Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02296631 2000-O1-19
Broadcasting Encrypted Messages Using Session Keys
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates generally to the field of data encryption. In
particular, the
invention relates to a system for broadcasting encrypted data to multiple
recipients.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Encryption involves encoding a message using a small secret in such a way that
an entity
knowing the secret can recover the message, while an entity that does not know
the secret cannot
recover the message in a reasonable amount of time. There are well-known
encryption schemes
that enable a single sender to encrypt a message for a single recipient
provided the sender and
the recipient share a secret. These schemes, however, are not well adapted to
situations where
a single sender desires to send an encrypted message to multiple recipients.
PGP and SMIME are the most common email techniques used for encrypting
Internet
email messages. The usual approach taken when the same message is sent to more
than one
recipient is to encrypt the message multiple times. First, the message is
encrypted using a secret
shared between the sender and the first recipient and then the encrypted
message is sent to the
first recipient. Next, the sender encrypts the message a second time for a
second recipient using
a secret shared between the sender and the second recipient and sends the
second encrypted
message. This process is repeated until the message has been encrypted for
each intended
recipient using the unique secret shared between that intended recipient and
the sender and the
encrypted messages have been transmitted. In a communication environment where
bandwidth
(information channel capacity) is limited, such as in a wireless
communications environment,
sending multiple versions of the same message wastes resources, is very
costly, highly inefficient
and very slow. Additionally, data terminals, such as cellphones, PDAs and two-
way pagers,
communicating via wireless communications networks tend to have considerably
less processing
power than typical data terminals, such desktops and workstations, connected
to the Internet;
-1-
CA 02296631 2000-O1-19
hence, multiple re-encryption associated with traditional encryption
methodologies pose
significant processing power demand on wireless data terminals - which is
undesirable.
Therefore, there remains a need in this art for a more efficient method for
sending the
same encrypted message to multiple recipients. There remains a more particular
need for a
system that allows a sender to broadcast an encrypted message a single time
for receipt by
multiple intended recipients whereby each intended recipients can decrypt the
message and an
unintended recipients will be impeded in its effort to decrypt the message.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention overcomes the problems noted above and satisfies the
need in this
field for a system that allows a sender to broadcast an encrypted message a
single time for receipt
and decryption by multiple intended recipients.
The present invention has many advantageous features. Not all of these
features are
simultaneously required to practice the invention as claimed, and the
following list is merely
illustrative of the types of benefits that may be provided, alone or in
combination, by the present
invention. These advantages include: (1) bandwidth savings through the use of
the system; (2)
the system's adaptability to different mail address types; (3) providing a
mechanism by which
all intended recipients can decrypt the message while impeding the efforts of
unintended
recipients from decrypting the message; (4) providing a system in which
information about an
intended recipient's secret or decryption key is not leaked to another
intended recipient or to any
other individual; and (5) the system's flexibility which allows its use with
both public key
(asymmetric), private key (symmetric) encryption schemes or some hybrid
combination thereof.
In accordance with the present invention, a device for sending encrypted data
to multiple
recipients is provided. The description in this paragraph assumes a sender
aims to transmit a
message to two intended recipients. A more general description is provided in
the case when
sending to more than two intended recipients. The device comprises a message
recorder, an
-2-
CA 02296631 2000-O1-19
encryptor, and a transmitter. The message recorder is operative to store a
message to be sent to
a first recipient and to a second recipient. The encryptor is operative to
encrypt the message
thereby generating a first encrypted message. The encryptor is also operative
to: select a session
key, encrypt the message using the session key thereby generating the first
encrypted message,
encrypt the session key with a first secret thereby generating a first
encrypted session key,
encrypt the session key with a second secret thereby generating a second
encrypted session key,
and generate a second encrypted message comprising the first encrypted session
key, the second
encrypted session key and the first encrypted message. The transmitter is
operative to transmit
the second encrypted message.
Also, provided is a method for encrypting a message to be sent by a sender to
multiple
recipients. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a session key;
encrypting the message
using the session key to generate a first encrypted message; encrypting the
session key using a
first secret thereby generating a first encrypted session key; encrypting the
session key using a
second secret thereby generating a second encrypted session key; encrypting
the session key
using a third, fourth, , n-th secret thereby generating a third, fourth, , n-
th encrypted session key,
respectively; and broadcasting an outgoing message comprising the first
encrypted message, the
first encrypted session key, and , the second, third, fourth, , n-th encrypted
session keys.
Also, in accordance with the present invention, a method for retrieving a
message is
provided. The method comprises the steps of: acquiring an encrypted message;
searching the
encrypted message for a first encrypted session key; decrypting the first
encrypted session key
to retrieve a session key; and decrypting a message block in the encrypted
message using the
retrieved session key. In one embodiment the "decrypting the first encrypted
session key" step
comprises the step of using a secret shared with the sender of the message to
decrypt the first
encrypted session key. In another embodiment the "searching the encrypted
message step"
comprises the steps of locating a globally unique identification that
corresponds to the recipient
and locating a first encrypted session key that corresponds to the globally
unique identification.
-3-
CA 02296631 2003-02-03
According to another aspect of the invention, there is provided a device for
sending
encrypted data to multiple recipients comprising: a message recorder that is
operative to
store a message to be sent to a plurality of recipients; an encryptor that is
operative to:
select a random session key, encrypt the message using the random session key
thereby
generating a first encrypted message, produce a plurality of encrypted session
keys each of
which comprises the random session key encrypted with a secret unique to a
respective
recipient, and generate a second encrypted message comprising the plurality of
encrypted
session keys and the first encrypted message; and a transmitter that is
operative to transmit
the second encrypted message.
According to another aspect of the invention, there is provided a method for
encrypting a message to be sent by a sender to multiple recipients comprising
the steps of
acquiring a session key; encrypting the message using said session key to
generate a first
encrypted message; encrypting said session key using a first secret thereby
generating a
first encrypted session key; encrypting said session key using a second secret
thereby
generating a second encrypted session key; generating an outgoing message
comprising
said first encrypted message, said first encrypted session key, and said
second encrypted
session key; and broadcasting the outgoing message comprising said first
encrypted
message, said first encrypted session key, and said second encrypted session
key.
According to yet another aspect of the invention, there is provided a method
for
encrypting a message to be sent by a sender to multiple recipients comprising
the steps of
acquiring a first globally unique identification for a first intended
recipient; acquiring a first
secret wherein said first secret is a secret shared between the sender and the
first intended
recipient; acquiring a second globally unique identification for a second
intended recipient;
acquiring a second secret wherein said second secret is a secret shared
between the sender
and the second intended recipient; acquiring a random session key; encrypting
the message
using said session key to generate a first encrypted message; encrypting said
session key
using a first secret thereby generating a first encrypted session key;
encrypting said session
key using a second secret thereby generating a second encrypting session key;
generating
an outgoing message comprising said first globally unique identification, said
first
encrypted session key, said second globally unique identification, said second
encrypted
session key, and said first encrypted message; and broadcasting the outgoing
message
According to yet another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a
method
for retrieving a message by a recipient comprising the steps of acquiring an
encrypted
message; searching said encrypted message for a first encrypted session key;
decrypting
-3a-
CA 02296631 2003-02-03
said first encrypted session key to retrieve a session key; and decrypting a
message block in
said encrypted message using said retrieved session key.
According to a further aspect of the invention, there is provided a method for
a
single recipient to decrypt a message broadcasted to multiple recipients
comprising the
steps of acquiring the broadcasted message; locating in the message a globally
unique
identification that corresponds to the recipient; locating a first encrypted
session key that
corresponds to said globally unique identification; decrypting said first
encrypted session
key to retrieve a session key using a secret shared with a sender of the
broadcasted
message; and decrypting a message block in the broadcasted message using said
retrieved
session key.
According to a further aspect of the present invention, there is provided a
method
for exchanging encrypted messages between a sender and a first intended
recipient and the
sender and a second intended recipient comprising the steps of acquiring a
random session
key; encrypting a message using said session key to generate a first encrypted
message;
encrypting said session key using a first secret shared between the sender and
the first
intended recipient thereby generating a first encrypted session key;
encrypting said session
key using a second secret shared between the sender and the second intended
recipient
thereby generating a second encrypted session key; generating an outgoing
message
comprising a first globally unique identification for the first intended
recipient, said first
encrypted session key, a second globally unique identification for the second
intended
recipient, said second encrypted session key, and said first encrypted
message;
broadcasting the outgoing message; acquiring said broadcasted outgoing message
by the
first intended recipient; locating in the broadcast message said first
globally unique
identification; locating said first encrypted session key that corresponds to
said first
globally unique identification; decrypting said first encrypted session key to
retrieve said
session key using said first secret; and decrypting a message block in said
broadcasted
message using said retrieved session key.
According to a fizrther aspect of the present invention, there is provided a
device for
sending encrypted data to multiple recipients comprising: a message recorder
that is
operative to store a message to be sent to at least a first recipient and a
second recipient; an
encryptor that is operative to select a random session key, encrypt the
message using the
random session key thereby generating a first encrypted message, encrypt the
session key
with a first secret thereby generating a first encrypted session key, encrypt
the session key
with a second secret thereby
-3b-
CA 02296631 2003-02-03
generating a second encrypted session key, and generate a second encrypted
message
comprising the first encrypted session key, the second encrypted session key
and the first
encrypted message; and a transmitter that is operative to transmit the second
encrypted
message.
According to yet a further aspect of the present invention, there is provided
a
method for encrypting a message to be sent by a sender to n recipients
comprising the
steps of (1) acquiring a session key; (2) encrypting the message using the
session key to
generate a first encrypted message; (3) encrypting the session key using a
secret
associated with a recipient thereby generating an encrypted session key; (4)
repeating step
(3) n-1 times thereby generating a plurality of unique encrypted session keys;
(5)
generating an outgoing message comprising the encrypted session keys and the
encrypted
message; and (6) broadcasting the outgoing message comprising the encrypted
session
keys and the encrypted message.
According to yet a further aspect of the present invention, there is provided
a
system for sending encrypted information to multiple recipients, comprising:
means for
selecting a session key; information encrypting means for encrypting
information using
the session key to thereby generate an encrypted message; key encrypting means
for
generating a plurality of encrypted session keys by encrypting the session key
using each
of a plurality of unique keys associated with the multiple recipients; means
for
assembling the encrypted message and the plurality of encrypted session keys
into a
transmission message; and a transmitter for transmitting the transmission
message.
According to still another aspect of the present invention, there is provided
a
device for decrypting a message broadcasted to a plurality of receivers,
comprising:
means for receiving the broadcasted message; means for searching a plurality
of
encrypted session keys in the broadcasted message to locate a particular
encrypted session
key; key decrypting means for decrypting the particular encrypted session key;
and
information decrypting means for decrypting a portion of the received message
using the
session key.
According to a yet another aspect of the present invention there is provided
a computer-readable program code stored in a computer readable medium, said
computer
readable program code executable on a computer to instruct the computer to
execute the
steps of selecting a session key; encrypting information using the session key
to thereby
generate encrypted information; for each of a plurality of intended receivers
to which the
information is to be sent, encrypting the session key using a unique secret
associated with
-3c-
CA 02296631 2003-02-03
each intended receiver to thereby generate a plurality of encrypted session
keys; and
combining the encrypted information and the plurality of encrypted session
keys into a
single message for transmission to the plurality of intended receivers.
According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a computer
readable program code stored in a computer-readable program medium said
computer
readable program code executable on a computer to instruct the computer to
execute the
steps of searching a plurality of encrypted session keys in a received message
for a
particular encrypted session key; upon detecting the particular encrypted
session key,
decrypting the particular encrypted session key; and decrypting a portion of
the received
message using the session key.
-3d-
CA 02296631 2000-O1-19
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The present invention will become apparent from the following description when
read
in conjunction with the accompanying drawings wherein:
FIG. 1 illustrates in block diagram form a system in which the principles of
the present
invention may be practiced;
FIG. 2 illustrates in flow diagram form a preferred algorithm for implementing
an
encryption method according to present invention;
FIG. 3 illustrates in flow diagram form a preferred algorithm for implementing
a
decryption method according to present invention;
FIG. 4 illustrates an exemplary generalized encrypted message block generated
in
accordance with the present invention;
FIG. 5 illustrates a more specific exemplary encrypted message block generated
in
accordance with the present invention;
FIG. 6 illustrates another example of the application of the present invention
in a
pay-per-use data communication broadcast; and,
FIG. 7 illustrates in flow diagram form a preferred algorithm for the method
of FIG. 2 as
applicable for an n-plurality of recipients.
-4-
CA 02296631 2000-O1-19
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
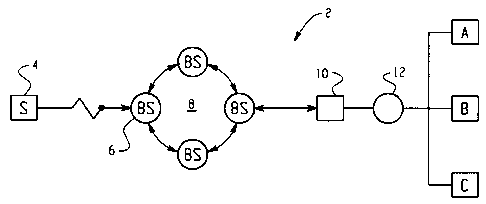
Refernng now to the drawings, Figure 1 sets forth generally a system 2 in
which the
present invention is useful. The inventive method allows a sender S to
transmit a single encrypted
message to multiple intended recipients through normal communication channels
and provides
each intended recipient with the ability to decrypt the encrypted message
using a unique secret
that that intended recipient shares with the sender S. A typical system for
which the present
invention is useful is a low bandwidth system such as one that utilizes an RF
link in the
communication path. Email or data communication systems having message
packaging and
redirection management being operative may also utilize the present invention.
An example of
such a system is set forth in co-pending United States Patent Application No.
09/087,623 titled
"System and Method for Pushing Information From a Host System to a Mobile Data
Communication Device". This application is hereby incorporated into this
disclosure by
reference. The system and method for pushing information from a host system to
a mobile
device described in the application is a preferred system and method for the
present invention
herein; however, it is to be understood other types of systems and methods
could be implemented
that utilizes the present invention.
In accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention, a sender S
transmits
an encrypted message once using a transmission device 4, such as a cellphone,
PDA or two-way
pager, to a base station 6 that is part of a communication network 8. The
message is forwarded
through the communication network 8 to a gateway device 10. The gateway device
10 transfers
the message from the network 8 to a wide area network 12 such as the Internet.
Intended
recipients A and B through their respective Internet connection method receive
the message
transmitted by the sender S. The intended recipients A and B then, using the
decryption method
of the present invention, decrypt the message. An unintended recipient C, who
may intercept the
message, however is impeded from deciphering the message because the
unintended recipient
C lacks a secret to decrypt the message. An important advantage of the
inventive method is that
-5-
CA 02296631 2000-O1-19
by only sending the message once bandwidth is saved. It is be understood that
although the
description herein generally refers to the present invention in application
with messages,
specifically email messages ,the present invention in no way is limited to the
application of such
messages, but may include any form of data communication or datagram that
require secures
transmission to the intended recipients.
The preferred transmission device 4 comprises a message recorder, an
encryptor, and a
transmitter. The device circuit is preferably configured to operate as a
wireless transceiver, such
as a two paging computer, a portable electronic messaging device or a hand-
held email client.
An example of such a device is set forth in co-pending United States Patent
Application No.
09/106,585 titled "Hand-Held Electronic Device With A Keyboard Optimized for
Use With the
Thumbs". This application is hereby incorporated into this disclosure by
reference. Although
this is the preferred circuit for such a device, other types of circuits could
be utilized in the
present invention.
The message recorder is operative to store the message that is to be sent to a
plurality of
intended message recipients. The message recorder could comprise a memory
element such as
RAM, a tape storage element, a disk storage medium, CD ROM storage medium or
other
mediums capable of use for storing a message entered by a sender. The message
could be in a
number of forms such as text, voice or others.
The encryptor is operative to encrypt the message thereby generating a first
encrypted
message. The encryptor could be composed of a number of different devices such
as a
microprocessor or other digital circuit, or could reside in programming that
performs the
encryption steps. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the
encryptor is software
residing in the device 4. The encryptor performs the encryption function by
(1) selecting a
session key, (2) encrypting the message using the session key thereby
generating the first
encrypted message and (3) encrypting the session key multiple times. This
latter step (3)
involves the encryptor encrypting the session key once using each secret that
the sender shares
-6-
CA 02296631 2000-O1-19
with the intended recipients thereby generating multiple encrypted session
keys. The encryptor
also at step (4) performs another encryption step thereby generating a second
encrypted message
which comprises all encrypted session keys and the first encrypted message. A
more detailed
description of the encryption algorithm is discussed below.
The transmitter is operative to transmit the second encrypted message. The
transmitter
could comprise a number of different devices such as an rf transmitter, a
modem, an optical
transmitter, and others that are capable of forwarding the encrypted message
to a network so that
it can be routed to the intended recipients.
An exemplary transmission device 4 is a two-way communications device such as
a cell
phone, two-way pager or PDA but other devices such a pay-per-view television
broadcast station
or satellite could be used as shown in Figure 6. In the pay-per-view
television broadcast
embodiment, a television show 60 to be broadcasted is encrypted once with a
single randomly
generated session key. Sometime before the encrypted show is to be broadcast,
the session key
is encrypted once for each paying customer and these (suitably labeled)
encrypted session keys
62, 64 broadcast. Paying customers would be able to acquire the session key by
monitoring the
list of encrypted versions of the session key, identifying the version
encrypted using their master
key, then decrypting the value. Hence, the show could then be broadcast once
in encrypted form.
An exemplary algorithm for sending an encrypted message according to one
aspect of the
invention is illustrated in flow chart form in Figure 2. In the preferred
system, the sender S and
a first intended recipient A share a secret K, and the sender S and a second
intended recipient B
share a secret L. In this preferred system, the first intended recipient A
does not know the secret
L and the second intended recipient B does not know the secret K. Finally, in
this preferred
system an unintended recipient C does not know the secret K or the secret L.
First, the sender S generates a random number to use as a session key R at
step 20. At
this point the randomly chosen session key R is only known to the sender S.
The sender S, then,
encrypts a message M once using the randomly chosen session key R to generate
an encoded
_7_
CA 02296631 2000-O1-19
message Ml at step 22. Next, the sender S encrypts the session key R
repeatedly using each
intended recipient's secret. The sender S, first, encrypts the session key R
using the secret K to
generate a first encoded session key Rl at step 24 and then encrypts the
session key R using the
secret L to generate a second encoded session key R2 at step 26. Finally, the
sender S transmits
an encoded message MZ which comprises a single copy of the encoded message Ml,
a copy of
the first encoded session key Rl, and a copy of the second encoded session key
R2 at step 28.
Optionally, a sender S could also include in the encoded message M2 a copy of
an ID for each
intended recipient to assist each intended recipient in identifying the
encoded session key
generated for the specific intended recipient. This system has been described
in terms of a single
sender S and two intended recipients A and B. However, one skilled in the art
could modify the
system for use with any number of recipients as illustrated in Fig. 7.
An exemplary algorithm for decrypting the message Ml according to another
aspect of
the invention is illustrated in flow chart form in Figure 3. To decrypt the
message Ml, the
intended recipients A and B use their secrets, K and L, respectively, to
decrypt the encrypted
session keys Rl and R2, respectively, to decrypt and recover the session key
R. The intended
recipients A and B then use the randomly chosen session key R to decrypt and
recover the
message M. Specifically, recipient A identifies the encrypted session key Rl
at step 30.
Recipient A then uses the shared secret K to decrypt and recover the randomly
chosen session
key R from the first encoded session key Rl at step 32. Recipient A then uses
the randomly
chosen session key R to decrypt the message Ml to generate the original
message M at step 34.
Recipient B decrypts the message Ml in a similar manner. First, recipient B
identifies the
encrypted session key R2 at step 30. Recipient B then uses the shared secret L
to recover the
randomly chosen session key R from the second encoded session key R2 at step
32. Recipient
B then uses the randomly chosen session key R to decrypt the message Ml to
generate the
original message M at step 34.
_g_
CA 02296631 2000-O1-19
An unintended recipient C who does not know either K or L cannot use either
the first
encoded session key Rl or the second encoded session key R2 to recover the
randomly chosen
session key R. Without the knowledge of the randomly chosen session key R, the
unintended
recipient C will be impeded in its effort to decrypt the message Ml to recover
the message M.
The algorithm for decrypting the message Ml optionally could include the
following
technique to assist recipient A in identifying the encrypted session key Rl
and recipient B in
identifying the encrypted session key R2. This technique is made clear in the
discussion below
describing the format of the transmitted message.
Figure 4 illustrates in block diagram form an exemplary, generalized encrypted
message
block that could be generated using the present invention. The exemplary
message block
comprises a header section 40 and a data section 42. The exemplary header
section comprises
a secret identifier block 44 for each intended recipient and a terminator
block 46. Each secret
identifier block 44 includes an identifier field 48 for the recipient and an
encoded session key
field 50 for the recipient. The identifier field 48 contains a globally unique
identifier for the
intended recipient to which that secret identifier block 44 is addressed. The
encoded session key
field 50 includes the encoded session key that has been encrypted using the
secret of the intended
recipient to which that block is addressed.
The inclusion of a secret identifier block 44 with each encrypted secret
allows each
intended recipient to immediately identify which encrypted header block should
be decrypted to
retrieve the value R used to encrypt the message. An example of a data block
that has been
generated according to one aspect of the present invention is shown in Figure
5.
While the present invention has been described with reference to a symmetric
key
scheme, one skilled in the art would recognize that the present invention
could be applied in both
a symmetric key scheme and in a public key scheme. In a symmetric key scheme,
for each pair
comprising the sender and a recipient, there is a common master key known to
both parties. In
a symmetric key implementation, the shared secret referred to in the present
invention is the
_9_
CA 02296631 2000-O1-19
master key known to both the sender and a single intended recipient. The
session key can thus
be passed from the sender to the recipient by encrypting the session key with
the shared master
key (for that recipient) and attaching the encrypted session key to the
encrypted message. A
suitable identifier is required so that the recipient can identify which
version of the session key
should be decrypted with its master key.
The present invention also works when used with a public key scheme. In a
public key
scheme, each party (sender and recipients) generates a public key/private key
pair. The public
key is published (made available globally) by placing it into a database
(commonly known as a
certificate authority). The corresponding private key is kept secret by the
party that generated the
pair. The fundamental idea behind a public key scheme is that (a) there is no
way to derive the
private key simply from knowledge of the public key, and (b) data encrypted by
one key of the
pair can only be decrypted using the other lcey of the pair. In order to
exchange a session key, the
sender encrypts the session key with the public key of the intended recipient.
The intended
recipient is the only party with access to the corresponding private key that
can be used to
decrypt, and thus recover, the session key. The "shared secret" referred to in
the present invention
is thus the combination of the senders knowledge of the recipient's public key
and the recipient's
knowledge of the corresponding private key. This invention only requires the
ability to pass a
session key from the sender to the intended recipients.
The bandwidth saving the can be achieved through the use of the present
invention can
be illustrated using the following example. For illustrative purposes, it can
be assumed that a
piece of encrypted data has the same size as the original (unencrypted) data.
Therefore, a
transmitted encrypted message M2 is approximately equal to twice the size of
the randomly
chosen session key R plus the size of the encrypted message Ml. Using example
sizes of
randomly chosen session key R being 20 bytes and the encrypted message Ml
being 2048 bytes,
this yields a transmitted encrypted message M2 of 2 x 20 + 2048 = 2088 bytes.
On the other
hand, if the encrypted message Ml were sent twice, once to recipient A and
once to recipient B
- 10-
CA 02296631 2000-O1-19
as is done in the prior art methods, the size of the encrypted messages sent
would be 2 x 2048
= 4096 bytes.
The present invention has the following additional advantages. The present
invention
provides a system whereby an unintended recipient C is impeded from recovering
the message
M. The present invention provides a system whereby the unintended recipient C
is prevented
from learning anything about secrets K or L. The present invention also
provides a system
whereby recipient A is prevented from learning anything about secret L and
recipient B is
prevented from learning anything about secret K. The present invention also
provides a system
with the capability to send an encrypted message to recipients having
different address types.
Having described in detail the preferred and alternate embodiments of the
present
invention, including the preferred modes of operation, it is to be understood
that the invention
. is capable of other and different embodiments, its several details are
capable of modifications in
various respects, and its operation could be carried out with different
elements and steps, all
without departing from the spirit of the invention. The drawings and
description of the preferred
and alternate embodiments are presently only by way of example and are be
regarded as
illustrative in nature and are not meant to limit the scope of the present
invention which is
defined by the following claims.
-11-