Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02323885 2000-09-14
WO 99/47961 PCT/GB99/00654
-1-
SIDE ENTRY CABLE GUIDE
This invention relates to a cable guide for use in a cable management or
organisation
system and in particular to a cable guide for use in a fibre optic management
or
organisation system.
Cables are used in a variety of technologies and it is necessary in many
instances for
specific steps to be taken to organise or manage the cables in a given system.
Cable management in fibre optic systems is particularly important because of
the nature of
the optical fibres themselves. Fibre optic cable being formed of glass fibres
has a limited
range of bending and must be maintained above a minimum bend radius during use
and
storage. Excessive bending can lead to impaired transmission and if severe
could lead to
transmission loss. Fibre optic management systems or distribution centres,
therefore, need
to be designed to minimise fibre optic impairment or damage by properly
supporting the
cables along predetermined paths and protecting them from bends sharper than a
given
minimum bend radius. In addition in certain industries the number of cables,
such as
optical fibres, required within a particular management system is constantly
increasing and
even simple systems have a high density of cables. It is necessary in such
cases to house
and organise the cables in an efficient manner to avoid excessive installation
and/or repair
times. In some cases the individual cables need to be readily identifiable and
accessible at
all times. Additional problems in organisation may also occur where there is a
need for
the system to allow for modification and expansion.
For some cables, in particular fibre optic cables, it is necessary to provide
means for
guiding and supporting cables as they pass from one area to another. Such
means may
generally take the form of a cable guide having a guide channel and a
protective wall
which encloses the cables on all sides to provide maximum protection. It is,
however,
necessary in certain instances, for example during modification or expansion
of the system
in which the cables are situated, to remove the cables from the cable guide.
In
conventional systems it would be necessary to disconnect the cable at one end
so that it
may be threaded longitudinally through the cable guide. Such a process is time
consuming
and leads to inefficient installation and/or repair of systems.
CA 02323885 2000-09-14
15~~~5-?OOU GB 009900654
~ ~ . .... .. .... .. ..
B352 PCT ~ . ~ . ~ .. . . . . . . . .
... . . ... . . .
~ ~ ~ . . . . , ,
~ ~ . ..
_ 2 _ ~ ... ... .. ... .. ..
There is, therefore, a need to improve means for guiding and supporting cables
which
allows the cables to be protected from external damage but which allows for
quick and
easy access to cables and in particular allows them be removed from the means
by which
they are supported and guided without requiring disconnection at one end. The
Prior Art
does not offer a solution to this problem.
US 5,661,891 discloses a cable guide for passing cables through a wall of a
building. The
cable guide consists of two concentrically mounted sleeves, each of which has
a
longitudinal slot. The sleeves may be rotated relative to each other to form a
complete
circular encasement of the cables.
US 5,079,389 discloses a wire guard coupler for shielding and retaining wires
in
buildings. The coupler comprises two cylindrical.members, each having a track
member
on a first side and a longitudinal slot on a second side. The second
cylindrical member
can be slidably fitted in the first cylindrical member.
According to one aspect of the present invention there is provided a cable
guide assembly,
comprising a sheath defining a through channel through which cables can be
substantially
longitudinally guided, and a support in which the sheath is rotatably
accommodated,
wherein the sheath is provided with a first passageway extending over the
entire length of
' the through channe, which cable guide assembly is characterised in that the
support is
provided with a second passageway to which the first passageway can be aligned
so. as to
allow cables to be passed out of the cable guide assembly laterally while
substantially
maintaining their longitudinal orientation.
I
The passageway may be open at all times or means may be provided for closing
the
passageway in the protective wall. For this purpose the cable guide may be
provided with
means for transposing it from a first, or closed protecting, position to a
second, or open,
position. A part of the protective wall may, for example, be movable to open
the
i
passageway and allow cables to be passed out laterally through that part of
the wall. For
I
this purpose that part of the wall may be formed from a flexible material to
allow the part
AMENDED SHEET
CA 02323885 2000-09-14
15-J5-2000 GB 009900654
~ ~ . .... .: .... .. ..
B3sz Pcr . . .. ., , , , , .
. . . ... . . ... . . .
. . .
~ ~ ~ : ' : : : ' : ::
-Via- ' ...... .. ... .. ..'
of the wall to be flexed from the open to the closed position or the part of
the wall could
be movably (e.g. pivotally) mounted with respect to at least another part of
the wall.
Alternatively the cable guide may be composed of more than one component, with
the
passageway extending through two or more of those components and those
components
being relatively- movable. The passageway may be fully open allowing cables to
be passed
' laterally out of the cable guide when the two components are properly
aligned, i.e. with
their passageways being properly aligned, and the passageway being closed
without such
alignment.
Means may be provided for retaining the passageway in one or either the open
or closed
positions. Such means may take any suitable form such as cooperating
engagement
1' means, e.g. resilient projections, lugs etc and corresponding retaining
recesses as
required.
i
AMENDED SHEET
CA 02323885 2000-09-14
WO 99/47961 PCT/GB99/00654
-3-
The passageway is preferably orientated and positioned in use so as to allow
removal of
cables in substantially the same plane as they are being directed, used or
stored.
The cable guide may be provided with means for mounting it within apparatus in
which it
is to be used. It may, for example, be provided with means for mounting it on
a housing
in a situation where it acts as an outlet guide for supporting and protecting
cables as they
pass out from that housing. The means of mounting the cable guide are
advantageously
such as to allow cables to be passed out through the passageway, i.e. the
mounting
preferably does not block access to the passageway. For this purpose the
mounting means
may itself be provided with an opening or groove which can be aligned with the
passageway on the cable guide. It is preferred that the cable guide be mounted
so that the
passageway is outside of any housing on which it is mounted. The cable guide
may be a
separate or integral component of any apparatus in which it is to be used. It
could, for
example, be an integral part of a housing or a separate component mounted
thereon.
The cable guide may be provided with means of dividing its guide channel so as
to allow
for further organisation of cables passing therethrough. A dividing rod may be
provided
for this purpose. It may be an integral component of the cable guide, but
preferably is
removable therefrom to provide maximum versatility, e.g. by variations in the
use,
positioning and orientation of the channel dividing means. In this way cables
having
differing functions or direction of travel can be separated.
The cable guide may be formed of any suitable material such as will be well
known to the
skilled man. It may take the form of a single component or it may be formed
from one or
more modular components. The cable guide may, for example, be formed from a
plurality
of components which can be interlocked together to form a protective wall
defining a
guide channel. It has been found advantageous to provide a set of modular
parts from
which a variety of cable guides may be constructed.
According to another aspect of the invention there is provided a kit of
modular
components capable of being fitted together to form a cable guide having a
protective wall
defining a guide channel in which cables enclosed by the protective wall may
be supported
and guided as they pass longitudinally through the cable guide, which kit of
parts may also
CA 02323885 2000-09-14
WO 99/47961 PCT/GB99/00654
-4-
be fitted together to form a second cable guide having a protective wall
defining a guide
channel in which cables enclosed by the protective wall may be supported and
guided as
they pass longitudinally through the cable guide, which second cable guide
differs in shape
and/or form from the first cable guide.
The kit of modular components may be such as to allow two or a variety of
differing
shapes of guide channel to be formed. The first cable guide may, for example,
have a
substantially circular cylindrical guide channel whereas the second cable
guide may have a
square or oval cylindrical channel. The kit of modular components is
preferably such that
one of the cable guides which may be formed is a cable guide substantially as
hereinbefore
described, i.e. one having a passageway for the lateral removal of cables from
the guide
channel.
Means for interlocking the individual modular components of the kit may take
the form of
a separate component or the individual modular components may be provided with
integral
means for their interlocking connection. The individual modular components are
preferably provided with integral means for their interconnecting snap
engagement.
The present invention is advantageous as it provides a cable guide able to
entirely
surround cables being guided and supported so as to provide them with maximum
protection at the same time as allowing them to be removed from the cable
guide without
requiring their disconnection at one end. Such a cable guide, i.e. one
provided with
means for the easy lateral removal of cables guided through its guide channel
allows for
quick installation of a cable within a given system and in particular allows
for the
modification of that system or its repair without the need for the cable to be
disconnected
and subsequently longitudinally threaded through the cable guide. Furthermore,
a kit of
parts for the formation of at least two differing cable guides is advantageous
as allows for
the shape and/or form of the cable guide to be varied as required for the
particular use or
application of the cables to be guided.
For a better understanding of the present invention, and to show how the same
may be put
into effect, for the purpose of illustration only, reference will now be made
to the
accompanying drawings in which:
CA 02323885 2000-09-14
WO 99/47961 PCT/GB99/00654
-5-
Figure 1 is a perspective view from the front and one side of a first
embodiment of
a cable guide according to the present invention;
Figure 2 is a perspective view from the rear of the first embodiment of Figure
1;
Figure 3 is a perspective view from the front and the other side of the first
embodiment shown in Figure 1;
Figure 4 is a perspective view from the front and towards one side of the
embodiment of Figures 1 to 3 shown in use in a fibre optic patch panel;
Figure 5 is a perspective view from the front and the other side of the
embodiment
shown in Figure 4;
Figure 6 is a perspective view of a kit of parts according to the present
invention
shown in their separate and interconnected form;
Figure 7 is a perspective view from the front and towards one side of a cable
guide
formed from the kit of parts shown in Figure 6;
Figure 8 is a front perspective view of the embodiment of Figure 7;
Figure 9 is a rear perspective view of the embodiment shown in Figures 7 and
8;
Figure 10 is a front perspective view of the embodiment shown in Figures 7 to
9
with an additional component; and
Figure 11 is a further embodiment of a cable guide according to the present
invention.
A first embodiment of a cable guide according to the present invention shown
in Figure 1
comprises a substantially funnel or trumpet shaped sheath 1 defining a through
channel 2
through which cables or fibres (not shown) can be longitudinally guided. So
that it may be
attached to apparatus to which it to be used the cable guide is mounted within
a mounting
bracket 3. The mounting bracket 3 is provided with a circular opening within
which the
cable guide can be mounted. To maintain it in the mounting bracket 3 the cable
guide is
provided with two parallel extending mounting collars 4, 5 one or both of
which may be
formed as an integral flange. One of the mounting collars 4 extends to the
front of the
mounting bracket 3 in use, whilst the other collar 5 extends to the rear. A
passageway or
slot 6 is formed throughout the entire cable guide, i.e. through sheath 1,
outer mounting
collar 4 and rear mounting collar 5. The passageway 6 is of a size such as to
allow a cable
to be passed therethrough and so be laterally introduced into or removed from
the guide
CA 02323885 2000-09-14
WO 99/47961 PCT/GB99/00654
-6-
channel 2. The passageway 6 is generally defined by parallel extending edges 7
of the
cable guide. The shape of those edges 7 may be varied to vary the shape of the
passageway 6. In the embodiment shown one edge 7a is provided with a
transversely
projecting part or nose 8 which extends into the passageway 6 and the other
edge 7b is
provided with a corresponding recess part which extends away so that together
they define
a sinuous bend in the passageway 6. This shaping of the passageway reduces the
likelihood
of cables accidentally slipping through the passageway 6. The mounting bracket
3 is
provided with its own passageway 8 which is also of a size to allow a cable to
be passed
therethrough. The cable guide 1 is turnable within the mounting bracket 3
about its own
longitudinal axis and when it is turned to a position in which the passageway
6 on the
cable guide is aligned with the passageway 8 on the mounting bracket 3 a cable
passing
through the guide channel 2 may be laterally removed without requiring
disconnection at
one end and subsequent longitudinal removal. The mounting bracket 3 is
provided with
two locating apertures 9. The locating apertures 9 are able to accommodate a
corresponding locating pin 10 provided on the cable guide. When the locating
pin 10 is
located in one of the locating apertures 9 the cable guide is locked into a
closed position as
shown in Figures 1 to 3 and when the locating pin 10 is accommodated within
the other
locating aperture 9 the cable guide is locked into an open position in which
the passageway
6 and passageway 8 are aligned to allow cables to be laterally removed. The
locating pin
is provided with an upwardly extending tab to facilitate its transposition
from the open
to the closed positions.
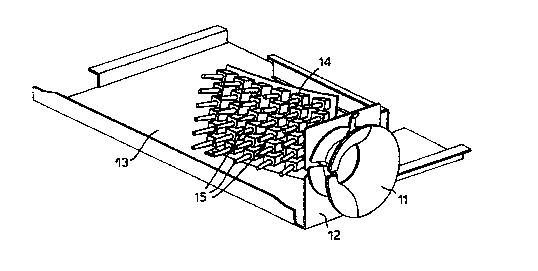
Figures 4 and 5 show a cable guide 11 according to the present invention
mounted upon a
bracket 12 which is in turn attached to a connection tray 13 of a fibre optic
connection
system. The connection tray 13 is provided with an upstanding fibre optic
patch panel 14
in which an array of connectors 15 are mounted. In use a plurality of fibre
optic cables
(not shown) would be connected to the connectors 15 and then guided out of the
connection tray 13 through the guide channel 11. Lateral movement of the
cables in and
out of the cable guide 11 can be effected by aligning a passageway 16 provided
in the
cable guide 11 with a passageway 17 provided in the bracket 12. The entire
passageway
(16 and 17) is open when aligned in substantially the same plane as that in
which the fibre
optic cables connected to the patch panel 14 are directed.
CA 02323885 2000-09-14
WO 99/47961 PCT/GB99/00654
_7_
A kit of parts for forming a variety of cable guides is shown in Figure 6. In
the left hand
side of the figure are shown four modular components (modules number 1 to 4)
and in the
right hand side four cable guides (A, B, C and D) which may be formed from the
modular
components. Module number 1 has an upstanding protective wall 17 which is
semicircular
cylindrical in shape. It is provided with an opening 18 and retaining tab 19
for
interlocking and engaging with other of the modular components. Module number
2 has
an upstanding protective wall 20 which is substantially linear. It is also
provided with a
projecting lug 21 and retaining tab 22. Module number 3 has an upstanding
protective wall
23 which is part-circular cylindrical in shape. It has an outwardly extending
projection
24, the function of which is discussed below. Module number 4 has an
upstanding
protective wall 25 which is also part-circular cylindrical. It also has a
inwardly extending
recess 26 substantially corresponding in shape and position to the projection
24 of module
number 3.
The modular components (modules l, 2, 3 and 4) can be assembled to provide a
variety of
cable guides. As an example two module number 1 components can be snap fitted
together to form a circular cylindrical cable guide A having a solid
protective wall. A
circular cylindrical cable guide B having a passageway 27 for the lateral
removal of cables
passing through the guide may be formed from a combination of modules l, 3 and
4. The
projection 24 of module number 3 and the corresponding recess 26 on module
number 4
serve to define a bend 28 in the passageway 27. An oval cable guide C can be
formed
from a combination of a pair of module 1 components with a pair of module 2
components
interspaced between them. A similar cable guide D, but this time having a
passageway 27
for the lateral removal of cable, can be formed by the combination of a pair
of module 2
components with a module 1, 3 and 4 component.
The cable guide C shown in Figure 6 is shown mounted upon a mounting bracket
28 in
Figures 7, 8 and 9. In more detail the cable guide C comprises an outwardly
tapering
funnel or trumpet shaped sheath formed of two end components 30 of
substantially
semicircular cross-section and two side components 31 is substantially of
linear cross-
section. The four components are interlocked together and held within an oval
aperture in
the mounting bracket 29. The cable guide C is retained in position by a
locating pin 32
CA 02323885 2000-09-14
WO 99/47961 PCT/GB99/00654
_g_
located within a locating aperture 33 provided on the mounting bracket 29. If
required,
the cable guide C can be dismantled during use by removing the locating pin 32
from the
locating aperture 33 and dismantling of the individual components (30 and 31)
from it.
Such dismantling would allow cable guided through the cable guide C to be
removed from
it without disconnection.
In Figure 10, the cable guide C is shown with an additional component, a
removable
dividing rod 34. The dividing rod 34 divides the guide channel into two
sections (35 and
36). The orientation and position of the rod 34 can be varied as required.
Cables passing
through the channel may be divided into two groups using the rod 34.
In Figure 11 a further embodiment of a cable guide 37 is shown. The cable
guide 37 is
provided with a substantially rectangular through channel 38 enclosed by a top
39, a
bottom 40 and two side walls 41a, b. A passageway 42 is provided between the
top of one
of the side walls 41a and the top wall 39. That top wall 39 is made of a
flexible material
so that it may be flexed upwardly to open the passageway 42 to allow cable to
be laterally
removed from the guide channel 38.