Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
21 0 3 91 1 ~
--1 ~
BASE_FOR ELECTRODEL~SS DISC~A~GE LA~P
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Field of the_Inve~tion
This invention relates to an electrically
non-conductive base for an electrodeless discharge
lamp. ~ore particularly thi~ invention relates to an
electrically non-conductive base for an electrodel~ss
arc discharge lamp having an outer envelope press
sealed over a tubular lamp stem containing a starting
aid, wherein the base is secured, in clamshell
fashion, to the press seal portion of the lamp and
contains means ~or coupling RF energy to the starting
aid for energizing the lamp.
Backaround oP the Disclosure
High intensity electroded arc discharge lamps
such as high pressure sodium lamps and m~tal halide
lamps are well known and include a light-transmi~sive
arc discharge chamber or tube hermetically sealed and
enclosing within a pair of spaced apart electrodes
and a suitable fill such as an inert starting gas and
one or more ionizable metals or metal halid~s. Two
of the major causes of lamp failure are sputtering o~
electrode material onto the lamp envelope and thermal
and electrical stresses which result in electrode
failure. More recently a new class o~ high intensity
arc discharge lamps has been devsloped called
electrodeless la~ps. Such lamps have a
light-transmissive, electrodeless arc chamber or t~be
generally shaped like a pillbox or oblate spheroid
and containing a fill which comprise~ a suitable
inert buffer g~s and one or more metal halides.
- ,
.~ . ~: -
:
LD0010405
2~3~8
-2-
Radio frequency (RF) energy applied or coupled to the
fill via capacitive or inductive coupling generates a
light-emitting arc. In operation of such a lamp via
inductive c~upling, the arc tube or chamber acts as a
single-turn secondary coil of a transformer and is
surrounded by an ~F energy excitation coil which acts
as a primary coil. Various embodiments of such lamps
are disclosed, for example, in U.S. Patents
4,810,938; 4,959,584; 5,039,903; 5,059,868 and
10 5/140,22~ all of which are assigned to the assignee
of the present invention. The electronics required
for starting and sustaining the arc discharge in : -
these lamps is costly and complex and also requires
the u~e of a rather large copper or aluminum
inductiv~ drive coil to function as the primary coil
for carrying the high frequency current required.
Hence some development has been directed toward ~:
replaceable electrodeless discharge lamps,
particularly o~ the high intensity type employing one
or more metal halides as the arc sustaining fill,
wherein the lamp itself is physically separate from
both the electronics and the inductive drive coil. -
one such attempt is disclosed in U.S. 4,959,584 as a
luminaire having a replaceable electrodeless, HID
metal halide arc discharge lamp wherein the arc
chamber is cradled in a thermal jacket which in turn
is contained within an outer envelope having a :
conventional metal screw base with a conductive lead
passing through the ~ase to the vicinity of the arc
tube. U.S. 5,059,868 discloses an HID electrodeless
arc discharge lamp wherein the arc chamber is
supported in an ou~er envelopa by means of a support .
rod which contains an electrical inlead for supplying -
electricity to the arc chamber,in order to start the
.. , . ~ ... ~., .. , . :. , - .: . -: - : . . - .
, . , -: . - , . ,- .;
LD0010405
2~0341~
--3-
arc. The arc chambar-outer cha~ber assembly
terminates at one end in a conventional metal base
having pin~ for securing in a socket. However, it is
preferable to minimize the amount o~ metal clos~ to
the drive coil, because metal (or any conductor) will
pick up energy from ~he coil which will result in
heating the metal and loss of system efficienay.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a lamp base
suitable for use with a lamp having an envelope
closed off by a pinch seal at one end and a tubular
stem portion ext2nding beyond the pinch seal and has
been found to be useful with electrodeless arc
discharge lamps, particularly a high intensity
electrodeless arc discharge la~p of surh
construction. A lamp base o~ this invention
co~prises at least two electrically non-conductive
members assembled into mating engagement and def ining
a bore axially extending from one end through a
portion o~ the base and terminating in an upwardly
opening cavity provided in a remaining portion of the
base, with the cavity in com~unication with the
bore. The cavity has means for retaining the pinch
seal portion of the lamp. The lamp is mounted to the
base with its envelope pinch seal re~ained in the
cavity and its stem extending into the bore. The
bore contains an electrically conductive means for
transferring RF en~rgy to the tubular portion of the
lamp which extends into the bore. The base has
further means for securinq the base into a suitable
~ixtur~ or luminaire. The fixture or luminaira will
contain means for coupling RF energy to the lamp and
to the conductive means in the,base. In most casas
LD001 0405
2103~18
-4- : :
the fixture or luminaire contains an RF coil which
surrounds the lamp in the vicinity of the arc chamber
for which the base of the invention provides accurate
alignment o~ the lamp with respect to the RF coilO -
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWING
Figure 1 is a schematic illustration of a lamp
base of the invention shown assembled in l(a) with :
l(b) being a top view, l(c) illustrating means for :
securing the base in a fixture and l(d) illustrating
RF energy transfer means.
Figure 2 schematically illustrates three views
of one of two clamping members which form a base of
the invention. ::
Figur~ 3 schematically illustrates a lamp-base
assembly according to the invention and a lamp useful
with the base. ::-
Figures 4(a) and 4(b~ schematically illustrate
one of two clamping members which form a base of the
invention having different embodiments of an RF
energy transfer means.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
The lamp base of the present invention,
generally indicated at 10, is formed by a pair of
opposing and cooperating shell-like, semicylindrical
(other shapes could be used) m~mbers 12, 12 shown in
mating engagement as seen in Figure 1 to form a
hollow, cylindrical structure having a top 32 and
bottom 34 and a bora 14 in which hollow, conductive
metal (e.g., brass~ bushing 50 is held. Members 12,
12 are identical and mate with each other along
surfaces 16, 16 to form base 10. The shell members
are made of a suitable electrically non-conductive
. . .
^~ LD0010405
21~3~
--5--
and heat-resistant material which includes ceramic
materials and plastics such as Delrin, Teflon,
poly~ulfones, liquid crystal polymers, such as Vectra
A130 by Celanese Corporation, polyetherimides such as
Ultem by GE and polyphenylene sulfides such as Supec
by GE and Ryton by Philips. In one embodiment
members 12, 12 are made of Delrin ~DuPont) and
assembled by means o~ a cavity 19 and a molded-in
Delrin pin 18, molded as part of each member 12, so
that th~ mating half 12 contains a matching and
opposing hole 19 and pin 18. A thin layer of epoxy
adhesive applied to flat surfaces 16, 16 illustrated
in Figure 2 providQs a permanent bond~ Other
suitable means such as ultrasonic welding, thermal
weldingr other adhesives, mechanical means, etc., may
be employed to as~emble and secure clamping members
12, 12 to form bas~ 10. Further, although it is
preferable that pins 18 be electrically
non-co~ductive, they could be separate and not molded
20 as part of one or both of the members. Figure l(d)
illustrates one embodiment of an ~F energy transf2r
means as a brass or other suitable conductive metal
bushing 50 comprising hollow cylindrical portion 52
open at one end and containing bore 54 for receiving
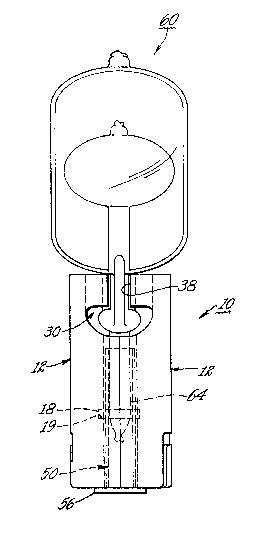
25 stem 64 of lamp 60 as illustrated in Figure 3(b) and
~lat disk or flange portion 56 at the other end.
Disk 56 could have a hole in it instead of being
solid as shown so that the bushing 50 would be open
at both ends. Figures 4(a) and 4(b) illustrate still
30 further embodiments of an RF energy transfer means,
such as an electrically conductive half-bushing 80
molded into cavity 13 of member 12. Mating member 12
will have an identical half-bushing molded into it to
form a bushing similar to 50 wh~n the two members are
.: . . . . . ~ .
LD001 0405
2~34:l~
-6- :
assembled into a base. Although 80 i5 shown having a
half disk or flange 81, it could be merely half a
cylinder without a flange. Yet another embodiment is
illustrated as a conductive metal plating 82 on the
surface of the cavity 13 as illustrated in Figure
4(b). Although not shown in Figure 4(b), conductive
plating 82 could extend around the exterior bottom
portion o~ the mem~ers in any desired configuration.
However, in yet another embodiment, the RF energy
transfer means could form a part of a fixture or
luminaire, so that when the base lamp assembly is
inserted into the fixture or luminaire, a suitable RF
energy transfer means forming part o~ ~he fixture is
inserted into the base cavity 14, and surrounds or
contacts at least a portion of lamp stem 64.
As illustrated in Figure 2, bore 14, which
extends through the lower portion of the base, is
defined by the mating of the cavities 13 formed in
both me~bers 12, 12. The upper end portions of the
memb~irs beyond cavities 13 and flat surfaces 16 are
formed with concavities 20 such that, when mated, the
concavities define a large diameter cavity 30 in open
communication with bore 14. Immediately above the
floor 22 of cavity 30, the opposed edges of the
concavities 20 are relieved as indicated at 26, to
provide enlarg~d, diametrically opposed side openings
into ca~ity 30. Member edges 38 above reliefs 26 are
set back from flat surfaces 16 such that, with the
members mat~d as seen in Figure l(a), diametrically
opposed slots 39 are provided. The upper interior
surface of cavity 30 is cylindrical as indicated at
28. While cavity 30 is illustrated as somewhat or at
least partially cylindrical in this embodiment, other
shapes may be useful to the practitioner.
~ LD001 0405
2~03~ 18
As seen in ~i~ure l(c), an L-shaped keyway 36
is formed in the lower portion near the ~ottom 34 of
each member to receive pins or other means serving to
secure base 10 in a suitable fixture or luminaire and
preferably one equipped to furnish RF energy to the
lamp mounted in ~he base. Other means may be
employed to secure the base in a fixture or
luminaire, the choice being left to the practitioner.
Turning to Figure 3, an electrodeless arc
discharge lamp 60 is illustrated as comprising
hermetically sealed arc chamber 62 to which is
attached a hermetically sealed tubular stem portion
64 containing a ga~eous fill (not shown~ which acts
as a starting aid as disclosed in U.S. Patent
5,140,227, the dis~losures of which are incorporated
herein by re~erence. Arc cham~er 62 is hermetically
sealed within a fused quartz outer envelope 68 closed
of~ by means of a hermetic pinch seal 70 formed by
pinching one end of 68 closed over tubular stem 640
Tubular stem portion 64 thus extends through pinch
seal 70 with its other end closed off by the wall of
arc chamber 62 as disclosed in the '227 patent. The
medial portion of pinch seal 70 is generally flat . :-
having sides 72 and a raised bottom ridge 74
25 protruding transverse to the longitudinal axis of the `~
lamp 60 as is shown in Figure 3(b). As seen in
Figure 3(b), lamp 60 i5 shown mechanically secured or . -:~
seated in base 10 by means of cavity 30 around pinch
seal 70. Stem 64 extends into bore 14 and into bore ~:~
54 of metal bushing 50. Pairs of opposed, raised ~or
recessed) flats 78 are formed in the pinch seal 70
during the pinch seal moldiny process in positions -- such that, with the lamp fully seated, 2ach flat is
confronted by or adjacent an edge surface 38 of the
. - - ~ . . .
---` LD001 0405
2 1 (~
base. Flats 78 are molded into both sides of pinch
seal 70 and also adjacent both sides o~ stem seal
portion 76. I~ desired, a suitable adhesive or
cement may be applied to bond or cement the four flat
sur~aces 78 of the pinch seal to each of
corresponding lamp base flat surfaces 38 to prevent
any movement of lamp 60 within base 10.
The foregoing embodiments are intended to be
illustrative, but non-limiting with respect to the
practice of the inYention. Some departure from these
embodiments is permissible within the SCOp2 of the
invention as those skilled in the art will know and
appreciate.
: - , , -.
- - - - .
.
: - =, -
:- :: : : .