Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
2~20~~~
Transdermal Therapeutic Systems with Crystallization Inhibitors
The invention relates to transdermal therapeutic systems,
which make available active ingredients to the organism through
the skin and are characterized in that crystallization inhibitors
are contained in the active ingredient-containing matrix.
Transdermal therapeutic systems (TDS) are, as is generally
known, plasters made of many layers, which are attached to the
skin and which continuously release the active ingredient
percutaneously over a prolonged period. Transdermal therapeutic
systems essentially consist of a cover film impermeable to water,
penetration enhancers and active ingredients, a matrix, which
comprises the skin contact adhesive, penetration enhancer and
pharmaceutical substance, and a detachable protective film.
High concentrations of dissolved active ingredient in the
matrix of transdermal therapeutic systems generally make possible
a high flow of active ingredients through the skin. In
particular, there have been frequent reports recently of so-
~called supersaturated systems, which make possible the desired
high transdermal flow of pharmaceutical substances (K. H. Ziller
and H. H. Rupprecht, Pharm. Ind. 52, No. 8 (1990), 1017-1022).
A problem of such supersaturated solutions is the
insufficient storage stability. Since easily crystallizing
compounds are involved in the incorporated active ingredients,
crystallization processes must be expected during the storage.
This tendency toward crystal formation or toward crystal growth
respectively is known, for example, in the case of suspensions
i i
CA 02120599 2002-04-29
2
and supersaturated solutions of steroid hormones (M.
Kuhnert-Brandstatter et al., Sci. Pharm. 35 (1967) 4, 287-
297). This phenomenon also applies to supersaturated
solutions of poorly soluble substances in acrylate
adhesive-enhancer mixtures.
Because of the crystallization process, the portion is
shifted from dissolved to crystallized active ingredient.
In this connection, optionally even the saturation
concentration of the active ingredient in the system can
fall short (Jian-wei Yu et al., Drug Development and
Industrial Pharmacy 17, 1991, 1883 ff). In addition,
crystal growth leads to the reduction of the crystal
surface, by which the rate of solution is reduced during
the administration.
To prevent crystallization processes in transdermal
therapeutic systems and to be able to administer the
therapeutically desired dose continuously, crystallization
inhibitors are added according to the invention (Fig. 1).
More specifically, the present invention provides a
transdermal therapeutic system, comprising a) a top coating
which is impermeable to water, penetration enhancer and
active ingredient, and b) an adhesive matrix, adhered to
the top coating comprising b1) an active ingredient, b2)
0.1 to 40o by weight relative to the total weight of the
I
CA 02120599 2002-04-29
2a
matrix of a vinylpyrrolidone-vinylacetate copolymer as
crystallization inhibitor, and b3) a skin contact adhesive.
Fig. 1 is a diagrammatic structure of an embodiment of
the transdermal therapeutic system having a cover film, a
matrix containing polyacrylate adhesive, penetration
enhancer, a pharmaceutical substance and a crystallization
inhibitor and a peeling-off film.
By the addition of crystallization inhibitors, a high
portion of active ingredient remains dissolved during the
storage time. The thus achieved physical stability of the
transdermal systems obtained is a basic requirement for the
use in practice. Transdermal therapeutic systems, in which
crystallization inhibitors are incorporated according to
the invention, are distinguished by very good in vitro
active ingredient release. Simultaneously, crystallization
processes of the active ingredients due to storage are
prevented in the TDS according to the invention
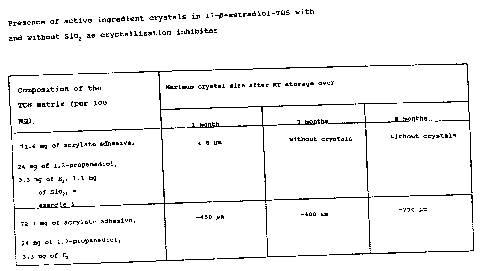
(Table 1). They are therefore particularly
3 2~~p~~;9
suitable to make the active ingredient continuously bioavailable
in humans in therapeutically relevant doses. Thus, for example,
a 17~-estradiol-TDS in the presence of a crystallization
inhibitor such as silicon dioxide indicated clearly less tendency
toward crystal formation than a comparison-TDS without a silicon
dioxide additive. While in the system according to the invention
no crystal growth was noted over the observatian period of 8
months at room temperature storage, large crystals-(-730 /gym) were
formed in the system without crystallization inhibitors -(Table
1). As crystallization inhibitors, highly dispersed silicon
dioxide or macromolecular substances are suitable. As
macromolecular substances, there can be mentioned, for example,
polyvinylpyrrolidones with an average molecular weight of about
1, 000 to 2, 000, 000 ( for example, Kollidon~R~ 12 PF, Kollidon~R~ 17
PF, Kollidon~R~ 25 PF, Kollidon~R~30, Kollidon~R~ 90 of the BASF
company, vinylpyrrolidone-vinyl acetate copolymers (such as
Kollidon~R~ VA 64 of the BASF company), crosslinked
polyvinylpyrrolidones (such as Kollidon~R~ CL of the BASF
company), polyvinyl alcohol, hydroxypropyl cellulose, ethyl
cellulose, gelatin, starch (derivatives), dextrins and dextrans,
such as, for example, a-, p- and y-cyclodextrin, dimethyl-/3-
cyclodextrin and 2-hydroxypropyl-p-cyclodextrin), sterols (such
as cholesterol) or bile acids (such as cholic acid or lithocholic
acid).
Here especially the polyvinylpyrrolidones, their copolymers
with vinyl acetate and highly dispersed silicon dioxide are
distinguished by a high crystallization-inhibitory potency.
4 2~.~OO~
Crystallization inhibitors can be used in all known
transdermal systems, such as, for example, in polyacrylate
systems or in systems based on silicon or synthetic rubber skin
contact adhesives, in which the inhibitor is incorporated in
concentrations of 0.1 to 40% by weight relative to the total
weight of the matrix. In addition to the skin contact adhesive,
active ingredient and crystallization inhibitor, the matrix can
optionally contain penetration enhancers, and all known
penetration enhancers and their mixtures are used in the usual
concentrations.
Suitable as penetration enhancers, for example, are:
monovalent and multivalent alcohols with up to 24 carbon atoms,
such as 1,2-propanediol, 1,3-propanediol, 1,2-ethanediol,
glycerol or lauryl alcohol; free carboxylic acids with up to 24
carbon atoms, such as lauric acid: fatty acid esters with up to
24 carbon atoms in the fatty acid component and up to 20 carbon
atoms in the monovalent or multivalent alcohol component, such as
isopropyl myristate, glycerol monopalmitate, dodecanoyl acetate;
terpenes, amides urea and mixtures of these penetration
enhancers.
The concentrations of the penetration enhancers or the
mixtures of the above-mentioned classes of substances can lie
between 0.5 and 40% by weight relative to the total weight of the
matrix.
Preferred conce:ltration ranges for 1,2-propanediol are 15-
25% by weight, for fatty acid esters, free carboxylic acids and
alcohol with 8-24 carbon atoms 0.5-15% by weight, and enhanoer
~~.~(l~~~l~
mixtures, which are possible in mixing ratios of 1:10 to 10:1,
for example, for 1,2-propanediol and lauric acid, 5-40% by
weight, preferably 20-30% by weight, relative to the finished
matrix.
Active ingredients, which are suitable for the production of
transdermal systems according to the invention, are preferably
those that are poorly soluble or insoluble in usual adhesive
systems and crystallize well, such as, for example, steroid
hormones, such as: gestagenically effective steroid hormones,
such as, for example, 13-ethyl-17~-hydroxy-18,19-dinor-17a-pregn-
4-en-20y1-one (=levonorgestrel), 13-ethyl-17/3-hydroxy-18,19-
dirior-17a-pregna-4,15-dien-20yn-3-one (=gestodene), 13-ethyl-17~-
hydroxy-11-methylene-18,19-dinor-17a-pregn-4-en-2oyn
(=desorgestrel) or 13-ethyl-11-methylene-178°hydroxy-18,19-dinor-
17a-pregn-4-en-3-one (3-keto-desogestrel).
Estrogenically effective steroid hormones, 3-hydroxy-1,3,5-
(10)-estratrien-17-one (=estrone), 1,3,5(10)-estratriene-3,17/3-
diol (=estradiol) or 1,9-nor-17a-pregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20yn-
~3,17~-diol (=ethinylestradiol), 17~-hydroxy-19-nor-17a-pregn-4en-
20yn-3-one (=norethisterone acetate), 14a,17a-ethano-1,3,5(10)-
estratriene-3,17p-diol (=cyclodiol) and l4a,l7a-ethano-1,3,5(10)-
estratriene-3,16a,17~-triol (=cyclotriol) and combinations of
these gestagens and estrogens.
Androgenically effective steroid hormones, such as 17p-
hydroxy-4-androsten-3-one (=testosterone) and its esters or 17a-
hydroxy-1a-methyl-5a-androsten-3-one (=mesterolone).
~~.~~~fi.~
Antiandrogenically active steroid hormones, such as 17a-
acetoxy-6-chloro-1/3,2~3-dihydro-3H-cyclopropa[1,2]-pregna-1,4,6-
triene-3,20-dione (=cypoterone acetate).
Corticoids, such as 11~,17a,21-trihydroxy-4-pregnene-3,20-
dione (=hydrocortisone), 11~,17a,21-trihydroxy-1,4-pregnadiene-
3,20-dione (=prednisolone), 11~,17a,21-trihydroxy-6a-methyl-1,4-
pregnatriene-3,20-dione (=methylprednisolone) and 6a-fluoro-
11~,21-dihydroxy-16a-methyl-1,_4-pregnadiene-3,20-dione
(=diflucortolone) and their esters.
suitable active ingredients are further: ;
Ergoline derivatives, such as lisuride, [=3-(9,10-didehydro-
6-methyl-8a-ergolinyl)-1,1-diethylurea], bromolisuride [=3-(2- .
bromo-9,10-dehydro-6-methyl-8a-ergolinyl-1,1-diethylurea],.
terguride [=3-(6-methyl-8a-ergolinyl-1,1-diethylurea] and
proterguride [=3-(6-propyl-8a-ergolinyl)-1,1-diethylurea].
Antihypertensive agents, such as 7a-acetylthio-17a-hydroxy-
3-oxo-4-pregnene-21-carboxylic acid-y-lactone (=spironolactone)
and 7a-acetylthio-158,163-methylene-3-oxo-17a-pregna-1,4-diene-
21,17-carbolactone (=mespirenone).
Anticoagulants, such as 5-(hexahydro-5-hydroxy-4-(3-hydroxy-
4-methyl-1-octen-6-ynyl)-2(1H)-pentalenylidene)]-pentanoic acid
(=iloprost) or (Z)-7-[(1R,2R,3R,5R)-5-chloro-3-hydroxy-2-[(E)-
(3R)-3-hydroxy-4,4-dimethyl-1-octenyl]-cyclopentyl]-5-heptenoic
acid (=nocloprost).
Psychopharmacological agents, such as 4-(3-cyclopentyloxy-4-
methoxy-phenyl-2-pyrrolidone (=rolipram) and 7-chloro-1,3-
dihydro-1-methyl-5-phenyl-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one (=diazepam).
Organic vitro compounds, such as isosorbide dinitrate
[=1,4,3,6-dianhydro-D-glucitol-dinitrate].
Beta blockers, such as propanolol {= 1-[(1-methylethyl)-
amino]-3-(1-naphthyloxy-2-propanolol), mepindolol {= 1-[(1-
methylethyl)-amino]-3-[(2-methyl-1H-inol-4-yl)-oxy]-2-propanol)
and carazolol {= 2-(9H-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-[(1-methethyl)-amino]-
2-propanol).
Carotenoids, such as a-carotene and ~-carotene.
~-carbolines are another group, such as 5-isopropyl-4-
methyl-~-carboline-3-carboxylic acid-ethyl ester and 5-isopropyl-
4-methoxymethyl-~-carboline-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester and
other ~-carbolines, which are described in European Patent
Applications 234,173 and 239,667. Also worth mentioning are
highly effective analgesics, such as, for example, 7,8-didehydro-
4,5-epoxy-17-methyl-morphinan-3,6-diol (=morphine), 4,5-epoxy-14-
hydroxy-3-methoxy-17-methyl-morphinan-6-one (=oxycodone), (-)-
(R)-6-(dimethylaminol-4,4-diphenyl-3-heptanone (=levomethadone)
or 3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-2,5-benzoxacin
~(=nefopam).
Finally, scopolamine can be mentioned as a suitable active
ingredient.
It is evident that the transdermal systems according to the
invention can also contain mixtures of these active ingredients.
The optimal concentration of active ingredient in the
transdermal therapeutic systems according to the invention is
dependent, of course, on the type of active ingredient, its
effectiveness, the type of penetration enhancers, the adhesive
2~20~~~
used, etc. and must be determined in the individual case by the
preliminary tests well-known to one skilled in galenicals. As a
rule, the active ingredient is dosed so that its concentration in
the finished matrix is 0.1 to 10% by weight relative to the
latter.
The transdermal therapeutic systems according to the
invention are preferably constituted so that they consist of a
top coating impermeable to the penetration enhancers and
optionally also to water, an active ingredient-containing
adhesive matrix adhering to the top coating, which contains a
crystallization inhibitor and a penetration enhancer, and a
removable protective layer.
This simplest form of a transdermal therapeutic system can
be produced so that a solution of the adhesive is mixed in a low-
boiling solvent with the active ingredient or active ingredient
mixture, the penetration enhancer and the crystallization
inhibitor, the mixture is applied filmlike on an impermeable
removable protective layer, the volatile solvent is removed by
heating and the product obtained is covered with a top coating.
Suitable solvents for dissolving the adhesive are, for
example, low-boiling alcohols, such as methanol, ethanol or
isopropanol, low-boiling ketones, such as acetone, low-boiling
hydrocarbons, such as hexane, or low-boiling esters, such as
ethyl acetate as well as their mixtures.
This process can be performed so that a solution or
suspension of the active ingredient, crystallization inhibitor,
penetration enhancers and adhesive in a volatile solvent is
g
applied to a removable protective layer and after the drying at
about 60°C to 90°C is provided with a plane, impermeable top
coating.
As removable protective layers, all films are suitable that
are usually used in transdermal therapeutic systems. Such films
are, for example, siliconized or fluoropolymer-coated.
As top coating, in this system, for example, 10 to 10o wm
thick films of PVC, PVDC or their copolymers EVA, polyethylene or
polyester as well as their coextrudates can be used alternatively
transparent, pigmented or metallized. The pharmaceutical agent
layer applied to this preferably has a thickness of 20 to 500 Vim.
The release of active ingredients preferably takes plane over an
area of 5 to 100 cm2.
It is obvious to one skilled in the art that the transdermal
therapeutic systems according to the invention can also be
configured significantly more complex than the already mentioned
simple matrix systems (Yie W. Chien: "Transdermal Controlled
Systemic Medications," Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York and Basel,
1987, Dr. Richard Baker: "Analysis of Transdermal Drug Delivery
Patents 1934 to 1984" and "Analysis of Recent Transdermal
Delivery Patents, 1984-1986~and Enhancers" Membrane Technology &
Research 1030 Hamilton Court Menlo Park CA 94025 (415) 328-2228).
But this generally should provide no significant advantages
whatsoever of the systems that justify the increased expezise for
their production.
The following embodiments are used for a more detailed
explanation of the invention:
I
CA 02120599 2002-04-29
Example 1
Transdermal therapeutic system with 17~-estradiol (3.3 mg/10 cm2)
3.00 g of 17Q-estradiol
35.00 g of 1,2-propanediol and
1.00 g of silicon dioxide, highly dispersed
TM
(e.g., Aerosil 200 of the Degussa AG,
Frankfurt/M, FRG)
are added in succession to 122 g of a 50% by weight solution of
TM
polyacrylate-skin contact adhesive Gelva 2723 (manufacturer:
Monsanto Chemical Company, Springfield, Massachusetts). The
forming cloudy mass is then rolled in a high-grade steel vessel
to keep a formation of bubbles low during the mixing.
The largely gas bubble-free mass is applied by a knife-over-
roll coating device on a siliconized polyester film (peeling-off
film: e.g., FDA-PET release liner) so that after the removal of
the volatile solvent (ethyl acetate) at 65-75°C over 2 to 3
minutes, a uniform film of 100 g/m2 develops. Then, it is
TM
laminated with a PVDC cover film (Saran 18L, 30 ~m of the Dow
Chemical company, Midland, MI, USA). The thus obtained laminate
is divided by a punching device into individual plasters of 2.5
cmz - 25 cm2, preferably 10 cmz of area, and packed in aluminized
bags. After removal of the protective film, the plasters adhere
to the skin and can be used for hormone substitution.
11
ExamQle 2
Transdermal therapeutic system with 17/3-estradiol (3.3 mg/10 cm2)
3.0o g of 178-estradiol
35.00 g of 1,2-propanediol and
1.00 g of cholesterol
are added in succession to 122 g of a 50% by weight solution of
polyacrylate-skin contact adhesive Gelva 2723 (manufacturer:
Monsanto Chemical Company, Springfield, Massachusetts).
The forming cloudy mass is then rolled in a high-grade steel
vessel to keep a formation of bubbles low during the mixing.
The largely gas bubble-free mass is applied by a knife-over-
roll coating device on a siliconized polyester film (peeling-off
film: e.g., FDA-PET release liner) so that after the removal of
the volatile solvent (ethyl acetate) at 65-75°C over 2 to 3
minutes, a uniform film of 100 g/m2 develops. Then, it is
laminated with a PVDC cover film (Saran 18L, 30 ~m of the Dow
Chemical company, Midland, MI, USA). The thus obtained laminate
is divided by a punching device into individual plasters of 2.5
~cm2 - 25 cmz, preferably 10 cm2 of area, and packed in aluminized
bags. After removal of the protective film, the plasters adhere
to the skin and can be used for hormone substitution.
12
Example 3
Transdermal therapeutic system with 17J~-estradiol
2.00 g of 170-estradiol
5.00 g of isopropyl myristate and
10.00 g of Kollidon~R~ VA 64
are dissolved in 20 g of isopropanol and added to 166 g of
Gelva~R~ 2723 (50% solution in ethyl acetate). The forming cloudy
mass is then rolled in a high-grade steel vessel to keep a
formation of bubbles low.
The production of the plasters takes place as described in
example 1.
13
Example 4
Transdermal therapeutic system with 176-estradiol
4.00 g of 17~°estradiol
12.00 g of Kollidon«~ 12 PF and
35.00 g of 1,2-propanediol
are dissolved in 20 g of isopropanol and added to 98 g of Gelva~R~
2723 (50% solution in ethyl acetate). The forming cloudy mass is
then rolled in a high°grade steel vessel to keep a formation of
bubbles low.
The production of the plasters takes place as described in
example 1.
14 2120~~19
Example 5
Transdermal therapeutic system with gestodene
2.00 g of gestodene
5.00 g of isopropyl myristate and
10.00 g of Kollidon~R' VA 64
are dissolved in 20 g of isopropanol and added to 166 g of
Gelva~R' 2723 (a0% solution in ethyl acetate). The forming cloudy
mass is then rolled in a high-grade steel vessel to keep,a
formation of bubbles low.
The production of the plasters takes place as described in
example 1.
15 2~205q9
Example 6
Transdermal therapeutic system with gestodene
4.00 g of gestodene
12.00 g of Kollidon~R~ 12 PF and
35.00 g of 1,2-propanediol
are dissolved in 20 g of isopropanol and added to 98 g of Gelva~Ra
2723 (50% solution in ethyl acetate). The forming cloudy mass is
then roiled in a high-grade steel vessel to keep a formation of
bubbles low.
The production of the plasters takes place as described in
example x.
16 212050
Example 7
Transdermal therapeutic system with levonorgestrel
2.00 g of levonorgestrel
5.00 g of isopropyl myristate and
10.00 g of Kollidon~R~ VA 64
are dissolved in 20 g of isopropanol and added to 166.g of
Gelva~R~ 2723 (50% solution in ethyl acetate). The forming cloudy
mass is then rolled in a high-grade steel vessel to keep a
formation of bubbles low.
The production of the plasters takes place as described in
example 1.