Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02286803 1999-10-15
1
METHOD FOR SUBSCRIBER-SIDE INFORMATION
TRANSMISSION IN A SUBSCRIBER LINE NETWORK
The invention is directed to a method for the subscriber-side
information transmission in a subscriber line network according to the
preamble of claim 1.
Modern telecommunication networks have digital subscriber line
networks available in the subscriber circuit area, these connecting one or
more
local exchanges to subscriber terminal equipment via subscriber lines.
Subscriber line networks were originally designed for the transmission
1 o of low-frequency information signals such as for example, in analog
telephony
or given the employment of narrow-band services. For example, the bit rate
transmitted in the subscriber line network at the subscriber side is defined
for
narrow band ISDN as 2 x 64 kbit/s for 2 B-channels (payload channels) plus 16
kbit/s for a D-channel (control channel), being defined such that the longest
subscriber lines that occur can still be used. However, a large part of the
bit
rate that can be reliably transmitted at a maximum, i.e. the maximum
bandwidth in the subscriber line network area with short subscriber lines,
remains unused. The degree of attenuation for symmetrical double leads of
copper subscriber lines that limits the range of the digital signal
transmission,
2 0 namely, increases with the line length. What is generally valid is that
the bit
rate to be transmitted via a subscriber line can be all the higher the shorter
the
length of a subscriber line. Consequently, subscriber line networks designed
for narrow band services can also be employed for the transmission of services
that are more broad band. In recent years, methods have thus prevailed with
2 5 which the existing copper lines in the subscriber line network can be
utilized
for the transmission of digital information signals. These include, for
example,
what is referred to as the asymmetrical digital subscriber line method ADSL
and what is referred to as the high bit rate digital subscriber line method
HDSL.
3 o DE 43 43 982 discloses a subscriber line network with subscriber lines
for the transmission of digital information signals wherein bit patterns are
CA 02286803 1999-10-15
2
transmitted from a local exchange via a subscriber line and the bit patterns
mirrored at the subscriber and sent back are evaluated in order to determine
the
maximally possible bit rate per transmission line. The evaluation of the
received bit patterns then ensues in the switching center. Dependent on the
results, the maximally possible bit rate is then defined.
A patent application not yet published as of the priority date of the
present application discloses a method for the transmission of information
signals in a subscriber line network via subscriber lines, whereby
transmission
parameters of the subscriber line are measured and settings are undertaken at
the exchange side and settings are undertaken at the subscriber side based on
the
criterion of the measured results. These settings are, for example, the
maximum bit rate that can be dependably transmitted and, potentially, the
transmission method. As a result thereof, it becomes possible to transmit even
more payload channels each having a respective bandwidth of 64 kbit/s in
addition to a D-channel having a bandwidth of 16 kbit/s. The maximum
plurality of payload channels which can be transmitted is thereby dependent on
the bandwidth of the individual subscriber line configuration, particularly on
the length of the subscriber line.
As a method for the subscriber-side information transmission in such
2 o subscriber line networks, the article by M. N. Huber and P. J. Kiin,
Modelling
of a Multi-Queue Polling System with Arbitrary Server Interrupts for the Idle-
Slot-Concatenation Packet Switching Principle in a Hybrid CS/PS Node,
Proceedings of the 12th International Teletraffic Congress, Torino, 1988,
discloses that an information transport frame be provided that is divided into
2 5 time slots of equal size. Each of these time slots is occupied either with
switching system data (CS data, circuit switching) or with packet data (PS
data,
packet switching), whereby all time slots not occupied with circuit switching
data are combined to form a remaining packet switching data transport channel
(idle slot concatenation). The traffic type with which the remaining packet
3 0 switching data transport channel is occupied, for example ATM or
LAN/Ethernet, is defined by the subscriber line configuration, particularly by
CA 02286803 1999-10-15
3
the packet data protocol that can be processed by the protocol evaluation
means
of the subscriber side.
The invention is based on the object of specifying a method for
subscriber-side information transmission that enables a more flexible
utilization
of subscriber line networks.
In a method for the subscriber-side information transmission in a
subscriber line network with the assistance of an information transport frame
divided into time slots of equal size, whereby at least some of these time
slots
are payload channel time slots whereof each is occupied either with circuit
switching data or with packet switching data and all payload channel time
slots
not occupied with circuit switching data are combined to form a remaining
packet switching data transport channel, the invention achieves this object in
that a protocol discriminator is inserted into every time slot of the
remaining
packet switching data transport channel. This protocol discriminator enables
an unambiguous allocation of the data contained in a time slot of the
remaining
packet switching data transport channel to a traffic type, so that a protocol
evaluation that is specific to traffic type can be respectively undertaken.
The inventive method thus enables the utilization of the remaining
packet switching data transport channel, which is also referred to as ISC
2 0 channel (idle slot concatenation) below, with different traffic types such
as, for
example, Atm and LAN.
Advantageous developments are recited in the subclaims.
One development of an inventive method thus provides that an
information about the length of a message precedes each message for the
2 5 transmission of messages with variable length in the remaining packet
switching
data transport channel. Given ATM cells, namely, the length of a message is
respectively prescribed by the constant length of an ATM cell, so that the
protocol discriminator suffices in order to know the length of each message at
the receiver side. Given messages of variable length, for example 16 bit
words,
3 o consequently, a length particular inserted per messages can be transmitted
in
CA 02286803 1999-10-15
4
said development of the invention in addition to the protocol discriminator
inserted into each cell.
Another development of the inventive method for the transmission of
variable-length messages provides that respectively one time slot of the
remaining packet switching data transport channel not be occupied between
two messages in the remaining packet switching data transport channel.
When the time slots of the information transport frame in a
development of the inventive method respectively correspond to 64 kbit/s
channel, the low-loss transmission of information of an ISDN basic access is
possible, this having two payload information channels each having a 64 kbit/s
transmission capacity and a signaling channel having a transmission capacity
of
16 kbit/s.
An especially beneficial development of an inventive method derives
when the duration of an information transport frame is respectively 0.125
milliseconds. As a result thereof, the structure of an inventive information
transport frame corresponds to a modified version of a standardized ISDN
primary rate access.
The plurality of time slots of an information transport frame preferably
lies between 5 and 32, dependent on the bit rate of a transmission system in
2 0 which the method is employed.
A beneficial embodiment of an inventive method for the subscriber-side
information transmission provides that a time slot of the information
transport
frame is employed for frame control and a time slot is employed for ISDN
signaling. Preferably, these time slots provided for the transmission of
control
2 5 information are arranged at permanently defined locations within the
information transport frame. The time slot employed for the frame control is
preferably provided at the start of an information transport frame in order to
enable a simple synchronization.
When the information transport frame is divided into an even-
3 0 numbered plurality of time slots, the synchronization is additionally
facilitated
when the time interval between the time slot employed for the frame control
CA 02286803 1999-10-15
and the time slot of an information transport frame employed for the ISDN
signaling is of the same size as the time interval between this time slot
employed for the ISDN signaling and the time slot of the following
information transport frame employed for frame control.
5 The invention is explained below on the basis of an exemplary
embodiment with reference to the figures.
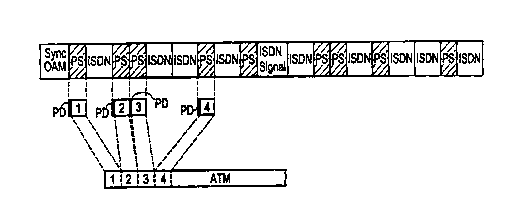
Figure 1 shows an exemplary embodiment of an information transport
frame as well as the transfer of the information of an ATM cell
into the ISC channel of this information transport frame; and
1 o Figure 2 shows a schematic block illustration of an exemplary
embodiment of a subscriber line network for the connection of a
subscriber unit to an ISDN network, an ATM network and a
LAN network.
As an exemplary embodiment, Figure 1 shows an information transport
frame having 20 time slots of equal size, whereof the first time slot Sync OAM
is provided for frame control and the eleventh time slot ISDN Signal is
provided for the ISDN signaling. The employment of the first and of the
eleventh time slot for the transmission of this control information is thereby
permanently prescribed. The remaining time slots 2 through 10 and 12
2 0 through 20 are fundamentally freely occupiable with circuit switching data
or
packet switching data. In the illustrated example, the time slots 3, 6, 7, 9,
12,
15, 17, 18 and 20 are occupied with circuit switching data in the form of ISDN
payload channel information. ISDN payload channel information can thereby
be, for example, facsimile information or voice information. The remaining
2 5 payload channel time slots, namely the time slots 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 13, 14,
16 and 19
together form an ISC channel for the transmission of packet data.
An ATM cell ATM shown in Figure 1 is transmitted in the ISC channel
of the information transport frame in the illustrated exemplary embodiment.
As shown in Figure 1, the information contained in the ATM cell ATM is
3 0 divided into the information parts 1, 2, 3, 4 for this purpose, whereby
each
information part 1, 2, 3, 4 is smaller than the information amount PS that can
CA 02286803 1999-10-15
6
be accepted by a time slot of the information transport frame. Each of the
information parts 1, 2, 3, 4 of the ATM cell information has a protocol
discriminator PD attached to it, this being arranged at the respectively left
side
in the illustration according to Figure 1, which means at the start of the
information PS for a time slot.
Figure 1 only shows the transfer of four information parts 1, 2, 3, 4 of
the ATM cell information. The remaining ATM cell information is
analogously packed in further time slots of the ISC channel.
In a schematic block illustration, Figure 2 shows a subscriber line
1 o network AN with a switching node CPN for the through-connection of
switching system data and packet data to a subscriber line and, in the
illustrated
exemplary embodiment, thus, for the connection of a subscriber line unit SSU
to an ISDN network ISDN-NET, to an ATM network ATM-NET and to a
local data network LAN.
The subscriber-side information transmission, i.e. the information
transmission between subscriber unit SSU and the subscriber line network AN
in the exemplary embodiment according to Figures 1 and 2 ensues with the
assistance of information transport frames according to Figure 1. The first
time
slot of an information transport frame is thereby respectively employed for
the
2 o transmission of the frame control information Sync OAM and the eleventh
time slot of an information transport frame is employed for the transmission
of
the ISDN signaling information between the subscriber unit SSU and the ISDN
network ISDN-NET.
A part of the time slots of an information transport frame is employed
2 5 for the transmission of ISDN payload information between the subscriber
unit
SSU and the ISDN network ISDN-NET. The remaining time slots of an
information transport frame together form an ISC channel and serve either for
the information transmission between the subscriber unit SSU and the local
data network LAN or between the subscriber unit SSU and the ATM network
3 o ATM-NET. The type of information transmitted in the time slots of the ISC
CA 02286803 1999-10-15
7
channel, i.e. the traffic type, is identified in every time slot PS with a
protocol
discriminator PD.
In the exemplary embodiment according to Figure 1, a part 1, 2, 3, 4 of
an ATM cell ATM is transmitted in each time slot of the protocol channel, so
that the protocol discriminator PD respectively contains the information
«A.hM".
Since the ATM cell has a constant length, the time slots with the packet
data information PS can be collected and composed at the receiver side, i.e.
either in the subscriber line network AN or in the subscriber unit SSU
(dependent on the transmission direction). The ATM cell composed in this
way can then either be processed at the subscriber side or can be forwarded
from the subscriber line network AN to the ATM network ATM-NET.
For the transmission of information between the local data network
LAN and the subscriber unit SSU, the protocol discriminator (not shown) of
each time slot of the ISC channel must correspondingly contain the
information LAN, so that a corresponding processing or forwarding of the
information can be undertaken.