Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02227566 1998-O1-20
Infeed Chute
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Field of the Invention
This invention relates to a chip distribution device, and more particularly,
to a
distribution device for uniformly feeding wood chips onto a wood chip sorter,
for use,
as an a:xample, in making pulp for paper production.
Background Art
Wood fiber is the basic ingredient used for paper production. More than half
the fiber for paper manufacture comes from trees that are cut specifically for
the
production of pulp. These trees are cut into logs that are reduced to pulp
either by being
mechanically ground into pulp or by being chipped and cooked in a chemical
solution.
Chemically digested wood chips generally result in a higher-quality paper than
mechanically ground pulp.
Two common processes are used to chemically reduce wood chips into pulp,
namely, the sulfite process and the sulfate, or kraft, process. In both of
these processes,
lignin is dissolved under heat and pressure in a digester, resulting in the
separation of
cellulose fibers. The processing time may be as long as twelve hours,
depending upon
the si~:e of the chips and the quality of the product desired. Processing
chemicals,
particles of undigested wood, and foreign materials are then removed, and the
pulp is
further processed into paper.
The processing time required depends upon the thickness of the wood chips
used. Thicker wood chips require more time for the processing chemicals to
penetrate
and dissolve their lignin, and thus require a longer processing period to
digest
completely. Otherwise, the undigested pan of the thicker chips would have to
be
mechanically treated, resulting in an inferior product. Therefore, to ensure
uniform
CA 02227566 1998-O1-20
7
processing time and paper quality, wood chips are sized before they are
digested, with
thicker wood chips being removed prior to pulping.
To size wood chips, the chips are dumped onto a screen of a wood chip sorter
having; openings through which chips smaller than a preselected thickness may
pass.
The chips are then agitated, causing the thinner chips to pass through the
screen. The
thicker chips may subsequently be sliced to the correct thickness, used in
other ways or
for other purposes, or discarded.
Several types of sorting screens are described in the background section of
U.S.
Patent Nos. 5,398,819 and 5,560,729, which are hereby incorporated by
reference. One
sorter uses pairs of spiral rolls to separate chips of various sizes. Wood
chips are
dumpE;d onto the rotating spiral rolls so that the chips move longitudinally
to an open
area between the rolls. Chips of a small size fall into a gap and are
collected for
processing under the screen. The thicker chips that are too large to fall
though the gap
continue to move longitudinally along the screen. Numerous gaps exist along
the
length of the screen. The larger chips that reach the discharge end of the
screen may be
discarded or collected for another use.
A second type of screen comprises an array of hubs and disks on parallel,
spaced-apart shafts. The chips are dumped on one end of the screen and,
because of the
rotation of the shafts, wood chips are brought into the region of intermeshed
disks,
where thinner chips fall through and are collected. Thicker chips remain on
the screen
and continue to move longitudinally off the end of the screen. In another
similar
embodiment, the intermeshed hubs and disks vary in size along the length of
the shafts
to provide an increased open area though which the smaller chips fall.
Still another type of screen comprises a series of parallel, elongated
rectangular
metal bars. An open area of a predetermined size separates adjacent bars to
permit
sufficiently thin wood chips to fall through for collection. The spaced-apart
bars are
CA 02227566 1998-O1-20
3
held together by frame supports at each end. Agitation is provided by shaking
the entire
frame assembly.
Screens comprising relatively thin, tensioned blades instead of bars are also
used. Often, this type of wood chip sorter is a dual-frame screen, in which
alternate
blades are supported on different frames (one inside the other). The frames
move
relative to one another to impart sufficient agitation to the wood chips to
ensure
efficient separation. This motion is imparted by moving the frames in a
reciprocating
motion relative to one another.
A11 the sorters require the wood chips to be fed onto the receiving end of the
screen. One example of a prior art feed system is shown in U.S. Patent No.
5,305,891,
in which reference numeral "34" shows an auger to distribute the chips on the
receiving
end of the bar screen. Other prior art devices include screw conveyors, rotary
valves,
and special feed chutes with various flow control devices. However, each of
the prior
art designs for feeding the chips have produced less than adequate results.
Using the prior art feed devices, wood chips tend to be concentrated at
particular
areas when they are dumped on the receiving end of the sorter. For example,
the chips
can be; concentrated at the center of the screen and the edges receive fewer
chips, which
reduces the efficiency of the screening operation. Chips of the desired size
or smaller
in the concentrated area are more likely to reach the discharge end of the
screen without
falling; through the gaps because of the large chip volume passing over the
gaps.
Productivity is further lowered because the portion of the sorter having a
less
concentrated flow of chips could efficiently process more chips.
Because papermaking is a continuous process, the rate at which the thinner
chips pass through the screen has proven to be a bottleneck that limits the
rate at which
paper can be produced. Evenly and efficiently increasing the percentage of
chips being
exposed to the open areas of a given sorter increases capacity of the screen
and,
therefore, alleviates the effects of this bottleneck in the papermaking
process.
CA 02227566 1998-O1-20
4
Therefore, a need exists in the art for a device that uniformly feeds wood
chips
across the width of the screen.
CA 02227566 1998-O1-20
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION .
The disadvantages of the prior art are overcome by the present invention,
which
provides an apparatus and method for uniformly distributing wood chips onto a
wood
chip sorter. The apparatus comprises a chute disposed above the receiving end
of the
sorter. a plurality of blades disposed within the chute, and a means for
rotating at least
one blade, and preferably all of the blades, to one of a plurality of desired
rotational
positions.
The chute has an external surface, an interior, an influent end, and an
effluent
end which is disposed over the receiving end of a wood chip sorter. Wood chips
enter
the in:~luent end of the chute, fall longitudinally through the interior of
the chute and
exit the effluent end onto the receiving end of the wood chip sorter.
Each blade has a face portion and axis of rotation about which the face
portion
is rotatable. The blades are twisted by the rotating means to one of a
plurality of
desired rotational positions. Rotation of the respective blades changes the
distribution
of wood chips exiting the effluent end of the chute onto the receiving end of
the wood
chip sorter. The blades can be adjusted until a uniform distribution of wood
chips is fed
onto the receiving end of the wood chip screen. The blades can be locked into
position
when the uniform chip flow distribution is achieved.
The present invention also comprises a means for laterally moving the blades,
preferably an opening through the chute along which the blade is laterally
moved. The
moving means, similar to the rotating means, affects the distribution of the
wood chips
exiting the effluent of the chute. Accordingly, the moving means and the
rotating
means ensure that the wood chips are uniformly fed onto the receiving end of
the wood
chip sorter.
CA 02227566 1998-O1-20
6
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FIGURES OF THE DRAWINGS
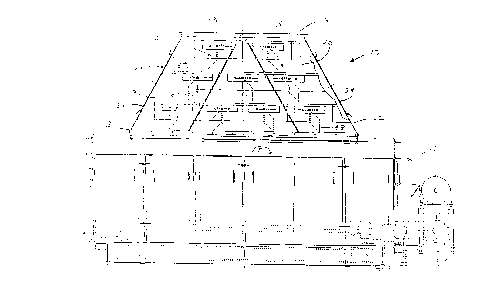
Fig. 1 is a front view partially in cross-section of a first embodiment of the
present invention disposed over a wood chip separator.
Fig. 2 is a side cross-sectional view of the invention of Fig. 1.
Fig. 3 is a side view partially in cross-section of a second embodiment of the
present invention.
Fig. 4 is a front view partially in cross-section of the invention of Fig. 3.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
1 S The present invention is more particularly described in the following
examples
that are intended as illustrative only since numerous modifications and
variations
therein will be apparent to those skilled in the art. As used in the
specification and in
the claims, "a" can mean one or more, depending upon the context in which it
is used.
The preferred embodiment is now described with reference to the figures, in
which like
numbers indicate like parts throughout the figures.
Referring generally to Figs. 1-4, the present invention is shown, which is an
apparatus 10 for uniformly distributing wood chips. The device 10 comprises a
chute
20, a plurality of blades 40 disposed within the chute 20, and a means for
rotating the
2S face portion 42 of each blade 40 to one of a plurality of desired
rotational positions. A
first embodiment of the present invention is shown in Figs. l and 2 and a
second
embodiment is shown in Figs. 3 and 4. The construction of the second
embodiment is
similar to the first embodiment and, accordingly, the same reference numerals
designate
the same parts.
CA 02227566 1998-O1-20
The chute 20 has an external surface 22, an interior 24, an influent end 26)
and
an effluent end 28 which is disposed adjacent to and over the receiving end 17
of a
wood chip sorter 1 ~ (shown in Figs. 1 and 2). Wood chips, which are shown
schematically in Figs. 2 and 4 by feed arrow A, enter the influent end 26 of
the chute
20, fall substantially longitudinally through the interior 24 of the chute 20
and exit the
effluent end 28 onto the receiving end 17 of the wood chip sorter 15. The
longitudinal
axis L of the chute 20 is shown in Figs. 3 and 4.
The chute 20 has four sides, a first side 30, an opposite second side 32, and
two
opposed end sides 34, 36, defining and enclosing the interior 24. The first
side 30 and
the second side 32 are preferably parallel to each other. Each end side 34, 36
has a first
edge attached to a portion of the first side 30.and a second edge attached to
a portion of
the second edge. The end sides 34, 36 are each substantially planar and are
also spaced
fizrthe:r apart from each other adjacent the effluent end 28 compared to the
separation
adjacent the influent end 26. Thus, the chute 20 laterally widens in the
direction that
the wood chips flow, as shown best in Figs. 1 and 4.
A plurality of blades 40 are disposed within the interior 24 of the chute 20.
Each blade 40 has a face portion 42 and axis of rotation R about which the
face portion
42 is rotatable. As shown in Figs. 2 and 3, the face portion 42 of the blades
40 do not
extend the entire width of the interior 24 of the chute 20 separating the
first side 30 and
second side 32, although longer blades 40 are a contemplated option. The face
portions
42 also depend downwardly in the preferred embodiment, but could be
horizontally
oriented if desired.
As shown for the first embodiment in Figs. 1 and 2, the face portion 42 of
each
blade 40 is a single member 43. Alternatively, as shown in the second
embodiment in
Figs. :3 and 4, each blade 40 comprises two members 44, in which each member
44 has
a top end 46 and a bottom end 48. The respective top ends 46 of the two
members 44
are connected to each other and the bottom ends 48 are spaced apart from each
other so
CA 02227566 1998-O1-20
g
that each blade 40 forms an inverted "V" in cross-section. The top end 46 of
the two
members 44 are preferably disposed along the axis of rotation R of that blade
40.
The rotating means enables rotation of the face portion 42 of each blade 40 to
one of a plurality of desired rotational positions about the axis of rotation
R. Each of
the desired rotational positions for each face portion 42 diverts the wood
chips
differently in a spatial orientation relative to that blade 40 as the wood
chips pass
through the interior 24 of the chute 20. Accordingly, rotation of the blades
40 changes
the distribution of wood chips exiting the effluent of the chute 20 onto the
receiving end
17 of the wood chip sorter 15.
The rotating means can be automated or manually operable. As shown, the
rotating means preferably comprises a plurality of handle members 50, in which
a
portion of each handle member 50 is disposed through either the first side 30
or the
second side 32 of the chute 20. As shown for the first embodiment in Fig. 2,
the handle
members 50 are disposed through the first side 30 of the chute 20. In
comparison, as
shown for the second embodiment in Fig. 3, some of the handles members are
disposed
through first side 30 of the chute 20 and other handle members 50 are disposed
though
the second side 32.
Each handle member 50 has a connecting end 52 fixedly attached to a portion of
one respective blade 40 and a gripping end 54 disposed adjacent and outside
the
external surface 22 of the chute 20. Rotation of the handle member 50, using
the
gripping end 54, rotates the face portion 42 of attached blade 40 about its
axis of
rotation R. The handle members are preferably independently movable.
The present invention preferably further comprises a means for locking each
blade 40 at the desired position to which it has been rotated. In the
preferred
embodiment, each locking means comprises a lock nut 56 movable along a portion
of
the handle member 50 intermediate its connecting end 52 and the gripping end
54. The
lock nut 56 preferably is located outside the external surface 22 of the chute
20. The
CA 02227566 1998-O1-20
9
lock nut 56 is movable between a locked position and a released_.position. In
the locked
position, a portion of the lock nut 56 contacts a portion of the external
surface 22 of the
chute ~?0 so that the blade 40 is held at the desired rotational position,
e.g., the lock nut
56 is tightened so that the handle member 50 is locked into position against
the first
side 30 or second side 32 of the chute 20. In the released position, the lock
nut 56 is
loosened and spaced apart from the external surface 22 so that the blade 40 is
rotatable
about i.ts axis of rotation R. The locking means can be automated or manually
operable.
The present invention also comprises a means for laterally moving at least one
blade 40 relative to the longitudinal flow of the wood chips. As shown best in
Figs. 1
and 4, the moving means comprises a laterally-extending opening 58 in the side
30, 32
of the chute 20 through which the handle member 50 is disposed. The handle
member
50 is laterally slidable within the opening 58 to a desired lateral position
relative to the
flow of the wood chips. As shown in the Figs. 1 and 4, the openings 58 are
oriented
substantially perpendicular to the longitudinal axis L of the chute 20.
However, other
angular alignments are contemplated to orient the laterally-extending openings
58
relative to the longitudinal axis L. As one skilled in the art will
appreciate, the locking
means, which preferably comprises a lock nut 56, can also lock the blade 40 in
the
desired lateral position in the opening 58 as well as lock the blade 40 at its
desired
rotational position. The moving means can be automated or manually operable.
Similar to the rotating means, one skilled in the art will appreciate that the
moving means also affects the distribution of the wood chips exiting the
effluent end 28
of the chute 20. Thus, the distribution of the wood chips is a function of
both the lateral
position of the blade 40 and its rotational orientation. Accordingly, the
operator can
adjust one or more blades 40 as necessary to ensure that the proper
distribution of wood
chips is fed onto the receiving end 17 of the wood chip sorter 15 for the most
efficient
operation of the sorter.
Referring again to Figs. 1-4, the blades 40 are laterally disposed in three
tiers in
the chute 20. A first tier 60 is disposed adjacent the influent end 26, a
third tier 64 is
CA 02227566 1998-O1-20
disposed adjacent the effluent end 28, and a second tier 62 is disposed
intermediate the
first tier 60 and the third tier 64. In the embodiment shown in Figs. 1 and 2,
the first
tier 60 has two blades 40, the second tier 62 has three blades and the third
tier 64 has
four blades. The second embodiment shown in Figs. 3 and 4, in comparison, has
one
5 blade 40 in the first tier 60, two blades in the second tier 62, and three
blades in the
third tier 64.
In operation, wood chips are fed or dumped into the interior 24 of the chute
20
through its influent end 26 using a conveyor (not shown) or other means known
in the
10 art. Tile wood chips pass through the influent end 26 and initially fall
longitudinally
through the interior 24 of the chute 20. If unobstructed, the chips would fall
straight
through the chute 20 and reach the receiving end 17 with the chip being
concentrated at
its center. However, the blades 40 deflect the falling wood chips so that the
chips are
diverted, although their path is substantially longitudinal through the
interior 24 of the
chute Z0.
- The operator, accordingly, rotates selected blades 40 to one of a plurality
of
desired rotational positions. The different desired rotational positions for
each blade 40
divert the wood chips differently relative to that blade 40 as a result of the
chips
contacting that blade 40 or other chips deflected from that blade 40.
Likewise, selected
blades 40 can be laterally moved to a different position in interior 24 of the
chute 20
relative to the downwardly flowing wood chips.
As the operator adjusts the blades 40 from outside the chute 20, he can
observe
the affects of the adjustment on the distribution of material across the width
of the
wood chip sorter 15. Once the desired uniformity of flow has been achieved,
the blades
40 can be locked into place using the lock nut 56 or other locking means. The
chute 20
will continue discharging wood chips from the effluent end 28 of the chute 20
onto the
receiving end 17 of the wood chip sorter 15. Also, the operator can easily re-
adjust the
flow of wood chips if the distribution changes over time.
CA 02227566 1998-O1-20
Although the present invention has been described with reference to specific
details of certain embodiments thereof, it is not intended that such details
should be
regardE:d as limitations upon the scope of the invention except as and to the
extent that
they are included in the accompanying claims.