Une partie des informations de ce site Web a été fournie par des sources externes. Le gouvernement du Canada n'assume aucune responsabilité concernant la précision, l'actualité ou la fiabilité des informations fournies par les sources externes. Les utilisateurs qui désirent employer cette information devraient consulter directement la source des informations. Le contenu fourni par les sources externes n'est pas assujetti aux exigences sur les langues officielles, la protection des renseignements personnels et l'accessibilité.
L'apparition de différences dans le texte et l'image des Revendications et de l'Abrégé dépend du moment auquel le document est publié. Les textes des Revendications et de l'Abrégé sont affichés :
| (12) Brevet: | (11) CA 2120510 |
|---|---|
| (54) Titre français: | CIRCUIT POUR DETECTER LES PARTIES NON ENREGISTREES D'UN SUPPORT D'ENREGISTREMENT |
| (54) Titre anglais: | CIRCUIT FOR DETECTING UNRECORDED PORTION OF RECORDING MEDIUM |
| Statut: | Périmé et au-delà du délai pour l’annulation |
| (51) Classification internationale des brevets (CIB): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventeurs : |
|
| (73) Titulaires : |
|
| (71) Demandeurs : |
|
| (74) Agent: | SMART & BIGGAR LP |
| (74) Co-agent: | |
| (45) Délivré: | 2001-05-01 |
| (86) Date de dépôt PCT: | 1992-11-30 |
| (87) Mise à la disponibilité du public: | 1994-06-09 |
| Requête d'examen: | 1999-10-15 |
| Licence disponible: | S.O. |
| Cédé au domaine public: | S.O. |
| (25) Langue des documents déposés: | Anglais |
| Traité de coopération en matière de brevets (PCT): | Oui |
|---|---|
| (86) Numéro de la demande PCT: | PCT/KR1992/000070 |
| (87) Numéro de publication internationale PCT: | KR1992000070 |
| (85) Entrée nationale: | 1994-03-31 |
| (30) Données de priorité de la demande: | S.O. |
|---|
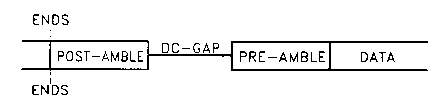
Circuit permettant de détecter une partie non enregistrée d'un support d'enregistrement, qui comprend une section (10) de comptage de fenêtres destinée à recevoir un signal d'entrée pour reconnaître si le signal d'entrée vient d'une partie non enregistrée du spport d'enregistrement et à compter un laps de temps prédéterminé pour générer un signal d'impulsion de fenêtre, et un générateur (20) de signaux de synchronisation qui est mis en service par le signal d'impulsion de fenêtre. Si le nombre d'impulsions du signal d'entrée n'est pas inférieur à un nombre prédéterminé le générateur reconnaît que le signal d'entrée concerné vient d'une région de données du support d'enregistrement et génère simultanément un signal de synchronisation. Mais si le nombre d'impulsions du signal d'entrée n'est pas supérieur à un nombre prédéterminé d'impulsions, le générateur reconnaît que le signal d'entrée concerné vient d'une région non enregistrée du support d'enregistrement et ne génère pas de signal de synchronisation. La partie non enregistrée est détectée avec précision, de manière à ce qu'un signal de synchronisation ne soit pas généré sur la base du bruit présent sur la partie non enregistrée du support d'enregistrement.
Disclosed is a circuit for detecting an unrecorded portion in a recording
medium,
which comprises a window counting portion (10) for receiving an input signal
to
recognize if the input signal comes from an unrecorded portion of the
recording medium
and counting a predetermined time to generate a window pulse signal, and a
sync signal
generator (20) which is enabled by the window pulse signal, in which if the
number of
pulses of the input signal is not less than a predetermined number, the
generator
recognizes the current input signal comes from a data region of the recording
medium to
simultaneously generate a sync signal, while if the number of pulses of the
input signal
is not more than a predetermined number of pulses, the generator recognizes
the current
input signal comes from an unrecorded region of the recording medium, not to
generate
the sync signal. The unrecorded portion is accurately detected not to generate
a sync
signal due to noise included in the unrecorded portion of the recording
medium.
Note : Les revendications sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
2024-08-01 : Dans le cadre de la transition vers les Brevets de nouvelle génération (BNG), la base de données sur les brevets canadiens (BDBC) contient désormais un Historique d'événement plus détaillé, qui reproduit le Journal des événements de notre nouvelle solution interne.
Veuillez noter que les événements débutant par « Inactive : » se réfèrent à des événements qui ne sont plus utilisés dans notre nouvelle solution interne.
Pour une meilleure compréhension de l'état de la demande ou brevet qui figure sur cette page, la rubrique Mise en garde , et les descriptions de Brevet , Historique d'événement , Taxes périodiques et Historique des paiements devraient être consultées.
| Description | Date |
|---|---|
| Le délai pour l'annulation est expiré | 2009-11-30 |
| Lettre envoyée | 2008-12-01 |
| Accordé par délivrance | 2001-05-01 |
| Inactive : Page couverture publiée | 2001-04-30 |
| Inactive : Taxe finale reçue | 2001-01-31 |
| Préoctroi | 2001-01-31 |
| Un avis d'acceptation est envoyé | 2000-10-10 |
| Un avis d'acceptation est envoyé | 2000-10-10 |
| Lettre envoyée | 2000-10-10 |
| Inactive : Approuvée aux fins d'acceptation (AFA) | 2000-09-22 |
| Modification reçue - modification volontaire | 2000-02-01 |
| Inactive : Dem. traitée sur TS dès date d'ent. journal | 1999-10-28 |
| Lettre envoyée | 1999-10-28 |
| Inactive : Renseign. sur l'état - Complets dès date d'ent. journ. | 1999-10-28 |
| Exigences pour une requête d'examen - jugée conforme | 1999-10-15 |
| Toutes les exigences pour l'examen - jugée conforme | 1999-10-15 |
| Demande publiée (accessible au public) | 1994-06-09 |
Il n'y a pas d'historique d'abandonnement
Le dernier paiement a été reçu le 2000-10-26
Avis : Si le paiement en totalité n'a pas été reçu au plus tard à la date indiquée, une taxe supplémentaire peut être imposée, soit une des taxes suivantes :
Les taxes sur les brevets sont ajustées au 1er janvier de chaque année. Les montants ci-dessus sont les montants actuels s'ils sont reçus au plus tard le 31 décembre de l'année en cours.
Veuillez vous référer à la page web des
taxes sur les brevets
de l'OPIC pour voir tous les montants actuels des taxes.
| Type de taxes | Anniversaire | Échéance | Date payée |
|---|---|---|---|
| TM (demande, 5e anniv.) - générale | 05 | 1997-12-01 | 1997-08-27 |
| TM (demande, 6e anniv.) - générale | 06 | 1998-11-30 | 1998-08-28 |
| TM (demande, 7e anniv.) - générale | 07 | 1999-11-30 | 1999-10-08 |
| Requête d'examen - générale | 1999-10-15 | ||
| TM (demande, 8e anniv.) - générale | 08 | 2000-11-30 | 2000-10-26 |
| Taxe finale - générale | 2001-01-31 | ||
| TM (brevet, 9e anniv.) - générale | 2001-11-30 | 2001-09-11 | |
| TM (brevet, 10e anniv.) - générale | 2002-12-02 | 2002-10-17 | |
| TM (brevet, 11e anniv.) - générale | 2003-12-01 | 2003-10-16 | |
| TM (brevet, 12e anniv.) - générale | 2004-11-30 | 2004-10-07 | |
| TM (brevet, 13e anniv.) - générale | 2005-11-30 | 2005-10-06 | |
| TM (brevet, 14e anniv.) - générale | 2006-11-30 | 2006-10-06 | |
| TM (brevet, 15e anniv.) - générale | 2007-11-30 | 2007-10-09 |
Les titulaires actuels et antérieures au dossier sont affichés en ordre alphabétique.
| Titulaires actuels au dossier |
|---|
| SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO., LTD. |
| Titulaires antérieures au dossier |
|---|
| KWANG-HEUI LEE |