Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02413118 2002-11-28
TEM FILE 256.3
TITLE: LOCAL AREA AND MULTIMEDIA NETWORK USING RADIO
FREQUENCY TRANSCEIVERS AND COAXIAL CABLE
Field of the Invention
This invention relates to cable television and Internet systems and to
telephone
Internet services and, more particularly, to a system and apparatus for
combining
transmission of multimedia and computer data from a cable television or
telephone line
or both and redistributing the signals to a local area network.
Background of the Invention
Rapid advances in telecommunications and digital technology and desire to
reduce the clutter of electronic cords, wires and set-top boxes have made it
desirable to
have a local area network in a building, such as a house or business, which
can receive
and convert diverse signals from varied outside services such that multiple
devices in that
building can be used to access multimedia and Internet signals at the same
time. The
outside services could include interactive services, cable video and audio
services, cable
Internet services, telephone company services, telephone Internet and network
services
and other types of information services.
1
_ _'__._ _.~__ ._
CA 02413118 2002-11-28
The need to share limited resources such as printers, scanners, data backup
and
Internet access in the home and business environments has created a demand for
data and
resource networking. This demand is coupled with concerns over limited choices
in
service providers. If all services introduced into a building were to be
limited to just one
service provider, such as the telephone company, there is reasonable
apprehension that
the user will not be paying the lowest competitive price for one or more of
those services.
A further consideration is the ability of multiple users within, for example,
a
home to have access to the Internet at the same time 'and to use a common
printer or data
storage device that might be located physically distant to the user's
location. There exists
a need for an architecture and system which would permit multiple users to
access
multiple services at the same time without the need to install expensive and
space-taking
cables, wires or set top boxes to decipher and access these different types of
data.
Canadian patent application 2,275,276 (referred to herein as '276) discloses
an in-
home network for distributing data such as video, audio or control data. To
practise this
invention it would be necessary to rely on a "set-top box" - a multi-media
computer that
augments the use of televisions with an external network interface module that
connects
to an external network and data provider. It would also be necessary for each
individual
device to connect to this set-top box directly or through a matrix. Unlike the
present
invention, in the '276 patent transmission of data and multimedia services to
and from the
terminals must flow through a central set-top box that preferentially connects
to a digital
2
CA 02413118 2002-11-28
broadband matrix. The network interface module is relatively expensive and
there would
need to be one set-top box for each end device.
Canadian patent application 2,238,394 ('394) discloses a home network
architecture to introduce entertainment services into an internal digital
network from an
external source, making these services available to all terminals connected to
the internal
network. Unlike the present invention, the invention disclosed in the '394
application
relies upon multiple set-top boxes and separate network interface units which
are coupled
together through a internal digital network insta~letk- in the home in order
to provide
interconnectivity at a reasonable cost to the consumer.
Canadian patent application 2,116,801 (' 801 ) discloses a system for
delivering
audio and/or video signals in connection with the provision of interactive
television
services to users through a distribution system such as a cable television
system or a
telephone network. Unlike the present invention, the '801 application does not
provide
for, or contemplate, distribution of these services as part of a local area
network so that
the various users can be in communication with each other or can operate
remote devices,
such as a fax machine, individually.
Canadian patent 1,332,635 ('635), which is based on U.S. Patent 1,332,635,
discloses an apparatus for transmitting data over a cable television channel
susceptible to
interference noise wherein the transmitted data is spread over at least a
portion of the
spectrum of the cable television channel preferably in the "noisy" 0 - 30
megahertz
upstream data transmission band of the cable television system spectrum. The
present
3
CA 02413118 2002-11-28
invention can be distinguished from the invention disclosed in the '635 patent
in that the
architecture refers to a means of encoding digital signals on a cable
television network
but does not contemplate use of analog signals as does the present invention.
US patent 6,307,862 ('862) discloses a method and apparatus for monitoring and
controlling a data network. The invention as disclosed uses new or existing
cable
television ("CATV") coaxial cable to transmit to or receive data from devices
coupled to
an electronic control and monitoring system. This network could be installed
in any
structure and would provide for two-way communication between the devices. In
the
preferred embodiment certain cable channels are removed or stripped from the
cable
television signal and those selected or stripped channels are used to carry
data signals and
become data channels, with the remaining CATV channels and the data channels
being
combined to form a new CATV signal which is transmitted on a standard CATV
cable. In
order for the network to operate properly a minimum of two CATV channels must
be
stripped, the absence of these channels could provide a disruption to existing
or planned
services normally being distributed on the CATV cable.
Summary of the invention
The present invention is a system and architecture comprised of a common
standard coaxial medium that enters a building, such as a house, at a single
point and then
terminates in a multiplicity of endpoints throughout the building. The system
is
comprised . of two components that include an access multiplexer which
converts
4
CA 02413118 2002-11-28
baseband data from a primary class of networks such as digital data, and/or a
second class
of service, which may originate as digital or analog telephone signals, and/or
access
control for multimedia services into a common local area network (LAN), and
then to a
radio frequency outside the set of frequencies in the range of 54-860 MHz, and
may then
also be combined with low voltage power onto a single CATV coaxial cable and
then
distributed in either a star and/or multidrop configuration to a multiplicity
of termination
points.
At each connection point a splitter separat~s'~he various signals being
carried by
the CATV cable, converts the data and/or second class of service to and from
the said
radio frequency and then the separated signals are relayed to their respective
end points,
such as a multimedia entertainment system via a standard coaxial cable, and/or
a data
terminal via a data cable, and/or a second terminal by a separate cable. All
classes of
services distributed throughout the building function independently, as if
distributed on
separate media, with concurrent two-way services to and from the various
endpoints
provided all classes of services. Additionally the data service connects to a
common point
permitting all data devices within the local area network to communicate with
each other
over the coaxial medium either in conjunction or independently with the
operation of the
plurality of multimedia entertainment systems and/or data terminals located at
various
and geographically diverse locations throughout the building.
This system is an improvement over existing systems that provide data and
multimedia signals through separate and independent systems throughout a house
or
5
CA 02413118 2002-11-28
other building because the invention uses a frequency outside the common set
of cable
system frequencies (i.e. 54 - 860 MHz) and includes a second class or service,
unlike
other systems which use common frequency or frequencies, such as cable
Internet
services, and may cause interference with said frequencies. The system is also
capable of
transmitting in both directions using the aforementioned frequency. The
present invention
is also an inventive improvement over the prior art in that the architecture
of the wall
plate in the present invention contains a radio frequency transceiver that
converts the
baseband data and/or a second class of service to a~d'~om the said radio
frequency.
The addition of LAN functionality to an existing or new cable television
network
in a building such as a home facilitates sharing of devices such as printers,
facsimile
machines, gaming devices and other resources. The LAN may also be used for the
distribution of services throughout the home.
A second embodiment of the wall plate can integrate a standard telephone jack,
as
well as the previously described services.
A third embodiment can integrate a data service for providing access to
restricted
television or other services that are accessed on a user pay basis.
Due to the nature of the LAN, many services can be simultaneously combined and
distributed on a common medium. The invention includes and replaces set-top
boxes,
dedicated servers and interconnection hubs normally found in a network, thus
affording a
lower cost alternative which can be installed in a relatively short period of
time using
familiar tools and equipment. In the commercial building environment, this
permits the
6
CA 02413118 2002-11-28
use of personnel not necessarily trained in the art to perform installations,
minimizes
mysterious disappearance of equipment due to the fact that it is concealed in
a wall outlet,
and also reduces overall system cost by eliminating the need for set top
boxes.
Brief Description of the Drawings
Embodiments of the invention will now be described, by way of example only,
with reference to the accompanying drawings, wherein:
Figure 1 shows a star configuration of the pxe~ent invention;
Figure 2 shows a multidrop configuration of the present invention;
Figure 3a is a front view of a wall transceiver of the present invention; and,
Figure 3b is a side view of the transceiver of fig.3a.
Description of Preferred Embodiments
The invention is described in detail with reference to Figures 1 to 3b, in
which
like reference numerals refer to like elements.
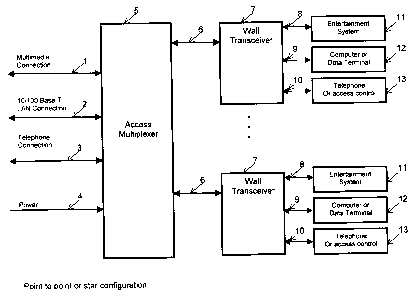
In general, Figure 1 shows a star configuration where each wall transceiver is
connected to an individual connector on the access multiplexer (5), and Figure
2 shows a
multidrop configuration using only a single connector at the multiplexer. In
use, either
one of or a combination of both of these techniques can be employed.
Referring now in more detail to Figure 1, an in-home network is shown that
combines an existing multimedia connection (1), a local area network
connection (2), a
7
CA 02413118 2002-11-28
telephone connection (3) and power (4) together onto a single coaxial cable
(6), by using
an access multiplexer (5). The cable is then connected to a wall mounted
transceiver (7),
which separates the previously multiplexed signals into a number of streams. A
first
stream comprises a multimedia signal (8), which is then connected to an
entertainment
system (11). A second stream comprises a local area network (9), which is then
connected to one or more computers or data terminals (12). A third steam
comprises a
third connection ( 10) which may be connected to a telephone, or may provide
another
data service for providing access to restricted tel'~vvfssion or other
services (13). In this
configuration individual cables connect from the access rnultiplexer to the
individual wall
transceivers in a star configuration.
Figure 2 shows another embodiment of the same network with the same
connections as in the Figure 1 embodiment, except that the wall transceivers
are
connected to the access multiplexer in a multidrop configuration using a cable
splitter
device (6A).
A wall transceiver 20 for the above network is shown in a front view in Figure
3a
and in a side view in Figure 3b. The transceiver has a wall plate 22 with
three individual
connections for multimedia 24, data 26 and telephone or access control 28.
These
connectors 24, 26 and 28 are also mounted onto a single printed circuit
assembly 30
contained in a housing 32, which is joined to the wall plate 22. The common
coaxial
connection 34 enters the rear of the housing 32 and also connects to the
circuit assembly
8
CA 02413118 2002-11-28
30. In use, the wall plate 22 is mounted to an outside face of a wall and
hides the housing
32 which is located within the wall.
In other embodiments of the invention, not all of the above features need be
provided by the network and wall transceiver. For instance, one alternative is
to combine
only data and telephone or control services onto the coaxial cable, in which
case both the
access multiplexes and the wall transceiver will have the unused function and
connections
omitted, namely the multimedia connection. In a different embodiment, the wall
transceiver may have only a coaxial multimedia conri~ction and one of either a
LAN data
connection or a telephone connection or an access connection, but both
features will still
be powered from the access multiplexes.
The above description is intended in an illustrative rather than a restrictive
sense,
and variations to the specific configurations described may be apparent to
skilled persons
in adapting the present invention to other specific applications. Such
variations are
intended to form part of the present invention insofar as they are within the
spirit and
scope of the claims below.
9