Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02281055 1999-08-27
- 1 -
CENTEON PHARMA GMBH 1998/Z011 - Ma 1184 - C19
Antithrombin III-beta-comprising pharmaceutical preparation
The invention relates to a pharmaceutical preparation for the parenteral
administration of antithrombin III-beta.
Antithrombin III (AT III) is one of the most important plasma inhibitors. AT
III belongs to the serine protease inhibitors family, which with their "target
proteases" form a complex approximating to a covalent bond. This complex
is very stable under physiological conditions and as a rule is eliminated
rapidly from the blood circulation. The reaction between AT III and
protease is drastically accelerated by heparin, the AT III undergoing a
slight change in conformation after association with the heparin belonging
to the glycosaminoglycans group and thus being able to enter into an
accelerated reaction with the protease. These processes play a role
physiologically, particularly on cell surfaces which contain
glycosaminoglycans e.g. of the heparansulfate type and thereby protect
the cells and the tissue from excessively increased proteolytic activity.
In addition, however, plasmatic coagulation and its regulation has an
important meaning. In the healthy state, no or insignificant amounts of
glycosaminoglycans circulate, such that these processes are especially
determined by the progressive, i.e. heparin-independent, and thus far
slower inhibition characteristics of antithrombin III. This is useful in order
to
guarantee wound closure while avoiding subsequent excessive activation
of clotting.
The regulatory function of AT III is particularly clear when its plasma level
sinks, which can be observed in the course of many diseases and
CA 02281055 1999-08-27
- 2 -
particularly drastically, for exmaple, in the case of disseminated intravasal
coagulation (DIC). Even falling below 70 % of the corresponding plasma
concentration is associated with a drastic increase in the probability of
mortality. A predominance of clotting processes frequently leads to
thrombotic occlusions of vessels and thus to organ failure. The
administration of AT III concentrates of human plasma has therefore
proven very helpful, particularly in cases of inherited or acquired deficiency
states.
In order to counteract the described pathophysiological processes, heparin
- in addition to the abovementioned substitution with AT III concentrates -
is sometimes also administered in order to reduce the predominance of the
proteolytic potential to a normal degree. However, this can only be
successful if adequate AT III is present. Since the administration of the
heparin, however, is also associated with an increased risk of hemorrhage,
which is all the higher, the more disregulated the blood clotting, a balance
must continuously be sought between pro- and anticoagulatory processes.
The inhibition of the proteases of blood clotting, such as thrombin and the
activated factors X and IX, by AT III is particularly important here. A
reinforcement of the progressive inhibitory properties, which contributes to
the regulation of hemostasis, but does not significantly increase the
proneness to hemorrhage, would be regarded as a considerable advance.
This also applies to inflammatory reactions, where both thrombin and FXa
can be regarded as connecting links between clotting and inflammatory
reactions. A moderate inhibition of these factors would thus also have an
influence on both systems.
AT III circulates in the plasma in a concentration of about 150 mg/I.
Approximately 90 - 95 % of the AT III is glycosylated at four sites in the
molecule. This isoform is called AT III-alpha. However, the beta-isoform
CA 02281055 1999-08-27
- 3 -
only has three glycosylation sites. A comparison of these two isoforms has
shown that one of the carbohydrate chains of the AT III-alpha is localized
in the vicinity of the heparin-binding domain of the AT III, but is absent in
the beta-isoform. In the end, an increased affinity of the beta-isoform for
heparin results from this. Studies on the subendothelial tissue have shown
that AT III-beta is preferably bound there, presumably to the exposed
glycosaminoglycans. To date, however, it is not known whether the
differing glycosylation has an influence on the progressive inhibition of
plasmatic processes.
Surprisingly, it has now been found that the beta-isoform of antithrombin III
inhibits the proteolytic activities of the activated coagulation factors F X
and
F IX in the absence of heparin better than the alpha-isoform.
The invention therefore relates to a pharmaceutical preparation for
parenteral administration of antithrombin III, which contains only the beta-
isoform of antithrombin.
The invention further relates to a pharmaceutical preparation which
contains a mixture of the alpha- and the beta-isoform of antithrombin III, in
which the beta-isoform makes up at least 15 % by weight of the total
amount of the antithrombin. The preparation of the two isoforms of
antithrombin III and their inhibition properties are explained in greater
detail
in Example 1.
The significant, but moderately increased inhibitory capacity of the beta-
isoform can be eliminated for the abovementioned reasons in patients with
inherited or acquired AT III-beta deficiency states by the use of a
pharmaceutical preparation which is to be administered parenterally and
which only contains the beta-isoform of antithrombin or the beta-isoform in
an amount of at least 15 % by weight of the total amount of the
CA 02281055 1999-08-27
- 4 -
antithrombin. The administration of this mixture of the two isoforms is
useful in AT III beta deficiency states, since this pharmaceutical
preparation has a higher content of the beta-isoform of antithrombin than
natural AT III concentrates.
The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical preparation which, in
addition to the pure beta-isoform of antithrombin III or an antithrombin III
having a content of at least 15 % by weight of the beta-isoform of
antithrombin, additionally contains a glycosaminoglycan, in particular
heparin. Using a preparation of this type, the inhibitory reactions of the
beta-isoform of antithrombin are considerably accelerated.
In pure form or as a constituent of an AT III concentrate, the beta-isoform
can also be used for the prophylaxis or therapy of diseases which possibly
exhibit no clear decrease in the AT III plasma concentration. This can, for
example, be the case in leg vein thrombosis, in cardiac infarct prophylaxis,
in rethrombosis prophylaxis or in septic conditions such as sepsis or septic
shock. The increased inhibitory action against the activated blood clotting
factor X or IX can make administration of the pure beta-isoform of
antithrombin and also of an antithrombin concentrate enriched in beta-
isoform appear useful. The administration of a pharmaceutical preparation
which in the beta-isoform of antithrombin is not associated practically with
any increased risk of proneness to hemorrhage. The more effective
inhibition of the activated blood clotting factors IX and X is associated with
an anti-inflammatory effect, which can therefore also be used for the
prophylaxis and therapy of these conditions.
The pharmaceutical preparation according to the invention can be
employed for injection or infusion. It is in general marketed as a dry
substance in an injection vial together with a separately packed solvent.
The amount of the active compound intended for single administration in
CA 02281055 1999-08-27
-5-
an injection vial is as a rule between 250 and 2500 I.E. Depending on the
formulation of the lyophilized solution, the solvent used is water (for
injection), a Ringer lactate solution or an isotonic aqueous solution which
can contain sodium citrate, glucose, sodium monohydrogenphosphate, one
or more amino acids but also human albumin (from plasma, prepared by
recombinant or transgenic means) or a plasma substitute infusion solution
such as Haemacel~. Antithrombin III-beta can also be supplied in the form
of a liquid preparation to be administered parenterally. On simultaneous
administration of heparin or another glycosaminoglycan, its dose should
not exceed 500 I.U./hr.
The invention is explained in greater detail by the following examples.
CA 02281055 1999-08-27
- 6 -
Example 1:
Antithrombin III-alpha and -beta were obtained by adsorption of the AT III
concentrate Kybernin~P (Centeon Pharma GmbH, Marburg) on heparin-
Fractogel~ and stepwise elution. The differing affinity of the isoforms for
heparin was used here for separation, AT III-alpha being eluted at lower
and AT III-beta correspondingly at higher salt concentrations. The isoforms
were characterized, inter alia, by means of their differing running behavior
or band patterns, by SDS-PAGE and isoelectric focusing. The preparations
were distinguished by very high purity. The protein concentrations were
determined by the Kjeldahl method.
For the estimation of the inhibitory potencies of both isoforms, activated
factors isolated from plasma and having increasing concentrations of the
inhibitor isoforms (based on total protein content according to Kjeldahl)
were treated in the absence or presence of heparin (2 IU/150 pg of ATIII)
and the remaining amidolytic activities of the protease were determined
photometrically with the aid of chromogenic peptide substrates.
For this, the activated forms of the factors II (thrombin), of F IX, of F X
and
of plasminogen (plasmin) were used. The chromogenic substrate (3 mM)
were purchased from the company Chromogenix AB (Sweden).
CA 02281055 1999-08-27
Table 1
Protease Source Conc. in Test Chromogenic
(IUIML) substrate
Human-a- Centeon 0.5 IU/ml S 2238
thrombin
FIXa ERL (UK) 2 Ng/ml S 2288
Fxa Stago/ 0.05 IU/ml S 2765
Boehringer
(Germany)
Plasmin Centeon 0.1 CTA/ml S 2251
S 2238: H-D-Phe-Pip-Arg-pNA x 2HC1
S 2288: H-D-Ile-Pro-Arg-pNA x 2HC1
S 2765: Z-D-Arg-Gly-Arg-pNA x 2HC1
S 2251: H-D-Val-Leu-Lys-PNA x 2HC1
Part A
Test batch:
50 pl of ATIII-alpha or -beta
+ 100 pl of buffer
+ 50 NI of protease (see Table 1 )
+ 50 NI of chromogenic substrate
In the case of the batches containing heparin, the mixture was incubated
for 10 min at room temperature before addition of the chromogenic
substrate. Change in the absorption at 405 nm was recorded with time.
The inhibition (%) was quantified by comparison with the uninhibited batch.
The concentrations of AT III-alpha and AT III-beta which inhibited 50 % of
CA 02281055 1999-08-27
_ g _
the protease activity were determined and expressed as an IC50 value
(Table 2).
IC 50 (Nglml)
AT III-a AT III-(3
-heparin / + heparin -heparin / +heparin
Thrombin 220 1.5 200 0.8
F Xa 500 5.0 240 3.0
F IXa 490 10.0 175 7.0
Plasmin 900 55.0 900 45.0
Results:
As expected, all inhibitory reactions were strongly accelerated in the
presence of heparin and led to a considerable decrease in the IC50 values.
Clear differences between both isoforms were not obvious due to the
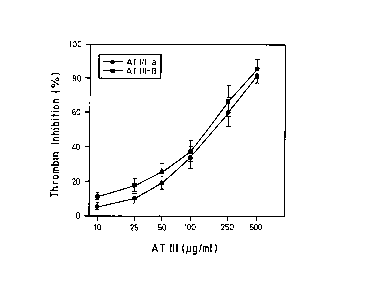
ranges of variability of the tests (Figures 1-4, in each case B), but relative
to thrombin, F IXa and F Xa show a tendency to higher inhibitory potency
of the beta-isoform.
In comparison with the alpha-isoform, AT III-beta concentrations reduced
approximately by the factors 2 and 3 were necessary for the 50
inhibition of F Xa and F IXa (Figures 1-4, in each case A).
Part B
The stronger inhibitory potency of AT III-beta was further intensified by
means of the following experiment, which was carried out in modified form
according to Example 1A:
CA 02281055 1999-08-27
_ g _
While the total concentration of the AT Ills employed in the test batch was
kept constant (at 100/250/500 Ng/ml), the content of AT III-beta was
increased.
Figure 5 shows an inhibition of the F IXa activity increasing with the AT III-
beta content. The curves of the absolute AT III specifications
correspondingly run parallel.
Example 2
The influence of both AT III isoforms on the plasma recalcification time was
determined according to Schnitger and Gross with the aid of
coagulometers. For this, AT III-deficient plasma which contained no
antithrombin III whatsoever was treated with increasing amounts of AT III-
alpha or AT III-beta and with 100 pl of imidazole buffer, incubated at
37°C
for 1 minute and the reaction was then started by addition of 100 NI of
calcium chloride (25 mM).
Result:
With increasing concentration, both AT III isoforms led to prolonged
recalcification times, AT III-beta causing the more marked prolongation
(Table 3).
CA 02281055 1999-08-27
U
N
N
C
O
f6
.>
N
L
M M O O 00 ~f7 I~
(n M m- M O r- O
M
I
I
C
N
.G >
~ 00 00 O O 1~ O I'
N N N N
Q ~ N N N N N N N
v
U
O
O
U
d
E O
C
' O
O
O ~
L
V
_
~ M O CflCO00 QO 1~
(!~M c- p r-c-
M
I I
C
N
s
a
~a >
_~ C 00 O O O O M N
I~ r1' I~ O M O r
Q ~ N N N N N N N
C
O
L
U
C
O
U ~.
E
-
O r- N tn O O
Q ~ O
O O O O ~ N