Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02124598 2002-11-22
APPARATUS FOR THE AUTOMATED APPLICATION OF SPACER MATERIAL
AND METHOD OF USING SAME
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
This invention relates to an apparatus and method for application of spacer
material to a substrate such as a glass substrate for the manufacture of
double-
glazed or insulated windows.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
At present, most double glazed windows are formed by manually applying a
length of spacer material about the peripheral edges of the glass. Various
types of
manual tools are known for this purpose in which the operator moves the foot
along
the sides and edges of a substrate while feeding a length of the strip or
spacer
material through or around the tool.
While very effective in applying strip or spacer material, manual operations
are labour-intensive and consequently, the operations tend to become
expensive.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
With the present invention, applicant has developed a method and apparatus
for automated application of spacer material to e.g. glass substrates. More
particularly, the method and apparatus of the present invention are intended
to
automatically apply spacer material to glass-lite assemblies including in-line
production.
In accordance with the present invention, according to one aspect thereof,
there is provided an apparatus for applying a length of spacer material to a
substrate having sides and ends comprising advancing means for advancing the
CA 02124598 2002-05-27
substrate laterally from a first position to a second position relative to an
applying
means; at least one applying means operatively spaced from the substrate for
applying spacer material to at least one side and one end of the substrate
including
means for placing a length of spacer material into juxtaposition with the
substrate
and means for partially cutting the spacer material at a corner position in
the length
of the spacer material; and means for reciprocally advancing the applying
means
transversely relative to the substrate.
In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the apparatus as defined
above includes means for rotating the applying means from a first direction to
a
second direction in which spacer material is to be applied to the substrate
during
lateral movement of the substrate.
In a still further preferred embodiment, the above apparatus includes means
for rotating the applying means to a third direction in which spacer material
is to be
applied to the substrate during reciprocal transverse movement relative to the
substrate.
In another embodiment, preferably the apparatus includes a second means
for applying an additional length of spacer material to one side of the
substrate, the
second means operating independently from the first means.
In a still further embodiment, the above apparatus includes advancing means
comprising at least one endless belt extending from an inlet end towards a
discharge end.
In a still further embodiment, the above apparatus includes advancing means
which comprise a pair of spaced-apart endless belts extending from an inlet
end of
the apparatus to a discharge end, means for advancing the belts in a time
related
sequence, means for mounting the applying means above at least one of the
belts to
suspend the applying means over a length of substrate to which the spacer
material
2
CA 02124598 2002-05-27
is to be applied, means for advancing the applying means between at least
first and
second spaced-apart positions where the spacer material is applied to the
substrate
during advancement.
In another preferred embodiment, the above apparatus includes the applying
means which comprise first applicator means, the applicator means including
means
for receiving a length of spacer material and for advancing the same from a
source
thereof to dispense a continuous length of the spacer material relative to the
substrate, means for effecting contact between the spacer material and the
substrate to thereby apply the spacer material to at least one length of the
substrate.
In a still further embodiment, the above apparatus includes means for
notching the spacer material to permit the '?pacer material to form a corner.
In a still further embodiment of the present invention, the apparatus includes
applying means which has second applicator means, the applicator means
including
means for receiving a length of spacer material and for advancing the same
from a
source thereof to dispense a continuous length of the spacer material relative
to the
substrate, means for effecting contact between the spacer material and the
substrate to thereby apply the spacer material to a length of the substrate.
In a still further embodiment of the present invention, the apparatus includes
a means for moving the second applicator means out of the way of the first
applicator means.
Still further, another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of
applying spacer material to a substrate, the method including the steps of
advancing
a substrate to a start position; receiving a length of spacer material in an
applying
means; discharging spacer onto the substrate surface at a start position;
advancing
the applying means and simultaneously applying spacer material to a first end
of the
substrate; cutting a discontinuity in the spacer material at the corner
location;
3
CA 02124598 2002-05-27
rotating the applying means forming a corner fold in the spacer material at
the cut;
advancing the substrate to a second position and simultaneously applying
spacer
material to a first side.
Still further, another aspect of the invention includes a travelling
applicator
head for applying adhesive spacer material to a substrate in a spacer
application
station in the production of insulated windows, comprising a traveller for
supporting
the applicator head at a distance from the substrate, a drive means for
selective
transverse reciprocating movement of the traveller and the applicator head, a
central housing rotatively supporting the applicator head on the traveller, a
lead
section comprising a pair of lead gripping members defining a first channel
therebetween a lag section comprising a pair of lag gripping members defining
a
second channel therebetween, at least one of the lag section and the lead
section
being mounted for pivotal movement relative to the other at the lead section
and the
lag section, defining in combination an application channel for positioning
the
spacer material on the substrate.
A still further aspect of the present invention includes an apparatus for
applying adhesive spacer material to a substrate, comprising a support means
for
supporting the substrate, a beam oriented transversely to the support means,
at
least one travelling applicator head for applying spacer material to the
substrate
supported on the beam spaced from the substrate, at least one feed reel for
supplying spacer material to the at least one travelling applicator head,
means for
advancing the at least one travelling applicator head relative to the
substrate,
wherein the at least one applicator head includes drive means for providing
reciprocal movement of the at least one applicator head on the beam, a central
housing secured to the drive means about which the at least one applicator
head is
rotatable, a lead section and a lag section mounted to the central housing and
defining an application channel for receiving the spacer material and applying
it to
the substrate, the lead and lag sections each comprising spaced-apart gripper
members, at least one of the lead and lag sections being mounted for pivotal
4
CA 02124598 2002-05-27
movement relative to the other of the sections.
The present invention has numerous advantages over manual or other types
of spacer element application to substrates. For example, the present
invention
provides an apparatus which can be adapted for in-line production, thus
eliminating
slow-downs and stockpiling of materials. Still further, the present invention
provides
an economical alternative to very complex apparatus which has been proposed
previously. Prior art proposals involve nurperous components which are movable
about the periphery of the glass substrate whereas in contrast, the present
invention
utilizes an apparatus which has a significantly reduced number of movements
and
consequently, is much simpler to construct and operate.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Having thus generally described the invention, reference will now be made to
the accompanying drawings illustrating preferred embodiments and in which
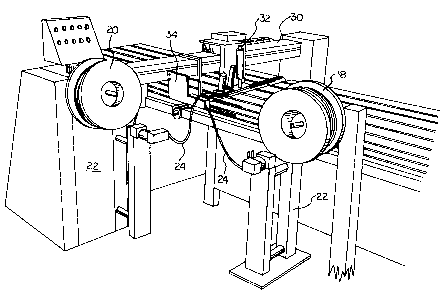
FIGURE 1 is a perspective view of an apparatus according to the present
invention which shows the advancing means for a glass lite production
line;
FIGURE 2 is a similar perspective view of the apparatus of Figure 1 showing
the sources of the spacer material;
FIGURE 3 is a perspective view of the discharge side of the apparatus with
the supporting means for the application means being shown which
extends transversely of the conveyor systems;
FIGURE 4 is an enlarged perspective view or close-up of the two applying
means showing the construction in greater detail;
CA 02124598 2002-05-27
FIGURE 5 is a close-up view of one of the applying means;
FIGURE 6 is a general perspective view from one end showing a first
applying means at one end of its travel and in a start position for
commencing the strip-applying operation;
FIGURE 7 is an enlarged view showing the first applying means and its
components including the drive system and notching means;
FIGURE 8 is an enlarged view showing the drive means in larger detail;
FIGURE 9 is an enlarged view of the portion of the first applying means after
it has travelled from a first position to a second position for application
of a spacer to a second side or length of the substrate;
FIGURE 10 is an enlarged view similar to Figure 9;
FIGURE 11 is an enlarged view showing a rack and pinion assembly with
piston assemblies attached to the racks which thus slide the racks to
rotate the gears which in turn rotate the first applying means;
FIGURE 12A is an enlarged view showing the supporting means for
maintaining a spacer strip out of contact with a substrate while it is
being fed to the first applying means and as well illustrates a portion of
the second applying component;
FIGURE 12B is an enlarged view of the second applying component of Figure
12A.
6
CA 02124598 2002-05-27
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
Referring now to the drawings, and in particular Figure 1, an example of an
apparatus according to the present invention is shown which includes a pair of
spaced-apart conveyors indicated generally by reference numerals 12 and 14
forming a conveying surface from an inlet end 10 to an outlet end 16 which
would
typically be encountered in a continuous production line. The conveyors 12 and
14
are in-line and meet at approximately the mid-point of the overall apparatus.
The
conveyors, of course, can be any suitable endless belt or other devices which
perform the same function. An edge member 26 provides an alignment guide.
The apparatus also includes, in the embodiment illustrated, a pair of supply
means 18 and 20 for supplying a length of spacer material. The supply means
are
roles of spacer material mounted for rotation about supporting stands 22, with
a lead
end of the spacer material being fed to the.apparatus (as described
hereinafter).
Thus, the two sources provide two separate lengths of spacer material 24, each
being a separate feed source for separate application means.
Referring to Figure 3, the apparatus includes an overhead support beam or
member 30 extending transversely of the conveyor belts and which is adapted to
mount at least one spacer material dispensing head or body, and preferably
both
dispenser heads, the latter being indicated by reference numerals 32 and 34
(Figure
3).
Referring to Figure 4, in the embodiment illustrated, one spacer dispensing
applying means 32 is preferably a device which applies spacer material to at
least
two and preferably three sides of a substrate. To that end, the applying means
is
mounted in a movable manner along the frame 30. Suitable means such as a rack
and pinion arrangement, the rack being indicated by reference numeral 36, and
a
pinion (not shown). Alternatively an endless belt can be used, driven on the
beam
7
CA 02124598 2002-05-27
30 and attached to the head 32. Movement is effected by suitable drive means
for
movement of the assembly transversely of the belts 36.
As also shown in Figure 4, the apparatus may include means for suspending
the strip applying material above a substrate as it is being fed to the
applying means
32. To this end, a pair of spaced-apart L-shaped brackets may be movably
journalled along the transverse assembly , the brackets being indicated by
reference
numerals 41 and 43. The bracket 43 is connected by a rod 45 to the frame
assembly of the applying means 32; the bracket 41 is likewise connected by a
rod
47 (and journalled through bracket 43) to connect to the same frame assembly
to
applying means 32. In this manner, the brackets 41 and 43 may be collapsed
together (see Figure 6) upon movement of the assembly 32 to its start
position.
Movement of the assembly 32 to the right (viewed from Figure 6) will result in
the
first bracket 43 being advanced and thereafter, in a spaced-apart manner,
bracket
41. As shown in Figure 4, the strip 24 is suspended on the lower arms of the
respective brackets 41 and 43 to be spaced above the substrate.
The applying means 32 includes a lower tape dispensing and feeding
component associated with it (see e.g. Figure 6 and enlarged view Figure 7 and
also
Figure 8), which as illustrated, includes a guide pulley 40 for guiding the
spacer
material 24 to turn the latter from its feeding direction to its application
direction. A
motor 42 is associated with the applying means 32 and operates a pair of drive
wheels 44 (only one being shown in Figure 7). Strip 24 passes from guide
roller 40
between the drive rollers 44 to effect movement of the strip. From between the
drive
rollers 44, the strip 24 is fed through the lower housing indicated generally
by
reference numeral 48 of the applying means 32 (a suitable channel being formed
by
appropriate frame members for that purpose); the strip 24 exits from the lower
housing through a gap in between adjacent frame members indicated generally by
reference numeral 50. Although a substrate is not illustrated in Figure 7, the
strip is
shown as it would have been applied to the surface of a substrate with the
assembly
32 moving from left to right as portrayed in Figure 7.
8
CA 02124598 2002-05-27
The assembly 32 may include suitable means such as a pressure roller within
the lower portion of the assembly to apply pressure to the strip as it is
dispensed
onto the substrate in order to have the strip 24 firmly engage the surface of
the
substrate. Depending on the type of strip materials the latter may be provided
with
suitable adhesive to thereby effect a bond between substrate and the strip.
As shown in Figures 6, 7 and 10, the assembly or applying means 32 has two
strip guiding and applying sections 46 and 47. These sections are conveniently
defined as the lag section and the lead section respectively. Each section is
mounted on the assembly 32, with hydraulic means 51 for raising and lowering
the
respective sections. In Figures 6 and 10 both sections are in a lowered
position,
and in Figure 7 the section 46, conveniently considered as the lag section, is
shown
raised.
Pressure devices, for example wheels 45 and 45a as indicated in dotted
outline in Figure 10, apply pressure to the strip. These wheels can be mounted
for
vertical movement towards and away from the strip.
In operation, to apply a length of strip material across a lite, both sections
are
down and the strip applied. At the corner, it is desired to rotate the
assembly 32 and
move the lite for application of a strip of material along a side edge. For
this to
occur, the section 46 is raised to be above the length of strip material
already
applied. That is, the section 46 must be raised clear of the strip. Rotation
of the
assembly 32 can then occur. Once the assembly 32 has rotated and the lite
starts
to move, the section 46 is lowered to assist in applying the strip material.
Associated with the applying means 32 is an optional notcher which can be
seen in greater detail in Figure 10. The notcher may have a punch portion
indicated
generally by reference numeral 60, actuated by a piston assembly 62. Thus, as
the
strip material is fed between the drive rollers 44, the apparatus (through
suitable
sensing means) senses the position of a corner and will notch the spacer
material
9
CA 02124598 2002-05-27
(by punching out a portion of the thickness of the material) to permit the
material to
form a "tight" corner bend (such as a 90° angle) when the assembly 32
is rotated
from a first side to a second side or end of~the glass panel.
Referring now to Figure 11, the mechanism for rotating the first applying
means 32 to permit it to apply a strip in the second direction is illustrated
in greater
detail. To that end, a rack and pinion arrangement may typically be used but
other
arrangements may equally be employed for that purpose. The applying means 32
at
its upper end journals a first gear 100 as well as a second gear 103 which
engage a
pair of racks 102 and 104 respectively. A piston assembly 106 (through
connecting
members 108) is effective to move rack 102. This rotates gear 100 and thus
rotates
applying means 32. Rotation of gear 100 also rotates gear 103, in engagement
with
rack 104 moving it laterally.
To reverse the movement, piston assembly 110, through brackets 112, is
effective to move rack 104 in the reverse direction with the rack 104 engaging
gear
103. This rotates the applying means 32 and also via gear 100 moves rack 102
back to the original position.
In operation, the two applying means or heads are initially positioned as
shown in Figure 6. A sheet of glass is delivered to the applying station by
virtue of
movement of one of the conveyors. Suitable sensing means, for example mounted
on applying means 32, will position the glass below the application station -
i.e. to
halt movement of the conveyor beneath the applying heads. Application head 32
will then be actuated to move transversely across the conveyor and apply a
first
length of spacer material along one side of the glass cite. Sensing means,
again for
example, mounted on the applying means 32, may be provided to detect the
corner
of the glass lite and thus halt advancement of the assembly 32 at an
appropriate
point. Actuation of the rotation means for the assembly to change the
direction of
the movement of the assembly 32 will then take place. Prior to changing the
direction of the head 32, the notching apparatus will be used to provide a
notch in
CA 02124598 2002-05-27
the length of sealant material at the point where the sealant material is to
be bent to
form a corner. The assembly 32 is thus in a position to apply the next side of
the
spacer material (see Figure 10).
At the same time the piston assembly of the other applying head 34 is then
actuated to lower the body into operative relationship with the glass lite.
The
conveyor systems are then actuated to advance the glass lite from one conveyor
over to the second conveyor and during the advancement, the spacer material is
then applied to both edges of the glass.
Thereafter, rotation of the applying head 32 is again effected to rotate the
same approximately e.g. 90°; the length of spacer material is further
notched to form
the corner. Thereafter, the applying body 32 is again moved back to its
initial
position (i.e. its home position) to thus complete application of spacer
material to all
four sides of the glass. If desired, at the initial and terminal points of
movement of
the applying means, the notcher may also be actuated to provide notches at the
lead
and terminal ends of the spacer material to accommodate the length of spacer
material laid down by the applying means 34. Still further, the applying means
34
may also be provided with a notcher as illustrated in Figure 12B; the notcher
being
actuated by piston assembly 214 and being constructed in a similar manner to
that
described with reference to the previous Figures.
Each of the applying means 32 and 34 may be provided with appropriate
severing means to sever the spacer material at the end of the operation. For
example, as shown in Figure 12B a piston assembly 216 may be connected to a
vertically aligned knife to sever the spacer material at a desired length.
Referring now to Figures 12A and 12B, the second applying means 34
includes a general frame assembly 200 mounting guiding means 202 for guiding a
length of strip material into guide bodies 210m 211 of the assembly 34. Bodies
210,
211 include one or more pressure rollers, shown dotted in Figure 12B at 212,
for
11
CA 02124598 2002-05-27
placing the strip material into engagement with a substrate surface. Rollers
212 can
be movable vertically.
To move assembly 34 out of the path of assembly 32, when required, a piston
assembly 206 is provided which is intended to engage with the lower body
portion to
raise the same. Suitable means may be provided for a time-actuated sequence
(such as through use of a sensor) to raise and lower the assembly 34 as
required.
Since assembly 34 is actuated when the conveyors are actuated for
movement of a substrate thereon, no drive means are required. Also, in the
embodiment illustrated, assembly 34 is only utilized for the application of
one length
of sealing material along the axis of travel of the substrate; it will be
understood that
assembly 34 may be constructed similar to assembly 32 so that assembly 34 may
provide a sealing member along two sides if desired. In the latter case,
assembly 32
would only apply sealing material along two sides.
It will be understood that various modifications can be made to the above-
described embodiments without departing from the spirit and scope of the
invention
and the preferred embodiments described.
12