Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02311799 2000-OS-26
t
SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR UTILIZING DATA PACKETS
INCORPORATION BY REFERENCE
U.S. Patent Application No. 09/034,773, which was filed on
March 2, 1998 and entitled "Agent-Based On-Line Information
Retrieval and Viewing System," is incorporated hereby, in its
entirety, by reference.
1G FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a field of utilization of
data packets which may include, e.g., audio, video, and other
materials.
BACKGROUND INFORMATION
A system known as "Internet radio" has become more popular
over the last few years. Internet radio allows a user to receive
a streaming flow of audio content which the user listens to in
real time. The way in which the user may store the content and
the streaming flow depends on the Internet connection of the
user. If the user has a bad connection, he or she will receive a
low quality audio.
Another system is known as "Jukebox-only" system. Jukebox
provides pitfalls in areas of legality and consumer experience.
First, the user cannot be provided with a "music-on-demand"
system without paying full royalties to song and song recording
copyrights holders. Moreover, such rights may be granted on a
voluntary basis, i.e., record companies may refuse to grant such
rights. With regards to the user experience, while it may be
beneficial for the user to be able to purchase digital music and
to play it in any preferable manner, this level of control may
not always be possible. For some users, selecting which record
to play is more burdensome than is preferable. Thus, there is a
need for a system which would allow to eliminate these and other
disadvantages of the prior art.
1
CA 02311799 2000-OS-26
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a system and method for
utilizing (e. g., playing) data packets, e.g., audio, music,
video, advertisement, informative materials. A server
arrangement provides the data packets to a user computing
arrangement. A storage device of the user computing arrangement
stores the data packets. The data packets are arranged in a
predetermined order using the server arrangement and/or the user
computing arrangement. The user computing arrangement executes a
set of instructions to utilize the data packets in the
predetermined order. A user of the user computing arrangement is
prevented from modifying the predetermined order.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
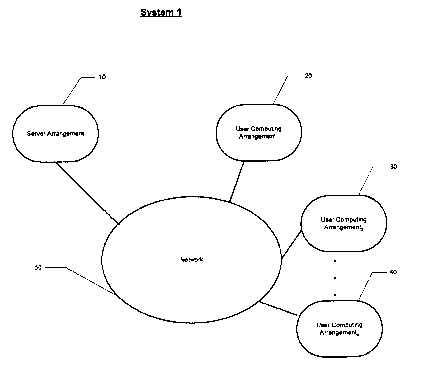
Figure 1 shows an exemplary embodiment of a system according
to the present invention.
Figure 2a shows an exemplary embodiment of a storage memory
device of a server arrangement according to the present
invention.
Figure 2b shows another exemplary embodiment of the storage
memory device.
Figure 3 shows an exemplary embodiment of a user computing
arrangement according to the present invention.
Figure 4a shows the user computing arrangement communicating
with a portable user arrangement.
Figure 4b shows an exemplary embodiment of the portable user
arrangement according to the present invention.
2
CA 02311799 2000-OS-26
Figure 5 shows an exemplary embodiment of a method according
to the present invention.
Figure 6 shows an exemplary embodiment of the system
utilizing a removable storage device according to the present
invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
The present invention generally relates to a system and
method for providing a predetermined group of data packets to a
user who may utilize (e. g., review, listen, watch, read, etc.)
such data packets with a user computing arrangement ("UCA"). The
data packets may be provided to the UCA from a server
arrangement, via a communication network (e.g., the Internet) or
via mail using a Removable Storage Device ("RSD"). When the data
packets are transmitted via a communication network, the
transmission may be continuous (e. g., without any interruptions
as long as there is a connection between the server arrangement
and the UCA) or periodic (e. g., the server arrangement provides
the data packets to the UCA every two hours).
Each data packet may include a single element/item, such as
a song, an advertisement, etc. The single element may be divided
into a plurality of subpackets. For example, when the data
packet is transmitted, each of the plurality of subpackets is
transmitted separately from each other. When the subpackets are
received by the UCA, they are "assembled" together into the data
packet.
The data packets may be utilized by the user in a predefined
manner. The user has only limited control over the order in
which the data packets are utilized. For example, the user may
skip a data packet (e. g., skip a single item) but cannot replay
or rewind the data packet, nor may the user choose which data
3
CA 02311799 2000-OS-26
packet will be played next.
The data packets may contain particular materials, for
example, information data (e.g.,advertisements, etc.),
entertainment information (e. g., video displays), educational
information (e.g., textbooks). The present invention allows the
user to review such data packets, e.g., as if the user was
listening to or viewing a broadcast on the conventional radio or
the television. The system and method of the present invention
also enables the user to gain more control over the materials
than in the use of conventional radio or television. By using
the system and method of the present invention, the user may skip
over, completely or partially, certain materials (e.g., by
skipping corresponding subpackets) when he or she desires. The
user may also instantaneously purchase the materials during or
after reviewing the materials.
Figure 1 shows an exemplary embodiment of a system 1
according to the present invention. The system may include a
server arrangement 10, a plurality of UCAs (e.g., UCA 20, UCA 30,
UCA 40) and a communication network 50. The network 50 may be an
arrangement of nodes and connecting branches for information
exchange. The network 50 may also be the Internet, a local area
network, a computer network, an intranet, a local area network, a
wide area network, an Extranet, a virtual private network, a
metropolitan area network, a wireless network, a satellite
network or any description for an arrangement of nodes and
connecting branches for information exchange.
The server arrangement 10 (among other elements) may be a
server or a computing device which includes a memory storage
device 75. Figure 2a depicts an exemplary embodiment of the
memory storage device 75 of the server arrangement 10. The
memory storage device 75 may store a plurality of databases,
e.g., a first database 60, a second database 80 and a third
database 90. Also, the memory storage device 75 may store a
4
CA 02311799 2000-OS-26
first software application 70 which determines the order in which
the data packets are utilized by the user.
The first database 60 collects and stores the data packets.
For example, the first database 60 may store audio, video,
advertisement, informative materials, etc. The informative
materials may be associated with the audio, the video and/or the
advertisement. The informative materials may be information
about a particular audio, such as a title, an artist, author of
lyrics, an album name, purchasing information, etc. The
informative materials may be accessed when the audio is played or
at any time before or after. The informative and advertisement
materials may be a form of text, audio, video, etc. The second
database 80 may store user data, e.g., user identification,
address, credit card information, etc. The third database 90 may
store user preference data, e.g., the type of music that the user
prefers, how many times the user listens to a particular song,
the rating given by user to the particular song, etc. Figure 2b
shows another exemplary embodiment of the memory storage device
75 which includes a second software application 100 which
facilitates a purchase of a particular data packet by the user.
Figure 3 depicts an exemplary embodiment of the UCA 20 which
may be a computer, a "dumb terminal", or any other stand-alone
microprocessor based device. The UCA 20 may include a processor
110, a first storage device 120 (e. g., RAM), a second storage
device 130 (e.g., a hard drive), an output arrangement 140, an
input arrangement 150 and a communication device 160. The output
arrangement 140 may include a monitor, audio speakers, a printer,
a disk drive, etc. The input arrangement 150 may include a
keyboard, a mouse, a touch screen, a voice-recognition device, a
disk drive, etc. The input arrangement 150 and/or the output
arrangement 140 may be physically connected to the UCA 20 or may
be wirelessly connected (e.g., via an infrared connection). The
communication device 160 may be a modem (e.g., a phone modem, a
cable modem, a wireless modem, etc.) or any other communication
5
CA 02311799 2000-OS-26
device capable of modulating and demodulating signals. The second
storage device 130 may store databases and software applications
which may allow the user to store and/or utilize the data
packets. The data packets may be categorized based on a
plurality of parameters. The first storage device 120 may
temporarily store the data packets (e. g., when they are received
or when the data packets are being utilized).
Figures 4a and 4b shows the UCA 20 in communication with a
portable user arrangement 170 (PUA). The PUA 170 may be
physically connected to the UCA 20 or may wirelessly interface
with the UCA 20. The PUA 170 is capable of performing functions
which are similar to the functions of the UCA 20 as they relate
to the present invention. Figure 4b depicts an exemplary
embodiment of the PUA 170. The PUA 170 may include an input
arrangement 175, an output arrangement 180, a processor 190, a
storage device 195 and a communication device 196. The storage
device 195 stores the data packets and a software application
which allows review of the data packets. The output arrangement
180 may be a portable monitor, portable audio speakers, a
portable printer, a portable disk drive, etc. The input
arrangement 175 may include a keyboard, a mouse, a touch screen,
etc. The communication device 196 may provide a connection to the
network 50 and/or to the UCA 20.
Figure 5 shows an exemplary embodiment of the method
according to the present invention. In Step 205, a connection is
established between the server arrangement 10 and the UCA 20,
e.g., via the network 50. The server arrangement 10 may be
connected to the UCA 20 continuously or periodically.
After the connection is established, the server arrangement
10 determines, by verifying the second database 80, whether the
user is an existing user or a new user (Step 210). If the user
is a new user (i.e., the user's identification is not found in
the second database 80), the server arrangement 10 adds the user
6
CA 02311799 2000-OS-26
information to the second database 80 and adds user's preferences
to the third database 90 (Step 215).
In Step 220, the server arrangement 10 generates a
predetermined group of data packets to be transmitted to the UCA
20. The data packets are encrypted so that the user cannot
exercise control over the data packets. The data packets can be
utilized, in a limited manner, by the user only after they are
decoded by the software application stored in the UCA 20. The
group of the data packets may be generated based on user's
preferences stored in the third database 90 for transmission to a
particular user. Alternatively, a group of data packets may be
generated to be transmitted (e.g., broadcasted) to a group of
users (e. g., classic music listeners).
The server arrangement 10 provides the data packets to the
UCA 20. (Step 225) The data packets are transmitted to the UCA
via a direct transmission using the network 50.
Alternatively, the transmission of the data packets may be
20 indirect, e.g., via mail (e.g., the Post Office) using the RSD
(as shown in Figure 6 and described below).
Once the group of data packets is received by the UCA 20,
the user may have the following options. The data packets may be
stored in the first storage device 120 and instantaneously
utilized by the user on a "one data packet at a time" basis (Step
230a - Option A). For example, as the audio is being received
from the server arrangement 10 by the UCA 20, it is being played
to the user. Alternately, or in addition, the data packets may
be stored in the second storage device 130 of the UCA 20. The
software application, which is stored in the UCA 20, and/or the
first software application 70 of the server application 10 may
determine the order in which the data packets are utilized by the
user (Step 230b - Option B).
The user may then utilize the materials of each data packet
7
CA 02311799 2000-OS-26
on an individual basis by accessing the stored data packets in
the predefined order (Step 235). The predefined order may be set
by the server arrangement 10 and/or the UCA 20. For example, the
predefined order may be the following: a first song, a second
song, an advertisement, a fourth song, etc.
The user utilizes the data packets via the output
arrangement 140. While utilizing the materials of a particular
data packet, the user may utilize the entire data packet, and/or
may elect to skip the current data packet and continue with the
following data packet. In alternative exemplary embodiment
according to the present invention, the user may skip a portion
of the data packet (e.g., by skipping some of the subpackets of
the corresponding data packet). For example, the user may skip
15 seconds of a song. Once the user elects to skip a particular
data packet, the user cannot immediately return to the skipped
data packet or the skipped subpackets (although, the skipped data
packet may be chosen, by the server arrangement 10 and/or the UCA
20, to be played again at a later time).
During the utilization of the data packets, the software
application may create a review database on the second storage
device 130. The review database may include a list of the
reviewed data packets. The user may access these reviewed data
packets and review only a short portion of the reviewed data
packet (e. g., first ten subpackets. This limited review feature
allows the user to revisit the content of the reviewed data
packet (e. g., to verify the data packet before purchasing).
The system and method of the present invention may also
include a rating system associated with each data packet. The
first software application 70 creates a rating for each data
packet and stores the rating information in a rating database
stored on the second storage device 130. The rating of a
particular data packet may take place, e.g., when the user is
utilizing the particular data packet. For example, if the user
8
CA 02311799 2000-OS-26
skips over a particular data packet or if the user utilizes an
entire data packet, the software application adjusts the rating
of that data packet according to a predetermined criteria. The
user may also directly rate the data packet during or after
utilizing it with a rating procedure. The rating procedure may
be a simple procedure, such as a "thumbs up" or "thumbs down"
rating, or a more complicated procedure, such as a sliding scale
rating from, e.g., 1 to 99.
The server arrangement 10 may also be provided with the
rating database of the UCA 20. The server arrangement 10 stores
the rating information for each user in the third database 90.
The server arrangement 10 may use the rating information, e.g.,
to determine a future grouping of the data packets that may be
transmitted to that user and/or to a plurality of users with
similar preferences. The server arrangement 10 may also utilize
the rating information to determine when to remove a particular
data packet from a group of the data packets. Once the data
packet achieves a rating which is below a predetermined value,
the server arrangement 10 may delete that data packet from the
group of the data packets and insert another data packet in its
place.
The user may elect to purchase any data packet for an
unlimited use. The purchasing process includes decoding the data
packet, storing it in the second storage device 130 and receiving
payment from the user for this data. There are a number of ways
for the payment to be effectuated. For example, the user may
have a prepayment option. In such a case, the software
application decodes the data packets and provides them to the
user, as long as there is a positive prepaid balance.
The user may also use a "pay-as-you-buy" option. Using this
option, the user buys the data packet and pays for it one at the
time. For example, when the user elects to purchase a data
packet, the software application marks the data packet for the
9
CA 02311799 2000-OS-26
purchase in the review database. The server arrangement 10
receives a purchase mark indication instantaneously, if the UCA
20 is connected to the server arrangement 10. However, if the
UCA 20 is not connected, the data packet remains marked for the
purchase and the server arrangement 10 receives the mark
indication upon the subsequent connection to the UCA 20. Once
the server arrangement 10 receives the purchase mark, it signals
to decode the data packet and provided the data packet to the
user. The user may then access the purchased data packets for an
unlimited use and for a complete control, thus allowing the user
to replay, rewind, and pause the purchased data packet at will.
While utilizing a particular data packet, the user may also
request the informative material associated with the particular
data packet. For example, while listening to the audio, the user
may request the video clip of the audio or the information about
the audio, etc.
As described above, the predefined order of the data packets
may be set by utilizing the server arrangement 10 and/or the UCA
20. For example, the server arrangement 10 set the order of the
data packets which are utilized as soon as they are received by
the first storage arrangement 120. In such case, the server
arrangement 10 completely controls the order and the UCA 20 has
no control over the order. The user can skip the currently
utilized data packet.
In alternative embodiment of the present invention, the
server arrangement 10 provides the data packets to the UCA 20.
The server arrangement 20 does not set the order of the data
packets. Instead, the order is set locally by the UCA 20 after
the data packets are stored in the second storage device 130.
Yet, in another embodiment of the present invention, the
order may be set by both the server arrangement 10 and the UCA
20. For example, the server arrangement 10 sets rules defining
CA 02311799 2000-OS-26
which data packets to be provided to the user (e.g., provide 40~
rock and 60~ classic; after every third song, an advertisement
must be inserted). Once the data packets are stored in the second
storage device 130, the order of the data packets is set by the
software application of the UCA 20 based on the rules set by the
server arrangement 10.
Another embodiment of the system 1 described above includes
the PUA 170 as described above and shown in Figures 4a and 4b.
The PUA 170, which functions in a similar manner as the UCA 20,
allows the user to have a portable access to the data packets.
The PUA 170 may allow the user to review the data packets
anywhere, and at any time. For example, the PUA 170 may be
connected to a music system of a mobile vehicle.
Figure 6 depicts a system 1', which is similar to the system
1 described above. In the system 1', the data packets and other
data (e. g., the rating information, etc.) are not transmitted
between the server arrangement 10 and the UCA 20 via the network
50. Instead, the transmissions are performed via mail using a
removable storage device ("RSD") 300.
The RSD 300 may be transmitted to and from the user via a
mail, such as U.S. Postal Service. The RSD 300 may be a compact
disc, a digital versatile (or video) disc, a zip disk, an optical
disk, etc. The RSD 300 may store a plurality of predetermined
data packets and/or databases. The stored data packets, which
are encrypted, are provided to the user.
In addition, the system 1' may be utilized to register a new
user. The user may provide his/her information to establish an
account with the server arrangement 10. Such information may be
provided via mail using the RSD 300. If the user decides to buy
a particular data packet, the transaction may be cleared with the
server arrangement 10. Once the user provides purchasing
information (i.e., an identification of the particular data
11
CA 02311799 2000-OS-26
packet, purchasing information such as credit card or checking
account), the server arrangement 10 may issue a permission
indication to complete the purchase of the particular data
packet, and such permission may be transmitted using the RSD 300.
Although the system 1 is capable of utilizing the data
packets as soon as they are received by the first storage device
120, in the preferred embodiment of the present invention, the
data packets are first stored in the second storage device 130
and then utilized. The advantage of the preferred embodiment is
that it allows to improve a quality of utilization of the data
packets. For example, when subpackets of a particular data
packet are transmitted over the network 50, they may be received
by the UCA 20 at different times. If the particular data packet
is utilized as soon as it is received by the UCA 20 and if one of
its subpackets is not yet received by the UCA 20, then the
quality of utilization would diminish (e. g., drop in audio play).
Such problem is avoided by receiving and storing all subpackets
of the particular data packets and then utilizing them. In
addition, if the data packet is stored in the second storage
device 130, then it may be utilized more than once because the
second storage device 130 may be, e.g., a hard drive, while the
first storage device 120 may be, e.g., RAM.
In alternative exemplary embodiment of the present
invention, only a portion of a particular data packet is provided
by the server arrangement 10 to the UCA 20. For example, 90% of
subpackets of the particular data packet are provided to the UCA
20 in advance. However, the particular data packet cannot be
utilized until remaining 10% of subpackets are received by the
UCA 20. The remaining subpackets may be provided at a
predetermined time (e. g., right before the particular data packet
is executed). This feature may serve, e.g., as a security
feature to prevent an unauthorized utilization of the particular
data packet. Also, after the particular data packet is utilized,
it is sufficient to remove a few subpackets to prevent any
12
CA 02311799 2000-OS-26
further utilization of the particular data packet. Consequently,
such feature allows to keep most of the particular data packet at
the UCA 20 and allows to quickly utilized the particular data
packet by providing the few missing subpackets in an expedited
manner.
Several embodiments of the present invention are
specifically illustrated and/or described herein. However, it
will be appreciated that modifications and variations of the
present invention are covered by the above teachings and within
the purview of the appended claims without departing from the
spirit and intended scope of the present invention.
13