Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
1
Internet Search Tool Using Geographically Selective Features
Field
The invention relates generally to the Internet, and more particularly to
Internet search
engines.
Background
Location is a fundamental, unifying principle humans use to organize their
"mental
maps" of the world. The following are relevant technologies that can be used
in various
technical solutions.
Geographic Information Systems
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) has for many years provided the tools to
generate, manipulate, and manage spatial data. Government agencies and
commercial
data vendors use GIS extensively to create and maintain the map data used by
location
services. Vendors provide street-centerline data sets that include address and
street name
data, which are essential to geo-coding and routing applications. Location
services that
incorporate GIS tools enable a wide range of spatial transactions that can be
delivered in
meaningful ways. Some commercially available database management systems
(DBMSs)
currently have basic spatial data management capabilities providing limited
support to
location services; however, these DBMSs are not competitive in terms of
performance,
flexibility, and scalability without direct access to a robust GIS at their
foundation.
Internet Mapping Systems
Distributing geographic information via the Internet allows for the real-time
display and
integration of data from around the world. A natural extension of traditional
desktop GIS,
Internet mapping and associated applications have been popularised by various
sites
which deliver maps to the end user via a browser. To date mapping on the
Internet has
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
2
been mainly a cartographic exercise; with minimal extensions into true
information
searching and adding of new content.
Desktop Mapping
A desktop mapping system uses the map metaphor to organize data and user
interaction.
The focus of such systems is the creation of maps: the map is linked to a
database
containing related information. Most desktop mapping systems, however, have
limited
data management, spatial analysis, and customization capabilities. Desktop
mapping
systems operate on desktop computers such as PCs, Macintoshes, and smaller
UNIX
workstations.
Computer Aided Design (CAD)
CAD systems evolved to create designs and plans of buildings and
infrastructure. This
activity required that components, with fixed characteristics, be assembled to
create the
whole structure. These systems feature few rules to specify how components can
be
assembled and very limited analytical capabilities. CAD systems have been
extended to
support maps but typically have limited utility for managing and analysing
large
geographic databases.
Remote Sensing and Global Positioning Systems (GPS j
Remote sensing is the art and science of making measurements of the earth
using sensors
such as cameras fitted to aircraft or satellites, GPS receivers, and other
measuring
devices. These sensors collect data in the form of images and data streams and
provide
specialized capabilities for manipulating, analysing, and visualizing those
images.
DBMS
Database management systems specialize in the storage and management of all
types of
data including geographic data. DBMSs are optimized to store and retrieve data
and
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
3
many GISs rely on them for this purpose.
Search Engine Technology
Internet search engine technology consists of software that continually
searches web
pages, creating index tables of the key content, mainly using Tags that are
imbedded by
web authors within the web pages themselves . Search Engines use the
accumulated
index data to perform searches on the index and return appropriate page links.
There are
a number of companies that develop and sell Internet searching technology.
Advertising Banner Serving Technology On the Internet
Advertising is possible on the Internet through the use of commercial software
that
manages the creation, deployment and billing of a particular ad campaign - so-
called
AdServer software. Typically, an AdServer product will collect the advertising
banner
information from a central database, then deliver this information in real-
time to each
web page that has contracted to display the advertisement. The integration of
the web
page showing the banner and the banner being delivered from another Internet
site is
done in a seamless manner, i.e. without the end-user realising that the web
page he is
viewing is coming from different servers on the Internet. Currently there are
a number
of leading software providers who sell Internet AdServer technology.
Other Relevant Areas
Other relevant technologies include: Protocols for transmitting Internet
content to mobile,
wireless devices; Internet Browser Software Programming (HTML/JAVA/XML);
Database Design and Operations Programming (SQL, RDBMS); Internet Application
Programming (C++),
Traditional Media
Traditional means of finding local content include: Reading the Local
Newspapers,
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
4
Searching Telephone Yellowpage Directories, Listening to the Radio, spotting
Billboards, seeing Local TV announcements or Advertising.
Internet Media
On the Internet today, some local content can be found using traditional
'yellowpage'
listing services, city content sites, local portals and ISPs.
Limitations
These services offer limited geographic scope and focus mainly on large
metropolitan
areas. All of these content sites provide elements of useful information, but
none provide
a continuum of data across the entire world, across all categories.
As well, none allow users to add local content to these databases.
In addition, to find any specific local content, the user has been required to
enter a known
geographic postal or street address to commence a search. This inhibits a user
in
performing 'real-world' searches where one might not know an address or postal
code.
Ultimately, finding local content at any point within a large geographic
extent or
internationally has been impossible from any single Internet information
provider.
Therefore, there exists a need for a geographically selective search algorithm
that
provides search results in tabular format with a linked map, along with a
platform to
allow users to add information to a geo-referenced database. All information
within the
application's database should be tied to a precise longitude and latitude and
can be
displayed on a variety of scaled, electronic maps over the Internet.
Summary
Disclosed are software tools and processes for searching, finding, editing and
adding
information spatially (by location) using the Internet. Location has
tremendous utility
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
in the development of superior Internet search tools because location is so
central to how
humans organize and relate to their physical and conceptual worlds.
In one embodiment, there is provided an Internet search tool using
geographically
selective features comprising: means to define a search area; means to detect
a minimum
5 search area needed to locate and retrieve a minimum, specified number of
search results;
means to index records beyond the defined search area and search and retrieve
records
search commencing at a point and for a search area beyond the defined search
area
availability of the record; means to create a dynamic set of categories to
present to the
user dependent on the current map setting; and means to evaluate all records
and
determine an appropriate default search area guaranteed to provide search
results in all
appropriate categories.
In one embodiment, there is provided an Internet search tool using
geographically
selective features comprising a map interface comprising: a semi-transparent
map target
to provide a visual reference for the user; means to re-position the semi-
transparent map
to the point indicated by the mouse pointer; optimising means to optimise the
map;
micro-mapping means to provide an integrated view of maps at various zoom
levels; roll-
out map controls to optimise the use of limited display space; view finder
control
to provide a panning function to the map; and custom spatial driving
directions to display
a list of routes on the map.
In one embodiment, there is provided a wireless Internet search tool using
geographically
selective features comprising: a geo-enabled messaging and conference module
to apply
spatial characteristics to each member of a conference or messaging service
and to enable
the members to selectively communicate with other members.
Other aspects and advantages of the invention, as well as the structure and
operation of
various embodiments of the invention, will become apparent to those ordinarily
skilled
in the art upon review of the following description of the invention in
conjunction with
the accompanying drawings.
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
6
Brief Description of the Drawings
Embodiments of the invention will be described with reference to the
accompanying
drawings, wherein:
FIG. 1 illustrates the user interface of the disclosed application; and
FIG. 2 illustrates the wireless use of the application.
Similar references are used in different figures to denote similar components.
Detailed Description
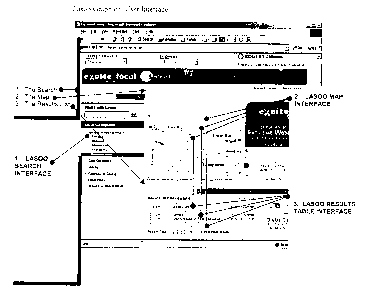
Referring to Figure l, the user interface of the disclosed Internet
application is illustrated.
The user interface includes a search interface, a map interface and a results
table
interface.
Search Interface
All search queries are specified within the searching frame, located on the
left hand side
of the interface. Queries can be initiated either through a direct keyword
input or by
clicking on any Category item.
A search can be conducted either through user keyword input or by selecting
from a
customized, 'clickable' category tree. Only populated categories appear.
Searching can
address both directory (business) and web sites.
The Search Interface incorporates the following features:
Polygon Search Module
The Polygon Search Module (PSM) software allows the definition and storage of
any
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
7
geo-spatial polygon, comprising an unlimited number of'sides' to the polygon,
defined
by the applicable latitude and longitude co-ordinates of each 'side'.
The PSM can be used to define a search area for any point located within the
boundary
of the polygon.
The PSM incorporates an automatic'clipping' engine which produces a radial
search area,
based on the current search position and search range, within which the
polygon is a geo-
spatial sub-set, then automatically removes or 'clips' any results that lie
outside of the
polygon, whenever a search based on the defined PSM is made, subject to
extension of
the searchable area using the Dynamic Search Range (as described below)
algorithms.
The PSM extends the search algorithm of the standard radial search to any geo-
spatial
polygon (any area, region, state, country, etc.).
Auto Rang Determination
The Auto Range Determination (ARD) is a software which will automatically
detect the
minimum range (geo-spatial distance) that needs to be set in order to locate
and retrieve
a minimum, specified number of search results, for a particular set or
classification of
records stored within a geo-located database, where each record has latitude
and
longitude attributes. The ARD algot-ithm takes as input, the location in terms
of latitude
and longitude setting, where the search is to be begun from.
Extended Range Record
Typically a search is based on a location and search range (distance). This
procedure
defines a Local Content search and is suited for searching for information,
businesses and
organisations located within the defined search zone.
However, there are important instances where information and/or records should
be
'searchable' (able to be found) for search locations and ranges that do not
contain the
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
physical location the information record is tied to. For instance, a Florist A
may want to
market flowers to anyone searching/residing within a 50 km radius of his store
location.
If someone was 35 km distance and searching for Florist shops within a 10 km
radius,
then such a search would not contain Florist A.
To solve this dilemma, the software algorithm provides for geo-spatial
indexing of
records beyond a standard containment area and allows for the search and
retrieval of
such a record for a geo-spatial search commencing at a point and for a range
beyond the
standard search area availability of the record. The Extended Range attributes
for any
single record can be set and the Extended Range Record (ERR) algorithm will
ensure that
the record will appear within appropriate geo-spatial searches using any
location and
range, from 1 metre to worldwide.
Dynamic Cate_o
The Dynamic Categories (DC) software creates a dynamic set of categories to
present to
the user dependent on the current map setting. The DC software automatically
identifies
any non-populated categories for the current map setting. In addition, the I)C
performs
a spatial count of records within each qualifying category that are
encompassed by the
current map setting. Thus the user is presented with a qualified list of
Categories relative
to the specific map setting and each qualified category in the tree structure
is displayed
along with the number of valid records contained within that Category (where
the number
shown is inclusive of any 'child' category records).
Options within the DC permit non-populated categories to be omitted from the
category
search tree or to be presented as 'unselectedl greyed out', with the further
option that
unselected categories, if chosen will use the ARD function to retrieve
records) for this
category (by automatically extending the search range appropriately).
The DC has the principle advantage that the end-user is presented with a
manageable,
relevant set of categories (as opposed to a much larger, less relevant list)
for the map
setting that the user has currently selected; thus, making searching much
quicker and
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
9
more effective.
Dynamic Filter
The Dynamic Filter (DF) software automatically senses the user's profile
depending on
( 1 ) the user's preferences (2) the category filter class that the user has
selected / specified
and (3) the category structure returned by the DC module.
The category filter class is one of several pre-established sub-sets of the
master category
structure designed by the system architect to reflect the category interests
of specific
groups.
The DF ensures that all of the user's settings and preferences are applied to
the DC to
produce a dynamic, fully customised set of categories for searching based on
the current
user's map setting.
Dynamic Search Range
Whenever the user selects a (new) location to begin a search (defining his
local search
position), the DSR algorithm evaluates, geo-spatially, all data, including ERR
data,
surrounding the specified location and automatically determines an appropriate
default
search range which is guaranteed to provide search results for this location
and range, in
all appropriate categories.
The parameters of the DSR can be dynamically altered at the moment the
algorithm is
invoked, to match the user's preferences in terms of categories of most or
primary
interest.
In addition, the DSR is utilised whenever a keyword search is invoked
(searching the
database of information based on the user entering a text string(s)). The DSR
guarantees
that relevant results will be returned, provided that relevant data exists at
some location
geo-spatially.
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
The DSR is an algorithm that guarantees the location of~the closest set of
search results
to the user's specified location, no matter what location and range was
initially specified
by the user for the search.
The DSR parameters can be adjusted to specify range limits and minimum
returned result
5 set.
Internet Database Link Control
The Internet Database Link Control (IDLC) software module can take database
content
from any DBMS (database system) and automatically enable access via the
Internet to
the information contained in the database, through auto re-direction of search
requests
10 emanating from any Internet search engine.
The IDLC produces this functionality by auto-creation of a specific web page
with
imbedded mega-tags and other information for each record in the set of records
that the
database manager wishes to make Internet accessible.
The software auto-directs search requests from any Internet search engine, for
any search
related to the key or index value of a record from the Internet linked
database. The IDLC
enables any search engine to create a suitable reference link to the desired
database
record, enabling the automatic display of this link reference within the
search engine's
result list. The reference link itself, on the search engine's results list,
emanates from the
search engine having crawled/scanried and indexed the auto-generated database
engine
stored by the IDLC on a URL and set of web pages specific to the target
database and
record.
Using this methodology, a database of Local Content information for instance,
can be
provided to all Internet search engines automatically, with the end-user being
linked to
a relevant site where Local Content information and appropriate GIS tools are
available.
Spatial Information Favourites
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
11
In order to facilitate Local Searching, the Spatial Information Favourites
(SIF) module
permits users to record their favourite search locations, by having the system
memorize
a currently selected location on the map or from the gazetteer.
In addition, the user may create as many Favourite Folders within which can be
recorded
details of the current search the user has performed, including retention of
specific record
result details, all of which can be used to automatically search and retrieve
relevant data
in future search sessions.
Map Interface
The map pane is where the search location, range and result points are
displayed and
configured.
The map interface includes a mufti-coloured circle with equidistant placed
concentric
rings forms the 'bulls eye' style target - the "Lasoo". Each coloured ring
forms a concise
geographic selection area - which increases in physical area as the radius
increases.
Results found in a particular query appear as dots within these rings.
In addition, this interface area provides important navigational and search
criteria
controls which include:
- Zooming Controls
- Location Finder (gazateer)
- Range ('Lasoo' Size) Control
- Viewfinder for fine tuning current location
- 'centre lasoo' control
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
12
'place lasoo' control
- Map 'panning' control
The Map Interface and map displays contain the following features:
Semi-Transparent Map Target
The imbedding of a Semi-transparent target on each map, provides a visual
reference for
the user that graphically outlines the search area the user has selected and
provides a
visual reference for multiple result points that are automatically positioned
on the map,
so that the user can easily determine visually their relative distance from
the centre of the
search location as well as the distance from each other.
The semi-transparent aspect of the Semi-Transparent Map Target (SMT) allows
all of the
underlying and overlying map details themselves to be readily distinguished.
The SMT module records the current geo-position of the device or that selected
by the
user, along with the currently selected or determined search range and feeds
this data
dynamically to other software objects.
SMT Auto and Dynamic Positioning
The SMT Auto and Dynamic Positioning (SMTAP) algorithm, allows the user to
click
anywhere on the map display to automatically re-position the SMT to the point
indicated
by the mouse pointer.
Also the SMTAP algorithm, automatically re-positions the SMT whenever the user
selects a new location from within the gazetteer or selects a previously used
location.
Dynamic. Map =point Position & Size
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
13
The result symbol (dot) on the map is evaluated using a boundary-subset
algorithm to
determine if one or more result points will overlap, causing visual confusion
and
deterioration of the data communication to the user.
If so, an optimising algorithm selects the points to combine in order to
eliminate overlaps
S and sizes the resulting point to a larger dimension to reflect visually that
it represents
more than one point.
The parameters of the algorithms are totally adjustable so as to suit design
parameters
pertaining to spacing requirements and aesthetics.
The entire algorithm set is re-computed as the map is drawn; thus, panning,
zooming, or
re-location of the map data results in dynamic re-assessment of the position &
size of the
map result points.
Micro Mapping
The Micro Mapping software links Computer Aided Design documents or scanned
images with geo-spatial positioning controls and map link controls, to provide
an
1 S integrated view of the interior of buildings and/or high-definition
mapping for precise
areas such as shopping centres, exhibit centres, fair grounds, manufacturing
plants, park
grounds, etc. The Micro Mapping software algorithms enable the precise
location of any
object or position on the micro map to be determined and displayed to the
user. The
Micro Mapping link control, enables the micro map to be integrated within the
standard
digital street level display, so that the user has a seamless means of
'drilling down' from
the digital street map to within the micro map.
In addition, the micro map zoom/pan control algorithms allow for zooming and
panning
within the micro map in a completely analogous manner to the zoom/pan controls
for the
standard digital maps.
Roll-out Man Controls
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
14
Roll-out Map Controls All of the Map controls - zoom / pan / range / location -
utilise a
unique roll-out feature. When the user clicks on the applicable control, an
expanded
control feature window appears to the side of the control. The user can then
select from
among the expanded list of available features for that control This technique
optimises
the use of limited display space and at the same time offers a full set of
expanded features
without the need to refresh the screen display, since the roll-out control and
its embedded
feature display list are downloaded, and instantly available from, the main
page the
control sits on.
View Finder Control
The View Finder control provides a unique means of panning a map. The
'viewfinder'
tool, allows the user to pan (scroll) the main map by 'moving' a viewfinder
control on
a roll-out index map which features a much larger geographical area than that
of the main
map. The user moves the viewfinder by pointing and clicking to the new desired
position
of the viewfinder. At the same moment as the viewfinder moves on the
underlying index
map, the main map in the map pane; re-freshes to show the new map determined
by the
viewfinder control's new position.
Three Dimensional Programmed Flyovers
Custom Spatial Driving Directions
The Custom Spatial Driving Directions (CSDD) software module allows the user
(owner
of a database record) to record customised driving directions onto a street-
level (or other
zoom level) map display by specifying a series of linked points on the map by
simply
clicking with the mouse pointer at the applicable places on the map. The
series of linked
points then become a 'route' on the map.
In addition, the CSDD module allows the user to add descriptive text, in an
adjacent text
box, explaining the route, and adding other useful information, for the end-
user. The
CSDD allows the user to add any number of custom'driving direction' routes to
the map
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
and to store these routes with the applicable database record(s).
Finally, the CSDD provides an end-user interface, whereby the end-user can
select from
a list of routes; see the route high-lighted on the map and view the
associated text box.
Geo-enabled Messa~~ and Conference Module
5 The Geo-enabled Messaging and Conference Module (GMCM) software module
automatically applies spatial characteristics to each member of a conference
or messaging
service and enables members to selectively communicate with other members
within the
SMT the user has defined. In this manner, members may view the locations of
all
members, or any desired geographical sub-set of members, on the map display
and select
10 which communications to process, on a geo-spatial basis.
Results Table Interface
The Results Table displays the search results in a table format. Each result
found in the
table is linked to a specific record point (dot) on the map. A user may
inspect results by
either rolling over a record within the Results Table or by Rolling over a
record point on
15 the Map.
Either procedure will yield a colour 'hot-link' between the mapped result and
the table
result for a specific record.
Any selected result record occurring in a 'Lasoo' search area on the map
appears in a
results table below the map. The results table is coloured coded depending on
the colour
lasoo ring in which a resulting dot is found. Results are displayed normally
from nearest
to farthest from the Lasoo centre. The user can sort the list according to
several,
alternative criteria.
The Results Table also features the following functions:
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
16
- Symbology associated with additional information for each record in the
table.
- Distance field, listing radial distance from Lasoo centre
- Extended range records
- Directory/Search Category labels
S - 'Next' and 'Back' Table Review Controls
- Hot-linked 'QuickPage' launch (row click)
- Hot-linked 'roll-over' map highlighter.
The Results Table Interface incorporates the following features:
Dynamic Search Results Updating
This software creates automatically~updated search results based on the
current position
of the SMT as the user moves or re-sizes the SMT controls within the map pane.
Whenever the user places the SMT in a new position or re-sizes the range of
the SMT,
then the Dynamic Search Results Updating (DSRU) algorithms, perform an
automatic
background update of the search results and automatically re-freshes the
search results
list.
Linked. Rollover Map/List Search Result Hi~_h~lighti~
When user rolls over a result dot on the map or a result row on the Results
List, the result
dot and row is highlighted.
Roll-out Thumbnail Map & Information
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
17
The Roll-out Thumbnail Map & Information (RTMI) function automatically
produces
a 'thumb-nail' map and other text information related to a result row,
displaying this
information to one side of the result row, whenever the user 'rolls-over' the
row with the
mouse pointer.
This function operates in real-time and is independent of the number of result
rows in the
results table. The thumb-nail map shows the precise street-level map view
associated
with the address in the applicable result row.
Referring to Figure 2, the application can also be used in a wireless
environment. The
GUI implementations will vary depending on wireless device specifications and
bandwidth. Maps are incorporated on devices with higher resolution displays.
The RIM
Model 957 featured in Figure 2.
Search Features
Using a Wireless Device a Key Word search and Location can be inputted or both
can
be determined automatically by links to the wireline and use of wireless
location
technology.
Street Intersection Locator
A search centre - a 'lasoo' - is identified by a specifying a street
intersection or using
auto- location technology.
Smart Street ID
If necessary, the wireless application returns a short list of eligible street
intersections.
User selects desired item.
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
1g
Result Features
Results are displayed in a scrollable list, sorted by distance from the centre
of the Lasoo.
In addition, the following features apply specifically to the wireless
application:
Dynamic Location Sensitive Auto Search
The Dynamic Location Sensitive Auto Search (DLSAS) software automatically re-
configures the position of the user's SMT on a wireless device as the user's
position
changes while the wireless unit is being transported.
The automatically re-positioned SMT has all of the characteristics and
attributes derived
from DC, DF, SMTAP, DSR, ARD and PSM.
Wireless Auto Configured Search
The Wireless Auto Configured Search (WACS) module allows the user to configure
the
local search engine to suit the characteristics of a wireless device, from the
user's wireline
desktop browser.
The WACS also automatically downloads this configuration information, along
with the
user's search preferences to the wireless device whenever the user activates
the wireless
unit.
Previously, the Internet has failed to 'deliver high performance spatial
search and retrieval
capability (including maps) to Internet Users around the World. With use of
the Spatial
Application Service Provider solutions (ASP) provide a new breed of high
performance
spatial search and retrieve software on the Internet.
Quickly and Easily Finding Local 'Content (relative to the user's location or
desired
location) on the Internet today is a labourious, convoluted and an
inconsistent experience
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
19
across the Internet. This application is explicitly designed to tear down the
barriers to
finding local content quickly and easily using innovative search, mapping and
display
functions.
Previously, Internet users require intimate and specific postal
code/positional information
in order for a search to be conducted for local content. This application
solves this by
providing simple 'point and click' entry to begin a search anywhere in the
World.
As well adding new information to the Internet is a bureaucratic and often
intimidating
process for most Internet Users and is normally associated with a fee. This
application
allows users (private individuals, businesses and organisations) to add new
content to the
Internet by simply clicking on a map and posting their own information.
Coupled with
this is the ability to have a calendar and bulletin board feature associated
with an entry.
No existing Internet site allows a user to employ both Wired and Wireless
Internet-
capable devices to conduct geo-spatial searches. This application provides an
integrated
Wireline and Wireless geo-spatial search solution including the unique
capability to
1 S automatically 'load' the wireless device with data, set-up and user
preference information
defined/obtained from the Wireline side.
Current Internet mapping and local search capabilities are limited to static
data, restricted
to a delimited geographic area, such as the USA, and do not guarantee an
optimal geo-
location search range for each record. This application provides detailed
mapping and
local content capability worldwide, including the unique ability to specify, a
dynamic,
adjustable search range for each individual geo-located record.
Classification of information by (Sub-)Category(s) is essential to successful
searching
on the Internet; however, the resulting size of the search catalogues, results
in time-
consuming scanning by users through too many categories and/or too many non-
relevant
results. This application's unique, dynamic category/content filtering
capabilities, allow
for the presentation to the end-user of just the sub-set of categories and
content relevant
to the user's specified search criteria and search location.
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
Delivery of relevant, geographically defined local information and advertising
is
impossible today due to the random access characteristics of the Internet.
This application
allows for the delivery of information targeted to specific locations and
demographic
profiles, using Lasoo's unique client positioning capabilities, regardless of
how and
5 where the client accesses the Internet.
The disclosed application provides many advantages. These can be grouped into
three
areas: Features, Searching and Display.
Advantage: FEATURES
1. Internet Database Link Control (IDLC): whereby all search engines worldwide
are
10 automatically geo-location / local content enabled by virtue of the Lasoo
IDLC
technology which auto-directs search requests, for any directory (business)
listing or
category, to the Lasoo local search results page for the desired location and
category/reference, by means of the IDLC result link displayed to the user
within the
search engine's result list.
15 2. Auto-install of geo-coded information tools on client and end-user
websites.
3. Provides for user insert/modification of geo-coded content within a
worldwide,
Internet searchable database.
4. Allows users to specify a precise search location without address
information being
a requisite, through map pointing functionality.
20 5. Stores and retrieves user preference information automatically with
respect to selected
location and search criteria, as well as permitting users to modify preference
data.
6. Dynamically eliminates categories that are not present in mapping area.
7. Dynamically modifies category information display based on user selectable
Category
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
21
Filters.
8. Dynamically extends the searchable range of any individual record in the
geo-coded
database, allowing users to automatically locate records outside their
specified search
range/location which nevertheless have a logical local presence within the
specified
search range/location.
9. Allows record owners to create date/time sensitive billboard Notes that are
automatically displayed in Local Content search results.
10. Provides a geo-coded, searchable, web-page presence automatically for all
businesses
(and organizations) in all major countries and markets worldwide.
11. Allows record owners to enhance the display characteristics and content of
their
records) within the geo-coded database.
12. Automatically links the geo-coded information database with associated
Internet web
pages and uniquely provides integrated search and retrieval of information
from database
and web simultaneously.
13. Allows users to create and deploy advertising and information
banners/announcements to targeted, local audiences, anywhere in the world.
14. Delivers Locally Targeted Advertising and information to any specific
location and
demographic profile using unique geo-location ad-serving capabilities.
15. Provides a seamless integration of Wireline and Wireless capabilities,
including the
automatic delivery and configuration of information to wireless devices, along
with
automatic detection of the wireless device type.
16. Integrates seamlessly with auto-location determination capabilities of the
wireless
device, to deliver automatically, location specific results and information to
the end-user
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
22
17. Automatically generates demographic profiling data by any user-defined
region
worldwide, greatly enhancing direct marketing capabilities while adhering to
enhanced
levels of privacy control.
18. Provides unique map navigation roll-out controls, offering superior
performance to
the user while simultaneously reducing display area requirements.
19. Provides high-definition maps for any location worldwide, including the
unique
ability to associate a multi-point result map display with a corresponding,
user-sortable
results list.
20. Provides unique user controlled map functions allowing users to enhance
and update
map information for private and public use.
21. Unique map functions and filters allow users to select the type of map
display
(topological, vegetation, interest-oriented) to utilize.
Advantage: SEARCHING
22. User defines desired search location by simply clicking on a map or
choosing from
1 S drop-down list controls (no typing required).
23. Integrated web/database search, whereby the search request is processed
among the
database of directory (business) records plus all of the associated web pages
for each
directory record. Searches and finds information records and their associated
web sites
using one, simple search interface.
24. Searches and retrieves information records and data from any user-
specified area,
including multiple countries or regions.
25. Searches by means of a simple, 'clickable', local content category
structure.
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
23
26. Searches conducted using detailed, high quality, worldwide maps featuring
zoom
levels down to street-level and a worldwide gazetteer offering city and place
names
worldwide.
27. Searches by advanced keyword combinations and provides ability to perform
multi-
tier searches, whereby searches of search results are performed automatically.
28. Searches and finds 10,000+ records spatially in less than 0.5 seconds.
29. Searches a precise. user defined/selectable area (the Lasoo).
Advantage: DISPLAY
30. Displays an intuitive mufti-coloured target/range ring on the map - the
'Lasoo' .
31. Displays multiple results on the map as a set of independent 'dots',
including a
unique feature that accumulates overlapping results into one 'dot' but allows
the user to
select from a pop-up window displaying the records belonging to the 'dot' when
the user
clicks on the 'dot'.
32. Displays search results in a list and mufti-point map format
simultaneously.
33. Unique functionality allows the user to sort the search results by several
criteria, such
as Distance, Category, Name, etc.
34. A unique map 'viewfinder' tool, allows the user to pan (scroll) the main
map by
'moving' a viewfinder control on a roll-out index map which features a much
larger
geographical area than that of the main map.
35. A unique rollover function allows the user to identify visually the
location of any
result by 'rolling over' either the result on the result list or by placing
the pointer over a
result 'dot' on the map. The item being rolled-over automatically highlights
(changes
CA 02335445 2001-02-09
24
colour) on the map and results list simultaneously.
36. A unique rollover, information expansion function automatically display
additional
information for a result whenever the user roll-overs the corresponding 'dot'
on the map
or the row in the result list. Additional information displayed to the side of
the results
lists may include a thumbnail street-level locator map, web link information,
etc.
37. Unique map control icons, 'roll-out' to offer detailed functionality
whenever the user
clicks on the control, resulting in advanced functionality within a reduced
space footprint.
38. A detailed QuickPage 'pop-ups' for any result whenever the user clicks on
the
applicable record in the results list or on the corresponding 'dot' on the
map, without
altering the underlying map/results list display. The QuickPage includes a
street-level
location map showing the precise location of the record; address and contact
information;
links to the corresponding web page (where applicable); and other text and
information,
which the record owner may add.
While the invention has been described according to what are presently
considered to be
the most practical and preferred embodiments, it must be understood that the
invention
is not limited to the disclosed embodiments. Those ordinarily skilled in the
art will
understand that various modifications and equivalent structures and functions
may be
made without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention as defined
in the
claims. Therefore, the invention as defined in the claims must be accorded the
broadest
possible interpretation so as to encompass all such modifications and
equivalent
structures and functions.