Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02359129 2001-10-15
BUS FAULT PROTECTION UNIT FOR AN ELECTRICAL POWER SYSTEM
This invention relates to a monitoring unit for use in protecting against
line faults in an electrical power supply system and to a method for
protection.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION:
In electrical power systems it is necessary to provide breakers and to
monitor for fault conditions so that the breakers can be actuated to
disconnect
various components of the system in the event of a fault.
The present Assignees manufacture various products such as a line
protection system which receives input from one or more sensors which detect
the
current on the line and provide the three phase input to the protection unit.
The
protection unit converts the signals from the sensor into digital values of
the three
phases and carries out various algorithmic calculations based upon the current
values and upon a voltage value to determine the present of a fault condition.
In the
event of a fault condition, the unit provides an output trigger which can be
used to
trip the breaker and/or other breakers on the same to prevent the fault
condition from
being transmitted to other associated power components. An example of the
above
device is shown in co-pending application filed on the same day as the present
application under docket number 84812-302 and now Serial No. INSERT, the
disclosure of which is incorporated herein by reference.
Thus equipment is available for monitoring and protecting the
conditions on a power line and these are widely established and widely used
both
using older electro mechanical equipment and also more current equipment which
uses digital calculations.
CA 02359129 2001-10-15
2
One example of an improvement of a device of this nature is shown in
co-pending application entitled "MONITORING WIDE AREA DYNAMIC SWING
RECORDINGS ON AN ELECTRICAL POWER SYSTEM", filed September 22, 2000,
Serial No: 09/667,582, the disclosure of which is incorporated herein by
reference.
In many cases a station includes a bus arrangement to which is
attached a plurality of transmission lines or feeder lines which transmit the
current
from the bus to end locations. The bus is attached to one or more supply lines
which supply current to the bus.
In many cases the individual line protection is considered satisfactory
to provide protection for the system at the station.
In other cases utilizing the conventional electro-mechanical systems
and utilizing high impedance current detection systems, attempts have been
made
to provide additional protection for the bus itself to ensure that no faults
on the bus
can cause a breakdown of the system which could be transmitted to other parts
of
the grid. In situations where the bus itself is relatively long and complex,
enhanced
protection for the bus is more important.
Up till now, however, no digital equipment has been available for
monitoring the bus to ensure that any fault developing on the bus itself is
properly
controlled by tripping the necessary breakers.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is one object of the present invention therefore to provide an
improved monitoring unit and an improved method using that unit.
CA 02359129 2001-10-15
3
According to one aspect of the invention there is provided an
apparatus for monitoring current flow in a power supply bus of a three phase
electrical power system and for controlling circuit breakers to provided
protection for
the system, the system comprising:
a power supply bus;
at least one three phase power supply line connected to the bus for
supplying current thereto;
at least one three phase power feeder line connected to the bus for
receiving current therefrom;
a plurality of circuit breakers each connected between a respective one
of the supply and feeder lines and the bus for disconnecting flow of current
therebetween;
a plurality of current sensors each responsive to the three phase
current flow between the bus and a respective one of the supply and feeder
lines to
provide three outputs indicative of the A-phase, B-phase and C-phase
respectively
of the three phase current flow;
and a voltage sensor responsive to the voltage on the bus to provide a
voltage output indicative thereof;
the apparatus comprising a monitoring and control unit associated with
a respective one of the lines having:
a plurality of current input terminals;
a voltage input terminal for receiving the voltage output of the voltage
sensor;
CA 02359129 2001-10-15
4
a processor element in the unit responsive to the outputs from the
terminals for generating digital data indicative of the instantaneous values
of the
voltage and of the currents;
a processor element in the unit for effecting pre-determined algorithmic
calculations on the digital values of the voltage and the currents to
determine a
presence of a fault condition in the current through any one of the breakers;
a processor element for summing the digital values of the currents to
determine that sum of currents flowing into the bus and the sum of currents
flowing
from the bus is equal to zero and for determining a fault condition in the
event that
the sum is not equal to zero.
a trip output generator for generating a trip output in response to said
fault condition for tripping all the circuit breakers associated with bus;
and recording means for recording data relating to said current values
in the event of a fault condition.
Preferably the unit is arranged such that it can be configured in a first
configuration and in a second configuration, wherein in the first
configuration each of
the three phases of each of the current sensors is connected to the respective
current terminals and the three phases are summed independently and wherein in
the second configuration only one of the phases from each of the current
sensors is
connected to the respective current terminals and said only one of the phases
is
summed.
Preferably the number of current input terminals on the unit is at least
18.
CA 02359129 2001-10-15
Preferably the number of current input terminals on the unit is at least
18 and wherein the unit is arranged such that it can be configured in the
first
configuration to receive the three phases from 6 lines and in the second
configuration to receive a single phase from 18 lines.
5 According to a second aspect of the invention there is provided a
method comprising:
providing a power supply bus;
connecting at least one three phase power supply line to the bus for
supplying current thereto;
connecting at least one three phase power feeder line to the bus for
receiving current therefrom;
locating between a respective one of the supply and feeder lines and
the bus a respective one of a plurality of circuit breakers for disconnecting
flow of
current therebetween;
providing a plurality of current sensors each responsive to the three
phase current flow between the bus and a respective one of the supply and
feeder
lines to provide three outputs indicative of the A-phase, B-phase and C-phase
respectively of the three phase current flow;
providing a voltage sensor responsive to the voltage on the bus to
provide a voltage output indicative thereof;
providing a monitoring and control unit for the bus;
providing on the unit a plurality of current input terminals and
connecting thereto a respective one of the three outputs of the current
sensors;
CA 02359129 2001-10-15
6
providing on the unit a voltage input terminal for receiving the voltage
output of the voltage sensor;
in the unit generating digital data indicative of the instantaneous values
of the voltage and of the currents in response to the outputs from the
terminals;
in the unit effecting pre-determined algorithmic calculations on the
digital values of the voltage and the currents to determine a presence of a
fault
condition in the current through any one of the breakers;
in the unit summing the digital values of the currents to determine that,
for each of the A-phase, B-phase and C-phase separately, the sum of currents
flowing into the bus and the sum of currents flowing from the bus is equal to
zero;
generating a fault condition in the event that the sum is not equal to
zero;
generating a trip output in response to said fault condition for tripping
all the circuit breakers associated with bus;
and recording data relating to said current values in the event of a fault
condition.
According to one arrangement, the bus is supplied by a transformer
and wherein there is provided a current sensor responsive to current which is
connected either upstream of the transformer or between the transformer and
the
bus and provides an input to the unit.
Alternatively, the bus is supplied by a transformer and wherein there is
provided a first current sensor responsive to current which is connected
upstream of
CA 02359129 2001-10-15
7
the transformer and a second current transformer between the transformer and
the
bus each of which provides an input to the unit.
Preferably the number of current input terminals on the unit is at least
18 and wherein the unit is arranged such that it receives each of the three
phases
from 6 lines.
According to a third aspect of the invention there is provided a method
comprising:
providing a power supply bus;
connecting at least one three phase power supply line to the bus for
supplying current thereto;
connecting at least one three phase power feeder line to the bus for
receiving current therefrom;
locating between a respective one of the supply and feeder lines and
the bus a respective one of a plurality of circuit breakers for disconnecting
flow of
current therebetween;
providing a plurality of current sensors each responsive to the three
phase current flow between the bus and a respective one of the supply and
feeder
lines to provide three outputs indicative of the A-phase, B-phase and C-phase
respectively of the three phase current flow;
providing a voltage sensor responsive to the voltage on the bus to
provide a voltage output indicative thereof;
providing a first, a second and a third separate monitoring and control
units for the bus;
CA 02359129 2001-10-15
providing on each of the units a plurality of current input terminals;
connecting to the current input terminals of the first unit a respective
one of the A-phase outputs of the current sensors;
connecting to the current input terminals of the second unit a
respective one of the B-phase outputs of the current sensors;
connecting to the current input terminals of the third unit a respective
one of the B-phase outputs of the current sensors;
providing on each of the units a voltage input terminal and connecting
thereto the voltage output of the voltage sensor;
in each of the units generating digital data indicative of the
instantaneous values of the voltage and of the currents in response to the
outputs
from the terminals connected thereto;
in each of the units effecting pre-determined algorithmic calculations
on the digital values of the voltage and the currents to determine a presence
of a
fault condition in the current through any one of the breakers;
in the first unit summing the digital values of the currents to determine
that for the A-phase the sum of currents flowing into the bus and the sum of
currents
flowing from the bus is equal to zero;
in the second unit summing the digital values of the currents to
determine that for the B-phase the sum of currents flowing into the bus and
the sum
of currents flowing from the bus is equal to zero;
CA 02359129 2001-10-15
9
in the third unit summing the digital values of the currents to determine
that for the C-phase the sum of currents flowing into the bus and the sum of
currents
flowing from the bus is equal to zero;
in each of the units generating a fault condition in the event that the
sum is not equal to zero;
in each of the units generating a trip output in response to said fault
condition for tripping all the circuit breakers associated with bus;
and recording data relating to said current values in the event of a fault
condition.
Preferably each unit has at least 18 current input terminals for
receiving one of the phases from the same number of lines.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
One embodiment of the invention will now be described in conjunction
with the accompanying drawings in which:
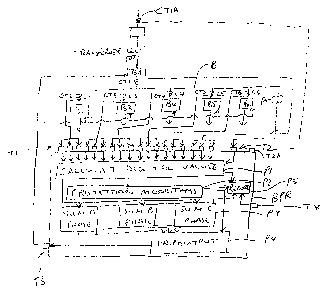
Figure 1 is a schematic illustration of a scheme according to the
present invention for protecting a bus against faults in a three phase
electrical power
system which has a limited number of lines connected to the bus allowing
protection
by a single unit.
Figure 2 is a similar schematic illustration of a scheme according to the
present invention for protecting a bus against faults in a three phase
electrical power
system which has a larger number of lines connected to the bus thus requiring
protection by three units each associated with a respective phase.
Figure 3 is a schematic illustration of one example of the Bus
CA 02359129 2001-10-15
protection unit of figure 1 showing examples of the specific algorithms and
protection
elements according to the known IEEE standard for such elements.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
In Figure 1 is shown a bus system of an electric power supply network
5 where the bus is indicated at B and connects to six lines L1 through L6. L1
acts as a
supply line from a transformer, generator or the like and the lines L2 through
L6 are
feeder lines to remote locations. The bus is supplied by a transformer.
Between each line and the bus is provided a breaker B1 through B6. A
current transformer is provided for detecting the current flowing between the
bus and
10 the line so that there are similarly six current transformers CT1 through
CT6.
It will be appreciated that the system shown in merely one example
and the number of lines may differ and also the arrangement of the line that
is the
number of supply lines relative to the number of feed lines may differ.
A protection relay BPR is provided which has eighteen current inputs
indicated at Terminal T1, an input T2 for receiving a signal representative of
the
voltage on the bus as indicated at PT and a plurality of output terminals
indicated at
T3.
In the arrangement shown the eighteen current input terminals at T1
are divided into six sets of three terminals so that the three phase current
inputs
from the current transformers CT1 through CT6 are supplied respectively to
each of
the sets of three terminals. In this way the relay receives signals relating
to the
current on each of the six lines together with the voltage at T2.
A first processor component P1 is provided which acts to convert the
CA 02359129 2001-10-15
11
input signals from the terminals to the digital values of the individual
currents and
voltage.
In a second processor component P2 there is provided a series of
protection algorithms which act to detect various parameters of the currents
and
voltage to determine a fault condition.
In Figure 3 is shown the series of protection algorithms which are
calculated and these numbers are taken from the IEEE standard C37.2-1979 which
defines the protection functions.
In a third processor component P3 the digital values of individual
currents are summed so as to effect a sum of the A phase components, the B
phase
components and the C phase components separately. The sum takes into account
the phase angle of the currents so that it acts as a differential calculation
to
determine the total current flowing into and out of the bus B. It will of
course be
appreciated that the current flow should equal 0 for each of the three
separate
phases and in the event that the sum does not equal 0 then a fault condition
has
developed.
The output from the processor component P2 in the event that
detection of a fault condition and the output from the processor component P3
in the
event of a detection of a fault condition dependent upon one of the sums being
different from 0 provides an output to a further processing component P4 which
acts
as a trip output for supply to the output terminal T3.
The output terminal T3 provides a trip signal which is communicated to
each of the breakers B1 through B6 to effect a tripping action of the whole of
the
CA 02359129 2001-10-15
12
current flow on the bus in the event of detection of a fault condition as set
forth
above.
After generation of a trip output to each of the breakers, the current
through the respective current transformer CT1 through CT6 continues to be
monitored for detection of a current which is different from zero, in which
condition a
breaker failure is detected. If a breaker failure is detected, action by the
monitoring
device is needed to clear the faulted line from the power system by tripping
breakers
next to the failed breaker. The unit can also be configured where the current
transformer CT1 is located as shown in dash line at CT1A. The unit can also be
configured using an additional input T2A to receive current from both
transformers
CT1 and CT1A. This arrangement can be used to provide a differential
protection
zone for the bus B andlor for the incoming transformer "Trans". The protection
system can then detect the area where the fault is located and isolate that
protection
area from the power supply system by tripping the appropriate breakers.
The unit also includes a recording component P5 which acts to record
the digital values of the currents and voltage in the event of a fault
condition being
detected.
Attention is also directed to copending application serial 09/667,582
filed September 22, 2000 which discloses a time stamp and sample
syncronization
recording system and the unit includes a terminal T4 which allows
communication
from an outside source to effect the recording action and is entitled
"MONITORING
WIDE AREA DYNAMIC SWING RECORDINGS ON AN ELECTRICAL POWER
CA 02359129 2001-10-15
13
SYSTEM".
The relay unit therefore provides the following functions.
It provides bus differential protection, that is the summing action of the
currents to ensure that the sum is zero in all conditions thus detecting bus
faults
independently of line faults.
It includes integrated breaker failure detection in that the status of the
current through the breakers is determined in the event of breaker action.
The algorithms can include over current protection functions from the
IEEE standard.
The recording system allows the digital values of the currents to be
recorded for metering the action of the bus and for fault oscillography.
The algorithms applied to the voltage values can be used to detect
overlunder bus voltage as well as overlunder frequency functions.
The unit can save costs by using the same current transformers used
by other relays in the system thus minimizing external wiring and eliminating
the
need for some special current transformers.
The unit provides metering functions for each line connection.
The unit includes off line analysis and setting software for viewing fault
records and creating relay settings offline. Th is feature allows for the
further
analysis of events and fault conditions that have taken place during a
particular fault
condition.
Turning now to Figure 2 three of the same units shown in Figure 1 and
shown in Figure 3 are used as indicated at BPR1, BPR2 and BPR3. In this
CA 02359129 2001-10-15
14
arrangement the units are configured so that each is associated with a
respective
one of the three phases of the bus system. Thus in this case the total number
of
lines is greater than 6 and may be up to 18 so that each current transformer
supplies
a signal indicative of the individual three phases to the terminals T1 of the
three
units. Thus BPR 1 receives all the A phases, BPR2 receives all of the B phase
and
BPR3 receives all the C phases
The same protection functions and the same summation are carried
out in each of the units so that for example the unit BPR1 acts to sum the A
phase
currents of all of the lines to ensure that the net current on the bus is 0.
The units can be readily reconfigured by software input to
accommodate either the scheme of Figure 1 of the scheme of Figure 2.
When the protection device is used as in Figure 2, a software setting is
invoked that allows each unit device to function as by adding individual phase
quantities instead of breaker currents.
Since various modifications can be made in my invention as herein
above described, and many apparently widely different embodiments of same made
within the spirit and scope of the claims without department from such spirit
and
scope, it is intended that all matter contained in the accompanying
specification shall
be interpreted as illustrative only and not in a limiting sense.