Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
WO 93/21668 PCT/GB93/00481
- 1 -
COIL CONSTRUCTION
TECHNICAL FIELD
This invention relates to a bifilar coil construction.
BACKGROUND ART
British patents GB 1520030 and GB 1600987 describe
signal separating devices which act to isolate the d.c.
power supply circuit for the heating element of an
electrically heated motor vehicle window from the antenna
circuit of a radio receiver or transmitter connected to the
heating element, so that the heating element can be used
simultaneously for heating purposes and as a radio
transmitting or receiving antenna.
The described devices use a bifilar coil for signal
separation purposes. The two windings of the coil are
connected respectively between opposite ends of the heating
element and positive and negative terminals of the d.c.
power supply circuit, whereby the coil can present a high
blocking impedance to radio signals with a low resistance
for d.c. currents. Signal separation can therefore be
effected in a particularly convenient and efficient manner.
Conventionally, bifilar coils are manufactured by
machine-winding two side-by-side wires together around a
former. This results in two windings which are wound in a
common direction, which have a common diameter and axial
length, and the turns of which lie axially next to each
other. For signal separation purposes as mentioned above,
~
. P~~,~~ ~9 3 l 0 0 ~ ~ ~
a L ty l P~,~ ~~
'~~74 7
- 2 -
the windings are enclosed within a pot core structure
(ferrous ceramic structure) with ends of the windings
projecting axially downwardly through openings in the
structure for connection purposes.
Present trends are towards the use of higher current
consumption motor vehicle window heating elements, say 30
amps or more, and there is therefore a requirement for
bifilar coils with thicker gauge windings. However, with
the abovementioned conventional construction, thicker
gauge windings result in increased axial bulk which is
undesirable. An axially compact construction is
desirable to permit easy mounting at a required position
close to the motor vehicle window so as to minimise
tuning problems due to lead inductance and capacitance.
Also, with the conventional construction, the projecting
connection ends of the windings follow a curved or bent
path where they feed into the adjacent end turns and, in
the case of axially side-by-side thicker gauge wires this
adds considerably to the axial bulk and also can be
difficult to achieve or control with conventional winding
equipment.
An object of the present invention is to provide a
signal separating device having a doublewound coil
construction which can be easily and conveniently
manufactured, and with which axial bulk can be
minimised, even with thicker gauge wires.
~...___. ~~_.._ ._...-.-..
~ ~ ., _ . . .<.r_, f~ ~ ..- ..J~1
CA 02133747 2002-02-15
-3-
DISCLOSURE OF THE INVENTION
In accordance with one aspect of the present invention there is
provided a signal separating device for use with a window heating element of
a motor vehicle, the device having a first pair of terminals for connection to
the
heating element, a second pair of terminals for connection to a d.c. power
supply for the heating element, and an antenna terminal for connection to
radio transmitting and/or receiving apparatus. The separating device includes
a double-wound coil having first and second separate and generally cylindrical
coil windings wound in the same direction and formed and disposed such that
the first coil winding closely fits within the second coil winding with the
turns of
the first winding being radially inward of the turns of the second winding.
The
windings have the same number of turns as one another and the heating
element is connected in series between the windings.
According to a second aspect of the invention there is provided a signal
separating device for use with a window heating element of a motor vehicle,
the device having a first pair of terminals for connection to the heating
element, a second pair of terminals for connection to a d.c. power supply for
the heating element, and an antenna terminal for connection to radio
transmitting and/or receiving apparatus. The separating device includes a
double wound coil having first and second separate coil windings, in which the
double wound coil and its first and second coil windings are formed as spiral
or helical coils formed and disposed such that they are disposed axially one
on top of the other, the coils being of common diameter and the windings
having the same number of turns as one another. The heating element is
connected in series between the windings.
CA 02133747 2002-02-15
-4-
The signal separating device may include other components as
appropriate for example including capacitors, diodes, chokes, matching
circuitry for matching the heating element to the antenna circuit of the radio
apparatus, and tuning circuitry to give efficient operation at different
frequency
bands (am, vhf).
A method of manufacturing the signal separating device of the
first aspect of the invention may include forming the first winding as a
generally cylindrical coil from wire having a transverse dimension of
greater than 2mm, forming the second winding as a separate generally
cylindrical coil from the same wire having an Internal diameter greater
than the external diameter of the coil of the first winding, fitting the
~~ 93~o04s~r
~~~7 z~ s~~Y t~~'
- 4a -
first winding within the second winding and placing the
double wound coil so formed within a 30mm pot core having
inner and outer parts respectively with and around the coil
structure whereby a current carrying capability of between
25 to 35 amps is possible in said windings.
Preferably the said internal and external diameters
are closely similar so that the outer surface of the first
winding contacts or is in close proximity to the inner
s~s.~,-.r~~t~r~ P~~,r"~tt Off~_.~ ,fit ~~~ ; ~"~':_.~T ~ ~'t,-'~'
Unitec'
M ~:. _ ~.
PCT ': ~__ __:. '."w: ~='-' _ ___ ,
WO 93/21668 PCT/GB93/00481
- 5 -
surface of the second winding for maximum space saving.
With this method, the windings can be formed easily and
conveniently, even with thicker gauge wire, especially
because the ends of the windings are fed into the adjacent
end turns as single wires whereby bends or curves between
the ends and the turns can be readily accommodated. Since
the winding turns are radially spaced the axial bulk can be
kept to a minimum, and the fact that the said bends or
curves of the ends occur in single, rather than twin wires
can also assist in this respect.
With inner and outer windings, the overall coil
structure is of generally cylindrical form and it is
possible (and preferred) to use a conventional core having
inner and outer cylindrical parts, respectively within and
around the coil structure, joined by integral end plates.
The core may be a pot core and may be formed in two sections
which are clamped together by an axially extending clamping
device such as a nut and bolt. Appropriate slots may be
provided for the connection ends.
In one embodiment each winding has final top and bottom
turns which terminate in respective bent ends with straight
terminal end portions which project alongside the coil in
the axial direction of the coil. Preferably, the bottom
said terminal end portion projects downwardly freely away
from the coil, and the top said terminal end portion
projects downwardly freely from the coil alongside and
PC1/6B 9 3 / 0 0 4 8 ~~
2 0 .IUIY 1994'
- 6 -
spaced from the outer surface thereof. Preferably also,
the terminal end portions are spaced circumferentially from
each other.
In a particularly preferred embodiment, at least one
of the top and bottom bent ends is stepped sideways so that
the top terminal end portions of the two windings are
spaced apart from each other, as also are the bottom
terminal end portions.
The core may have top and bottom radially extending
slots through which the top bent ends and the bottom bent
ends respectively project.
United s'. ~_ ~,...~ n ,"._, nif;.,., , ; _
PCT i : ~. : ~ ;
p6! ~ ~ f .-, r - ,
_ _~ -. v] n~ aj '. i ~_ ,
:~ ~ ~k ~ ~: ,; ,. _ _
:, ~,
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The invention will now be described further by way
of example only and with reference to the accompanying
drawings in which:
Fig. 1 is a simplified diagram of one form of a
signal separating device including a bifilar coil
construction according to one embodiment of the
invention;
Fig. 2 is a sectional view through the bifilar coil
construction on the line A-A of Fig. 4;
Figs. 3 and 4 are views from below and above of the
construction of Fig. 2;
Fig. 5 is a side view of the outer winding of the
coil construction.
Figs. 6 and 7 are views from above and below of the
two windings of the coil construction; and
Fig. 8 is a sectional view on the line B-B of Fig.
6.
BEST MODE OF CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
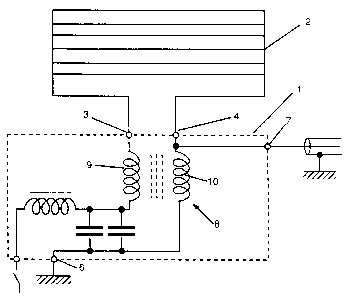
The signal separating device shown is for use with a
~~'n'I i:itv:.'::.i;;~. . , . ' ' ~ ~~~..%~~wi ~ i1 ~ ~lT~ SHEET
___.__.... __.
WO 93/21668 PGT/GB93/00481
_ g _
conventional heated rear window of a motor car to enable
this to be used as a receiving antenna for a car radio.
The device comprises a housed circuit 1 which is fixed
close to the heated window 2 e.g. beneath the rear parcel
shelf or within the roof lining.
The housed circuit 1 has five terminals, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7,
two of which 3, 4 are connected to the heating element 2 of
the window, another two of which 5, 6 are connected to d.c.
positive and earth of the car d.c. power supply via the
usual dash board switch, and the other of which 7 is
connected by a shielded cable to the car radio antenna input
circuit.
The housed circuit 1 includes a bifilar coil 8 having
two windings 9, 10 of common direction or hand which are
interposed respectively between d.c. positive and earth and
the two ends of the heating element 2.
The antenna terminal 7 is linked to the heating element
2 between the heating element 2 and the bifilar coil
construction 8. Other components for matching, tuning,
assistance in isolation, balancing of the signals at the
ends of the heating element etc. may be incorporated but are
not all shown here.
The bifilar coil construction comprises two separate
windings 9 , 10 each of say 5 turns of a thick gauge copper
wire capable of carrying said 30 amps without overheating
and without significant voltage loss due to resistance.
WO 93/21668 PGT/GB93/00481
- 9 -
Each winding coil 9, 10 has a bottom turn which
terminates in a downwardly bent end 11, 12 projecting freely
away from the coil parallel to its axis. Each coil also has
a top turn which terminates in a downwardly bent end 13, 14
projecting freely from the coil alongside and spaced from
the outersurface of the coil parallel to its axis.
The inner coil 9 has an outer diameter which is very
slightly smaller than the inner diameter of the outer coil
10. The end 11 of the inner coil is bent directly
downwardly whereas the ends 13, 12, 14 of the inner and
outer coil are stepped to one side before being bent
downwardly.
The inner coil 9 is fitted within the outer coil 10 so
that they are closely in contact with each other. The
bottom projecting ends 11, 12 are alongside each other but
are spaced apart due to the above mentioned stepping. A
similar arrangement applies to the top projecting ends 13,
14.
Due to the fact that the end 11 is bent directly
downwards whereas the other ends 12-14 are stepped as
described, it will be understood that the coil 9 can be
quickly and easily inserted into the coil 10 after winding
without any further bending or forming of the ends 11-14.
The coils so far described can be readily formed with a
conventional winding machine since it is a single wire which
is being wound. In particular, the ends 11, 12, 13, 14 can
WO 93/21668 PCT/GB93/00481
- to -
be readily bent and fed in to (or fed out of) the associated
end turn in a particularly simple and accurate manner, and
without requiring undue axial distortion or displacement of
the end turn, even with the thick gauge wire.
The resulting coil construction 8 has reduced axial bulk
due to the radial spacing of the turns of the two windings
9, 10 and due to the above mentioned reduced displacement of
the end turns.
The coil construction 8 is accurately shaped and
configured and so it can be easily assembled with a
conventional pot core, as shown in the drawing.
The pot core is formed in two halves 15, 16 each
consisting of an inner hollow cylinder, 17, an outer hollow
cylinder 18 and an end plate 19. These cylinders 17, 18 and
the end plate 19 are formed integrally in one piece from a
ferrous ceramic structure.
There is a gap in the outer cylinder 18 and the end
plate 19 forming a radial slot 20, and there is a central
hole 21 in the end plate 19.
The core halves 15, 16 are assembled top and bottom
around the coil construction with the radial slots 20 offset
to receive the projecting ends 1l, 12, 13, 14. The halves
15, 16 are clamped in position tightly in contact with each
other with a bolt 22 passed through the holes 21 and the
inner cylinders 17 and engaging a nut 23.
It is of course to be understood that the invention is
WO 93/21668 PCT/GB93/00481
- 11 -
not intended to be restricted to the details of the above
embodiment which are described by way of example only.
10
20