Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02427725 2003-05-O1
ROlILIY JTlJ.LCd"641.G C'Jl'4 alillyr.iE
OLD ~?F 'THE IN VENT.It~l~1
The present invenrion relates tn hydrogen storage cantainexs, and,
particularly, to
containers tbr coritainLng xrletal laarticles capanle of tomamg meter
t~ryanaes:
BAC'L~.CrROUN.A C1~ THE llV'VEI'~"fI(~lrT
Metal hydrides are used to score hydrogen in :many different sizes and. shaped
canisters.
ht order to facilitate the a6sarpxion ox desorption of the hydrogen, ~~e
canister and, consequently,
tile metal hydride, needs to be cooled or heated To facilitate good
perforn2ance-~f thp firr~rapP
canister (desorption rate, fzllitlg time, etc.), the inside of the caxti stet
requires efficient heat
exchange means to improve the ahsaxptianldesorptiozt l~netics.
.Also, during absorption of the hydrogen, the metal hydride expatxds due to
its reaction
~~T~'~~l~Il~~'' ~"ere~Y3t~~q8'.~~ ~3fQf ~~e in the canister. It is desirable
to
a 1 1: 4 i a wssw4svaar wssrua+.-.sv ~ w
canistez is mitigated ar avoided.
BRIEF DESCRll'TIUN CAF DRAWINGS
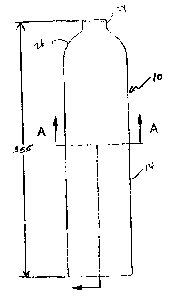
Figure 1 is a franc elevation view of a container of the presemt invention;
Figure 2 is a partly fragmentary side elevation view of the container in
Figure 1;
Figure 3 is a cross-sectional view of the eontainer in p'igure 1, taken. along
lines A-As
Figure 4 is a top-perspective view of the liner o f the container in Figure l;
and
fiigure 5 is a tap-plan view ofthe liner illustrated in Figure ~..
CA 02427725 2003-05-O1
DETA1R.ET.S DESCRIPTION
Referriatg to figure 1, the present ixwention provides a cautainer 10 for
contaizzixtg
metallic particles 12 capable of forming hydrides. The metallic particles 12
are capable of
absorbing hydrogen to assume an absoxbed state and are also capable of
desorbirag the absorbed
hydrogen to assume a desorbed state. In the absorbed state, the metallic
particles 12 occupy
greater volume than. in the desorbed state.
The container 10 includes a pressure vessel 14 including an inner surface I6
defining a
storage volume 20. A structure 18 is disposed within the storage vaiume 20
a'nd is configured to
effect thermal communication between the i~er surface i~ attd the metallic
particles 12
disposed within the storage volume 20. A resilient liner 22 is also disposed
in the storage
volume 24 and is configured to isolate metal particles 12 disposed in the
stoxage volume ZO from
the inner surface 1~. A space is defined between the liner 22 and the ixxuer
surface 16. As the
raetallic particles 12 in the storage volume 20 assume au absorbed state from
a desorbed state,
the space contracts in response to forces imparted by the metallic particles
an the liaxer 22. This
is because the metallic particles t2 expand upon absorption of hydrogen,
causing the liner 22 to
defaxm and move closes to the ituu'r surface i6.
Figures 1 and 2 illustrate the container 10 of the present uavention including
a pressure
vessel 1~ having an tinier surface 1~ defining a storage volume 20. A nozzle
24 is provided at
cite end 2$ of the container 10, defuung an inlet far effecting fluid
communication between the
storage volume 20 azid the extexiox of the container iC~. The atozzle extends
24 ~rom a dome 2fi
formed at the end 28 of the container 10. The aaz2le 24 is configured for quid
coupling to a
conduit for effecting delivery of hydrogen from within the storage volume 20
to a d4wtastxeam
apetatlon, such as a fuel cell or irtterxtal combustion engine. The conduit
also facilitates supply
of hydrogen to the pressure vessel i~ to effect charging of the metallic
particles 12. In one
embodiment, the pressure vessel I O has a length of 3S~ rnm, an outside
maximum. diameter of 89
mm, and a wall thickness of 2.54 uzut. The material of construction of the
pressure vessel 14 is
aluminum.
CA 02427725 2003-05-O1
The storage volume 20 of the pressure vessel 14 is configured to receive
nxetallic
particles 12 capable of forming hydrides. Such metallic particles 12 iraust be
capable of
absorbing hydrogen t~ effect storage of hydrogen for l2ter use, such as for
use as a fuel in a fuel
cell or in an internal combustpon engine. Further, such metallic particles 12
mast be capable of
desorbing the absorbed hydxogen upon demand from. au unfit operation, such as
when ~°equired
for use as a fuel in a fuel cell or in. an internal combustion engine. Upon
absorption of hydrogen,
the metallic particles 12 have a tendency td expand, and thereby increase Che
volume occupied.
T~uriug desorption, the metallic particles 12 have a tendency to contract, and
thereby reduce the
volume occupied.
Absorption of hydrogen by the metallic particles 12 is an exotheamic process.
rxt
contrast, desorption of the absorbed hydrogen and gas from the metallic
particle I2 is an
endothermic process, To effect heat transfer >aetween the mr~tallic particles
12 and the
environment external to the pressure vessel 14, the structure 18 is disposed
in the storage volume
20 and is configured to effect thermat communication between the inner surface
16 and the
metallic particles 12 disposed within the storage volume 20. Heat is imparted
to, and dissipated
from, the pressure vessel by contacting the pressure vessel with a fluid
(liquid or gas, such as
water or ambient aix) which acts as a heat sink or heat source as required,
deferring to Figures 2
and 3, the Structure 1 g includes a plurality of elongated aluminum tubes 30
disposed in a storage
volume 20. The aluminum tubes 30 extend from the bottom 32 of the pressure
vessel 34. and
ate just below the dome 25 of the pressure vessel l~. bath of the aluminum
tubes 30 has
an outside diameter of 12.7 mm, a wall thickness of X1.8 mm, and a length of
280 mm. for a
pressure vessel 14 having the dimensions specified above, 31 of these tubes 30
can be disposed
in the storage volume 20 of the pressuxe vessel 14 to facilitate the desired
heat transfer.
To facilitate migration of hydrogen gas during absorption and desozption fmm
the
metallic particles 12, the aluminum tubes 30 can include a plurality of very
small circular holes
or other shaped pexforations. These circular holes or perforations have a
diameter of 1132" or
smaller. This would be small enough to allow the migration of the hydrogen gas
hut not allow
the metallic particles 12 within the tubes 30 to migrate outside of the tubes
30 and thereby exert
additional forces on adjacent materials or surfaces during expansion.
CA 02427725 2003-05-O1
At least one of the plurality of tubes 3b can be in the farm of a solid
sintered ~3ter cube
that Would provide a permeable solid to assist in _ _the absorption-and.-
!le..>~~..~i~on-ofhyr_lrnge" gac
while not allowing the xxligratiou of metallic particles.
To take up the expansion of the metallic particles 12 as they absorb hydrogen,
the
resilgent liner 22 is disposed within the storage volume 20 of the pressure
vessel 1~ and
s~y , _ ~ . . .,. _ _. _.._"~ _ ~ ~_a__ , n s_~. ..A.a ...:.~L:.e .t _
~.__..~.. ....7....,... '9n .~...,... 41"..
inner surface 16. den metallic particles 12 axe disposed in the storage volume
20 in a desoxbed
state, a space is defined between the liner 22 and the inner surface 1 ~ of
the pressure vessel 14.
lUpon absorption of hydrogen by the metallic particles 12, the metallic
particles 12 a>xpand,
occupying a larger volume of space within the storage volume 20, and press
upon the liner 22 so
as to effect a reduction in volume irt the space deigned laetween the liner 22
and the il7nex surface
16. Yn this respect, the disposition of the litter 22 within the storage
volume 20 of the pressure
vessel 14 provides space around the inside periphery of the pressure vessel 14
to allow volume
to be taken up by the expansion of the metallic particles 12, Furdxer, the
liner 22 provides a
means to better distribute stress then the pressure vessel 14 wall due to
localized conglomeration
of the expanding metallic particles 12. In this respect, the liner 2~! carl be
comprised of spring
steel.
Deferring to Figures 4 and S, in one erubodixnent, the liner 22 is in the form
of a cube with
a corrugated profile. The corrugated profile provides wall space between the
inner wall 1 ~i of the
pressure vessel 1~4 and the liner 22 wkten the liner 22 is disposed in the
storage volume 20 of the
pressure vessel 14. Upon expansion of the trcetallic particles 12, the
metallic particles 12 apply a
force to the liner 22, causing the corrugations to flatten out. 'fhe tubular
form of the liner 22
de.~tes a space which receives the aluminum tubes ~0 and the metallic
particles 12. Vahen
assembled. the liner 22 contains the aluminum tubes 30 arid the metallic
particles 12. In relation
to the aluminum tubes ~dl, the metallic particles 12 occupy a space inside the
tubes 3Q and tha
void space between the tubes 30. ~'he metal particles 12 taxi also occupy the
space within the
dome 26 of the pressure ves$el 12. 'The liner 22 has a length of 280 mm, a
diameter of267 mxn,
arid is O.1S mm thick.