outer telescopic
tube member (13) has an axial slot at one place of the
circumference and can be tightened by means of a tightening
device (50, 51) acting in the circumferential direction for
the purpose of setting and adjusting the engagement of the
splines of the telescopic tube members.
9. Spring-cushioned saddle support according to claim 8,
characterised in that the tightening device is a tensioning
strap (50) inserted into a circumferential groove (14) of
the outer telescopic tube member (13) with a tension lock
(51).
10. Spring-cushioned saddle support according to any one of the
claims 1 to 9, characterised in that the profiled section
of the splines or the key-way of one of the two telescopic
tube members (13, 23) is made of plastic material.
11. Spring-cushioned saddle support for bicycles, characterised
-by:
- a top part (10) which has at the top a saddle carrier
spigot (11), and a bottom part (20), which at the bottom
has a tube extension (21) which can be inserted into the
saddle support tube of a bicycle frame,
- a helical compression spring (30), which is provided
between a spring rest (72) of the top part which spring
rest is in the vicinity of the saddle carrier spigot and a
spring rest (22) of the bottom part which spring rest is
in the vicinity of the tube extension,
- a central guide rod (40) which is fastened in the top
part, extends centrally through the spring (30) and is
axially displaceably guided in the bottom part,
- a dampened (41) stop (42) which is fastened to the bottom
end of the guide rod (40) which protrudes from the tube
extension (21) of the bottom part, which stop interacts
with the bottom face of the tube extension to limit the
possible expansion of the spring, and
- a relative rotation preventing mechanism (16, 26; 61, 62),
which is fastened in a rotation preventing manner on the
top part (10) and on the bottom part (20) above and below,
respectively, of the spring rest, and which can be
expanded and compressed in the longitudinal direction of
the saddle support.
12. Spring-cushioned saddle support according to claim 11,
characterised in that the relative rotation preventing
mechanism has complementing telescoping members which may
have any cross-section, which are provided laterally offset
relative to the spring (30), are fastened rigidly on the
top part (10) and the bottom part (20), respectively, and
extend parallel to the guide rod (40).
13. Spring-cushioned saddle support according to claim 11,
characterised in that the relative rotation preventing
mechanism has a guide profile (26) which is provided
laterally offset relative to the spring (30) fastened
rigidly on the top part (10) and the bottom part (20),
respectively, and a sliding pad (16) fastened on the top
part (10) which is guided in it.
14. Spring-cushioned saddle support according to claim 11,
characterised in that the relative rotation preventing
mechanism is a tensioning strap 60 consisting of at least
two members (61, 62) which are connected with each other by
a hinge (63), which is fastened and hinged on the top part
(10) and the bottom part (20) by means of a hinge (64) each
with the axes of the hinges situated perpendicularly to the
longitudinal axis of the saddle support.
15. Spring-cushioned saddle support for bicycles, characterised
by:
- a top part (10) which has at the top a saddle carrier
spigot (11), and a bottom part (20), which at the bottom
has a tube extension (21) which can be inserted into the
saddle support tube of a bicycle frame,
- a helical compression spring (30), which is provided
between a spring rest (12) of the top part which spring
rest is in the vicinity of the saddle carrier spigot and a
spring rest (22) of the bottom part which spring rest is
in the vicinity of the tube extension,
- a central guide rod (40) which is fastened in the top
part (10), extends centrally through the spring (30) and
is axially displaceably guided in the bottom part,
- a dampened (41) stop (42) which is fastened to the bottom
end of the guide rod (40) which protrudes from the tube
extension (21) of the bottom part, which stop interacts
with the bottom face of the tube extension to limit the
possible expansion of the spring, and
- an axial keyway (45) formed in the guide rod, with which
at least one key (25), inserted in the tube extension (21)
of the bottom part (20), engages, while the key and the
keyway are designed to allow relative axial displacement.
16. Spring-cushioned saddle support for bicycles, characterised
by:
- a top part (10) which has at the top a saddle carrier
spigot (11), and a bottom part (20), which at the bottom
has a tube extension (21) which can be inserted into the
saddle support tube of a bicycle frame,
- a helical compression spring (30), which is provided
between a spring rest (12) of the top part which spring
rest is in the vicinity of the saddle carrier spigot and a
spring rest (22) of the bottom part which spring rest is
in the vicinity of the tube extension,
- a central guide rod (40) which is fastened in the top
part (10), extends centrally through the spring (30) and
is axially displaceably guided in the bottom part,
a dampened (41) stop (42) which is fastened to the bottom
end of the guide rod (40) which protrudes from the tube
extension (21) of the bottom part, which stop interacts
with the bottom face of the tube extension to limit the
possible expansion of the spring, and
a relative rotation preventing mechanism (17, 27) between
the top part (10) and the bottom part (20) with a-tubular
axial extension having at least two axially situated slots
(27) provided on either the top or bottom part and on the
other part with axially protruding fingers (17), which
engage the slots (27) and are axially displaceable in
these.
17. Spring-cushioned saddle support according to claim 16,
characterised in that the tubular axial extension has an
externally tapered end region (28) and an adjacent region
which is provided with an outer thread (29), and a clamping
nut (70) which is screwed on the outer thread and has a
tapered inner surface t71) corresponding with the tapered
end region.
18. Spring-cushioned saddle support according to claim 16 or
17, characterised in that the elements preventing the
relative rotation are radially disposed internally of the
spring (30).
19. Spring-cushioned saddle support according to claim 16 or
17, characterised in that the elements preventing the
relative rotation surround the spring (30) on the outside.
20. Spring-cushioned saddle support according to any one of the
claims 16 to 19, characterised in that the elements to
prevent the relative rotation have two diametrically
opposed fingers (17) and two corresponding slots (27),
while the edge surfaces (17a, 27a) on both sides of each
finger and slot, are situated in a plane parallel with each
other.