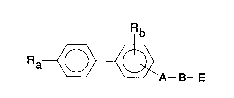Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
" 2098158
-- 1 --
59730~000.562
Biphenyl Derivatives
The present invention relates to biphenyl derivatives,
processes for their preparation and pharmaceutical
composi~tions containing them.
We have found that certain novel biphenyl derivatives
have valuable pharmacological properties, in particular
aggregation-inhibiting effects.
Thus, viewed from one aspect, the present invention
provides compounds of formula I:
Rb
Ra~A--B--E
(I)
(wherein
with the proviso that where E denotes a (C23-
alkoxycarbonyl) group or a benzyloxycarbonyl group, Ra
does not denote an amidino group optionally substituted
by a (C23-alkoxycarbonyl) group or by a
benzyloxycarbonyl group,
Ra denotes an amidino group optionally substituted by an
R1-CO-O-(R2CR3)-O-CO-, (C16-alkoxy)carbonyl, phenyl(C1-6- ~
alkoxy)carbonyl, (C3s-alkenyl)oxycarbonyl or phenyl(C3s-
alkenyl)oxycarbonyl group, wherein
R1 denotes a straight-chained or branched C1s-alkyl
or C1s-alkoxy group, or a Cs7-cycloalkyl, Cs 7-
cycloalkyloxy, phenylalkyl, phenylalkoxy, phenyl or
phenoxy group,
: ~ ..
2098158
-- 2
R2 denotes a hydrogen atom or a C16-alkyl, C3 7-
cycloalkyl, or phenyl group and
R3 denotes a hydrogen atom or a C16-alkyl group;
Rb denotes a hydrogen atom or an alkyl, hydroxy or alkoxy
group;
A denotes a bond or a -CH2-, -CO-, -CH2CO- or -O-CH2CO-
group, wherein the -CH2CO- and -O-CH2CO- groups are each
connected to the group B via the carbonyl group;
B denotes an -NR4-CH2CH2-X-(CH2) n~ group (wherein X
denotes a bond or an -HCRs- or -NR5- group), or an
NR4 CH2CH2 R6C CH , NR4 CO (CH2)m- or -Y-W- group,
wherein Y denotes an -NR4- group or, if A denotes a bond,
Y may also denote an oxygen atom, the above-mentioned Y
or -NR4- groups each being linked to the group A, and
wherein
n denotes the number O or l,
m denotes the number 2, 3, 4 or 5,
R4 denotes a hydrogen atom or an alkyl or
- phenylalkyl group and
R5 denotes a hydrogen atom, or
R4 and Rs together or R4 and R6 together denote an
ethylene group, and
W denotes a straight-chained C25-alkylene group, in
which the ethylene group may be substituted by a
phenylalkylaminocarbonyl group, or W denotes a 1,4-
cyclohexylene group; and
2098~8
-- 3
E denotes a (C26-alkoxy)carbonyl or phenylalkoxycarbonyl
group, a (C4l0cycloalkyloxycarbonyl) group in which a
C58-cycloalkyl moiety may additionally be substituted by
l or 2 alkyl groups,
a (C68-cycloalkyloxycarbonyl) group in which, in the
cycloalkyloxy moiety, a methylene group in the 3- or
4-position is replaced by an oxygen atom or by an imino
group itself optionally substituted by an alkyl,
phenylalkyl, phenylalkoxy-carbonyl, or C26-alkanoyl
group, and wherein the cycloalkyloxy moiety may
additionally be substituted by 1 or 2 alkyl groups,
a (C58-cycloalkenyl)oxycarbonyl, (C35-alkenyl)-
oxycarbonyl, phenyl(C35-alkenyl)oxycarbonyl, (C35-
alkynyl)oxycarbonyl or phenyl(C35-alkynyl)oxycarbonyl
group wherein the carbon attached to the oxycarbonyl
moiety does not itself carry a double or triple bond, a
(C38-cycloalkyl)alkoxy-carbonyl group, a (C810-
bicycloalkyloxycarbonyl) group which may additionally be
substituted by one or two alkyl groups in the
bicycloalkyl moiety, an R1-CO-O-(R2CR3)-O-CO- group
wherein R1, R2 and R3 are as hereinbefore defined, an
R7-CO-CH2-O-CO- group wherein R7 denotes an amino group
optionally substituted by 1 or 2 C16-alkyl groups or by
a C38-cycloalkyl group,
a pyrrolidinyl, piperidinyl, hexamethyleneimino,
morpholinyl or N-alkyl-piperazinyl group, or a 1,3-
dihydro-3-oxo-1-isobenzofuranyloxy-carbonyl group;
whilst unless otherwise specified any alkyl or alkoxy
moiety contains 1 to 3 carbon atoms, and
any phenyl nuclei mentioned above in the definitions of
groups Ra~ B and E may be mono- or disubstituted by
fluorine, chlorine or bromine atoms or by methyl, ethyl,
, - :- ; , ' ~ -
2098158
4 --
n-propyl, isopropyl, hydroxy, methoxy, ethoxy, n-
propoxy, isopropoxy, trifluoromethyl, nitro, amino,
methylamino, ethylamino, n-propylamino, isopropylamino,
acetamino, methanesulphonylamino, carboxy,
methoxycarbonyl, ethoxycarbonyl, n-propoxycarbonyl or
isopropoxycarbonyl groups, and the substituents may be
identicà~l or different);
and the stereoisomers thereof, including the mixtures
and the salts thereof.
Preferred compounds according to the invention include
those of formula I wherein, with the proviso that Ra does
not represent an amidino group optionally substituted by
a (C23-alkoxycarbonyl) group or an amidino group
substituted by a benzyloxycarbonyl group if E denotes a
(C23-alkoxycarbonyl) group or a benzyloxycarbonyl group,
Ra denotes an amidino group optionally substituted by an
R1-CO-O-(R2CR3)-O-CO-, (C13-alkoxy)carbonyl, phenyl (C~ 3-
alkoxy)carbonyl or (C34-alkenyl)oxycarbonyl group,
wherein
R1 denotes a straight-chained or branched C1s-alkyl
-- group or a phenyl(C13-alkyl), C13-alkoxy, Cs 7-
cycloalkyl, Cs7-cycloalkoxy, or phenyl group,
R2 denotes a hydrogen atom or a C13-alkyl, Cs 7-
cycloalkyl or phenyl group and
R3 denotes a hydrogen atom;
Rb denotes a hydrogen atom or a hydroxy or C13-alkoxy
group;
A denotes a bond or a -CH2-, -CO-, -CH2CO- or -O-CH2CO-
group, whilst the -CH2CO- and -O-CH2CO- groups are each
- . ~
- -.. .
~.
20981~8
5 --
linked to the group B via the carbonyl group;
B denotes an -NR4-cH2cHz-x-(cH2) n~ group (wherein X
denotes a bond or an -HCR5- or -NR5- group), an
-NR4-cH2cH2-R6c=cH-~ -NR4-CO-(CHz)m- or -Y-W- group~
wherein Y denotes an -NR4- group or, if A denotes a bond,
Y may aiso denote an oxygen atom, whilst the above-
mentioned Y or -NR4- groups are each linked to the group
A, and wherein
m denotes the number 2, 3, 4 or 5,
, ~ n denotes the number O or 1,
R4 denotes a hydrogen atom or a C13-alkyl or benzyl
group and
R5 denotes a hydrogen atom, or
R4 and Rs together or R4 and R6 together denote an
ethylene group, and
W denotes a straight-chained C2s-alkylene group, in
which the ethylene group may be substituted in the
- ~-position by a phenylethylaminocarbonyl group, or
W denotes a 1,4-cyclohexylene group; and
E denotes a (C26-alkoxy)carbonyl group, a
benzyloxycarbonyl group, a (C410cycloalkyloxycarbonyl)
group wherein a Cs8-cycloalkyl moiety may additionally
be substituted by 1 or 2 C13-alkyl groups,
a (C68-cycloalkyloxycarbonyl) group in which, in the
cycloalkyloxy moiety, a methylene group in the 3- or 4-
position is replaced by an oxygen atom or by an imino
group optionally substituted by a methyl, benzyl,
benzyloxycarbonyl or Cz4-alkanoyl group,
.
' ~ ' ' ':
. ' ~
20981~8
6 --
a (Cs7-cycloalkyl)(C1.2alkoxy)carbonyl group, a (C89-
bicycloalkyloxycarbonyl) group which may additionally be
substituted by one or two methyl groups in the
bicycloalkyl moiety, an R1-CO-O-(R2CR3)-O-CO- group
wherein R1, R2 and R3 are as hereinbefore defined, an
R7-CO-CH2-O-CO- group wherein R7 denotes an amino group
optionally substituted by l or 2 C13-alkyl groups or by
a C57-cycloalkyl group,
or E represents a pyrrolidinyl, piperidinyl,
hexamethyleneimino, morpholinyl or N-methyl-piperazinyl
group, or a l,3-dihydro-3-oxo-l-
isobenzofuranyloxycarbonyl group;
whilst any phenyl nuclei mentioned above in the
definitions of groups Ra~ B and E may each be mono- or
disubstituted by fluorine, chlorine or bromine atoms or
methyl, hydroxy, methoxy, trifluoromethyl, nitro, amino,
methylamino, acetamino, methanesulphonylamino, carboxy,
methoxycarbonyl, ethoxycarbonyl, n-propoxycarbonyl or
isopropoxycarbonyl groups, and the substituents may be
identical or different;
and the stereoisomers thereof, including the mixtures
and the salts thereof.
More particularly preferred compounds according to the
invention include those of formula I above wherein, with
the proviso that Ra does not represent an amidino group
optionally substituted by a (C23-alkoxycarbonyl) group
or an amidino group substituted by a benzyloxycarbonyl
group if E denotes a (C23-alkoxycarbonyl) group or a
benzyloxycarbonyl group,
Ra denotes an amidino group optionally substituted by an
R1-CO-O-(R~CR3)-O-CO-, (C13-alkoxy)carbonyl,
benzyloxycarbonyl or allyloxycarbonyl group, wherein
- ` ,, ~
2Q9~1~8
R1 denotes a straight-chained or branched C14-alkyl
group, a C13-alkoxy group or a cyclohexyloxy group,
R2 denotes a hydrogen atom or a methyl group and
R3 denotes a hydrogen atom;
Rb denotes a hydrogen atom or a methoxy group;
A denotes a bond or a -CH2-, -CO-, -CH2CO- or -O-CH2CO-
group, whilst the ~CH2CO- and -O-CH2CO- groups are each
linked to the group B via the carbonyl group; and
B denotes an -NR4-CH2CH2-X-(CH2) n~ group (wherein X
denotes a bond or an -HCRs- or -NRs- group~, an
-NR4-CH2CH2-R6C=CH-~ -NR4-CO-(CH2)m~ or -Y-W- group,
wherein Y denotes an -NR4- group or, if A denotes a bond,
Y may also denote an oxygen atom, whilst the above
mentioned Y or -NR4- groups are each linked to the group
A, and wherein
m denotes the number 2, 3 or 4,
n denotes the number O or 1,
R4 denotes a hydrogen atom, a C13-alkyl group or a
benzyl group and
R5 denotes a hydrogen atom, or
R4 and Rs together or R4 and R6 together denote an
ethylene group, and
W denotes a straight-chained C25-alkylene group, in
which the ethylene group may be substituted in the
~-position by a methoxyphenylethylaminocarbonyl
group, or W denotes a 1,4-cyclohexylene group; and
:
~ '
~0~81~8
E denotes a (C26-alkoxy)carbonyl group, a (C610-
cycloalkyloxycarbonyl) group in which the cyclohexyl
moiety may additionally be substituted by l or 2 C13-
alkyl groups,
a (C68-cycloalkyloxycarbonyl) group in which a methylene
group in the 3- or 4-position in the cycloalkyloxy
moiety is replaced by an oxygen atom or by an imino
group optionally substituted by a methyl, benzyl,
benzyloxycarbonyl or acetyl group,
a (C56-cycloalkyl)(C12-alkoxy)carbonyl group, a (C8
bicycloalkyloxycarbonyl) group, an R1-CO-O-(RzCR3)-O-CO-
group wherein R1, R2 and R3 are as hereinbefore defined,
an R7-CO-CH2-O-CO- group wherein R7 denotes an amino
group optionally substituted by l or 2 methyl groups or
by a cyclohexyl group,
or E denotes a piperidinyl or morpholinyl group, or a
l,3-dihydro-3-oxo-l-isobenzo~uranyloxycarbonyl group;
and the stereoisomers thereof, including the mixtures
and the salts thereof.
Particularly preferred compounds according to the
invention include those of formula I above wherein, with
the proviso that Ra does not denote an amidino group
optionally substituted by a (C23-alkoxycarbonyl) group
or an amidino group substituted by a benzyloxycarbonyl
group, if E denotes a (C23-alkoxycarbonyl) group or a
benzyloxycarbonyl group,
Ra denotes an amidino group optionally substituted by an
R1-CO-O-(R2CR3)-O-CO-, methoxycarbonyl or
allyloxycarbonyl group, wherein
R1 denotes a straight-chained or branched C14-alkyl
,
~ .-
2 ~
group, a C13-alkoxy group or a cyclohexyloxy group,
R2 denotes a hydrogen atom or a methyl group and
R3 denotes a hydrogen atom;
Rb denotes a hydrogen atom or a methoxy group;
A denotes a -CH2- or -CO- group;
B denotes an -NR4-CH2CH2-X-CH2- group wherein X denotes an
-NR5- group, or B denotes an -NR4-CH2CH2-R6C=CH- or -Y-W-
group wherein Y denotes an -NR4- group, whilst the above-
mentioned Y or -NR4- groups are each linked to the group
A, and wherein
R4 denotes a hydrogen atom or a methyl group or
R4 and R5 together or R4 and R6 together represent an
ethylene group and
W denotes a 1,4-cyclohexylene group;
E denotes an isopropyloxycarbonyl, isobutyloxycarbonyl,
2-butyloxycarbonyl, 2-amyloxycarbonyl, 3-amyloxycarbonyl
or neopentyloxycarbonyl group, a (C69-cycloalkoxy-
carbonyl) group wherein the cyclohexyl moiety may
additionally be substituted by 1 or 2 C13-alkyl groups,
a (C56-cycloalkyl)(C12alkoxy)carbonyl group, a (C8
bicycloalkyloxycarbonyl) group, or an
R1-CO-O-(R2CR3)-O-CO- group in which R1, R2 and R3 are as
hereinbefore defined;
and the stereoisomers thereof, including the mixtures
and salts thereof.
The present invention particularly relates to the
20~o81~8
following compounds of formula I:
4-amidino-4'-t4-(cyclohexyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl;
4-amidino-4'-[4-(cyclopentyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl;
4-amidino-3'-[4-trans-(cyclohexyloxycarbonyl)-
cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-4'-methoxy-biphenyl;
4-amidino-3'-[4-trans-(cyclohexylmethoxycarbonyl)-
cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-4'-methoxy-biphenyl;
4-amidino-4'-t4-(cycloheptyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl;
4-amidino-4'-t4-((exo)-norbornyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl;
4-amidino-4'-[4-((-)-menthyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl;
4-amidino-4'-[4-(pivaloyloxymethyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl;
4-[4-[(1-(ethoxycarbonyloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl)-methyl]-
piperidinocarbonyl]-4'-amidino-biphenyl;
4-[N-allyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-[4-
(methoxycarbonylmethyl)-piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl;
4-tN-allyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-t4-(carboxymethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl; and
4-[4-(cyclohexyloxycarbonylmethyl)-piperidinocarbonyl]-
4'-[N-methoxycarbonyl-amidino]-biphenyl;
, . . ~ ,
- :.
: ~. .. .
-
:
20~181~8
and the stereoisomers thereof, including the mixtures
and the salts thereof.
Viewed from a further aspect, the invention provides a
process for the preparation of compounds of the
invention, said process comprising at least one of the
following steps:
a) (to prepare compounds of formula I wherein E denotes
a (C37-alkoxycarbonyl) group, a phenylalkoxycarbonyl
group, a (C410-cycloalkyloxycarbonyl) group wherein a -^-
Cs8-cycloalkyl moiety may additionally be substituted by
1 or 2 alkyl groups, a (C68-cycloalkyloxycarbonyl) group
in which in the cycloalkyloxy moiety a methylene group
in the 3- or 4-position is replaced by an oxygen atom or
by an imino group optionally substituted by an alkyl,
phenylalkyl, phenylalkoxycarbonyl or C26-alkanoyl group,
and the cycloalkyloxy moiety may additionally be
substituted by 1 or 2 alkyl groups, a (Cs8-
cycloalkenyl)oxycarbonyl, a (C35-alkenyl)oxycarbonyl,
phenyl(C35-alkenyl)oxycarbonyl, (C3s-alkynyl)oxycarbonyl
or phenyl(C35-alkynyl)oxycarbonyl group in which he
carbon attached to the oxycarbonyl moiety carries no
double or triple bond, a (C38-cycloalkyl)alkoxycarbonyl
group, or a (C810-bicycloalkyloxycarbonyl) group, which
may additionally be substituted in the bicycloalkyl
moiety by one or two alkyl groups) esterifying a
carboxylic acid of formula II
Rb
Ra ~ A-B-COOH
(II)
(wherein
Ra~ Rb, A and B are as hereinbefore defined) or a
, . ,
t
. ~ `
,
:
209~1.58
- 12 -
reactive derivative thereof optionally formed in the
reaction mixture, with an alcohol of formula III
HO - R8 (III)
(wherein
R8 denotes a C26-alkyl group, a phenylalkyl group, a C3 9-
cycloalkyl group in which a Cs8-cycloalkyl moiety may
additionally be substituted by 1 or 2 alkyl groups, a
Cs7-cycloalkyl group in which a methylene group in the
3- or 4-position is replaced by an oxygen atom or by an
imino group itself optionally substituted by an alkyl,
phenylalkyl, phenylalkoxycarbonyl, or C26-alkanoyl
group, and the cycloalkyl moiety may additionally be
substituted by 1 or 2 alkyl groups, a Cs8-cycloalkenyl,
C35-alkenyl, phenyl(C35-alkenyl), C35-alkynyl or
phenyl(C3s-alkynyl) group in which the carbon attached
to the hydroxyl carries no double or triple bond, a
(C38-cycloalkyl)alkyl group, or a C7~-bicycloalkyl group
optionally substituted by one or two alkyl groups;
b) reacting a carboxylic acid of formula IV
Rb
Ra~) ~A--B--COOH
(IV)
(wherein
Rb, A and B are as hereinbefore defined and
Ral denotes an amidino group substituted by an
R1-CO-O-(R2CR3)-O-CO-, (C16-alkoxy)carbonyl, phenyl(C16-
alkoxyjcarbonyl, ( C3 5-alkenyl)oxycarbonyl or phenyl( C3 s-
alkenyl)oxycarbonyl group, or Ral denotes an amidino
group protected by a protecting group) or a carbanion
thereof, with a compound of formula V
,
.' ~ '' ;
2lQ98l~8
Z~ - R9 (V)
(wherein
R9 denotes a C26-alkyl group, a phenylalkyl group, a C39-
cycloalkyl group wherein a C5 8-cycloalkyl moiety may
additionally be substituted by 1 or 2 alkyl groups, a
C57-cycloalkyl group in which a methylene group in the
3- or 4 position is replaced by an oxygen atom or by an ~;
imino group itself optionally substituted by an alkyl,
phenylalkyl, phenyloxycarbonyl or C26-alkanoyl group and
in which the cycloalkyl moiety may additionally be
substituted by 1 or 2 alkyl groups, a C58-cycloalkenyl
group, a C3s-alkenyl, phenyl(C35-alkenyl), C35-alkynyl or
phenyl(C35-alkynyl) group wherein the Zl attached carbon
carries no double or triple bond, a (C38-
cycloalkyl)alkyl group, or a C79-bicycloalkyl group
optionally substituted by one or two alkyl groups, an
Rl-CO-O-(R2CR3)- group wherein Rl, R2 and R3 are as
hereinbefore defined, an R7-CO-CH2- group wherein R7
denotes an amino group optionally substituted by 1 or 2
C16-alkyl groups or by a C38-cycloalkyl group, a
pyrrolidinyl, piperidinyl, hexamethyleneimino,
morpholinyl or N-alkylpiperazinyl group, or a 1,3-
dihydro-3-oxo-1-isobenzofuranyl group and
Z1 denotes a nucleophilic leaving group such as a halogen
atom, e.g. a chlorine or bromine atom) and if necessary
subsequently cleaving any protecting group used;
c) (to prepare compounds of formula I wherein Ra denotes
an amidino group substituted by an Rl-CO-O-(R2CR3)-O-CO-,
alkoxycarbonyl, alkenyloxycarbonyl, phenylalkoxycarbonyl
or phenylalkenyloxycarbonyl group) acylating a compound
of formula VI
.:
,
~49~1~8
I b
HN\C~A--B--E
(VI)
(wherein
Rb, A, B and E are as hereinbefore defined) with a
compound of formula VII
:"~
.. Z2 ~ R10 (VII)
(wherein
R~o denotes an R1-CO-O-(R2CR3)-O-CO-, alkoxycarbonyl,
alkenyloxycarbonyl, phenylalkoxycarbonyl or
phenylalkenyloxycarbonyl group and
Z2 denotes a nucleophilic leaving group such as a halogen
atom, e.g. a chlorine or bromine atom or a p-nitrophenyl
group)
d) resolving a compound of formula I thus obtained into
the enantiomers and/or diastereomers thereof;
e) converting a compound of formula I obtained into 2
i salt thereof, more particularly for pharmaceutical use
into a physiologically acceptable salt thereof with an
inorganic or organic acid, or converting a salt of a
compound of formula I into the free compound; and
f) performing a process as defined in any one of steps
(a) to (e) above on a corresponding protected compound
and subsequently removing the protecting group used.
The esterification of step (a) is conveniently carried
out in a solvent or mixture of solvents such as
.. , . ~ . ~ .
,.,
. . , . , ,. :: . .
, ;: , ~: ~ ,
. : , - :
:. . . - . : -- - . : ~ ~ ~ -
-,: ,; ~ . . .. : .
2098158
methylene chloride, dimethylformamide,
dimethylsulphoxide, toluene, chlorobenzene,
tetrahydrofuran, toluene/tetrahydrofuran or dioxane, ~-
optionally in the presence of an acid such as
hydrochloric acid or in the presence of a dehydrating
agent, e.g. in the presence of a chloroformate such as
isobutylchloroformate, thionylchloride,
trimethylchlorosilane, titanium tetrachloride,
hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, methanesulphonic
acid, p-toluenesulphonic acid, phosphorus trichloride,
phosphorus pentoxide, N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide,
N,N'-dicyclohexyl-carbodiimide/N-hydroxysuccinimide or
l-hydroxy-benzotriazole, N,N'-carbonyldiimidazole or
N,N'-thionyldiimidazole, optionally in the presence of a
base such as a pyridine substituted in the 4-position by
a secondary amino group such as 4-dimethylamino-pyridine
or triphenylphosphine/carbon tetrachloride, at
temperatures between -30 and 100C, preferably at
temperatures between -10 and 60C.
In step (b), examples of protecting groups for the
amidino groups include the tert.butyloxycarbonyl,
allyloxycarbonyl or 9-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl group
and
examples of protecting groups for the hydroxy group
include the trimethylsilyl, tetrahydropyran-2-yl,
benzyl, benzhydryl or triphenylmethyl group.
The reaction of step (b) is conveniently carried out in
a solvent such as methylene chloride, tetrahydrofuran,
dioxane, dimethylsulphoxide or dimethylformamide,
optionally in the presence of a reaction accelerator
such as sodium or potassium iodide and preferably in the
presence of a base such as sodium carbonate, potassium
carbonate or sodium hydroxide solution or in the
presence of a tertiary organic base such as N-ethyl-
. '
- : :
`:' :
20~15~
- 16 -
diisopropylamine, N-methyl-morpholine, pyridine or 4-
dimethylamino-pyridine, which may simultaneously be used
as solvent, or possibly in the presence of silver
carbonate or silver oxide, at temperatures between -30
and 100C, but preferably at temperatures between -10
and 80C.
A protecting group used for the amino, amidino or
hydroxy group is preferably cleaved hydrogenolytically,
depending on the protecting group used and the
particular group to be protected, e.g. using hydrogen in
the presence of a catalyst such as palladium/charcoal,
in a solvent such as methanol, ethanol, ethyl acetate or
glacial acetic acid, optionally with the addition of an
acid such as hydrochloric acid, at temperatures between
0 and 50C, but preferably at ambient temperature, and
under a hydrogen pressure of 1 to 7 bar, but preferably
of 3 to S bar, using an aqueous mineral acid such as
hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid or sulphuric acid,
with the aid of an organic acid such as formic acid or
trifluoroacetic acid in a solvent such as methanol,
ethanol, ethyl acetate, methylene chloride or glacial
acetic acid, with the aid of a secondary amine such as
piperidine or morpholine in a solvent such as
dimethylformamide or methylene chloride or with the aid
of a catalyst such as tetrakis-(triphenylphosphine)-
palladium(0) and morpholine in a solvent such as
tetrahydrofuran or dioxane, at temperatures between 0
and 50C, but preferably at ambient temperature.
The reaction of step (c) is conveniently carried out in
a solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, methylene chloride,
chloroform or dimethylformamide, appropriately in the
presence of a base such as sodium carbonate, potassium
carbonate or sodium hydroxide solution or in the
presence of a tertiary organic base such as
triethylamine, N-ethyl-diisopropylamine, N-methyl-
: ,
- : . ~
20~8158
- 17 -
morpholine or pyridine, which may simultaneously be used
as solvent, at temperatures between -30 and 100C, but
preferably at temperatures between -10 and 80C.
In the reactions described hereinbefore, any reactive
groups present such as hydroxy, carboxy, amino,
alkylamino, imino or amidino groups may be protected
during the reaction by means of conventional protecting
groups which may be cleaved again after the reaction.
For example, suitable protecting groups for a hydroxy
group include trimethylsilyl, acetyl, benzoyl,
tert.butyl, trityl, benzyl and tetrahydropyranyl groups,
suitable protecting groups for a carboxyl group include
trimethylsilyl, methyl, ethyl, tert.butyl and benzyl
groups, and suitable protecting groups for an amino,
alkylamino or imino group include acetyl, tert.-
butoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, benzyl, benzhydryl,
trityl, methoxybenzyl, 2,4-dimethoxybenzyl, 9-
fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl and allyloxycarbonyl groups.
The optional subsequent cleaving of a protecting group
used may, for example, be carried out hydrolytically in
an aqueous sol~ent, e.g. in water, isopropanol/water,
tetrahydrofuran/water or dioxane/water, in the presence
of an acid such as trifluoroacetic acid, hydrochloric
acid or sulphuric acid or in the presence of an alkali
metal base such as sodium hydroxide or potassium
hydroxide or aprotically, e.g. in the presence of
iodotrimethylsilane, at temperatures between -10 and
lOCC, preferably at temperatures between 0 and 60~C.
However, a benzyl, methoxybenzyl, benzyloxycarbonyl,
benzhydryl or trityl group may for example be cleaved
hydrogenolytically, eg. using hydrogen in the presence
of a catalyst such as palladium/charcoal in a solvent
such as methanol, ethanol, ethyl acetate or glacial
- . ~ ., . .. , ~: . -
20981~8
- 18 -
acetic acid, optionally with the addition of an acid
such as hydrochloric acid, at temperatures between 0 and
50C, but preferably at ambient temperature, under a
hydrogen pressure of 1 to 7 bar, preferably 3 to 5 bar.
A methoxybenzyl group may also be cleaved in the
presencè of an oxidising agent such as cerium(IV)-
ammonium nitrate in a solvent such as methylene
chloride, acetonitrile or acetonitrile/water at
temperatures between 0 and 50C, but preferably at
ambient temperature.
A 2,4-dimethoxybenzyl group, however, is preferably
cleaved in trifluoroacetic acid in the presence of
anisole.
A tert.butyl or tert.butyloxycarbonyl group is
preferably cleaved by treating with an acid such as
trifluoroacetic acid or hydrochloric acid, optionally
using a solvent such as methylene chloride, dioxane, or
ether.
A 9-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl group is preferably
cleaved using a secondary amine such as piperidine or
morpholine in a solvent such as dimethylformamide or
methylene chloride at temperatures between 0 and 50C,
but preferably at ambient temperature, and an
allyloxycarbonyl group is preferably cleaved in the
presence of a catalyst such as tetrakis-
(triphenylphosphine)-palladium(0) and morpholine in a
solvent such as tetrahydrofuran or dioxane at
temperatures between 0 and 50C, but preferably at
ambient temperature.
Furthermore, the compounds of formula I obtained may be
resolved into their enantiomers and/or diastereomers as
mentioned hereinbefore. Thus, for example, cis/trans
- : ~
- ~
20981~
-- 19 --
mixtures may be resolved into their cis and trans
isomers, and compounds having at least one optically
active carbon atom may be resolved into their
enantiomers. Thus, for example, the compounds of
formula I which occur in racemate form may be separated
by methods known er se (see Allinger N. L. and Eliel
E. L. in "Topics in Stereochemistry", Vol. 6, Wiley
Interscience, 1971) into their optical antipodes and
compounds of formula I having at least 2 asymmetric
carbon atoms may be separated on the basis of their
physical-chemical differences using known methods, e.g.
by chromatography and/or fractional crystallisation,
into the diastereomers thereof which, if they occur in
racemic form, may subsequently be separated into the
enantiomers as mentioned above.
The separation of enantiomers is preferably effected by
column separation on chiral phases or by
recrystallisation from an optically active solvent or by
reacting with an optically active substance which forms
salts or derivatives such as esters or amides with the
racemic compound, especially acids and the activated
derivatives or alcohols thereof, and separation of the
diastereomeric salt mixture or derivative thus obtained,
e.g. on the basis of their different solubilities,
whilst the free antipodes may be released from the pure
diastereomeric salts or derivatives by the action of
suitable agents. Particularly common, optically active
acids include, for example, the D- and L-forms of
tartaric acid or dibenzoyltartaric acid, di-o-tolyl
tartaric acid, malic acid, mandelic acid,
camphorsulphonic acid, glutamic acid, aspartic acid or
quinic acid. Examples of optically active alcohols
include for example (+)- or (-)-menthol and examples of
optically active acyl groups in amides include for
example (+)- or (-)-menthyloxycarbonyl.
~ ~ '
20298158
Moreover, the compounds of formula I obtained may be
converted into the salts thereof, particularly for
pharmaceutical use into the physiologically acceptable
salts thereof with inorganic or organic acids. Examples
of suitable acids for this purpose include hydrochloric
acid, hydrobromic acid, sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid,
acetic acid, fumaric acid, succinic acid, lactic acid,
citric acid, tartaric acid or maleic acid.
The compounds used as starting materials are known from
the literature in some cases or may be obtained by
methods known from the literature. In addition, some of
them are described in EP-A-4~6378 (not previously
published). Thus, for example, compounds of formulae II
and IV are obtained by acylating a corresponding
amidine, whilst the amidine required for this is
appropriately prepared by reacting a corresponding
iminoester with a corresponding amine. A compound of
formula II thus obtained is then converted by hydrolysis
into a corresponding compound of formula VI.
As already mentioned, the new biphenyl derivatives of
formula I and the salts thereof, particularly the
physiologically acceptable salts thereof with inorganic
or organic acids or bases, have valuable properties.
Thus, the new compounds, in addition to having an
inhibitory effect on inflammation and bone degradation,
have in particular antithrombotic, antiaggregatory and
tumour- or metastasis-inhibiting effects.
By way of example, the compounds of formula I were
investigated for their biological effects as follows:
The inhibition of thrombocyte aggregation after oral
administration of the test substance is determined ex
vivo in Rhesus monkeys.
. ' '
,,
209~8
- 21 -
Immediately before the oral administration of the test
substance suspended in Natrosol, a blood sample is taken
from the animal's cubital vein as a reference value. At
defined times after administration of the substance,
more blood samples are taken and investigated as
follows
. ~
The whole blood mixed with 3.14% sodium citrate in a
volume ratio of 1:10 is centrifuged at 200 g for 15
minutes. The supernatant of platelet-rich plasma is
carefully removed. The platelet-poor plasma is obtained
as supernatant from the erythrocyte-rich sediment by
centrifuging at 4000 g for 10 minutes.
The thrombocyte aggregation in these ex vivo samples
initiated with collagen (Hormonchemie, Munich; 2 ~g/ml
final concentration in platelet-rich plasma) is
photometrically measured using the Born and Cross method
(J. Physiol. 170: 397 (1964)). The maximum light
transmittance of the platelet-rich plasma, measured
after collagen stimulation, is compared with the
reference value in order to determine the inhibition of
aggregation at the various times of blood sampling after
the administration of the substance relative to the
reference value.
The compound of Example 1 inhibits the collagen-induced
thrombocyte aggregation ex vivo after the oral
administration of 3 mg/kg for more than 4 hours.
The compound according to the invention is well
tolerated, since no toxic side effects were observed at
the dosages administered.
In the light of their inhibitory effect on cell-cell or
cell-matrix interactions, the new biphenyl derivatives
of formula I and the physiologically acceptable addition
2098158
- 22 -
salts thereof are suitable for combating or preventing
diseases in which smaller or greater cell aggregates
occur or in which cell-matrix interactions play a part,
e.g. in treating or preventing venous and arterial
thrombosis, cerebrovascular diseases, lung embolism,
cardiac infarction, arteriosclerosis, osteoporosis and
the metàstasis of tumours and the treatment of
genetically caused or acquired disorders of cell
interactions with one another or with solid structures.
They are also suitable for parallel therapy in
thrombolysis with fibrinolytics or vascular
interventions such as transluminal angioplasty or in the
treatment of shock, psoriasis, diabetes and
inflammation.
Thus, viewed from a further aspect the present invention
provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising a
compound of formula I or a physiologically acceptable
salt thereof together with at least one physiologically
acceptable carrier or excipient.
Viewed from a still further aspect the invention
provides the use of a compound of formula I or a
physiologically acceptable salt thereof for the
manufacture of a therapeutic agent for combating or
preventing diseases in which smaller or greater cell
aggregates occur or in which cell-matrix interactions
play a part.
In particular, the invention provides the use of a
compound of formula I or a physiologically acceptable
salt thereof for the manufacture of a therapeutic agent
for treating or preventing venous and arterial
thrombosis, cerebrovascular diseases, lung embolism,
cardiac infarction, arteriosclerosis, osteoporosis and
the metastasis of tumours and the treatment of
genetically caused or acquired disorders of cell
.
:
- ~ .-: .
209~1~8
interactions with one another or with solid structures,
in particular, for parallel therapy in thrombolysis with
fibrinolytics or vascular interventions, or for the
treatment of shock, psoriasis, diabetes or inflammation.
Viewed from a yet still further aspect the invention
provides a method of treatment of the human or non-human
animal body to combat or prevent diseases in which
smaller or greater cell aggregates occur or in which
cell-matrix interactions play a part, said method
comprising administering to said body a compound of
formula I or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof.
More particularly, the invention provides a method of
treatment of the human or non-human animal body for
treating or preventing venous and arterial thrombosis,
cerebrovascular diseases, lung embolism, cardiac
infarction, arteriosclerosis, osteoporosis and the
metastasis of tumours and the treatment of genetically
caused or acquired disorders of cell interactions with
one another or with solid structures, in particular, for
parallel therapy in thrombolysis with fibrinolytics or
vascular interventions, or for the treatment of shock,
psoriasis, diabetes or inflammation, said method
comprising administering to said body a compound of
formula I or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof.
For treating or preventing the diseases mentioned above
the dosage is conveniently between 0.1 ~g and 30 mg/kg
of body weight, preferably 1 ~g to 15 mg/kg of body
weight, given in up to 4 doses per day. For this
purpose the compounds of formula I produced according to
the invention, optionally in conjunction with other
active substances such as thromboxane receptor
antagonists and thromboxane synthesis inhibitors or
combinations thereof, serotonin antagonists, ~-receptor
antagonists, alkylnitrates such as glycerol trinitrate,
:,
. -
' ' ' ~
2 0 9~ 5 8 27169-219
phospho-diesterase inhibitors, prostacyclin and the analogues
thereof, fibrinolytics such as tPA, prourokinase, urokinase,
streptokinase, or anticoagulants such as heparin, dermatane
sulphate, activated protein C, vitamin K antagonists, hirudine,
inhibitors of thrombin or other activated clottlng factors, may be
incorporated together with one or more inert conventional carriers
and/or diluents, e.g. with corn starch, lactose, sucrose,
microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate,
polyvinylpyrrolidone, citric acid, tartaric acid, water,
water/ethanol, water-glycerol, water/sorbitol,
water/polyethyleneglycol, propyleneglycol, stearylalcohol,
carboxymethylcellulose or fatty substances such as hard fat or
suitable mixtures thereof, into conventional galenic preparations
such as plain or coated tablets, capsules, powders, suspensions,
solutions, sprays or suppositories.
- The invention also extènds to a commercial package
containing a compound of the invention, together with instructions
for its use in treating any of the above conditions.
The following non-limiting Examples are provided to
illustrate the invention. All percentages and ratios are by
weight, other than eluant or solvent ratios which are by volume.
-
.;. :- :
: - ::
- - :. ~
: . :: :
- .. ~
2Q92~158
Example I
4'-Cyano-biphenylyl-4-acetic acid
A mixture of 11.3 g of 4'-bromo-biphenylyl-4-acetic acid
(melting point: 172-175C, prepared from 4-acetyl-4'-
bromo-biphenyl by treating with morpholine and sulphur
and subsequent hydrolysis with potassium hydroxide),
3.48 g of copper(I)-cyanide and 100 ml of
dimethylformamide is refluxed for 12 hours and
evaporated down after cooling. The residue is
distributed between lN sodium hydroxide solution and
`~i~ methylene chloride to which some methanol is added. The
aqueous phase is acidified and extracted with methylene
chloride. The methylene chloride phase is treated with
activated charcoal and evaporated down, the solid
residue is triturated with a mixture of ether and
petroleum ether and filtered off.
Yield: 5.1 g (55% of theory),
Rf value: 0.46 (silica gel; methylene chloride/ethanol =
9 : 1 )
The following compound is obtained analogously:
(1) Methyl 4-cyano-biphenylyl-4'-carboxylate
Melting point: 140-142C
The necessary starting compound, methyl 4-bromo-
biphenylyl-4'-carboxylate (melting point: 140-142C), is
obtained by esterifying the acid with methanolic
hydrochloric acid. 4-Bromo-4'-biphenylyl-carboxylic
acid is obtained by reacting 4-acetyl-4'-bromo-biphenyl
with bromine and sodium hydroxide solution.
.. . .
2Q92~l~8
Example II
4-Cyano-4'-hydroxymethyl-biphenyl
A solution of 5 g (0.0224 mol) of 4'-cyano-biphenyl-4-
carboxylic acid and 2.27 g (0.0224 mol) of triethylamine
in 100 ml of tetrahydrofuran is mixed at 5C with a
solution of 2.43 g (0.024 mol) of ethylchloroformate in
20 ml of tetrahydrofuran, within 5 minutes, with
stirring. The mixture is then stirred at 5C for
another hour. The triethylamine-hydrochloride
precipitated is suction filtered and the mother liquor
is added dropwise to a solution of 2.12 g (0.056 mol) of
sodium borohydride in 20 ml of water at 10-15C with
stirring. After another 4 hours stirring at ambient
temperature the mixture is acidified to pH 2-3 using 2N
hydrochloric acid, the aqueous phase produced is
separated off and extracted with ethyl acetate. The
organic phases are combined, washed with 10% sodium
hydroxide solution and then with water. After drying
over sodium sulphate the mixture is evaporated to
dryness under reduced pressure.
Yield: 2.5 g (53.3% of theory) of an amorphous product.
Example III
4-Chloromethyl 4'-cyano-biphenyl
2.5 g (0.0119 mol) of 4-cyano-4'-hydroxymethyl-biphenyl
are dissolved in 70 ml of dichloromethane and after the
addition of 2.4 g (0.0239 mol) of triethylamine the
mixture is slowly combined with 2.7 g (0.024 mol~ of
mesylchloride at ambient temperature with stirring.
After standing overnight the clear solution is
evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure and the
residue is chromatographed over silica gel, using
methylene chloride as eluant.
.. . .
.
- :' ~` "'' ~
- , ., - .
20~781~8
Yield: 2.6 g (96% of an amorphous solid)
Example IV
4-Cyano-4'-iodomethyl-biphenyl
2.4 g (0.0087 mol) of 4-chloromethyl-4'-cyano-biphenyl
are refluxed together with 6.26 g (0.042 mol) of sodium
iodide in 100 ml of acetone for 3 hours. The suspension
is then evaporated to dryness in vacuo and the residue
is extracted several times with dichloromethane. The
combined dichloromethane solutions are evaporated to
dryness. The crude residue thus obtained is used in
Example V without any further purification.
Exam~le V
4-Cyano-4'-[4-(methoxycarbonylmethyl)-piperidinomethyl]-
biphenyl
The crude product obtained in Example V is dissolved in
100 ml of chloroform. After the addition of 2.5 g of
methyl piperidinoacetate hydrochloride and 2.57 g of
triethylamine this solution is refluxed for 4 hours.
After cooling, the precipitated triethylamine-
hydrochloride is suction filtered and the mother liquor
is evaporated to dryness. The residue is
chromatographed over silica gel using
dichloromethane/methanol t40:1) as eluant.
Yield: 2.2 g (59.6% of theory)
: ~' :' ' ' . ,' ' ',
' ~ . , " ~ :
20981~8
- 28 -
Exam~le VI
4-Amidino-4'-[4-(methoxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinomethyl]-biphenyl
HCl gas is introduced for 2 hours into a suspension of
2.1 g (0.006 mol) of 4-cyano-4'-[4-(methoxycarbonyl-
methyl)-piperidinomethyl]-biphenyl in 100 ml of absolute
methanol whilst cooling with ice and stirring. The
reaction mixture is then left to stand for 4 hours at
ambient temperature. The solution is evaporated to
dryness in vacuo, the residue is dissolved in methanol
and the solution thus obtained is mixed with sodium
carbonate until a basic reaction is achieved. The
suspension thus produced is evaporated to dryness ln
vacuo. The residue is chromatographed over silica gel,
using dichloromethane/methanol/conc. ammonia in the
ratio 9:1:0.1 as eluant.
Yield: 0.72 g (29.7% of theory),
Melting point: 148-150C
Example VII
4-Amidino-4'-~4-(hydroxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinomethyl]-biphenyl
0.59 g of 4-amidino-4'-[4-(methoxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinomethyl]-biphenyl are dissolved in 15 ml of
tetrahydrofuran and 11 ml of water. 8.1 ml of a lN
a~ueous lithium hydroxide solution are added to this
solution wit~ stirring. After another 3 hours, 433 mg
of ammonium chloride are added, whereupon a colourless
substance is precipitated. The tetrahydrofuran is
distilled off in vacuo and the substance precipitated is
then filtered off.
Yield: 420 mg (74.7% of theory),
Melting point: 318-320C (decomp.)
- - :. , , . :-- -~ , , .
,
2092981~8
Example VIII
3-Carboxy-4'-cyano-4-hydroxy-biphenyl
A solution of 12 g of 4-cyano-4'-methoxy-biphenyl in
75 ml of methylene chloride is added dropwise to a
mixture of 25 ml of oxalylchloride, 50 ml of methylene
chloride and 25 g of aluminium chloride which is stirred
for 30 minutes at -20C. The resulting mixture is
stirred for 5 hours at -20C, initially whilst cooling
with ice, and then allowed to come up to ambient
temperature in the course of 16 hours, after which it is
stirred for a further 3 hours. It is poured onto ice
water, stirred for 30 minutes, extracted with ethyl
acetate and the ethyl acetate phase is evaporated down
until crystallisation occurs.
Yield: 10.3 g (75% of theory),
Melting point: 244-246C
Example IX
4-(tert.Butyloxycarbonylmethyloxy)-4'-cyano-biphenyl
. _
Prepared analogously to Example 13 from 4-cyano-4'-
hydroxy-biphenyl and tert.butyl-bromoacetate.
Melting point: 110-112C
Example X
4-(Carboxymethyloxy)-4'-cyano-biphenyl
32.9 g of 4-(tert.butyloxycarbonylmethyloxy)-4'-cyano-
biphenyl are dissolved in 250 ml of methylene chloride
and slowly combined with 137 ml of trifluoroacetic acid.
The resulting mixture is stirred for 3 hours at ambient
temperature, evaporated to dryness and the residue is
'~
20~o~158
triturated with water.
Yield: 26.3 g (98% of theory),
Melting point: 202-204C
Example XI
4-Cyano-4'-[[[3-(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-phenyl]-
aminocarbonyl]-methyl]-biphenyl
... . _ _
A solution of 1.4 g of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide in 20 ml
of tetrahydrofuran is added dropwise, whilst cooling
with ice, to a mixture of 1 g of 4'-cyano-biphenylyl-4-
acetic acid, 1.2 g of methyl 3-(3-aminophenyl)-
propionate, 0.57 g of l-hydroxy-lH-benzotriazole-hydrate
and 100 ml of tetrahydrofuran. The mixture is stirred
for a further hour, allowed to come up to ambient
temperature and the dicyclohexylurea precipitated is
filtered off. The filtrate is evaporated down and the
residue is purified by chromatography on silica gel
(eluant: methylene chloride/methanol = 30:1).
Yield: 1.58 g (95% of theory),
Melting point: 166-168~C
Example ~II
4-Cyano-4'-[(2-ethoxycarbonyl-ethylamino)-carbonyl]-
biphenyl
A mixture of 2 g of 4'-cyano-biphenylyl-4-acetic acid,
1.9 ml of N-methyl-morpholine and 100 ml of
tetrahydrofuran is cooled to -30C and mixed with 1.1 ml
of isobutylchloroformate. The mixture is stirred for
one hour, 1.3 g of ~-alanine ethylester-hydrochloride is
added and the resulting mixture is stirred for 50 hours
at ambient temperature. The solution obtained is
stirred into 300 ml of 0.5 molar potassium hydrogen
.
, . -:
- , ~: . ~ . . :
, ,, :
20981~8
- 31 -
sulphate solution and extracted with ethyl acetate. The
ethyl acetate phase is evaporated down and mixed with
ether, whereupon the product is obtained in crystalline
form.
Yield: 1.1 g (39% of theory),
Melting point: 132-136C
Exam~le XIII
[4-Amidino-4'-(5-methoxycarbonyl-pentyloxy)-biphenyl]-
dihydrogen carbonate
75 ml of methanol are covered with 30 ml of petroleum
ether and hydrogen chloride gas is piped in, whilst
cooling with ice, until saturation point is reached.
Then 2.1 g of 4-cyano-4'-(5-ethoxycarbonyl-pentyloxy)-
biphenyl are added and the mixture is stirred for 18
hours at ambient temperature. It is evaporated to
dryness in vacuo, the residue is suspended in methanol,
5.3~ g of ammonium carbonate are added and the mixture
is stirred for 16 hours at ambient temperature. The
precipitate obtained is filtered off and purified by
stirring with methylene chloride/methanol (85:15) and
water.
Yield: 1.75 g (75% of theory),
Melting point: 185-189~C (decomp.)
20981~8
- 32 -
Exam~le l
4-Amidino-4'-[4-(cyclohexyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
Hydrochloric acid gas is piped into a suspension of 1 g
(0.0027 mol) of 4-amidino-4'-[4-(carboxymethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl in 20 ml of dichloromethane
and 20 ml of cyclohexanol at ambient temperature until
saturation is reached. Then the clear solution thus
obtained is left to stand for one hour and heated to
40C for 3 hours. The solution is evaporated down under
reduced pressure and the solid residue remaining is
crystallised from ether, suction filtered and washed
with ether.
Yield: 1.1 g (83.1% of theory),
Melting point: 227-230C
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
(1) 4-amidino-4'-[4-(cycloheptyloxycarbonyl)-
butyrylamino]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
(2) 4-amidino-4'-[4-(2-cyclohexyl-ethoxycarbonyl)-
butyryl-N-methyl-amino]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
(3) 4-amidino-4'-tN-(3-(cyclopentylmethyloxycarbonyl)-
propyl)-aminocarbonyl]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
(4) 4-amidino-4'-[N-(3-(cyclopentylmethyloxycarbonyl)-
propyl)-N-benzyl-aminocarbonyl]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
(5) 4-amidino-4'-[4-(2-cyclohexyloxycarbonyl-ethyl)-
piperazinocarbonyl]-biphenyl-dihydrochloride
(6) 4-amidino-4'-[4-(cyclooctyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
- .,-
- ~, ;
-
-
.
209815~
- 33 -
(7) 4-amidino-4'-[4-(cyclopentyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
Melting point: >240C, sintering from 219C
(8) 4-amidino-3'-[4-trans-(cyclohexyloxycarbonyl)-
cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-4'-methoxy-biphenyl-
hydrochioride
Melting point: 238-241~C (decomp.)
(9) 4-amidino-3'-[4-trans-(cyclohexylmethoxycarbonyl)-
cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-4'-methoxy-biphenyl-
hydrochloride
Melting point: 247-250C (decomp.)
(10) 4-amidino-4'-[4-(cycloheptyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
Melting point: >240C, sintering from 215C
(11) 4-amidino-4'-[4-(cyclohexyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinomethyl]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
(12) 4-amidino-4'-[4-[(2,2-dimethyl-propyloxy)-
carbonylmethyl]-piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl-
hydrochloride
Melting point: 235-240C
Rf value: 0.73 (silica gel, methylene chloride/methanol
= 4:1)
(13) 4-amidino-4'-t4-[(3-pentyloxy)carbonylmethyl]-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
Melting point: 205-207C
R~ value: 0.52 (silica gel, methylene chloride/methanol
= 4:1)
(14) 4-amidino-4'-[4-[((R)-2-butyloxy)carbonylmethyl]-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
Melting point: 203-205C
2098158
- 34 -
Rf value: 0.56 (silica gel, methylene chloride/methanol
= 4:1~
~15) 4-amidino-4'-[4-[((S)-2-butyloxy)carbonylmethyl]-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
Melting point: 205-208C
Rf valuè~ 0.56 (silica gel, methylene chloride/methanol
= 4 1)
(16) 4-amidino-4'-[4-[(2-methyl-propyloxy)-
carbonylmethyl]-piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl-
hydrochloride
This is done without the addition of methylene
chloride and the mixture is left to stand for 18 hours
at ambient temperature.
Melting point: 218-223C
Rf value: 0.64 (silica gel, methylene chloride/methanol
= 4:1)
(17) 4-amidino-4'-[4-trans-(isopropyloxycarbonyl)-cyclo-
hexylaminocarbonyl]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
This is done without the addition of methylene
chloride and, after the introduction of hydrogen
chloride, the mixture is left to stand for 5 days at
ambient temperature.
Rf value: 0.41 (silica gel, methylene chloride/methanol
= 8:2)
(18) 4-amidino-4'-[4-(isopropyloxy)carbonylmethyl]-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
The same procedure is used as in (16).
Melting point: 248-250C
Rf value: 0.25 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18, methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
,
~ : ` . -'~.,. .: :
~;, ~ ' ' . .
- 35 -
Example 2
4-Amidino-4'-[4-(cyclohexylmethyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl
A suspension of 4-amidino-4'-[4-carboxymethyl-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl, hydroxymethylcyclohexane
and trimethylchlorosilane in a molar ratio of 1:4:10 is
refluxed for 36 hours in dry tetrahydrofuran. It is
then evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure,
diluted with dichloromethane and washed with 2N ammonia
and then with water. After drying over sodium sulphate
` the mixture is evaporated to dryness under reduced
pressure. The residue is purified by chromatography
over a silica gel column.
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
(1) 4-amidino-4'-[4-(N-methyl-piperidin-4-
yloxycarbonylmethyl)-piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl
(2) 4-[4-(N-acetyl-piperidin-4-yloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-4'-amidino-biphenyl
(3) 4-amidino-4'-[4-(tetrahydro-4H-pyran-4-
yloxycarbonylmethyl)-piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl
(4) 4-amidino-4'-[4-(cyclopentyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl
(5) 4-amidino-4'-[5-(N-benzyl-piperidin-4-
yloxycarbonyl)-pentyloxy]-biphenyl
(6) 4-amidino-4'-t4-(tetrahydrofuran-3-yloxycarbonyl)-
butyloxy]-biphenyl
(7) 4-amidino-4'-[4-trans-(N-methyl-piperidin-4-
yloxycarbonyl)-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-biphenyl
` ., ~ ~:
~' ' : ' :
'
2098158
- 36 -
(8) 4-amidino-3'-[4-trans-(N-methyl-piperidin-4-
yloxycarbonyl)-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-4'-methoxy-
biphenyl
Example 3
4-Amidino-4'-[4-(N-methyl-piperidin-3-yloxycarbonyl)-
piperidinocarbonylmethyloxy]-biphenyl-dihydrochloride
a) 4-[N-Benzyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-[4-(N-methyl-
piperidin-3-yloxycarbonyl)-piperidinocarbonyl-
`~ methyloxyl-bi~henyl
A solution of 4-[N-benzyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-[4-
(carboxymethyl)-piperidinocarbonylmethyloxy]-biphenyl
and N-methyl-piperidin-3-ol in a molar ratio of 1:2 in
dichloromethane/dimethylformamide is mixed with a
solution of 1.1 molar equivalent of dicyclohexyl-
carbodiimide in dichloromethane, with stirring, in the
presence of a catalytic amount of 4-dimethylamino-
pyridine. After standing overnight at ambient
temperature, the dicyclohexylurea precipitated is
filtered off and the solution is evaporated to dryness
under reduced pressure. The residue is taken up in
ethyl acetate and washed with 5% sodium bicarbonate
solution and then with water and dried over sodium
sulphate. The remaining solution is evaporated down
under reduced pressure and the residue is purified by
chromatography over a silica gel column.
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
(1) 4-[N-benzyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-[4-
(cycloheptyloxycarbonyl)-piperidinocarbonylmethyl]-
biphenyl
(2) 4-[N-benzyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-[4-
(dimethylaminocarbonylmethyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
.. ~ -
~ .
: . : ~. . ,
,~ r
20~81~8
- 37 -
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl
(3) 4-[N-benzyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-[4-
(cyclohexylaminocarbonylmethyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl
(4) 4-[4-(aminocarbonylmethyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-4'-[N-benzyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-
biphenyl
(5) 4-[N-benzyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-3'-[4-trans-
(dimethylaminocarbonylmethyloxycarbonyl)-
cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-4'-methoxy-biphenyl
(6) 4-[N-ben2yloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-methoxy-3'-[4-
trans-(piperidinocarbonylmethyloxycarbonyl)-
cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-biphenyl
(7) 4-[N-benzyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-methoxy-3'-[4-
trans-(morpholinocarbonylmethyloxycarbonyl)-
cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-biphenyl
b) 4-Amidino-4'-[4-(N-methyl piperidin-3-yloxycarbonyl)-
~ iperidinocarbonvlmethyloxy]-biphenYl-dihydrochloride
The product obtained in a) is hydrogenated in a solution
consisting of dimethylformamide, water and lN
hydrochloric acid, in a ratio by volume of 20:1:1, in
the presence of (10%) palladium on charcoal for one hour
under a pressure of 5 bar. After the catalyst has been
suction filtered the remainder is evaporated down under
reduced pressure and the residue is suspended in acetone
and suction filtered.
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
(1) 4-amidino-4'-[4-(cycloheptyloxycarbonyl)-piperidino-
carbonylmethyl]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
. , . :
.. : .. . .
. . . . .. ::: : :
- -: '~
.. . .
2098158
- 38 -
(2) 4-amidino-4'-[4-(dimethylaminocarbonylmethyloxy-
carbonylmethyl)-piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl
(3) 4-amidino-4'-[4-(cyclohexylaminocarbonylmethyloxy-
carbonylmethyl)-piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl-
hydrochloride
(4) 4-amidino-4'-[4-(aminocarbonylmethyloxycarbonyl-
methyl)-piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
(5) 4-amidino-3'-[4-trans-(dimethylaminocaxbonyl-
methyloxycarbonyl)-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-4'-methoxy-
biphenyl-hydrochloride
(6) 4-amidino-4'-methoxy-3'-[4-trans-(piperidino-
carbonylmethyloxycarbonyl)-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-
biphenyl-hydrochloride
(7) 4-amidino-4'-methoxy-3'-[4-trans-(morpholino-
carbonylmethyloxycarbonyl)-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-
biphenyl-hydrochloride
Example 4
4-Amidino-4'-[4-((exo)-norbornyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidino-carbonyl]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
A suspension of 0.4 g (0.0011 mol) of 4-amidino-4'-[4-
carboxymethyl-piperidinocarbonyl] biphenyl in 10 ml of
thionylchloride is refluxed for 2 hours. The solution
thus obtained is evaporated to dryness in vacuo and the
residue remaining is mixed with 30 ml of dichloromethane
and 0.3 g of (exo)-norborneol. After heating to 40C
for 12 hours the mixture is evaporated down in vacuo and
the residue remaining is purified over a silica gel
column, using dichloromethane/methanol mixtures as
eluant.
:. ~-
20~98l58
Yield: 150 mg (26.6% of theory),Melting point: 175-180C
The following compound is obtained analogously:
(1) 4-amidino-4'-[4-((-)-menthyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
Melting point: >260C
Example 5
4-Amidino-4'-[4-(pivaloyloxymethyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
a) 4-(N-Benzyloxycarbonyl-amidino)-4'-[4-
(pivaloyloxymethyloxycarbonylmethyl)-piperidino-
carbonyl]-bi~henyl
A mixture of 1.7 g (0.0034 mol~ of 4-[N-
benzyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-[4-(carboxymethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl, 1 ml (0.0068 mol) of
chloromethyl-pivalate, 1.1 g (0.0068 mol) of potassium
iodide, 0.7 g (0.0068 mol) of potassium bicarbonate and
1 g (0.0068 mol) of potassium carbonate in 40 ml of
dimethylformamide is stirred for 2 days at ambient
temperature. Then it is poured into 150 ml of water and
the suspension thus produced is extracted three times
with ethyl acetate. The combined organic phases are
dried over sodium sulphate and evaporated to dryness
under reduced pressure. The residue remaining is
purified by chromatography over a silica gel column,
using cyclohexane-ethyl acetate mixtures as solvents.
In this way 1.45 g (68.5% of theory) is obtained in the
form of a foamy product which is used for the following
stage of synthesis without any further purification.
Rf value: 0.5 (silica gel; methylene chloride/ethanol =
9/1)
: `' ~: ` ` ` ' :
2400981~8
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
(1) 4-[4-[(1-(ethoxycarbonyloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl)-
methyl]-piperidinocarbonyl]-4'-[N-benzyloxycarbonyl-
amidino]-biphenyl
Oil, Rf value 0.65 (silica gel; methylene
chloride/ethanol = 9:1)
(2) 4-[N-benzyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-[4-
(pivaloyloxymethyloxycarbonylmethylidene)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl
(3) 4-[4-[(1-(ethoxycarbonyloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl)-
methyl]-piperidinomethyl]-4'-[N-benzyloxycarbonyl-
amidino]-biphenyl
(4) 4-[N-benzyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-[(2-
(pivaloyloxymethyloxycarbonyl)-ethyl)-
aminocarbonylmethyl]-biphenyl
(5) 4-[2-(1-ethoxycarbonyloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl)-
aminocarbonylmethyloxy]-4'-[N-benzyloxycarbonyl-
amidino]-biphenyl
(6) 4-[N-benzyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-[1-[2-(4-
methoxyphenyl)-ethylaminocarbonyl]-2-
(pivaloyloxymethyloxycarbonyl)-ethylamino]-
carbonylmethyl]-biphenyl
(7) 4-[benzyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-[4-[1-
(cyclohexyloxycarbonyloxy)-ethyloxycarbonylmethyl]-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl
(8) 4-[benzyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-methoxy-3'-[4-
trans-(pivaloyloxymethyloxycarbonyl)-
cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-biphenyl
.. -
.. : :
2 04~8 1~
(9) 4-[N-allyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-[4-
(pivaloyloxymethyl-oxycarbonylmethylidene)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl
(10) 3-[4-trans-[1-(ethoxycarbonyloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl]-
cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-4'-[N-benzyloxycarbonyl-
amidino~-4-methoxy-biphenyl
b) 4-Amidino-4'-[4-(pivaloyloxymethyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
~iperidinocarbonyll-biphenyl-hydrochloride
The product obtained in a) (1.43 g = 0.0023 mol) is
dissolved in a mixture of 20 ml of dimethylformamide and
2.3 ml of 0.5N hydrochloric acid. This solution is
hydrogenated at ambient temperature in the presence of
0.2 g of (10%) palladium on charcoal under a pressure of
5 bar for 2.5 hours. After the catalyst has been
removed by suction filtering, the solution is adjusted
to a pH of 3 and evaporated to dryness under reduced
pressure. The residue is suspended in acetone. The
solid product is suction filtered.
Yield: 0.8 g (69.8% of theory),
Melting point: 168-172C
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
(1) 4-[4-[(1-(ethoxycarbonyloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl)-
methyl]-piperidinocarbonyl]-4'-amidino-biphenyl- ;
hydrochloride with l-chloroethyl-ethyl-carbonate
Melting point: 178-182~C
(2) 4-amidino-[4'-[4-(pivaloyloxymethyloxycarbonyl-
methylidene)-piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
with pivalate-chloromethylester
(3) 4-[4-[(1-(ethoxycarbonyloxy)-athoxycarbonyl)-
methyl]-piperidinomethyl~-4'-amidino-biphenyl-
hydrochloride
20981~8
- 42 -
(4) 4-amidino-4'-[(2-(pivaloyloxymethyloxycarbonyl)-
ethyl)-aminocarbonylmethyl]-biphenyl
(5) 4'-amidino-4-[2-(1-ethoxycarbonyloxy)-
ethoxycarbonyl)-aminocarbonylmethyloxy]-biphenyl-
hydrochloride
(6) 4-amidino-4'-[1-[2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-
ethylaminocarbonyl]-2-(pivaloyloxymethyloxycarbonyl)-
ethylamino]-carbonylmethyl]-biphenyl
(7) 4-amidino-4'-[4-[1-(cyclohexyloxycarbonyloxy)-
ethyloxy-carbonylmethyl]-piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl
with 1-chloroethyl-cyclohexyl-carbonate
(8) 4-amidino-4'-methoxy-3'-[4-trans-
(pivaloyloxymethyloxy-carbonyl)-
cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-biphenyl
(9) 4'-amidino-3-[4-trans-[1-(ethoxycarbonyloxy)-
ethoxycarbonyl]-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-4-methoxy-
biphenyl
Example 6
4-Amidino-4'-[4-(phthalid-3-yloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl
a) 4-[N-Allyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-~4-
(methoxycarbonylmethyl ? -piperidinocarbonyl~-biphenyl
To a solution of 2.5 g (0.006 mol) of 4-amidino-4'-[4-
(methoxycarbonylmethyl)-piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl in
250 ml of dichloromethane are added, at ambient
temperature and with stirring, 0.75 ml (0.007 mol) of
allylchloroformate and 13 ml (0.013 mol) of lN sodium
hydroxide solution. This mixture is stirred for 3 hours
.
- : .-: .. :
: . - , ~,- :
.
.
.
20~81~8
- 43 -
at ambient temperature, then left to stand overnight at
ambient temperature. The organic phase is separated
off, dried over sodium sulphate and stirred with 2 g of
activated charcoal. After the drying agent and
activated charcoal have been filtered off the solution
is evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure. The
residue is dissolved in dichloromethane/methanol = 1:1;
20 ml of~isopropanol are added and the mixture is
concentrated down to 20 ml. After the addition of ether
crystallisation sets in. The crystals are suction
filtered and washed with water.
Yield: 2.4 g (86.3% of theory),
Melting point: 148-152C
The following compound is obtained analogously:
(1) 4-[N-allyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-[[1-[2-(4-methoxy-
phenyl)-ethylaminocarbonyl]-2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl]-
aminocarbonyl]-biphenyl
b) 4-[N-allyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-[4-(carboxymethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyll-biphenyl
1.95 g (0.042 mol) of the compound prepared in a) are
dissolved in 20 ml of tetrahydrofuran and 4 ml of water.
To this solution are added 21 ml of a 1 molar lithium
hydroxide solution (0.021 mol) and the mixture is left
to stand for 2 hours at ambient temperature. It is then
poured into an aqueous potassium hydrogen sulphate
solution, the pH is adjusted to 6.S and the mixture is
extracted exhaustively with ethyl acetate. The combined
ethyl acetate phases are dried and evaporated down. The
residue is triturated with ether and suction filtered.
Yield: 1.2 g (63.6~ of theory),
Melting point: 189-192C (decomp.)
The following compound is obtained analogously:
.: , .
.
~0~8~58
(1) 4-[N-allyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-[[1-[2-(4-methoxy-
phenyl)-ethylaminocarbonyl]-2-hydroxycarbonyl-ethyl]-
aminocarbonyl]-biphenyl
c) 4-[N-allyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-[4-(phthalid-3-
vloxy-carbonylmethyl)-piperidinocarbonyl~-biphenyl
0.3 g (0.0007 mol) of the compound prepared under b) are
dissolved in 30 ml of dimethylformamide. This solution
is mixed with 0.4 g (0.004 mol) of potassium hydrogen
carbonate and 0.71 g (0.00~3 mol) of 3-bromophthalide
are added thereto with stirring at 0-5C and stirring is
continued for 3 hours at this temperature. After this
time, the mixture is poured into ice water and extracted
with ethyl acetate. The combined ethyl acetate phases
are washed with water, dried over sodium sulphate and
evaporated down under reduced pressure. The residue is
purified by chromatography over silica gel.
The following compound is obtained analogously: -
(1) 4-[N-allyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-t[1-[2-(4-methoxy-
phenyl)-ethylaminocarbonyl]-2-(phthalid-3-
yloxycarbonyl)-ethyl]-aminocarbonyl]-biphenyl
d) 4-Amidino-4'-[4-(phthalid-3-yloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl
The compound obtained in c) is dissolved in
tetrahydrofuran. Under an inert gas atmosphere, 1
equivalent of morpholine and 0.1 equivalent of tetrakis-
(triphenylphosphine)-palladium(o) are added dropwise,
with stirring, and stirring is continued for a further
hour.
The following compound is obtained analogously:
(1) 4-amidino-4'-[[1-[2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-ethylamino-
carbonyl]-2-(phthalid-3-yloxycarbonyl)-ethyl]-
~ . ' ~ , ,'- , ..~ . - -
'~ . .
204~81~8
aminocarbonyl]-biphenyl
Example 7
4-[4-(Cyclohexyloxycarbonylmethyl)-piperidinocarbonyl]-
4'-[N-methoxycarbonyl-amidino]-biphenyl
-
0.6 g (0.0012 mol) of 4-amidino-4'-[4-
(cyclohexyloxycarbonylmsthyl)-piperidinocarbonyl]-
biphenyl-hydrochloride are suspended in 200 ml of
dichloromethane. 0.1 g (0.0012 mol) of
methylchloroformate and 24.8 ml (0.0025 mol) of O.lN
sodium hydroxide solution are added with stirring and
the mixture is then stirred for a further 2 hours,
thereby forming a solution. The aqueous phase is
separated off, the dichloromethane solution is dried
over sodium sulphate and evaporated to dryness. The
residue is triturated with ether, suction filtered and
washed with ether.
Yield: 0.44 g (76.2% of theory),
Melting point: 218-220C
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
(1) 4-[N-allyloxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-[4-
(cyclohexyloxycarbonylmethyl)-piperidinocarbonyl]-
biphenyl
(2) 4-[N-methoxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-[4-(N-methyl-
piperidin-4-yloxycarbonylmethyl)-piperidinocarbonyl]-
biphenyl
(3) 4-[N-methoxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-[4-(tetrahydro-4H-
pyran-4-yloxycarbonylmethyl)-piperidinocarbonyl]-
biphenyl
(4) 4-[N-(cyclohexylmethyloxycarbonylmethyl)-
. , . ,: :
:-
.
:
2098158
- 46 -
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl
(5) 4-t4-(cyclopentyloxycarbonylmethylidene)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-4'-tN-methoxycarbonyl-amidino]-
biphenyl
(6) 4'-[4-(4-cycloheptyloxycarbonyl-butyrylamino)]-4-~N-
methoxycarbonyl-amidino]-biphenyl
(7) 4-[4-(cyclohexyloxycarbonylmethyl)-piperazino-
carbonyl]-4'-tN-methoxycarbonyl-amidino]-biphenyl
(8) 4-tN-methoxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-t4-trans-(N-methyl-
piperidin-4-yloxycarbonyl)-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-
biphenyl
(9) 3-t4-trans-cyclohexyloxycarbonyl-cyclohexylamino-
carbonyl]-4-methoxy-4~-tN-methoxycarbonyl-amidino]-
biphenyl
~10) 4-tN-methoxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-methoxy-3'-t4-
trans-(N-methyl-piperidin-4-yloxycarbonyl)-
cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-biphenyl
(11) 4-[4-(methoxycarbonylmethyl)-piperidinocarbonyl]-
4'-[N-(pivaloyloxymethoxycarbonyl)-amidino]-biphenyl
(Pivaloyloxy-methyl)-(4-nitrophenyl)-carbonate and N-
ethyl-diisopropylamine are used.
(12) 4-[N-(acetyloxymethoxycarbonyl)-amidino]-4'-[4-
(methoxycarbonylmethyl)-piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl
Acetyloxymethyl-(4-nitrophenyl)-carbonate and
N-ethyl-diisopropylamine are used.
(13) 4-[N-~l-acetyloxy-ethoxycarbonyl)-amidino]-4'-[4-
(methoxycarbonylmethyl)-piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl
Acetyloxyethyl-(4-nitrophenyl)-carbonate and N-ethyl-
.- -
2098158
- 47 -
diisopropylamine are used.
(14) 4-[4-[~2,2-dimethyl-propyloxy)carbonylmethyl]-
piperidinocarbonyl]-4'-(N-methoxycarbonyl-amidino~-
biphenyl
Melting point: 168-170C
Rf valuè: 0.50 (silica gel, ethyl acetate)
(15) 4-(N-methoxycarbonyl-amidino)-4'-[4-[(3-
pentyloxy)carbonylmethyl]-piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl
Melting point: 148-152C
Rf value: 0.58 (silica gel, methylene chloride/methanol
= 9:1)
(16) 4-[4-[((R)-2-butyloxy)carbonylmethyl]-
piperidinocarbonyl]-4'-(N-methoxycarbonyl-amidino)-
biphenyl
Melting point: 135-138C
Rf value: 0.56 (silica gel, methylene chloride/methanol
= 9:1)
(17) 4-[4-[((S)-2-butyloxy)carbonylmethyl]-
piperidinocarbonyl]-4'-(N-methoxycarbonyl-amidino)-
biphenyl
Melting point: 130-132C
Rf value: 0.51 (silica gel, methylene chloride/methanol
= 9:1)
(18) 4-(N-methoxycarbonyl-amidino)-4'-[4-[(2-methyl-
propyloxy)carbonylmethyl]-piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl
Melting point: 146-152C
Rf value: 0.51 (silica gel, methylene chloride/methanol
= 9:1)
(19) 4-[4-(isopropyloxy)carbonylmethyl]-
piperidinocarbonyl]-4'-(N-methoxycarbonyl-amidino)-
biphenyl
'-: ~ ~ - : . '
24~9-~l58
Melting point: 146-148~C
Rf value: 0.38 (silica gel, methylene chloride/methanol
= 9:1)
Example a
4-Amidino-4'-[4-(piperidin-4-yloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl-hydrochloride
a) 4-Amidino-4'-[4-(N-benzyloxycarbonyl-piperidin-4-
' yloxycarbonylmethyl)-piperidinocarbonyll-biPhenyl
A suspension of 4-amidino-4'-[4-carboxymethyl-
piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl, N-benzyloxycarbonyl-
piperidin-4-ol and trimethylchlorosilane in a molar
ratio of 1:4:10 is refluxed for 36 hours in absolute
tetrahydrofuran. It is then evaporated to dryness in
vacuo, taken up in dichloromethane and the organic phase
is washed with 2N ammonia and then with water. After
the organic phase has been dried over sodium sulphate it
is evaporated down in vacuo and the residue obtained is
purified by chromatography over silica gel.
b) 4-Amidino-4'-[4-(piperidin-4-yloxycarbonylmethyl)-
piperidino arbonyll-biphenyl-hydrochloride
The product prepared in a) is dissolved in
dimethylformamide/0.5N hydrochloric acid (10:1) and then
hydrogenated in the presence of 10% palladium on
charcoal at ambient temperature under a hydrogen
pressure of 5 bar.
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
(1) 4-amidino-4'-[4-trans-(N-benzyloxycarbonyl-
piperidin-4-yloxycarbonyl)-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-
biphenyl
`
, - : - ,
: ' , :
- ~g81S8
(2) 4-amidino-4'-[4-trans-(N-benzyloxycarbonyl-
piperidin-4-yloxycarbonyl)-cyclohexyl-N-methyl-
aminocarbonyl]-biphenyl
(3) 4-amidino-4'-[4-trans-(piperidin-4-yloxycarbonyl)-
cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-biphenyl-dihydrochloride
(4~ 4-amidino-4'-[4-trans-(piperidin-4-yloxycarbonyl)-
cyclohexyl-N-methyl-aminocarbonyl]-biphenyl-
dihydrochloride
Example 9
4-[N-Methoxycarbonyl-amidino~-4'-[4-(piperidin-4-
yloxycarbonylmethyl)-piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl-
hydrochloride
a) 4-[4-(N-Benzyloxycarbonyl-piperidin-4-yloxycarbonyl-
methyl)-piperidinocarbonyl]-4'-[N-methoxycarbonyl-
amidino]-biphenyl __
4-Amidino-4'-[4-(N-benzyloxycarbonyl-piperidin-4-
yloxycarbonylmethyl)-piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl is
suspended in dichloromethane and reacted, with stirring,
with an equimolar amount of methylchloroformate in the
presence of an equivalent quantity of O.lN sodium
hydroxide solution at amhient temperature. The
dichloromethane solution is washed with water, dried and
evaporated down. The residue is purified by column
chromatography over silica gel.
The following compound is obtained analogously:
(1) 4'-[4-trans-(N-benzyloxycarbonyl-piperidin-4-
yloxycarbonyl)-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-4-[N-
methoxycarbonyl-amidino]-biphenyl
.
2098~8
- 50 -
b) 4-[N-Methoxycarbonyl-amidino]-4-[4-(piperidin-4-
yloxycarbonylmethyl)-piperidinocarbonyl]-biphenyl-
hydrochloride ___
The product obtained in c) is hydrogenated, as described
in Example 8b, in the presence of (10%)
palladium/charcoal.
The following compound is obtained analogously:
(1) 4-[N-methoxycarbonyl-amidino]-4'-[trans-(piperidin-
4-yloxycarbonyl)-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl]-biphenyl
Exam~le 10
Dry ampoule containing 2.5 mg of active substance per
1 ml
Composition:
Active substance 2.5 mg
Mannitol 50.0 mg
Water for injections ad 1.0 ml
Preparation:
The active substance and mannitol are dissolved in
water. After transferring the solution to the ampoule,
it is freeze-dried.
At the point of use, the solution is made up with water
for injections.
. .
- . . ~ ~ .. .~
.
. ... . . -
: . . ,
~ ;, .
2098158
- 51 -
Example 11
Dry ampoule containing 35 mg of active substance per
2 ml
Composition:
Active substance 35.0 mg
Mannitol 100.0 mg
Water for injections ad 2.0 ml
Preparation:
The active substance and mannitol are dissolved in
water. After transferring the solution to the ampoule,
it is freeze-dried.
At the point of use, the solution is made up with water
for injections.
Example 12
Tablet containing 50 mg of active substance
. ~ ~
Composition:
(1) Active substance 50.0 mg
(2) Lactose 98.0 mg
(3) Corn starch 50.0 mg
(4) Polyvinylpyrrolidone 15.0 mg
(5) Magnesium stearate 2.0 mq
215.0 mg
:.; : ~ .. - : . . :. - :
. .. . , . :: .
~: . . . : ;
: . . ~ :
20~81~g
- 52 -
Preparation:
(1), (2) and (3) are mixed together and granulated with
an aqueous solution of (4). (5) is added to the dried
granules. From this mixture, compressed tablets are
produced, biplanar, facetted on both sides and notched
on one side. Diameter of tablets: 9 mm.
Example 13
Tablet containing 350 mg of active substance
Composition:
(1) Active substance 350.0 mg
(2) Lactose 136.0 mg
(3) Corn starch 80.0 mg
(4) Polyvinylpyrrolidone30.0 mg
(5) Magnesium stearate 4.0 mg
600.0 mg
Preparation:
(1), (2) and (3) are mixed together and granulated with
an aqueous solution of (4). (5) is added to the dried
granules. From this mixture, compressed tablets are
produced, biplanar, facetted on both sides and notched
on one side. Diameter of tablets: 12 mm.
209~1~8
- 53 -
Example 14
Capsules containing 50 mg of active substance
Com~osition:
(1) Actlve substance 50.0 mg
(2) Dried corn starch 58.0 mg
(3) Powdered lactose 50.0 mg
(4) Magnesium stearate 2.0 mg
160.0 mg
Pre~aration:
(1) is triturated with (3). This triturate is added to
the mixture of (2) and (4), with thorough mixing.
This powdered mixture is packed into size 3 hard gelatin
oblong capsules in a capsule filling machine.
Example 15
Capsules containing 350 mg of active substance
; .. _.
Composition:
(1) Active substance 350.0 mg
(2) Dried corn starch 46.0 mg
(3) Powdered lactose 30.0 mg
(4) Magnesium stearate 4.0 mg
430.0 mg
Preparation:
(1) is triturated with (3). This triturate is added to
the mixture of (2) and (4), with thorough mixing.
-: : ,
: - : , ~ :
2098~58
- 54 -
This powdered mixture is packed into size O hard gelatin
oblong capsules in a capsule filling machine.
, - , : , ~
- -
- : .. ~ ;: .
. . .