Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02303789 2000-03-13
WO 99/2139? PCT/GB98103131
1
RESONANT MODE PANEL-LOUDSPEAKERS
Z~ DESCRIPTION
TECHNICAL FIELD
The invention relates to loudspeakers and more
particularly to panel-form loudspeakers of the kind adapted
to be excited by launching bending waves into a resonant
panel to cause . it to resonate to produce an acoustic
output. Such loudspeakers are described in our
International patent application W097/09842, and are known
as distributed mode loudspeakers.
BACKGROUND ART
In conventional pistonic loudspeakers, a movincr
diaphragm, usually a cone, is held in position on a frame
or chassis by at least one flexible member which forms a
resilient suspension. This suspension performs at least the
following functions, namely:-
CA 02303789 2000-03-13
WO 99/21397 PCTIGB98/03131
2
1. location in the frame of an assembly comprising
the diaphragm and a vibrator usually including a
moving coil motor;
2. allows motion of the diaphragm in an axial
direction but restrains motion in directions
normal to the axis, and
3. provides a degree of damping to vibration of the
diaphragm by means of its material choice and
treatment.
These requirements are usually met by a flexible
corrugated moulded member, sometimes known as a roll
surround, usually made from a rubber-like material, which
is connected between the outer periphery of the diaphragm
and the surrounding frame and a corrugated flexible member,
sometimes known as a spider, which is connected between the
region of the diaphragm apex and the frame. Although not
always used, the common execution with two separate
suspension members gives satisfactory performance in the
three functions listed above. In the case of traditional
moving coil loudspeakers the attachment of suspensions at
other positions will introduce unwanted resonances and
disturb the vibrational characteristics of the diaphragm.
It is among the obj ects of the invention to provide a
suspension adapted to the needs of a resonant panel
loudspeaker. In the case of a resonant panel loudspeaker we
have discovered that a number of regions exist within the
panel which have low .average velocities by reason of the
inherent nature of the panels and have concluded that it
CA 02303789 2000-03-13
WO 99/21397 PCTIGB98/03131
3
might be possible to locate a suspension at or near these
panel positions and that the low velocity in such regions
will mean that the suspension will have little or no effect
on the vibrational characteristics of the panel as a whole.
DISCLOSURE OF INVENTTON
According to one aspect of the invention there is
provided a resonant panel-form loudspeaker comprising
suspension means located wholly in one or more panel
regions of low average velocity. Such suspension means may
be used to suspend the panel in a support and/or to support
a vibration exciter on the panel.
The support may comprise a surrounding area of the
panel, which surrounding region may be acoustically
inactive. The resonant panel-form loudspeaker may comprise
a panel having an acoustically active area and panel
regions of low average velocity surrounding the
acoustically active area, with slots or grooves in the
panel structure defining the acoustically active area. The
slots or grooves may be such that they extend only partly
through the panel structure.
Thus the idea of using low energy regions of the
panel for the mechanical support of the panel itself or of
an exciter on the panel may be extended to include the use
of slots or through incisions in the panel for the purpose
of areal definition of a desired acoustically active panel
area for distributed mode operation or at least desired
acoustic vibration behaviour set within, or as a part of a
larger panel component. Such slotting will, for example,
CA 02303789 2000-03-13
WO 99/21397 PCT/GB98103131
4
permit a wide range of distributed mode type vibrating
panels to be produced as an integrated design with
arbitrarily formed and contoured vehicle trim panels. The
slots may be of any suitable form or shape consistent with
the desired vibration behaviour in the required frequency
range. FEA (finite element analysis) techniques facilitate
the rapid design and analysis of indicated slot perimeter
shape and resulting geometric forms.
The low vibration energy in the suspension regions
has the benefit of allowing the use of stronger suspension
elements than would otherwise be possible, so increasing
the durability of the resulting assembly.
A compliant suspension may be created by incising the
panel to form integral finger-like cantilever members. The
incisions may comprise a parallel pair of slots through the
panel structure. The cantilever members may be straight or
otherwise, e.g. curved. As concerns a suspension for a
vibration exciter, straight cantilevers might be preferred
in order better to span the distance between areas of low
average velocity and a region of high activity where the
exciter is coupled to the panel. The suspension may
consist of an array of such cantilever members. Thus the
panel may be incised to form cantilever members which
retain stiffness in the plane of the panel and which are
compliant in the plane of a frame or the like supporting
the panel. Alternatively or additionally a separate
compliant suspension e.g. of a rubber-like material may be
fixed, e.g. by means of an adhesive, to the panel in the
CA 02303789 2000-03-13
WO 99!21397 PCTIGB98/03131
said regions) of low average velocity. Where the rubber-
like suspension is used in addition to the cantilevers, the
rubber-like suspension may be mounted on the cantilevers.
The resonant panel-form loudspeaker may comprise a
5 distributed mode acoustic radiator, e.g. of the kind
defined in International patent application W097/09842.
From another the invention is a decorative trim panel,
e.g. for a vehicle or the like and incorporating a
loudspeaker as defined above.
From a further aspect, the invention is a vehicle,
e.g. an automobile, comprising a loudspeaker as defined
above or a decorative trim panel as defined above.
From yet another aspect the invention is a method of
making a resonant panel acoustic device characterised by
identifying the location of at least one panel region of
low average velocity and positioning suspension means
within the said region(s).
The method may comprise defining an acoustically
active area of the panel by locating panel regions of low
average velocity surrounding the acoustically active area
and disrupting the panel structure in the said regions to
form panel suspension means. The method may comprise
defining the acoustically active area by slotting the panel
structure. The slots may be such that they extend only
partly through the panel structure.
Where the suspension is intended for supporting a
vibration exciter, the method may further comprise
identifying the desired panel location, e.g. an anti-node,
CA 02303789 2000-03-13
WO 99/21397 PCT/GB98/03131
6
for coupling the vibration exciter to drive the panel, and
identifying one or more nodal regions adjacent to the drive
location in which to position the exciter suspension.
The method may comprise incising the panel material to
define cantilevers forming the suspension means. The
suspension means may be such as to have at least three
cantilevers.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS
The invention is diagrammatically illustrated, by way
of example, in the accompanying drawings, in which:-
Figure 1 is a cross-sectional side view through part
of a resonant panel-form loudspeaker and showing a
suspension for a vibration exciter;
Figure 2 is an underneath plan view to smaller scale
of the resonant loudspeaker panel of Figure 1;
Figure 3 is an underneath plan view of a resonant
loudspeaker panel showing three embodiments of vibration
exciter suspension;
Figure 4 is a plan view of a panel incorporating a
resonant panel-form loudspeaker;
Figure 5 is a scrap plan view, to an enlarged scale,
of detail ~A' of Figure 4, and
Figures 6 and 7 are alternative scrap cross-sectional
views on the line A-A of Figure 5.
B~.'s'2' Mnn~'..~' FC1R C'~1?TwTAT!"- fITTT mTST, -rwrcsc~mmr~,,,
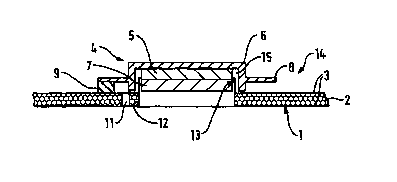
In the drawings, and referring more particularly to
Figures 1 and 2, there is shown a resonant panel-form
loudspeaker 14 e.g. of the general kind described in
CA 02303789 2000-03-13
WO 99/21397 PCT/GB98/03131
7
International patent application W097/09842 and comprising
a resonant generally rectangular flat panel 1 usually of a
stiff lightweight material forming an acoustic radiator and
an inertial vibration exciter 4 mounted on the panel 1 to
induce bending wave vibration in the panel to cause it to
resonate to produce an acoustic output. The panel may be
of monolithic construction, but as shown comprises a
cellular core 2 sandwiched between opposed face skins 3.
The inertial vibration exciter 4 comprises a voice
coil/tubular coil former assembly 13 mounted, e.g. by
bonding in a circular aperture 12 in the panel 1 whereby
the assembly 13 extends from one face of the panel (the
upper face as shown in Figure 1) and projects into an
annular gap 15 in a magnet assembly 5,6,7 and defined
between a disc-like pole piece 7 and a pole cap 6 which
together sandwich a disc-like magnet 5.
The assembly comprising the magnet 5 and poles 6 and 7
is mounted on the panel 1 for axial movement relative to
the coil/former assembly 13, when the coil is energised
with a signal, on a compliant suspension attached to an
annular flange 8 projecting from the cup 6 and comprising
three equi-spaced rubber-like pads 9, only one of which is
visible in Figure 1. In turn the pads 9 are mounted on
finger-like cantilevers 10 formed by incising U-shaped
slots 11 through the panel and equi-spaced round and
concentric with the aperture 12 as best can be seen in
Figure 2 in panel regions of low average velocity, such
that the inner ends 16 of the cantilevers are free for
CA 02303789 2000-03-13
WO 99121397 PCT/GB98/03131
8
movement normal to the plane of the panel 1.
The pads 9 are attached near to the free ends 16 of
the cantilevers 10. It will be understood that, if
desired, the pads 9 might be omitted and the magnet
assembly 5,6,7 might instead be mounted directly on the
cantilevers 10.
Figure 3 of the drawings show various alternative
embodiments of cantilever for suspending a vibration
exciter on the panel 1. These include a single straight
finger-Like cantilever 10 defined by a U-shaped slot or
incision 11 of the kind shown in Figures 1 and 2, a curved
cantilever 17 defined by a spiral slot 18, and a resilient
suspension comprising a cantilever member 19 defined
between an opposed pair of arcuate slots 20 and having a
central part circular portion 21 and an opposed pair of
projections 22 attached at their distal ends to the panel,
with the magnet system connected at a central position 23
of the portion 21.
Figures 4 to 7 disclose an embodiment of resonant
panel-form loudspeaker I4 of the general kind described
above and having a resonant panel 1 forming part of a
larger panel 24, which may, for example, be a decorative
trim panel in an automobile or the like vehicle. In this
embodiment the loudspeaker 14 has a rectangular resonant
panel 1 defined within the larger panel 24 by grooves or
slots 25, the panel 1 being suspended in the panel 24 by
suspension cantilevers 27 defined by opposed parallel slots
26 arranged to bridge the slot 25 in regions round the
CA 02303789 2000-03-13
WO 99/21397 PCT/GB98/03131
9
panel 1 of low average velocity. One cantilever is
disposed on each side of the panel 1. The vibration
exciter 4 may be suspended as described above or
conveniently as desired. As shown in Figure 6, the slot 25
may extend only partly through the panel 1. As shown, the
slot 25 extends through the upper skin 3 and through the
core 2 of the panel 1 to leave the lower skin intact and
covering the slot. Alternatively as shown in Figure 7, the
slot 25 may extend completely through the panel 1.
In regard to the application of the present invention
to automobile trim panels and the like decorative
structures, the slotting may be made at an early stage of
manufacture, a . g . with laser or water j et cutting and the
slots need only be wide enough to achieve a stable
clearance for the vibrating component. In practice a
width of lmm or 2mm may generally be sufficient. The width
of the suspension component depends upon the effective
cantilever length, the toughness and linear stiffness of
the panel in that region and the acceleration forces which
the whole assembly might be reasonably required to
sustain. Values of about 4 to about 25mm have proved
effective for cantilever width.
Another benefit concerns durability in respect of
lateral acceleration forces. A relatively narrow slot
width allow for a safe grounding of the panel in contrast
to surface configurations using adhesive bonding to
compliant suspension components. In this later case the
suspension may suffer damage due to de-bonding.
CA 02303789 2000-03-13
WO 99/21397 PCTIGB98/03131
Where the acoustic arrangement suggests that
separation of the radiation is required between front and
rear panel faces, the larger general panel may act as a
baffle, generally augmented by local structures such as
5 vehicle door frame or some overall framing and support. In
an architectural application the structural panel will be
augmented by the design of the room or building. Acoustic
leakage via the narrow slots is likely to be negligible
between front and back. Such low leakage is also
10 beneficial in respect of stray noise isolation from the
back to the front of the panel which may be important in
some applications.
In connection with vehicle trim panels a later stage
of manufacture concerns the lamination of a lightweight
relatively flexible decorative film of cloth on a thin
layer of soft open, cell polyurethane foam. This structure
may be applied over the slots without significant
impairment of the operating principle. As regards the
user, no witness of the slots is then apparent. Some
small further improvement in acoustic isolation may result
from the finite acoustic resistance of the foam and cloth
covered slots.
INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY
The advantages of arrangements as shown in the
drawings are as follows, namely:-
1. suspension can use same material as panel, so
cost is law;
2. suspension may be located within the panel
CA 02303789 2000-03-13
WO 99/21397 PCT/GB98/03131
11
thickness, or with only a small increase of
thickness;
3. a number of such suspension positions can be
found either to suspend the panel to the
relatively stationary part of a vibration
exciter, e.g. a magnet assembly, and/or to
suspend the panel to a frame or other support,
and,
4. simple cantilever/beam calculations readily
provide the desired value of the compliance.