Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02372299 2002-02-14
A METHOD FOR TRANSMITTING LOCATION INFORMATION
ON A DIGITAL MAP, APPARATUS FOR IMPLEMENTING THE METI30D,
AND TRAFFIC INFORMATION PftOVISION~RECEPTION SYSTEM
BACKGBOZJND OF THE INVENTION
l.Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to an information transmission
method for transmitting location information such as traffic
jams and accidents for example in a traffic information provision
system and apparatus for exchanging location information using
the method, and in particular to such a method and apparatus
that can correctly report a location on a digital map.
1~ 2.Deacription of tha Related Axt;
In recent years, the number of vehicles that have car-mounted
navigation apparatus has bean increasing rapidly. The
car-mounted navigation system has a digital map database and
is capable of displaying the map around the vehicle on a screen
based on the latitude/longitude data received b!t a GPS receiver
as well as displaying the travel locus and the result of search
for a route to the destination on the snap.
In Japan, digital map databases are prepared by several
companies. The pxoblem is that map data contains errors inherent
~1-
CA 02372299 2002-02-14
in the reduced-scalQ map . The errors depend on individual digital .
maps. Some of the maps on the market drawn on the scale of 1:25000
contain errors of about 50 metefs depending on the location.
Latitude/Longitude data obtained from a GP5 receiver may
contain errors of several tens of meters.
Some models of car-mounted navigation apparatus on the market
receives traffic jam information and accident information from
a traffic information provision system and displays the traffic
jam and accident locat~.o;ns on the map or performs route search
using such information as additional search conditions.
In a related art traffic information provision system. as
shown in Fig. 7, traffic information is provided from a traffic
information collecting renter 71 that has local jurisdiction
over an area to an information delivexy center 72. Traffic
information edited for each transmission medium including FM
broadcasts, road beacons and cell phones is transmitted via
respective media.
The traffic information collecting center 71 exchanges
traffic information with a traffic information collecting center
78 in other areas to collect traffic information in a wide sQrvice
area including the peripheral areas.
In the traffic information, far example, in case
latitude/longitude data on the location is presented alone in
2g order to report a traffic jam location or accident location,
various errors are contained depending on tho kind of digital
.2.
CA 02372299 2002-02-14
map database of the car-mounted navigation apparatus as mentioned
earlier. Thus, different accident locations ors the road could
be recognized by the car-mounted navigation apparatus rQtaining
a digital map database tram ~CompanyAand the car-mounted navigation
apparatus retaining a digital map database from Company B.
In order to alleviate incorrect infarmation transmission,
as shown in Fiq. 8A, crossings a and b on a road network are
assumed as nodes, and a road c connecting the codes as a link.
Each node is assigned a node number uniquely representing the
node (a~illl, b=3333y . Each link is assigned a link number uniquely
representing the link (c=1111333:3) . In the digital mnp database
of each company, the node numbers and link numbers thus assigned
are stored, in correspondence with each crossing and road.
In traffic information provision service, a point on the
road is represented by 'first specifying a link number then the
distance in mntars from the start of the link. For example,
a display "Location 200 meters from the start of the road with
link number~11113333 " allows the user to obtain the location
8 on the same road by tracing the road with link number=11113333
a0 as tar as 200meters from the node wi th node number 1111, irrespective
of what digital map data is used by the car-mounted navigation
system in question.
Node numbers and link numbers defined on a road network
must be changed to new numbers in case a road d is constructed
a5 or a road is modified as shown in Fig. 8B. Such modifications
to node numbers and link, numbers require upda=ing of digital
CA 02372299 2002-02-14
map data from each company.
Construction of or modification to a road continue into
the future. As long as on-road location representation is made
using node numbers and link numbers, maintenance of digital map
databases is permanentlyaccompaniedbyhuge workload and resulting
costs.
The information delivery center must send information that
complies with past node numbers and 1 ink numbers for a predetermined
period, fox example three to five years. as well as the information
or the latest year, in order to support navigation systems sold
in the past. This causes huge maintenance workload.
SUN~ARY OF THE INVENTION
The invention solves such related art problems and lima
at providing a location :information transmissipn method that
can transmit a location on a digital map without excessive
maintenance workload and apparatus fox implementing the method.
In a location information transmission method according
to the invention, an information provider transmits on-road
location infox~raation by using road shape data consisting of a
string of coordinates representing the road shape of a road section
having a length that depends on the situation and relative data
indicating the on-road location in the road section. A party
receiving theon-road location information performs shape matching
-4-
CA 02372299 2002-02-14
to identify the road section on the digital map a.nd uses relativt
data to identify the or.-road location in this road section.
In location information transmission apparatus according
to the invention, apparatus at an information provider compriaea
a location information converter for converting transmit on-road
location information to z~oad shape data consisting of a string
o! coordinates representing the road shape of a road section
having a length that depends on the situation and relative data
indicating the on-road iocation in the road section. Apparatus
at a party that receives t:he on-road location information comprises
a shape matching section for perfonainq shape matching by using
the received road shape data, identifying the road section on
a digital map and identifying the on-road location in the road
section by using the relative data.
Thus it is possible to correctly transmit a location on
a digital map as wall as the travel direction of the vehicle
without defining node numbers or link numbers on a road network.
BRTEF DESCRIPTION OF T.HE DRAWINGS
Fig. 1 is a block diagram showing a configuration of location
inrormation transmission apparatus in the first embodiment of
the invention. .
Fig. 2 is a flowchart showing the operation of location
information transmission apparatus in the first embodiment of
.5.
CA 02372299 2002-02-14
the invention.
Fig. 3 is an explanatory drawing illustrating road shape
data and distance data constituting the road locationinformation.
Fig. 4 is an explanatory drawing showing an example of shape
matching.
Fig. 5 is a block diagram showing a configuration of location
information transmission apparatus in the second embodiment of
the invention.
Fig. 6 is a block diagram showing another configuration
x0' of location information transmission apparatus in the second
embodiment.
Fig. 7 is an explanatory drawing showing a traEtic information
provision system.
Fig. 8A is an explanatory drawing of node numbers and link
numbers.
Fig. 8H is an explanatory drawing of modif'_cations to node
numbers and link nua~bers made when a new road is constructed.
DESCRIPTION OF'rHE PREP"ERRED EMBODIMENTS
20 The first aspect of the invention is a location information
transmission method for transmitting on-roadlocation on a digital
map. characterized in that an information provider transmits
on-road location information by using road shape data including
the on-road location information consisting of a string of
2~ coordinates representing the road shape of a road section having
CA 02372299 2002-02-14
a length that depends on the situation and relative data indicating .
the on-road location in the road suction and that a party receiving
the .on-road location inlormatian performs shape matching to
idQntify the road section an the digital map and uses the xelative
data to identify the on-raad location in the road section. This
makes it possible to correctly report a location on a digital
map without defining node numbers or link numbers on a rondnetwork.
The second aspect of the invention uses a stringof coordinates
arranging latitude/longitude~ data of the road point per
predetermined distance interval as a ~trinq of coordinates
representing the road shape. A party receiving the on~road
location information uses the latitude/longitude data of each
point to parform~ahape matching thus identifying the road section
15 having, tha same road shape.
Th~ third aspect of the invention uses distance data from
a specific point in the road section as the relative data. A
party receiving the on-road locationinformation uses the distance
data to identify the on-road location after identifying the road
20 section.
The fourth aspect of the invention is location information
transmission apparatus for exchanging information about tht
on-road location on a digital map, characterised in that apparatus
at an information provider comprises a location information
25 converter for converting transmit on-road location information
to road shape data including the on-read location consisting
-?-
CA 02372299 2002-02-14
of a string of coordinates representing the road shape o! a road
section having a length that depends on the situation and relativa
data indicating the vn-road location in the road section. and
that apparatus at a party receiving the on-road location
g information comprises a shape matching section for performing
shape matching by using the road shape data, identifying the
road section on a digital. map and identifying the on-road location
in the road section by using the relative data.. This makes it
possible to correctly exchange information about the location
14 on a digital map without defining node numbers or link numbers
on a road network.
The fifth aspect of the invention uses a string of coordinates
arranging latitude/longi.tude data of the road point per
predetermined distance interval as a string of coordinates
representing the road shape. The shape matching section of the
apparatus at a party receiving the on-road location infortaation
uses the latitude/longitude data of each road point to perform
shape matching thus identx.fying the road section having the same
road shape.
;Z4 The sixth aspect of the invention uses distance data from
a specific point in the road section as the relative data. The
shape matching section of the apparatus at a party receiving
the on-road location information uses the distance data to identify
the on-road location after identifying the road section.
,:t5 The seventh aspect of the invention is a traffic information
provisionlreception syst:ern to which location information
_$.
CA 02372299 2002-02-14
.
transmission'apparatus accordingw to the fourth aspect of the
invention is applied. This m'ake's it possible to r_orrsctly report
the location on a digital ;map without using node numbers or link
numbers.
The eighth aspect of the invention is characterized in that
apparatus at the information provider is a center for collecting
traffic information in the area and that apparatus at the party
receiving the onyroad location information is a center for
collecting traffic information .in other areas. This makes it
:l0 possible to use the location information transmission zaethod
for exchange of traffic information between centers.
The ninth aspect of the invention is characterized in that
apparatus at the information provider is an infrastructure for
providing traffic information and that apparatus at the party
receiving the on-road :Location information is a car-mounted
navigation apparatus. This makes it possi'b1e to use the location
information transmission method fox information provision to
car-mounted navigation apparatus.
Embodiments of the invention will be described referring
;;p to the drawings .
(First embodiment)
In the first embodiment, a location information transmission
method according to the invention will be described taking as
an example the case where traffic information is exchanged between
traffic information col.le:cting. centers in Fig. 7
The traffic information collecting center A, as shown in
_S.
CA 02372299 2002-02-14
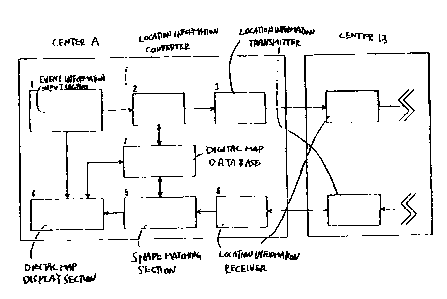
Fig. 1, comprises an event information input section 1 for inputting
. event information such as; traffic accidents and traffic jams,
a location information converter 2 for generating location
information representing the event location, a location
information transmitter 3:~or transmitting the generated location
information, a location information receiver 6 for receiving
the location information's a shape matching section 5 for performing
shape matching and identifying the event location from the location
information, a digital map display section 4 for displaying the
LO event location on a map. and a digital map database 7. The traffic
information collecting center 8 has the same configuration as
the traffic information collecting center A.
Operation flow of the traffic information collecting cantor
is shown in Fig. 2.
15 (Step 1:) when an event such as a traffic accident or a traffic
jam takes place, (Step 2 : ) The event details and the event location
information are input to the event information input section
1 of the traffic information collecting center. For example,
when information indicating occurrence of a traffic jam is input
20 to a vehicle detector installed on the roadr (Step 3: ) the location
infoxrnationconverter 2 generates road shape data including traff is
jam location consisting of a string of coordinates rep:cesenting
the road shape of a road suction having a predetertained length
and distance data indicating the distance from the start paint
;25 0! the road section to the traffic jam location, in ordQr to
report the traffic jam information to the traffic information
-10-
CA 02372299 2002-02-14
collecting center B.
FiQ. 3 is a schematic view showing the location information
generated by the location infor=nation converter 2. In case a
traffic jam has occurred in the section A to B on the road, the
road shape o! the road including the section is represented in
a string of coordinates consisting of 601 points in 5-meter
intervals, Po (xo, yo) , f~ (x~. Y~) . ... . pcoo (xcoo,
ycoo) . Here, Xk
and yk are latitude and longitude data, respectively, o! the
on-road point px acquired fronn the digital database '7. Further,
;l0 the distance 1~ from the point Po(xo, yo) to the traflic jam start
point A and the distance 1~ from the point Po (xo. yo) to the traffic
jam end point 8 are obtained and t2~e Yoad shape data : (xo, yo) (xi.
Y~) ... (xaoar yaoo) and traffic jam distance data: 1, to 1= m are
generated as location information.
;l5 Rank information indicating the degree of traffic jam arid
information indicating the type of a digital map database used
art added to the location information to create transmit
infor~aation, and (Step 4: ) the location inlonaation transmitter
3 transmits the information to the traffic information collecting
canter 8.
(Stop 5:) In the traffic information collecting enter.
receiving the information at the'location information receiver
6, (Step 6: ) the shape matching :action 5 performs shape matching
ofmap data in the digital map dat abase ~ and the string of coordinates
~t5 indicating the xoad shape to identify_the road section on the
CA 02372299 2002-02-14
digital map, then identifies the traffic jam section on the digital
map based on the distance data from the start point of the road
section.
Fiq. 4 shows an example of shape matching.
Roads Q and R included within the error range around the
Po (xo. yo) point of map data read from the digital map database
~ are selected as candidates.
Then, locations Qa. Ro on each candidate road closest to
Po (xo~ yo) are obtained and distance Po-Qa and distance Po-Ro are
calculated.
This operation is carried out for each point Po (xo, yo)-~
P1 (xm W ) . ,.. . p~oo (x~oo. ysoo) and the road section where the summation
value of the root mean sauare of the distances from each point
Po. p~. ... . p~oo is sma5.lest i.~ obtained.
Then the section 11~-lz m from the start point of the road
section is identified as a traffic jam section.
(Step 7: ) The digital-map display section ~, reads data from
the digital map database 7 and displays a iaap, then paints the
colors corresponding to the traffic jam levels in the traffic
2p jam section obtained by the shape matching section 5:
In this way, the party receiving information can perform
shape matching and identify the road section having th~ road
shape without defining node numbers or link numbers when the
information provider represents the road shape using a string
of coordinates.
12-
CA 02372299 2002-02-14
While the interval of points used to indicate th~ shape
o! the road section is 5 meters and the number of points is 601
in this embodiment, the interval and the number .sre not intended
to limit the invention.
while latitude and longitude data is used as coordinate
data in a string of coordinates in this embodiment, other coordinate
data may be used so long as the data can be shared by the information
provider and the infos~aation receiver.
By adding effective auxiliary information to the t=ans~nit
location infor~xation, it is possible to enhancr. the efficiency
of shape matching at the receiving party.
As a shape matching algo=ithm, a method other than the
illustrated least square method may be used.
(Second embodiment)
x~ In the aQCOnd embodiment, transmission of location
information between the infrastructure of the era='fic info.ratation
provision .system (intarmation provider's and '.he Car-anounted
naviqatioa apparatus.will ba described.
Nera, infrastructure refers to such social infrastructures
$p as broadcasting stations traffic signs, traffic aiqual lights
or trafficmonitoring cameras and so on. The social infrastructures
may involve centers to control the forementioned stations, signs
or other elements that are parts of the infrastructure.
Fig. 5 shows an infrastructure 51 that pxovides information
and car-mounted navigation apparatus6lthat receive~information.
. 1g .
CA 02372299 2002-02-14
The infrastructure 51 comprises an event information input
section 52 for inputting event information, a location inforiaation
converter 53 for generating location informat:,on repressnting
the event location, a location information trunsmitter 59 for
transmitting the generated location infonaation, a digital map
display section 55, sad a digital map database 56.
The car-mounted navigation apparatus 61 comprises s location
information receiver 62 :eon receiving location in=ormation, a
shape matching section Ei3 for performing shape matching and
identifying the event location fzom the location information,
a digital map display section 64 for displaying the event location
on a map, and a digital rnap database 65.
Operation of the infrastructure is the same as the operation
of step 1 through stop 4 of Fig. 2. Operation of the car-xaounted
navigation apparatus is t:he same as the operation of step 5 through
step 7 of Fig. 2.
In the traffic information provision. system, the
infrastructure provides information including the string of
coordinates of the road section of apredetermined :.enqth including
the event location and t:he information on the event location
that uses the road section as a reference, via PM broadcasts
and beacons. The car=mounted navigation apparatus identities
the road section from the string of coordinates and identifies
the event location by using the road section as a reference.
Thus, it is possible to correctly report the location on a digital
map without defining pads numbers or link numbers.
CA 02372299 2002-02-14
Fig. 6 shows a case where the car-mounted navigation apparatus
comprises an event information. input section, a location
information converter, a location information transmitter, a
location information receiver, a shape matching section, a digital
map display section, and a digital map database. The car-mountsd
navigation apparatus can transmit the accident location to the
infrastructure it an accident takes place.
in this practice, 'the car-mounted navigation apparatus
acquires from the digital map database coordinate data 'of a
plurality of locations in the road section of a predetermined
longth including the accident location. Than the car-mounted
navigation apparatus transmits the coordinate data andinformation
on the event location r.~sing the road section as a reference.
The center recsivss the information and performs shape matching
to identify the road section from the road shape, then identifies
the accident location.
As understood from the foreQoiny description, a location
information transmissionmethod and apparatus can correctly report
the location on a digital map to a distant party without a:inq
Qp node numbers or link numbers on a road network.
With this method. it is possible to substantially reduce
workload and costs for maintenance of digital map databases thus
reducing the socials Costa for maintaining the tra»fic information
provision system.
-ls-