Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02273019 1999-OS-26
WO 98/23440 PCT/GB97/03178
_1..
MANUFACTURE OF SELF'-ADHESIVE LABELS
The present invention relates to a method of and apparatus
for producing a succession of self-adhesive labels carried on a
backing of release material.
A number of methods for making multi-layer self-adhesive
labels in web form are known. For example EP-A-0153185 discloses
a method of producing two-layer .self-adhesive labels employing
two webs in an on-line operation in which two webs are printed,
adhered together and die-cut to form self-adhesive labels in
single pass. W091/04850 and W091,~04851 also disclose methods of
producing self-adhesive labels, in particular overlaminated
labels. EP-A-0684129 discloses a. method of producing labels in
which a web is cut to form folded leaflets which are then adhered
to a web. EP-A-0179575 discloses an apparatus for making labels
off-line.
The present invention aims to provide an improved method of
and apparatus for producing labels.
Accordingly, the present invention provides a method of
producing a succession of self-adhesive labels carried on a
backing of release material, the method comprising the steps of
(a) providing a first web of release material carrying a
succession of folded leaflets; (b) conveying the first web along
a pathway by a web conveyor; (c) printing a second web with a
succession of images along its length by at least one print
station, the or each print station being driven independently of
the web conveyor and being directly or indirectly registered with
reference to the first web or the :Folded leaflets; (d) laminating
the printed second web over the succession of folded leaflets;
and (e) die-cutting thxough at least the second web as far as the
release material to form a succe:~sion of self-adhesive labels.
The present invention further provides an apparatus for
producing a succession of self-adhesive labels carried on a
backing of release material,. the apparatus comprising a web
conveyor for conveying a first web carrying a succession of
CA 02273019 1999-OS-26
WO 98/23440 PCT/GB97/03178
-2-
folded leaflets, at least one print station for printing a
succession of images on a second web, a laminating station for
laminating the first and second webs together, with the folded
_ leaflets being disposed therebetween, a die-cutting station for
cutting a succession of self-adhesive labels out of a laminated
assembly comprising the first and second webs and the folded
leaflets therebetween, and a control system for directly or
indirectly registering the or each print station with reference
to the first web or the folded leaflets.
Embodiments of the present invention will now be described
by way of example only, with reference to the accompanying
drawings, in which:-
Figure 1 is a schematic side view of an apparatus for
manufacturing labels in accordance with a first embodiment of the
present invention;
Figure 2 is a schematic representation of a control system
of the apparatus of Figure 1;
Figure 3 is a schematic side view of an apparatus for
manufacturing labels in accordance with a second embodiment of
the present invention; and
Figure 4 is a schematic side view of an apparatus for
manufacturing labels in accordance with a third embodiment of the
present invention.
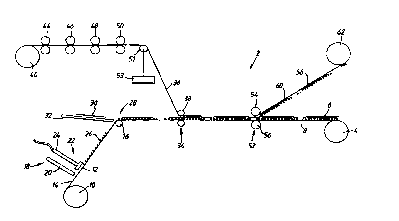
Referring to Figure 1, there is shown an apparatus,
designated generally as 2, for producing a reel 4 carrying a
succession of self-adhesive labels 6. The reel 4 comprises an
indeterminate length of a backing web a of release material,
typically comprising a silicone-faced backing paper The backing
web 8 is provided in~a reel 10 of duplex labelstock material 12
comprising a self-adhesive web 14 of paper or plastics which is
coated on its reverse side with a pressure-sensitive adhesive and
is carried on the release material web 8. For convenience, in
Figure 1 the two webs 14,8 comprising the labelstock material 12
are shown as an integrated single web. The reel 10 is mounted
in the apparatus 2 as a supply reel.
The self-arlhesiv~e web 14 of the labelstock material 12 has
CA 02273019 1999-OS-26
WO 98/23440 - PCT/GB97/03178
_3.. ,
- been subjected to an initial pre-treatment step prior to being
supplied as the reel 10 in the apparatus 2~:--In particular, the
self-adhesive web 14 has been printed and/or die-cut. In such _
a pre-printing operation, the upp~=r surface of the self-adhesive
web 14 is printed with a succession of images along its length,
each image being intended to be present in a respective resultant
self-adhesive label 6. In such a die-cutting step, the self-
adhesive web 14 is die-cut to form a succession of self-adhesive
base labels along the length of th.e release material 8 , each base
label being intended to be incorporated into a respective
resultant self-adhesive label 6 as a support piece therefor.
Following the die-cutting step, the waste web skeleton of the
self-adhesive web surrounding the die-cut base labels is removed
from web . _
The labelstock material 12 ao pre-treated is fed out from
the reel 10 thereof over one or more guide rollers 16 of a web
conveyor, which web conveyor may also drive the reels 10 and 4.
The labelstock material 12 initially passes to a detecting
station 18 at which a sensor 20, which is preferably a
photodetector, is adapted to detect a succession of pre-printed
marks along the length of the labelstock material 12 or
alternatively, when the labelstoc:k material has been die-cut as
described above to form a succession of base labels, to detect
the succession of base labels. The labelstock material 12 then
passes to an adhesive applying station 22 at which an adhesive
applicator 24 extrudes adhesive, for example a water-soluble or
hot melt adhesive) as a series of patches 26 onto the upper
surface of the labelstock material 12. When the self-adhesive
web 14 is pre-printed with a smccession of images along its
length, the adhesive patches are applied in registration with the
printed images.
Thereafter the labelstock material 12 is conveyed to a
leaflet applying station 28 at which a succession of folded
leaflets 30 are applied to the succession of patches 26 of -
adhesive by a folded leaflet: applicator 32. In this
specification, the term "leaflet" is intended to cover not only
leaflets but also booklets and other folded paper pieces. The
CA 02273019 1999-OS-26
WO 98/23440 PCTIGB97/03178
-4- s
folded leaflet applicator 32 is represented simply by a ramp in
Figure 1 but may comprise a label feed system such as disclosed
in EP-A-0684129. The folded leaflet applicator 32 may
incorporate a servo control system which is adapted
instantaneously (or after a delay? to advance or retard the
operation of the folded leaflet applicator 32 so that the
application of the folded leaflets 30 can "chase" the position
of the underlying labelstock material 12 so that the folded
leaflets 30 are applied in registration with the patches 26 of
adhesive and the labelstock material 12.
The sensor 20 operates in conjunction with a control system
to coordinate the application of the adhesive patches 26 and of
the folded leaflets 30 to the self-adhesive web 12 so that both
the adhesive patches 26 and the folded leaflets 30 coincide at
the correct point on the web in registry with any printed images
on the self-adhesive web 14 and, where appropriate, coincide in
registry with the underlying die-cut self-adhesive base labels.
If desired a delay may be present between the detection of the
succession of pre-printed marks and the operation of the adhesive
applicator 24 and/or the folded leaflet applicator 32.
The labelstock material carrying the folded leaflets 30
adhered thereto by the patches 26 of adhesive then passes to a
laminating station 34 at which a printed web 36 of paper or
plastics is laminated over the assembly of the folded leaflets
30 on the labelstock material 12. The combined webs 36,12, and
the folded leaflets 30 therebetween are passed through a pair of
opposed laminating rollers 38. The overlaminating web 36 has
been supplied in-the apparatus 2 as an unprinted reel 40 thereof
which is unwound and, upstream of the laminating station 34,
printed on either one or both sides thereof by a succession of
print stations 44,46,,48,50. Each of the print stations
44,46,48,50 is independently driven and is registered with
reference either to the labelstock material 12 or to the applied
folded leaflets 30 whereby each image printed by the printing
stations 44, 46, 48, 50 on the laminating web 36 is in registry with
a respective folded leaflet 30 which in turn is in registry with
the underlying printed self-adhesive web 14 or base Label die-cut
CA 02273019 1999-OS-26
WO 98/23440 PCT/GB97/03178
-5 -
therefrom.
Each of the print stations 44,46,48,50 is not only
independently driven with respects to each of the other print
stations 44,46,48,50, but also independently driven with respect
to the web conveyor for the labelstock material 12. Accordingly,
each of the print stations 44,46,48,50 may be individually
registered with respect to the laminating web 36 so that the
images printed by the print stations 44,46,48,50 may in turn be
registered with respect to the labelstock material or to a
subsequent operation, such as die-cutting, performed on the
labelstock material 12 . Since the: print stations 44, 46, 48, 50 are
independently driven, and thus c:an be rotated relative to the
laminating web when the print stations 44,46,48,50 require re-
registration with respect to the laminating web 36, it is
necessary in accordance with t:he preferred aspects of the
invention for the print units of the print stations 44,46,48,50
to be moved without moving the laminating web 36. Otherwise, the
laminating web could be moved with respect to the labelstock
material to which the laminating web is intended to be laminated
following the printing steps, which could in turn lead to mis-
registration problems.
Accordingly, the web drive, represented by roller 51 but
also preferably driving the reel 40, incorporates a web tension
control 53 illustrated schematically in Figure 1. The web
tension control 53 operates to ;prevent inadvertent additional
forward or backward movement of the laminating web as a result
of the printing process over and above the predetermined speed
of the laminating web which is imparted by the web drive 51. The
web tension control 53 acts to :isolate the laminate web drive
from influence by the printing processes, which involve relative
- movement of the print stations and the moving laminating web 36.
Typically, the web tension control 53 may comprise a brake which
is provided at the upstream end of the web drive 51 so as to
prevent forward movement of the laminating web being imparted by
the printing operation. Alternatively the web tension control
may comprise a series of wraps downstream of the printing
stations which are arranged to constrain any forward movement of
CA 02273019 1999-OS-26
WO 98/23440 PCTLGB97/03178
-6-
the laminating web imparted thereto as a result of the printing
operation.
The composite overlaminated assembly then passes from the
laminating station 34 to a die-cutting station 52 comprising an
upper die-cutting roller 54 and an opposed lower backing roller
56 between which the composite assembly is passed. The die-
cutting roller 54 cuts out from the overlaminating web 36, the
applied folded leaflets 30, the underlying patches of adhesive
26 and the self-adhesive web 14, or base labels previously die-
cut therefrom a succession of the self-adhesive labels 6 carried
on the backing of release material 8. The waste web remnant 58
comprises the waste skeleton 60 of the overlaminating web
together with waste portions of the folded leaflets 30 and the
adhesive patches 26 adhered thereto and is wound into a waste
reel 62. Like the print stations, the die-cutting roller 54 is
also independently driven and registered with reference to the
self-adhesive web 14 or the applied folded leaflets 30.
Figure 2 shows a control system, designated generally as 63 ,
for registry of the printed images printed on the laminating web
36 by the printing stations 44, 46, 48, 50 with the applied adhesive
patches 26 and folded leaflets 30 and with the subsequent die-
cutting operation performed at the die-cutting station 52.
As shown in Figure 2, the sensor 20 is coupled in the
control system 63 to the adhesive applicator 24 and to the
leaflet applicator 32. Thus when the sensor 20 detects a pre-
printed mark on the labelstock- material 12, or detects a
- previously die-cut base label of the labelstock material 12, a
signal is emitted from the sensor 20 which is employed by the
control system 63 to ensure that the patches of adhesive 26 are
applied in registry .,with the labelstock material 12 by the
adhesive applicator 24 and also the folded leaflets 30 are
applied in registry with the patches 26 of adhesive by the
leaflet applicator 32 (which may incorporate a servo control
system as aforesaid) . The signal from the sensor 20 is also
employed to control a respective servo control system 64 , 66 , 68 , 70
for the respective series of independently driven print stations
CA 02273019 1999-OS-26 _
WO 98/23440 PCT/GB97/03178
44,46,48,50. Thus the printing of the images on the laminating
web 36 is controlled with respect to the underlying labelstock
material web 12 so as to ensure that in the resultant self-
- adhesive labels 6, the images printed on the laminating web 36
are in registry with any underlying printed images on the
labelstock material 12.
The sensor 20 also emits a signal to control a servo control
72 for the die-cutting roller 54 so that the resultant self-
adhesive labels 6 are accurately die-cut in registry with the
printed images on the laminating and labelstock webs 36,12 and
with respect to the applied folded leaflets 30. Each servo
control 64, 66, 68, 70 far the printing stations 44, 46, 48, 50 and the
servo control 72 for the die-cutting roller 54 act
instantaneously or after a delay to advance or retard either the
printing cylinder or the die-cutting roller whereby the printing
cylinder or the die-cutting roller is registered with respect to
the underlying labelstock material.
In an alternative embodiment of the control system
illustrated in Figure 2, the sensor 20 which emits a signal which
is employed to control the leaflet. applicator 32 may not directly
employ a registration signal for registering the print stations
44,46,48,50. Rather, the servo ~~ontrols 64,66,68,70 for those
print stations 44, 46, 48, 50 may re~~eive a signal derived from the
leaflet applicator 32 which in turn has been registered to the
labelstock web 12 by the sensor ~i0-.
In a yet further alternative embodiment of the control
system illustrated in Figure 2, the sensor 20 emits a signal
which is employed to control the: operation of the die-cutting
roller 54 and then the operation of the print stations
' 44,46,48,50 may be controlled with respect to a signal derived
.;
from the die-cutting station 52. The signal which is employed
to control the leaflet applicator 32 may come either from the
sensor 20 or from the die-cutting station 52. In this way, the
position of the die-cutting roller 54 can be employed to control
the printing of the laminating we:b 36 which is required to be in
registry with the die-cuts made to form the resultant self-
CA 02273019 1999-OS-26
WO 98/23440 PCT/GB97/03178
_$_
adhesive labels 6 and/or to control the operation of the leaflet
applicator 32 which is required in turn to apply leaflets 30 to
the labelstock material 12 which are ultimately in registry with
the die-cuts made to form the self-adhesive labels 6.
In a still further embodiment of the control system
illustrated in Figure 2, the sensor 20 can provide a control
signal to the servo control 64 of the first i.e. most upstream
print station 44 and further control signals are sent in cascade-
fashion from the first print station 44 to the remaining print
stations 46,48,50 whereby the second and succeeding print
stations 46,48,50 are independently controlled so as to be in
registry with the first print station 44.
In a further embodiment of the present invention the
laminating web 36 may be self-adhesive, preferably a transparent
plastics self-adhesive web. When such a web is employed, the
reel 40 may comprise a web of such self-adhesive material carried
on a backing of release material, and the backing of release
material is removed from the self-adhesive web after the printing
operation and prior to lamination at the laminating station 34.
As an alternative to a self-adhesive laminating web 36, the
laminating web 36 may be heat sealable to the underlying folded
leaflets 30 and/or self-adhesive material 14. The heat sealed
area may be patterned so that for example the folded leaflet 30
is heat sealed around its periphery but not heat sealed directed
to the upper surface of the folded leaflet 30. The heat sealing
may be achieved by using heated laminating rollers 38.
When a self-adhesive or heat sealable laminating web 36 is
employed, the method and apparatus of the invention may not
require the use of adhesive applied by the adhesive applicator
.J
24. Accordingly, in certain embodiments of the invention, the
folded leaflets 30 may simply be sandwiched between the
labelstock material 12 and the laminating web 30 without being
directly adhered to the upper surface of the labelstock material
12, with the folded leaflet 30 being held in a closed
configuration by the adhesion of the laminating web 36 to the
CA 02273019 1999-OS-26
WO 98/23440 PCT/GB97/03178
underlying self-adhesive material 14 and/or release material 8.
In the illustrated embodiments of the present invention, the
- print stations 44,46,48,50 may comprise flexographic printing
stations as are conventionally employed in the manufacture of
. self-adhesive labels. Alternatively, the print stations
44,46,48,50 may comprise digital print stations as disclosed in
EP-0684130. Each digital print :station preferably working with
a dry toner process which typically is of a type similar to those
employed in colour photocopiers or laser printers or with a wet
toner process. The printing process may a direct or off-set
digital process. When the print stations 44,46,48,50 are digital
print stations, this provides the technical advantage of the
present invention permitting the marrying of digital printing for
the top surface of the label coup7_ed with the use of conventional
flexographic web printing for the underlying base web. In
addition, the method of the invention can provide the advantage
that digital printing units can pz°int variable information on the
overlaminating web.
Figure 3 illustrates-a second embodiment of an apparatus
designated generally as 102 fox producing labels in accordance
with the present invention which is a modification of the
embodiment of Figure 1. In Figure 3, the laminating web 136 is,
in the same manner as the embodiment o.f Figure 1, printed by a
plurality of independently driven print stations 144,146,148,150.
The so-printed laminating web 136 is laminated to a web 108 of
release material to which have already been applied a succession
of folded leaflets 130 each being carried on a respective self-
adhesive support piece 114. In this embodiment also, the
laminating web 136 is self-adhesive and a release backing web 137
is removed therefrom upstream of the laminating station 134
- comprising the laminating rollers; 138, the release web 137 being
wound into a reel 139. The laminating web 136 and the release
- backing web 137 are formed as a reel 140 which is fed
successively through the print stations 144,146,148,150 by the
web drive device, represented schesmatically bp-the roller 151 and
with the web drive device 151 having a web tension control 153
as schematically illustrated in Figure 3. The print stations -
- CA 02273019 1999-OS-26
WO 98123440 - PCTIGB97/03178
-10-
- 144,146,148,150 are arranged to print only the upper surface of
the laminating web 136. - --
A reel 110 comprising a backing 108 of release material
carrying a succession of die-cut self-adhesive support pieces 114
thereon, with each support piece 114 having adhered thereto by
a layer 126 of adhesive a folded leaflet 130, is fed out past a
detecting station 118 at which a sensor 120 detects either a
printed registration mark printed on the support piece 114 or the
folded leaflet I30 or the leading or trailing edge of the
intermediate label 121 comprising the assembly of the folded
leaflet 130 adhered to the support piece 114. The web is fed
over a guide roller 116 to the laminating station 134 comprising
the laminating rollers 138 at which the laminating web 136 is
laminated over the intermediate labels 121 with the printed
images on the laminating web 136 being in registry with the
underlying succession of intermediate labels 121.
The composite laminated assembly then passes to a die-
cutting station 152 comprising an upper die-cutting roller 154
and a backing roller 156 at which a succession of self-adhesive
labels 106 are cut out and the waste web remnant 158 comprising
the waste web skeleton 160 of the laminating web 136 together
with waste portions of the folded leaflets 130 and support pieces
114 adhered thereto are wound into a waste reel 162. The release
backing material 108 carrying the self-adhesive labels is wound
into a reel 104.
A further embodiment of the apparatus of the present
invention is illustrated in Figure 4. The apparatus, generally
designated as 202, oJf Figure 4 is a further modification of the
apparatus of Figure 1. In this apparatus, the laminating web 236
is printed by a plurality of print stations 244,246,248,250 in
.r
a manner similar to that described with reference to Figure 1 and
the laminating web 236 is laminated over a succession of folded
leaflets 230 which are carried on either an unprinted labelstock-
material 212 or in a further modification, over a printed
labelstock material which has been printed in line by at least
one printing station 213 illustrated in phantom in Figure 4. The
CA 02273019 1999-OS-26
WO 98/23440 PCTLGB97/03178
-11- ,
assembly of overlaminated folded leaflets 230 then passes from
the laminating station 234, constituted by the laminating rollers
238, to a die-cutting station 252, constituted by an upper die-
cutting roller 254 and a lower backing roller 256, at which a
succession of self-adhesive labels 206 is cut out from the
laminar material 236, the folded leaflets 230 and the self-
adhesive material 214 of the labelstock material 212. The
succession of self-adhesive labels 206 carried on the backing 208
of release material is wound int=o a reel 204. The waste web
remnant 258 produced in the cutting step and including the waste
web skeleton 260 of the lamin<~ting material 236 and waste
portions of the folded leaflets 230 and of the self-adhesive
material 214 are wound into a reel 262.
The labelstock material 21:? is fed out from a reel 210
thereof through the optional at least one printing station 213
directly to the laminating station 234. At the laminating
station 234, a succession of folded leaflets 230 are fed by the
folded leaflet applicator 232 into a nip point formed by the
laminating rollers 238 whereby th~~ succession of folded leaflets
230 are sandwiched between the upper laminating material 236 and
the lower self-adhesive materi<~l 214. In the illustrated
embodiment, the laminating material 236 is self-adhesive and a
backing web 237 of release material has been removed from the
laminating material 236 and wound up into a reel 239 thereof
downstream of the series of print stations 244,246,248,250. The
laminating material 236 together with the release web 237 have
been wound out from a reel 240 thereof, through the print
stations 244,246,248,250 and fed by a web conveyor represented
_ generally at 251 which, as in the other two embodiments, is
provided with a web tension control illustrated schematically at
253.
The embodiment of Figure 4 comprises an on-line apparatus
in which no pre-treatment in the :form of die-cutting or printing
has been carried out on the labelstock material 212. The folded
leaflet applicator 232 is pre-set so that the folded leaflets 230
are applied in the correctly spaced succession along the length
of the labelstock material 212. Since the labelstock material
CA 02273019 1999-OS-26
WO 98/23440 PCT/GB97/03178
-12-
212 has not been subjected to a previous printing or die-cutting
operation, there is no requirement for a sensor to re-register
the labelstock material 212 in the apparatus with respect to the
subsequent folded leaflet 230 application. The at least one
printing unit 213 for the labelstock material 212 may in turn be
linked mechanically to the web conveyor for the labelstock
material 212.
The print stations 244,246,248,250, being independently
controlled and controlled independently of the web conveyor for
the labelstock material, may be controlled so as to ensure that
the images printed thereby are ultimately in registry with the
respective self-adhesive labels. Accordingly, the print stations
244,246,248,250 may receive electrical control signals from the
die-cutting station 252 or the folded leaflet applicator 232.
In the case where the control signal is emitted from the die-
cutting station 252, the die-cutting station as a master unit
from which the print stations 244,246,248,250 and also the label
applicator 232 are controlled. Similarly, when the label
applicator 232 is the master control unit, the print stations
244,246,248,250 and also the die-cutting station 252 are slaved
to the label applicator 232. In the alternative arrangement
where on-line printing of the labelstock material is performed
by the optional print unit 213, in a similar manner the print
unit 213 could act as a master or slave control along with the
print stations 2442,46,248,250, the die-cutting station 252 and
the label applicator 232. Finally, in this embodiment it is
possible for the first independently driven print station 244 to
constitute the master unit and for all of the other remaining
print stations 246,248,250 as well as the applicator 232 and the
die-cutting station X52 to be slaved to the first print station
244.