Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
-1-
CRYPTOGRAPHIC TOKEN AND SECURITY SYSTEM
Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to a cryptographic token and security
system for use in securing transmission of data across communication
systems.
Background of the Invention
With the growth of the communication of information across
communications systems such as the Internet, telecommunication
systems, video and satellite communication systems, and the inter
communication between these systems, more interest is being shown in
securing the communication of data across such communication systems.
Various different standard algorithm protocols have been developed and
implemented by the communications industry to encrypt data at the point
of origin of the transmission and decrypt the data at the final intended
point of reception for the data.
In an Internet communication system, the data is provided with an
application header, a transport header, an Internet header, and a data link
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
-2-
header. Link encryption occurs when the data link header includes an
encryption method or algorithm that encrypts the remainder of the signal.
The layers of encryption increase as the data link header, the Internet
header, the transport header and the application header introduce
encryption protocols to encrypt the data. While these levels of
encryption are currently the standard levels or layers of encryption
associated with Internet communications, there is continual movement in
the industry to improve security protocols.
While these layers of security algorithms are standard protocols
and have been adopted by the communications industry, it is the user's
key that locks and unlocks the manner in which the standard protocol
security algorithms encrypt and decrypt the data.
In the industry, it is known to submit a session key that is a
symmetrical key that is generated for that session of data transmission
between a point of origin and a receiving node. The symmetrical key is
transmitted with the data from the point of origin to allow the party
receiving the encrypted code to decrypt the data with the session key.
The problem with using a session key is that the unauthorized reception
of the transmission session may result in the session key being used by
an unauthorized person to decrypt the data.
Alternatively, asymmetrical keys such as a public key and a
private key may be used. When the private key and the public key are
used, the public key is forwarded to an intended receiving party and
subsequently the data is transmitted after encryption by the private key.
The receiving party uses the public key to unlock or decrypt the
encrypted data. With the asymmetrical key, only the public key is
transmitted over the Internet network and the private key remains private.
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
-3-
Consequently, the unauthorized decryption of the data requires an
unauthorized party to receive or intercept the transmission of the public
key and the encrypted data.
Another problem associated with the security of information
transmitted over communication mediums relates to social engineering.
It is common for users large and small to continue using the same
asymmetrical keys for extended periods of time. Further, these keys are
typically stored in a computer or other data bus storage means where the
software for the encryption and decryption of the data is also stored.
Consequently, it is possible for an unauthorized third party to copy the
hard drive or storage medium and subsequently analyze the storage
medium without time constraints to determine the user's asymmetrical
and symmetrical keys. Once having obtained such key information, this
third party can then intercept the communication and utilize the key to
unlock or decrypt the transmitted data.
Accordingly, there is a need to improve the security of data
communicated across communication systems where third parties may
gain unauthorized access to the transmission of the data.
Summar~Of The Invention
The present invention relates to a secure communication system
for transmitting, encrypting, receiving and decrypting data. In the secure
communication system of the present invention, a security module is
used for encrypting and decrypting data in accordance with
predetermined security protocol associated with the industry standards
for that communication system. In order to effectively have the security
module encrypt and decrypt the transmission of data across this
communication system, the present invention utilizes a cryptographic
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
-4-
token which bears the user's cryptographic key information. The
cryptographic key information is used or superimposed upon the
encrypting and decrypting protocol used to encrypt and decrypt the data.
By using a cryptographic token, the cryptographic key information of the
user is stored on the token and not in the security module per se. This
effectively increases the security of the secure communication system
since the user cryptographic key is now stored remotely of the security
system or the security module used in this security system.
It is contemplated within the realm of the present invention that
the security module may be a separate device having an input port
coupled to a communication port of a first data transceiver or the security
module may form part of the first data transceiver in the secure
communication system. The security module is contemplated to pass
data through the module from the first data transceiver without
encrypting or decrypting the data when the user cryptographic key is not
present. Thus, in order for the security module to function, it must be
provided with a cryptographic token which bears the cryptographic key
information.
It is contemplated, that the cryptographic token may have a
connection interface port for temporary connecting the token with the
security module. When the token is connected to a hardware receiving
interface port of the security module, the cryptographic token is able to
make available the user's cryptographic key information to the security
module to enable the security module or a cryptographic logic device
located within the security module to encrypt and decrypt the data
transmitted from and to the first transceiver in accordance with a
predetermined security protocol for the communication system used. It
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
-5-
should be understood that the most secure practice of the present
invention is to maintain the cryptographic key or private key within the
cryptographic token. The security module routes the data, possibly
already encrypted, through the cryptographic token and the
cryptographic token applies the cryptographic key to encrypt and decrypt
the data. In the lesser secure system, the cryptographic token may
temporarily transfer the cryptographic key to the security module to have
the security module perform all the encryption and decryption.
However, this latter approach is less preferred.
It is contemplated that the security module may include a data
broadcasting transceiver coupled between the cryptographic logic device
and a second output device for transceiving the data over a transmission
medium to a second data transceiver. This data broadcasting transceiver
may be in the form of a modem. The first and second data transceivers
may each be selected, for example, from one of a computer, a telephone,
a video phone and a radio telephone such as, for example, cellular or
satellite communication telephones.
It is within the realm of the present invention that the
cryptographic token may include a user interface accessible by the user
so as to enable the cryptographic token to function and transmit the user
cryptographic key or other user information to the security module. To
accomplish this, the cryptographic token includes an authentication
processor connected to the user interface for verifying the authenticity of
the user. This interface and authenticity check may be conducted off line
from the security module such that it is improbable to tap into the
cryptographic token through the security module to gain unauthorized
access to the user's cryptographic key information.
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
-6-
While the present invention has application with various
communication systems, such as voice communication, video
communications, and telecommunications, a preferred application for the
secure communication system is via the Internet. In accordance with the
present invention the predetermined security protocol implemented by
the security module cryptographic logic device comprises a standard
security protocol which may include, for example, link encryption,
network encryption, secure socket layer encryption, and application layer
encryption.
It is contemplated within the realm of the present invention that
the cryptographic token has a power source to operate the cryptographic
token off line from the security system. Alternatively, the cryptographic
token may rely on its power being supplied from the security system
when the cryptographic token is coupled to the security system. The
token includes memory for storing the user cryptographic key
information required by the security system for the encryption and
decryption of data. The token further includes a connection interface
port for transferring cryptographic key information to the security system
when the cryptographic token is enabled and coupled to the security
system. The token includes a contact sensitive graphical interface
accessible to user for capturing and enrolling user ideogram signature
information. The token further includes a user authentication processor
for creating a user identification template from the user ideogram
signature information, preferably off line, from the security system and
storing the user identification template in the memory. The
authentication processor includes a comparison function or comparator
for comparing receipt of user ideogram signature information with the
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
user identification template either off line from the security system when
the cryptographic token has its own power supply or in concert with the
security system when the cryptographic token utilizes the power supply
of the security system. The comparator generates an authentication
signal when the comparison of the user ideogram signature information
matches the user identification template. The authentication processor in
response to receiving the authentication signal enables the cryptographic
token. With the token now enabled, preferably off line, it in turn enables
the security module to encrypt and decrypt data in accordance with the
cryptographic key information.
It is within the realm of the present invention that the
cryptographic token can be in the form of a rectangular card such as, for
example, a printed circuit card having an input/output port that is PC
card compatible. Such a PC card may have its own power supply.
Alternatively, the cryptographic token can be in the form of a card, such
as an IC card or Smart Card. Such IC and Smart Cards typically do not
have an independent power supply.
When reference is made to the term cryptographic key information
in the present application, this refers to the key utilized by
encryption/decryption protocol algorithms to encrypt data in accordance
with the algorithm and the key information. The cryptographic key
information may include either or and both symmetrical and
asymmetrical keys. The symmetrical key may be used during data
transmission and may be the only key information transmitted together
with the data to the intended target receiver. The asymmetrical key may
comprise a public key and a private key. The public key is normally
transmitted to or received by the intended transmitter or receiver of the
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
_g_
data prior to the data being encrypted with the public key. Upon receipt
of this encrypted data information, the public key is used decrypt the
data. The cryptographic key information may comprise a bit stream of
information in the range of 7 to 4096 bytes, for example.
The graphical interface is a contact sensitive interface that may be
sensitive simply to contract or to contact and pressure contact. The
graphical interface may include a graphical contact sensitive tablet,
which is pressure sensitive, over which a stylus is manipulated by a user
to enter an ideogram signature information. Alternatively a contact
sensitive display may be used for the graphical interface that may or may
not echo the ideogram signature information. It is further contemplated
that the display may generate a menu of user selection activation prompts
to guide a user in entering ideogram signature information to create a
user identification template to be stored in the cryptographic token. The
menu may further prompt the user to create or generate new
cryptographic keys within the system and prompt the user for a password
in addition to the other security levels. Preferably, the cryptographic
token of the present invention may contain at least three authentication
factors for encryption. The first factor is something the user knows such
as, for example, the password. The second authentication factor is
something the user has which is the token and the cryptographic key
information stored on the token. The third authentication factor is
something the user does which is provide ideogram signature
information on the token. Additionally, the first and third authentication
factors are something the user can change thereby adding a layer or level
of security.
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
-9-
Throughout the disclosure and claims references is made to the
term ideogram signature information. It should be understood that this
term refers to a graphic representation made by user's on the contact
sensitive graphic interface. The term signature is used to represent the
user's graphic representation of it's personal signature or, is used in
combination with the term ideogram to represent the personal
characteristics of the user in creating an ideogram. This ideogram
signature is referred to as information since it is codified and interrogated
by the authentication processor of the cryptographic token to create an
identification template of information that is subsequently used to verify
the authenticity of a user.
It is further contemplated to be within the realm of the present
invention that the cryptographic token includes a watchdog or tampering
circuit which in the event of an intrusion erases from the memory of the
cryptographic token the cryptographic key and ideogram signature
template. Further, it is contemplated that the display or a light emitting
diode display may be utilized by the cryptographic token to provide a
visual indication of when the token is properly activated.
The cryptographic token may further include a buzzer for
sounding alarms related to proper or improper activation of the token.
In accordance with another aspect of the present invention there is
provided a secure communication system for transmitting, encrypting,
receiving and decrypting data. The system comprises:
a first data transceiver for transmitting and receiving data to and
from a first communication port;
a security module having a first input port coupled to the first
communication port of the first data transceiver, the security module
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
-10-
having a second communication port from which data is transmitted and
received with a second data transceiver, the security module having a
cryptographic logic device coupled between the first input port and the
second output port for encrypting and decrypting data transmitted
between the first and second transceivers in accordance with a
predetermined security protocol when the security module is enabled,
and the security module having a hardware enabling receiving interface
port connected with the cryptographic logic device; and,
a cryptographic token bearing user cryptographic key information
and having a connection interface port for temporary coupling the
cryptographic token to the hardware receiving interface port of the
security module to make available the user cryptographic key
information and to enable the cryptographic logic device of the security
module to encrypt and decrypt data transmitted between the first and
second transceivers in accordance the predetermined security protocol
and the user cryptographic key information borne on the cryptographic
token.
In accordance with one aspect of the present invention there is
provided a cryptographic token operable with a security system to permit
encryption and decryption of data communicated through the security
system. The cryptographic token comprises:
memory for storing cryptographic key information required by the
security system for the encryption and decryption of the data;
a connection interface port for communicating data with the
security system when the cryptographic token is enabled and coupled to
the security system;
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
-11-
a contact sensitive graphical interface accessible to a user for
capturing user ideogram signature information;
a user authentication processor for creating a user identification
template from the user ideogram signature information and storing the
user identification template in the memory; and,
the authentication processor including a comparator for comparing
receipt of user ideogram signature information with the user
identification template, the comparator generating an authentication
signal when the comparison of the user ideogram signature information
matches the user identification template, and the authentication processor
in response to the authentication signal enabling the cryptographic token.
It is also within the realm of the present invention to store user
information on the cryptographic token that can be downloaded to or
uploaded from the secure communication system when the cryptographic
token has been enabled by a user authenticated by the cryptographic
token. The user information may relate to personal user information
such as bank account number, credit card numbers and or up to date
account balances. In addition the personal information may include birth
dates of family members and telephone numbers. In order to enable the
cryptographic token to operate with the secure communication system
the cryptograhpic token will have to be enabled by the user inputting
user information already stored on the token for verification by the token.
This user information may include information, such as, for example,
passwords, personal identification numbers, personal information, and
behavioral and physical biometric information including but not limited
to finger prints, retina or iris scans, palm and face patterns, voice
patterns, handwriting, blood type and DNA.
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
- 12-
In accordance with yet another aspect of the present invention,
there is provided a secure communication system for secure transmission
of data across the secure communication system comprising:
a first data transceiver for transmitting and receiving data to and
from a first communication port;
a security module having a first input port coupled to the first
communication port of the first data transceiver, the security module
having a cryptographic logic device coupled to the first input port for
encrypting and decrypting data transmitted to and received from the first
transceiver in accordance with a predetermined security protocol when
the security module is enabled, and the security module having a
hardware enabling receiving interface port connected with the
cryptographic logic device; and,
a cryptographic token storing user information and having a
connection interface port for temporary coupling the cryptographic token
to the hardware receiving interface port of the security module, the
cryptographic token including a user interface for receiving inputted user
information and an authentication processor connected to the user
interface to verify authenticity of the inputted user information with the
stored user information and enable the cryptographic token when the
inputted information is successfully verified to enable the cryptographic
logic device of the security module to transmit and receive data with the
first transceiver in accordance with the predetermined security protocol.
In accordance with yet another aspect of the present invention
there is provided a cryptographic token operable with a secure
communications system to permit secure transmission of data through
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
-13-
the secure communications systems when the cryptographic token is
enabled by a user, the cryptographic token comprising:
a connection interface port for communicating data with the secure
communications system when the cryptographic token is enabled and
coupled to the secure communications system;
a contact sensitive graphical interface accessible to a user for
capturing user ideogram signature information inputted from a user;
a user authentication processor for creating a user identification
template from the user ideogram signature information and memory for
storing the user identification template; and,
the authentication processor including a comparator for comparing
receipt of a newly inputted user ideogram signature information with the
user identification template, the comparator generating an authentication
signal when the comparison of the inputted user ideogram signature
information matches the user identification template, and the
authentication processor in response to the authentication signal enabling
the cryptographic token.
Brief Description Of The Drawings
For a better understanding of the nature and objects of the present
invention reference may be had to the following detailed description
when taken in conjunction with the accompanying diagrammatic
drawings wherein:
Figure 1 is perspective view of the cryptographic token and
security system used as an interface between a personal computer and an
Internet site;
Figure 2 is a block diagram of the cryptographic token with its
own off line power supply;
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
- 14-
Figure 3 is a perspective view of the cryptographic token showing
a preferred contact sensitive liquid crystal display and stylus;
Figures 4 and 5 show the display of the token prompting the user
with menu selections;
Figure 6 is a block diagram of the Internet security module
utilizing the cryptographic token of Figure 2;
Figures 7 to 14 are flow charts showing the steps involved in
setting up and logging into the cryptographic token; and,
Figure 15 is a block diagram of the cryptographic token dependent on a
remote power supply.
Detailed Description Of The Preferred Embodiment
Referring to Figure 1 there is shown a preferred embodiment for
the secure communication system 10 of the present invention. In the
preferred embodiment the secure communication system 10 operates in
conjunction with personal computers 12 and 14 to provide for secure
transactions and data communication across the Internet 16. The first
personal computer or computer 12 is in effect a first data transceiver for
transmitting and receiving data to and from a first communication port
18. The communication port 18 of computer 12 is connected via cable
20 to an Internet security module 22. The Internet security module has
an output port 26 in the form of a telephone jack for connecting through
standard telephone line 28 the Internet security module 22 to the Internet
16. The Internet 16 then routes the data across the Internet to the
telephone or communication line 30 of the second computer 14. It
should be understood that the second computer 14 may simply be
another user in the system or may be a computer that provides a service
through which a secure transaction and the exchange of money or credit
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
-15-
may flow from computer 12 through the Internet security module 22, the
Internet 16, to the computer 14. It should be understood that the security
module 22 may be alternatively connected to a single port for
transmission of information with that single port. Such a single port
arrangement would have application in an ATM banking machine
environment.
In accordance with the present invention, in order to activate the
Internet security module 22 a cryptographic token card 24 is required to
be inserted into a hardware enabling receiving interface port 32 of the
Internet security module 22. The cryptographic token 24 is a temporary
coupling which may be inserted into the port 32 and removed from the
port 32 as indicated by arrow 34.
The cryptographic token 24 is shown in Figure 1 to comprise a
printed circuit card which has an outer casing 36, a connecting port 38,
and a contact sensitive graphical interface 40.
The cryptographic token 24 bears cryptographic key information
which is utilized by the Internet security module 22 when the
cryptographic token 24 is inserted into the receiving port 32 of the
Internet security module 22. The cryptographic key information includes
either a symmetric or an asymmetric key. The asymmetric key includes
both a public key and a private key. These keys are preferably
maintained in the cryptographic token 24 away from the Internet security
module 22 for use by the Internet security module 22 with standard
Internet security protocol algorithms. Such standard Internet security
protocol encrypting and decrypting algorithms are, for example, a link
encryption, network encryption, secure socket layer encryption, and
application layer encryption. In accordance with the present invention
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
- 16-
the preferred encryption used by the Internet security module 22 is secure
socket layer encryption. Furthermore, the cryptographic token 24, once
enabled with the security module 22, would be able to download and
upload sensitive data to and from the security module and Internet.
Referring to Figure 2 a block diagram of the cryptographic token
has a battery 42 connected to a power conditioning circuit 44. The
power conditioning circuit 44 is further connected to an input power
connection 46 to the PC card host controller or hardware receiving port
32 of the Internet security module 22. When the cryptographic token 24
is not connected to the Internet security module 22 it is considered to be
off line from the Internet security module 22 and power to the
cryptographic token 24 is provided by battery 42. Upon insertion of the
cryptographic token 24 into the host controller 32 of the Internet security
module 22, power is fed along line 46 through the power conditioning
circuit 44. The power conditioning circuit 44 acts to regulate the power
source of the cryptographic token 24 from the battery 42 to the Internet
security module 22. The power conditioning circuit 44 has an output
power line 48 which provides an operating voltage to the other
programmed operating hardware of the cryptographic token 24.
User defined information is communicated to the cryptographic
token 24 through the contact sensitive graphical interface 40. The
contact sensitive graphical interface 40 is shown to include a contact
sensitive liquid crystal display 50 connected to a graphical interface 52.
The graphical interface 52 converts information pressed onto the liquid
crystal display into a graphic pattern and transmits this graphic pattern
across the data bus 54 to the user authentication processor 56. The user
authentication processor 56 may also be considered as a cryptographic
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
-17-
controller which controls the overall cryptographic operation of the
cryptographic token 24. Prompts for information obtained from a user
are transmitted across the bus 54 from the authentication processor 56
through the graphic interface 52 and echoed or displayed on the liquid
crystal display 50. The user authentication processor 56 includes a
comparator 58, and a real time clock and random number generator 60.
The real time clock and random generator number is utilized by the
authentication processor 56 to generate cryptographic key information
such as symmetrical keys and asymmetrical keys in the form of private
and public keys when so instructed or requested by a user.
The cryptographic token 24 also includes memory 62 in the form a
flash memory 64 and a scratch pad random access memory 66. The flash
memory 64 is connected to the authentication processor 56 by data
transfer bus 68. The scratch pad RAM memory 66 is connected to the
authentication processor 56 by data transfer bus 70. The operation of the
authentication processor 56 is stepped and controlled by a control clock
72.
The authentication processor 56 communicates with the Internet
security module 22 through a data transfer bus 74 to the connection
interface port 38 when the port is plugged into the PC host controller 32
of the Internet security module 22. The PC card interface or a connection
interface port 38 is a standard interface port and may comprise as
computer compatible PC card.
The authentication processor is further connected to one or more
LED's 76 and an audible transducer or buzzer 78.
The cryptographic token 24 further includes a tampering circuit 80
that detects an intrusion of the cryptographic token 24 and sends a signal
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
-18-
to the flash memory 64 to delete the program templates and
cryptographic keys normally stored in this flash memory.
Referring to Figures 2 to 5 and 7 to 14, the operation of the
cryptographic token 24 is described. One authentication factor of the
cryptographic token 24 resides in the contact sensitive liquid crystal
display 50 and the manner in which this display can capture information.
In Figure 3 the display 50 is shown with the words "Jane Doe' ". This
signature may be a written signature, a graph or symbol such as, for
example, a dog or a house, or anything the user wishes to write onto the
display 50. The user may utilize the stylus 90 to create the signature
shown. This signature is in effect the ideogram signature information 92.
The relative placement of the letters on the display in effect creates a
signature unique to the handwriting characteristics of the user.
The cryptographic token 24 provides through the battery 42 an off
line token which stores a user's cryptographic keys in the flash memory
64 together with a template of the user's ideogram signature information.
The flash memory 64 may also store the password of the user. The
cryptographic token 24 prompts the user with menu selection once the
card is activated. The main menu 82 is displayed on the display 40 to the
user allowing the user to select the options of log in or setup. The main
menu 82 is shown in Figure 4. In the event the user selects the setup
menu, then the setup menu 84 shown in Figure 5 is displayed to the user.
The setup menu includes five options of create new template, edit
existing template, generate symmetrical key, generate asymmetrical key,
and enter/change passwords.
Depending on the selection of the main menu shown in Figure 4
and the set up menu shown in Figure 5, the authentication processor
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
- 19-
verifies the activation of the cryptographic token 24 by an authorized
user. Once the activation of cryptographic token 24 is authenticated, the
cryptographic token 24 is then enabled permitting the transference of
data across data transfer bus 74 from the authentication processor 56 to
the connection interface port 38.
Referring to Figures 7 through 14 the method of enabling and
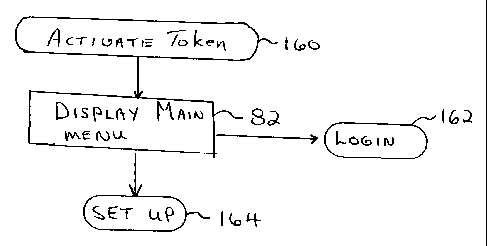
operating the cryptographic token 24 is shown.
In Figure 7, the cryptographic token 24 is activated at 160. This
activation may simply comprise tapping the contact sensitive LCD
display SO three times in a row to have the authentication processor 56
prompt the cryptographic token 24 to have the main menu displayed as at
step 82 in Figure 7. This main menu in Figure 7 is similar to the one
shown in Figure 4. The user then has the option to select the login
feature at 162 or go to the setup feature at 164.
In the event that the user chooses the setup feature 164, then the
system shown in Figure 8 displays the setup menu 84 which is similar to
the menu shown Figure 5. The user then has the ability to create a new
template at 166 or edit an existing template 168, generate symmetrical
key information 170, generate asymmetrical key information 172 or
create/edit the password 174.
In the event the user determines that they wish to create the new
template 166 then the template may be created in accordance with the
methodology shown in Figure 9. The processor 56 sets a counter N=0 at
220. The authentication processor 56 then requests the display 50 to
prompt the user to enter ideogram signature information (ISI), such as,
for example, the ideogram signature information 92 shown in Figure 3.
This information is entered on the contact sensitive graphical interface
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
-20-
50. Next, the authentication processor 56 at 224 applies a pattern
recognition algorithm to the ideogram signature information and stores
the pattern result in a memory 62. The processor then checks to see that
the number count N=0 at 226 and in the event that the number count is
N=0, it then moves to step 228 sets the program counter N=N+1 and
returns to step 222 to step through the process a second time.
In the event N not equal to 0, at 226 is no, then the processor 56
applies a smoothing algorithm to start to weigh the pattern results with
previous pattern results to create a user identification template at 230.
The processor 56 then checks at 232 to determine if this counter has
reached N=3 and in the event that it has not it then issues a command to
increment the counter 228 and again go through the display prompt user
steps 222 and 224.
In the event the inquiry at 232 is N=3, then the processor 56 stores
the user identification template information in flash memory 64 at 234
and then proceeds to step 236 ending the creation of the template
process. It should be understood that in the process for creating the new
template may only occur when no template has been entered into the
system. In the event that a template has been entered into the system,
then a default to the edit routine occurs.
In the event the user requests to edit the existing template 168
from the display setup menu 84 in Figure 8, then the process in Figure 10
is implemented by the processor 56. At this point, the processor checks
to determine if an identification template is already stored in the a flash
memory 64 at 176. In the event that there is no template stored then the
processor 56 returns to the setup menu 178. In the event there is an
existing template stored in the flash memory 64, step 179 is performed
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
-21 -
whereby the processor goes to the log in procedure to authenticate that
this is in fact the authorized user wishing to change there ideogram
signature information. The log in procedure is discussed subsequently in
more detail with respect to Figure 15.
After the login procedure is accomplished at 179, the next step is
at 180 to erase the existing template stored in the flash memory 64 and
then the system returns to create the new template menu at 182.
In the event a user selects from Figure 8 the create/edit password
174 step, then the process of Figure 13 is enacted. First the processor 56
determines at step 196 if the password is stored in the flash memory 64.
If the answer is yes then the step 198 displays an alphanumeric key pad
and prompts the user to enter the password. The processor 56 then
compares the entered password with the password stored in flash
memory 64 at 200. The processor 56 determines if the passwords
entered and stored match at 202 and in the event that there is no match
the process either ends or returns to the main menu 204 thereby rejecting
the request to create or edit the password. In the event the decision box
202 comes out in a positive answer or in the event the decision box 196
indicates that there is no existing password, then the process at 206
displays an alphanumeric keypad and prompts the user to enter a new
password. The new password is then stored in the memory 60 at 208 and
the process displays for a second time the alphanumeric keypad and
prompts the user to re-enter the new password at 210. The processor
compares the entered and re-entered passwords at 212. A decision on the
password matching is made at step 214. In the event that these
passwords do not match then the system initiates the password editing or
creating procedure once again by returning to process box 206. In the
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
-22-
event the decision from the matching of the passwords at 214 is positive
then the password is stored in a flash memory 64 at step 216 and the
create/edit password routine is ended at 218.
In the event the user wishes to create a new or another symmetrical
key in the process the user simply chooses this selection at 170 (Figure
11) which causes the processor 58 and random number generator 60 to
generate the symmetrical key at 184. The symmetrical key is stored in a
flash memory 64 at 186 and the process comes to an end at 188.
With respect to the generation of the asymmetrical keys the user
selects item 172 from Figure 9 and Figure 12 shows the process of the
processor 58 and random number generator 60 generating the
asymmetrical keys or private and public keys at 190, and storing the keys
information in flash memory 64 at 192 and bringing the procedure to an
end at 194. There is no password protection associated with this
procedure since this key information is a feature that is proprietary to the
cryptographic token 24 and the more frequently the key is changed the
better. Hence it is a step that is made simple for the user to effectively
change the key.
Referring to Figure 7, when the log in procedure is chosen at 162
then a log in procedure or method is shown in Figure 14. The processor
asks if the password is stored in the flash memory at 238 and in the event
that there is an affirmative answer the processor at 240 displays the
alphanumeric keypad and prompts the user to enter the password. At 242
the system compares the entered password with the stored password and
if there is no match it brings the log in procedure to an end at 244
without enabling the cryptographic token 24. In the event that there is an
affirmative decision from decision box 242 then the process continues to
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
- 23 -
step 246. In the event that there is no password stored in the memory to
begin with at 238 then step 246 is implemented immediately. Step 246
calls for the user to be prompted to enter an ideogram signature
information 92 on the contact sensitive graphical interface 50.
The authentication processor 56 at step 248 applies the pattern
recognition algorithm to the ideogram signature information 92 to create
the new pattern. The comparator 58 compares the new ideogram
signature information pattern with the user identification template stored
at the flash memory 64 at step 250. At decision box 252 a decision is
made as to whether the pattern matches the user identification template
and in the event the answer is no, then the system simply ends the login
procedure without enabling the cryptographic token 24 at step 244. In
the event there is a positive match at step 252 the processor enables itself
at step 254 to communicate over the data bus 74 with the connection
interface port 3 8 of the cryptographic token 24. Next the system brings
the sign on or login procedure to an end at step 244. Once the
cryptographic token 24 is enabled, then it is in a position to make
available its cryptographic key information to the Internet security
module 32.
Referring now to Figure 6 the Internet security module 22 is
shown. The Internet security module 22 has its own power conditioning
circuit 100 connected to a battery backup 102 and through a power input
line 104 to a wall plug adapter 106. The power conditioning circuit 100
regulates the power supply to the Internet security module 22. The
power conditioning circuit 100 has a power output line 108 which is
connected to the hardware components located within the Internet
security module 22 to provide sufficient power to these components.
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
-24-
The Internet security module 22 preferably had a touch sensitive liquid
crystal display 110 connected through a data bus 114 to main processor
112. The liquid crystal display displays to the user the activities of the
Internet security module 22 during the operation of the Internet security
module 22. The main processor 112 is an xx86 class processor. This
processor is connected through data bus 120 to a cryptographic co-
processor 116 and a real time clock and random number generator 118.
The cryptographic co-processor and real time clock and random number
generator accelerate the application of the encrypting and decrypting
protocols to the data main processor 112 to the telephone line 28. The
main processor 112 is further connected through to LED 128 and an
audible signal beeper 130. Memory for the main processor is connected
through a flash memory 132 which stores programs and other keys. The
Internet security module 122 further includes a scratch pad and random
access memory 134 for temporary storing calculations made by the main
processor 112. The main processor 112 is further connected through
signaling ports 124 to a universal serial bus interface 122 or an RS/232
serial interface 122. These interfaces are connected to the
communication ports 18 to the first computer 12. The main processor
112 is further connected through a communication line 126 to the PC
card host interface or having the hardware receiving slot 32. The
diagram shows the cryptographic token 24 connected through the PC
card interface for communicating data.
The main processor manipulates a data signal coming from the
computer 12 through the input or interface port 122 and the
communication lines 124 with an encrypting and decrypting algorithm
provided in the co-processor 116 and random number generator 118.
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
- 25 -
This data is further encoded with the key information made available by
the cryptographic token 24. The information encrypted is then
transmitted from the main processor 112 through the modem 138 and the
output 26 to the telephone line 28 and thus onto the Internet. In the event
the cryptographic token 24 is not present, then the main processor 112
performs no encryption or decryption of signals passing through the
main processor between the telephone line 28 and the first computer 12.
The main processor 112 also decrypts data received from the computer
12.
The flash memory 132 stores cryptographic keys received from the
cryptographic token 24. When the token 24 is removed from the Internet
security module 22, the keys are erased from the flash memory 132. In
the event the module 22 is subject to intrusion, the tamper circuit 136
sends a signal to the flash memory 132 to erase the memory 132.
Referring to Figure 15 a block diagram of an alternative
embodiment for the cryptographic token 24 of Figure 2 is shown. The
components of the cryptographic token card 24 of Figure 15, including
their reference numerals and functionality are identical to that shown and
described for Figure 2 except for the differences explained hereafter. In
Figure 15 the block diagram of the cryptographic token card differs in
that it relies on the power from the security module 22 of Figure 6 at line
46 of Figure 15. The power from security module 22 is fed through the
hardware receiving port 32 of the security module at connecting line 46
into the power conditioning circuit 44 of the cryptographic token card
24. In this embodiment, the cryptographic token card 24 preferably
comprises either an IC card or a Smart Card. As a result of the
cryptographic token card 24 having to rely on a source of power from the
CA 02296208 2000-O1-17
2AB0009A
-26-
security module 22, or an other power source, the cryptographic token
card 24 must be coupled to the security module 22, or the other power
source, so as to operate the cryptographic token card 24 in accordance
with the method of operation previously described for Figures 2 to 5 and
7 to 14.
As is apparent from the foregoing disclosure, various other
embodiments and alterations and modifications which may differ from
the embodiments disclosed may be readily apparent to one skilled in the
art. It should be understood that the scope of the patent shall be defined
by the claims and those embodiments which come within the scope of
the claims that follow.