Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02196227 1999-07-OS -
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
2196227
Traditional truck mounted V-shaped Highway maintenance spreaders consisting of
a V-
shaped box mounted directly over a conveyor system are gradually being
replaced by a more
flexible, versatile type of truck mounted spreader body.
Traditional application of the Highway maintenance truck is generally subject
to the following
equipment mounting cycle. In the fall, the conventional dump body intended to
haul bulk
material is being replaced by a V-type spreader box for aggregate and/or
deicing material.
1o After its seasonal winter use, this V-type hopper spreader is removed again
in the spring.
Although becoming increasingly more popular because of their better
flexibility of application,
the new type of combination dump body spreader is still subject to several
restrictions based on
operational and increased maintenance problems.
The combination dump body spreaders currently available on the market today
are provided
with a conveyor reloading mechanism that is operated by generally 2 or more
hydraulic
cylinders that are of identical construction, either nested vertically in the
front and rear corner
post of the body side opposite the longitudinal conveyor or submounted under
the body
understructure.
The hydraulic fluid supplied to these hydraulic cylinders is pumped towards
each cylinder
through a flow divider valve intended to share the flow evenly and equally
into each hydraulic
cylinder.
Due to uneven load, pressure conditions, design or wear condition, most flow
dividers do not
precisely share the flow of hydraulic fluid to the cylinders actuating the
raising and lowering
of the conveyor reloading mechanism, resulting in uneven, jerky operation of
the conveyor
reloading mechanism. This resulting uneven operation of the conveyor reloading
mechanism
will make it jam and wedge causing structural damage to the unit and involve
costly repairs.
2
CA 02196227 1999-07-08
219622T,
Combination dump body spreaders currently available on the market today are
known to have
a heavy tare weight when used as a conventional dump body unit. Further they
are provided
with a conveyor reloading mechanism, where the pivotally connecting axis
(hinge shaft) is
continuous along most of the entire length of the pivotal connection making
the hinge shaft
very difficult to remove and re-install in case the user wishes to replace the
conveyor
reloading mechanism for servicing or to achieve a seasonal lighter tare weight
when the unit
needs only to be use as a conventional dump body spreader.
Combination dump body spreaders currently available on the market today are
provided with
1o a conveyor drive assembly consisting of the gear reducer, hydraulic motor,
main drive shaft,
drive sprockets and flange bearings that cannot be removed from the
combination dump body
spreader without having to damage it seriously because the conveyor drive
components are
frozen by corrosion on the main drive shaft.
Combination dump body spreaders currently available on the market today do not
provide
any way to segregate and crush coarse aggregate coming out of the conveyor
system which
adversely affect the spreading projection pattern of the aggregate being
dumped on the
rotating spreading disc, thus increasing the amount of de-icing agent required
to maintain the
road surface.
Combination dump body spreaders currently available on the market today are
provided with
a conveyor system making use of a conveyor chain consisting of transverse pin
connected
links very subject to premature wear and freezing due to the corrosive action
of snow and ice
melting agent mostly hauled with these types of unit.
A combination dump body spreader having at least one longitudinal conveyor
located along
one of its body side being fed by an adjacent pivotally connected conveyor
reloading
mechanism generally operated by two or more hydraulic cylinders should be
designed to
include the following features.
3
CA 02196227 1999-07-OS . 2 1 g 6 2 2 7
There are a number of features that are important in the design of a
combination dump body
spreader:
~ A desirable feature is that the displacement extension and retraction
strokes of each
cylinder ram are precisely kept equal at every stage of the extension or
retraction cycling
of the cylinder ram.
~ Another desirable feature is that the amount of hydraulic fluid being fed to
each of the
hydraulic cylinders causing the raising and the lowering of the conveyor
reloading
mechanism is precisely calibrated on both raising and lowering cycle.
~ A desired feature is that, the pivotally connected conveyor reloading
mechanism must at all
time operate evenly, regardless of the load distribution being moved towards
its adjacent
conveyor, that is the hydraulic cylinder components actuating the raising and
lowering of
the reloading mechanism must at all time work in phase.
~ Another desirable feature is to achieve the above with the least amount of
hydraulic
components in order to minimize future maintenance.
~ Another desirable feature is that the conveyor reloading mechanism should be
easily
dismountable from the combination dump body spreader for servicing.
~ Another desirable feature is that the conveyor reloading mechanism should be
easily
dismountable from the combination dump body spreader for replacement by a
lighter type
one when the overall tare weight of the unit becomes critical.
~ A further desirable feature is that the entire conveyor drive system is
removable as a
complete assembly from the combination dump body spreader unit in the least
amount of
time without damaging any components.
~ It is further desirable that the size of the granular material coming out of
the longitudinal
conveyor is evenly controlled to achieve a more effective spreading operation
and optimize
the action of the snow and ice melting agents on the road surface.
~ It is further desirable that the combination dump body spreader is provided
with a
conveyor system on which the conveyor chain provides a longer life with the
least amount
of lubrication maintenance.
4
CA 02196227 1999-07-08
21 9 6227_
~ It is further desirable that the combination dump body spreader is provided
with a
conveyor system on which the conveyor chain will not freeze under the
corrosive action
of snow and ice melting agent.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The invention is directed to an improved construction of the combination dump
body
spreader having at least one longitudinal conveyor located along one of its
body side being
fed by a conveyor reloading mechanism provided with a specially braced "L-
shaped" vertical
structure pivotally connected along side of it and generally operated by two
differential
displacement hydraulic cylinders. The conveyor drive system located at one end
of the
combination dump body spreader longitudinal conveyor features a slotted
mounting to the
conveyor structure, a coarse aggregate crusher to regulate material flow at
the spreader
conveyor discharge. The longitudinal conveyor chain is made with an elongated
open link
chain. The improvements to the conveyor system are thoroughly adaptable to the
traditional
hopper type spreader.
One of the aim of the present invention is to provide a combination dump body
spreader with
a conveyor reloading mechanism operated by two hydraulic cylinders constructed
in such a
2o manner so that in the extension mode the volumetric displacement of oil
entering the lower
chamber of the first cylinder will cause the ram displacement length of the
first cylinder along
with the volumetric displacement of the hydraulic fluid located in the first
cylinder upper
chamber, to be pushed in the second cylinder lower chamber. The second
cylinder volumetric
displacement being dimensioned so that the amount of hydraulic fluid coming
from the first
cylinder upper chamber will cause the ram of the second cylinder to move the
same exact
displacement length as the first cylinder ram for a given amount of hydraulic
fluid fed in the
lower chamber of the first cylinder.
In the retracting mode, the hydraulic fluid enters the upper chamber of the
second cylinder
3o causing the piston of the second cylinder to push the hydraulic fluid back
into the upper
5
CA 02196227 1999-07-OS
21 9 6227_
chamber of the first cylinder causing the ram of the first cylinder to move
the same exact
displacement length as the ram of the second cylinder.
To further assist the stabilizing effect of the differential displacement
hydraulic cylinders,
two or more diagonal cross braces are adapted to the vertical structural
elements of the
conveyor reloading mechanism assembly to increase its tortional rigidity.
Another aim of this invention is that the conveyor reloading mechanism of the
combination
dump body spreader is operated by a multiple cylinder arrangement where the
total force and
1o displacement developed by each of the individual cylinder elements is
generated by the
hydraulic flow and pressure applied to one of the cylinder.
The invention provides a way to eliminate the use of hydraulic fluid divider
commonly used
to control the cylinder displacements of the conveyor reloading mechanism on
combination
dump body spreaders.
A further aim of the invention is to provide a new and improved modular
matching section
pivotal connections for the conveyor reloading mechanism to the combination
dump body
spreader structure where the two hinge sections can be disassembled and
reassembled
2o together through a mechanical fit that does not require the removal of the
hinge shaft from
the hinge tube assembly but instead the removal and replacement of two very
common bolts
and lock nut. This aspect of the invention is of most importance to the
maintenance of the
unit.
Another aim of the invention is that the reloading mechanism with its floor,
front angle
bracing closure plate, and its specially braced "L-shaped" vertical and
supporting structure
can be replaced by the proposed floor panel arrangement when the body is to be
used as a
conventional dump body. The proposed floor panel arrangement tare weight is
less than 40%
the weight of conventional conveyor reloading mechanism.
6
CA 02196227 1999-07-08
- ~ 21 9 62 27
The complete conveyor drive system including the gear reducer, the hydraulic
motor, the
main drive shaft, its supporting bearings and the two drive sprockets can be
pulled out upon
disconnection of the conveyor chain and taken apart from the combination dump
body
spreader as a complete unit in the minimum amount of time without damaging any
components.
The invention includes a rotating crusher agitator consisting of a cross shaft
supported by
two adjustable bearing. The cross shaft is provided with moving blades or
fingers. The
assembly can be either self propelled by the traction of the material coming
through the
conveyor discharge or assisted by the driving force of the conveyor.
An object of the invention is to provide a cross bar type conveyor system
where the cross
bars are clamped to elongated type pivotless oval shaped chain links which
apertures fits into
each of the drive sprockets tooth, similar sprockets are used as followers to
keep the chain
properly aligned. To further assist the tracking of the chain system and allow
proper scraping
effect to the conveyor cross bars the conveyor floor is provided with two
matching section
guideways. The round pivotless links offers very minimum contact area thus
remains
flexible under most corrosive conditions.
2o Other objects and advantages will appear in the following description.
A better understanding of the invention will be obtained from the following
detailed
description and the accompanying drawings of an illustrated application of the
invention.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
In the drawings:
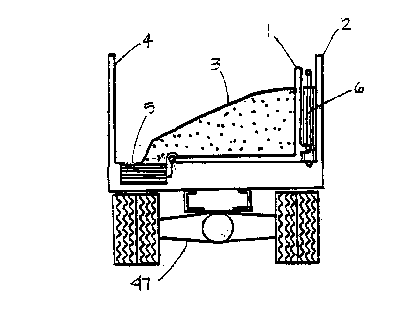
Figure 1: Shows a transversal end view of a truck (47) mounted combination
dump
body spreader (2) partially loaded with unevenly distributed material (3) with
its conveyor
3o reloading mechanism consisting of a specially braced "L-shaped" vertical
(1) and supporting
structure in the horizontal position, along with its conveyor reloading
cylinders (6) vertically
7
_. CA 02196227 1999-07-08 2 1 9 6 2 2 ~~
nested in the retracted position. The longitudinal conveyor (5) being mounted
along one of
the body side (4) and partially loaded with material (3).
Figure 2: Shows a transversal end view of a truck (47) mounted combination
dump
body spreader (2) partially loaded with unevenly distributed material (3) with
the conveyor
reloading mechanism consisting of a specially braced "L-shaped" vertical (1)
and supporting
structure in the raised position (50), with the vertical conveyor reloading
cylinders (6) in the
extended position (51). The longitudinal conveyor (5) being mounted along one
of the body
side (4) and completely loaded with material (3).
Figure 3: Shows an alternate transversal end view of truck (47) mounted
combination
dump body spreader (48) with its conveyor reloading mechanism consisting of a
specially
braced "L-shaped" vertical ( 1 ) and supporting structure in the horizontal
position, along with
its conveyor reloading cylinders (7) submounted under the body understructure
in the
retracted position. The longitudinal conveyor (5) being mounted along one of
the body side
(49) and partially loaded with material (3).
Figure 4: Displays the same unit (47) as figure 3, but with the conveyor
reloading
mechanism consisting of a specially braced "L-shaped" vertical (1) and
supporting structure
2o in the raised position (50) along with its conveyor reloading cylinders (7)
submounted under
the body understructure in the extended position (52). The longitudinal
conveyor (5) being
mounted along one of the body side (49) and completely loaded with material
(3).
Figure 5: Shows an isometric view of an easily dismountable conveyor reloading
mechanism (10) consisting of a specially braced "L-shaped" vertical and
supporting structure
from the combination dump body (53).
Figure 6: Shows an isometric view of the alternate floor panel arrangement
fitting to the
combination dump body spreader. (53)
;a~~,.
8
CA 02196227 1999-07-08
Fi ug re 7: Shows an assembled side view of the male (11) and open slot female
(12)
matching section pivotal connection used for connecting the conveyor reloading
mechanism
(10) of Fig. 5 consisting of a specially braced "L-shaped" vertical and
supporting structure to
the combination dump body structure.(53)
Figure 8: Shows a disassembled side view of each of the male (11) and open
slot
female (12) matching section pivotal connection used for connecting the
conveyor reloading
mechanism (10) of Fig. S consisting of a specially braced "L-shaped" vertical
and supporting
structure to the combination dump body spreader.(53)
to
Figure 9: Is an isometric view of the conveyor reloading mechanism (10)
consisting of
a specially braced "L-shaped" vertical and supporting structure fitted to the
combination
dump body spreader (53).
Figure 10: Shows an isometric view of a rotating crusher agitator (18)
consisting of a
cross shaft (42) mounted unit in the self propelled traction mode.
Fi urg a 11: Shows an isometric view of the conveyor extension structure.
2o Figure 12: Shows an isometric view of a rotating crusher agitator (16)
consisting of a
cross shaft (57) mounted unit operated by the driving force (59,56) of the
conveyor.
Fi urg a 13: Shows a side view of the crusher agitator (60) previously shown
in figures 10
and 12 in the normal operating mode.
Figure 14: Shows a side view of the crusher agitator (60) previously shown in
figures 10
and 12 in the full tripped mode.
Fi urg a 15: Outlines and shows the operating hydraulic schematic of the
conveyor
3o reloading mechanism consisting of a specially braced vertical and
supporting structure.
9
_ CA 02196227 1999-07-OS
2196227_
Figure 16: Shows an isometric view of the easily removable conveyor drive
mechanism
module (66) from the combination dump body spreader conveyor extension
structure (40,41)
shown in Fig. 11.
Figure 17: Shows an isometric view of cross bar (44) type conveyor system
consisting of
pivotless oval shaped links (21 ) driven through conveyor floor (70) provided
with special
recessed guideways.
DESCRIPTION OF ILLUSTRATED EMBODIMENTS
Refernng now to the drawings in detail wherein like numerals are using the
same or like
parts:
Fi ug re 1 illustrates an end view of a truck (47) on which is mounted a
combination dump
body spreader (2) consisting of a conveyor (5) reloading mechanism (1) mounted
opposite a
2o body side (4) with its vertically nested cylinders (6) in the retracted
mode partially loaded
with material (3).
Figure 2 shows same unit as in figure 1 with the conveyor (5) reloading
mechanism (1) in
the raised position (50) where vertically nested cylinders (6) are extended as
in (51).
Figure 3 illustrates an alternate end view of a truck (47) partially loaded
with material (3) on
which is mounted a combination dump body spreader (48) consisting of a
conveyor (5)
reloading mechanism (1) mounted opposite a body side (49) where the cylinders
(7) are
submounted under the body understructure and are in the retracted mode.
10
CA 02196227 1999-07-OS -
21 9 62 27;
Fi ure 4 displays same unit as in figure 3 with the conveyor (5) reloading
mechanism (1) in
the raised position (SO) where submounted to the body understructure.
Cylinders (7) are
extended as in (52).
Figure S shows in more details the fitting of the conveyor reloading mechanism
(10)
consisting of a specially braced " L-shaped" vertical and supporting structure
including its
front angle bracing closure plate (32), its diagonal set of bracing (8),
mounted in the vertical
wall of the conveyor reloading mechanism intended to improve the torsional
rigidity of the
conveyor reloading mechanism structure ( 10) along with the male adapter
consisting of the
1o male hinge tube (64) and hinge shaft (11) part of the pivotal connection.
F~ure 6 displays the alternate lighter floor panel (9) provided with the male
hinge tube (64),
the hinge shaft (11) and bolts (13) part of the pivotal connection shown in
figures 7 and 8
assembled to the side mounted female clevis bracket (12) part of combination
dump body
structure (53). Floor panel (9) can be further fastened to body side part of
(53) by fasteners
(65) for seasonal combination dump body usage.
Figures 7 and 8 illustrate the pivotal connection in the assembled Fig.7 and
disassembled
Fig.B mode. The pivotal connection consisting of the male adapter hinge tube
(64) part of the
conveyor reloading mechanism (10) of Fig.6 along with its hinge shaft (11) can
be
assembled as in Fig.7 or disassembled as in Fig.8 from a pair of side mounted
female clevis
brackets (12) by removing bolts and lock nut (13).
The pair of side mounted female clevis brackets (12) are fastened to
combination dump body
structure (53) of Fig.6. The number of modular matching section pivotal
connections may
vary with the length of the combination dump body spreader unit.
Fi urg a 9: displays conveyor reloading mechanism ( 10) pivotally connected to
the
combination dump body spreader structure (53) dumping material (3) on
longitudinal
3o conveyor (5).
11
CA 02196227 1999-07-OS
21 9 62 27.
As best seen in figure 10 the conveyor extension structure (40,41) is shown
with a self
propelled spring loaded crusher agitator ( 18) which may take the form and be
mounted as
illustrated and consisting of cross shaft (42) provided with continuous
angular distributed
blades (18) or fingers (16) as in Fig. 12, connected to tension levers (54)
and tension springs
(55) operating through safety trip slot arrangements (68).
Fieure 11 displays the conveyor extension assembly shown in either figures
10,12,13,14,16
further mounted and adapted to combination dump body spreader structure (53).
to Fi urg a 12: the conveyor extension structure (40,41) is shown with a
traction driven version
of the proposed crusher agitator (16) which may take the form, be mounted as
illustrated and
consisting of cross shaft (57) equipped with angular distributed fingers (16)
or blades (18) as
in Fig.lO connected to tension levers (54) and tension springs (55) operating
through slots
arrangement (68). Cross sham (57) is further driven by friction wheels (56)
and (59),
mounted on conveyor driven shaft (35) part of the conveyor drive connection
(33).
Fi ug-re 13 best illustrates either Fig. 10 self propelled spring loaded
crusher agitator or Fig.
12 traction driven crusher agitator safety slotted trip mechanism (60) at work
in the normal
not tripped mode thus achieving normal breakaway of material (14) from bulk
material (17).
2o The above mechanism being mounted in the conveyor extension structure shown
in Fig. 11.
Figure 14 shows either Fig.lO self propelled crusher agitator or Fig.l2
traction driven
crusher agitator safety slotted trip mechanism (60) at work in the full
tripped mode thus
allowing extra clearance for extra hard to break material ( 14) coming through
bulk material
(17). The above mechanism being alternatively mounted in the conveyor
extension structure
shown in Fig. 11.
Fi re 1 illustrates a hydraulic schematic where the hydraulic fluid (63) in
reservoir (69) is
pumped as in (61) through line (23) in the lower chamber (29) of cylinder
(19). The pumping
3o pressure generated by (61) will cause the cylinder piston and ram (24) to
extend and displace
captured hydraulic fluid (63) from cylinder (19) upper chamber (25) through
line (26) to
12
CA 02196227 1999-07-08 -
21 9 62 27
cylinder (20) lower chamber (27), thus causing cylinder (20) piston and ram
(28) to extend
and exit hydraulic fluid (63) through line (30).
For a given volumetric capacity of cylinder (19) upper chamber (25) the
volumetric
displacement capacity of cylinder (20) lower chamber (27) can be determined in
terms of
bore versus stroke extension along with the volumetric displacement capacity
of cylinder
(19) upper chamber (25) in term of piston and ram (24) diameter dimension
versus stroke
extension so that an incremental volumetric displacement of hydraulic fluid
(63) in chamber
(29) of cylinder (19) will cause cylinder (19) ram (24) to extend the very
same stroke as
to cylinder (20) ram (28).
In the retracting mode the hydraulic fluid (63) in reservoir (69) is pumped as
in (61) through
line (30) in the upper chamber (31) of cylinder (20). The pumping pressure
generated by (61)
will cause the cylinder piston and ram (28) to retract and displace captured
hydraulic fluid
(63) from cylinder (20) lower chamber (27) through line (26) to cylinder (19)
upper chamber
(25), thus causing cylinder (19) piston and ram (24) to retract and exit
hydraulic fluid (63)
through line (23). For a given volumetric capacity of cylinder (20) lower
chamber (27), the
volumetric displacement capacity of cylinder (19) upper chamber (25) can be
determined in
terms of bore versus stroke retraction along with the volumetric displacement
capacity of
cylinder (20) lower chamber (27) in term of piston and ram (28) diameter
dimension versus
stroke retraction so that an incremental volumetric displacement of hydraulic
fluid (63) in
chamber (31) will cause cylinder (20) ram (28) to retract the very same stroke
as cylinder
(19) ram (24).
Fi re 16 illustrate the conveyor drive mechanism module (66) consisting of the
gear
reducer (33), the hydraulic motor (34), the main drive shaft (35), its
supporting bearing (36),
drive sprockets (37) that can be disassembled from the conveyor extension side
plates (40)
and (41) by removing fasteners (38) and (39) and sliding down conveyor drive
system (66)
through slots (67) made in the conveyor extension structure.
13
CA 02196227 1999-07-OS
21 9 62 27
Figure 17 illustrates elongated type oval shaped conveyor chain (21) onto
which are clamped
with "U" shaped fasteners (22) cross bars (44) both drive and driven sprockets
(45) and (46)
operating in matching section shaped conveyor floor guideways (70).
While preferred embodiments of the present invention have been shown and
described,
various modifications and substitutions may be made thereto without departing
from the
spirit and scope of the invention. Accordingly it is to be understood that the
present
invention is not limited to the disclosed embodiments.
14