Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
ANALYTICS DELIVERY PLATF~RM
FIELD
The present disclosure relates to an analytics delivery platform, and
more particularly to creating and viewing content on a wide array of
devices and seamlessly transitioning from viewing content on one device to
viewing the same content on a second device.
BACKGROUND
Enterprises are collecting vast amounts of data about all facets of
their operation. The raw data often exists in an operational database where
it is stored in rows and columns of numbers and codes. These enterprises
need a means for making meaningful sense of this large amount of data.
Analytics delivery platforms are designed to facilitate the interpreting,
analyzing, compiling, and understanding of such data.
The analytics delivery platform allows the user to create various
reports. For example, users can create reports to identify their best
performing product, store, product representative, or the like. The reports
enable the user to make better decisions.
1
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
Analytics delivery platforms of the prior art developed based on the
traditional client-server paradigm. Users now also desire to receive web-
enabled reports. Therefore vendors have bolted web-functionality onto their
products. Web-functionality constitutes the content creator creating the -
same content in a web report format. Likewise, users now desire wireless
access to reports. Thus vendors have also bolted wireless-functionality onto
their products. The bolt-on architecture of current analytics delivery
platforms requires content to be generated specifically for each format.
Each format of a particular content is stored by the analytics delivery
platform. The storage of separate formats is necessary because user device
interfaces differ significantly from device to device.
Therefore, content created in one format cannot be used by a device
requiring the content in a different format. The content creator must create
a separate report of each particular content in the format utilized by each
different device. Furthermore, when a new device is added to the system,
the content creator must create a separate report of each particular content
in the format utilized by the new device.
In the prior art, the server stores reports in multiple formats, one
format for each device. The content creator specifies the format of the
report. Therefore, the report in the stored format is only effectively
accessible to a particular device.
As information is more widely distributed in an organization, more
and more people need access to the data. Most users' primary
2
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
responsibilities are managing some aspect of the enterprise. Hence the
users are managers and executives, not tech-savvy report creators. These
' additional users prefer easier tools to use. The tools of an analytics
delivery
platform preferably create reports easily, or allow the user to view reports
created by others easily. It is also preferable that the methodology and
terminology of the tools be easier to use, and follow the business
terminology that the user understands. A desirable feature from the user's
perspective is to be able to select from any number of devices to analyze the
data on. Another desirable feature is the ability to transition from one
ZO device to another seamlessly, so that the content displayed on the second
device corresponds to the content which was displayed on the device that the
user was previously using.
Thus, what is required is a solution for effectively analyzing content
on any number of devices. Furthermore, what is also required is a solution
for seamlessly switching the analysis of content from one device to another
device.
3
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
SUMMARY
The analytics delivery platform of the here described , includes an
intuitive user interface, the ability to view content on any number of
different devices, and the ability to seamlessly transfer from one device to
another while analyzing content.
The present disclosure provides a solution for creating and viewing
content very easily. The user interface provides the user with a summary
of the user's organization or department. The user interface provides the
user with various user defined alerts, indicators, shortcuts to reports,
shared documents, and launching functions. The user interface is
replicated across any number of data and voice devices in a configuration
best suited for use on the particular device a user is utilizing.
The present disclosure also provides a solution for viewing reports on
any number of devices. The dynamic device support of the present invention
1~ stores content in a device neutral format. The content can then be re-
formatted according to the characteristics of the device and the browser
utilized by the device. Hence the content is saved separately from the
presentation format. This allows content to be created once on any device,
and then viewed on any other device without any additional changes
needing to be made.
Furthermore, the present disclosure provides a solution to seamlessly
transition from viewing a report on one interface medium, to viewing the
4
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
same location in the report on a second interface medium. The multi-
modal navigation system of the present invention utilizes the device neutral
format of content for switching to a new device, with the system
remembering the state at which analysis was at in the first device and
reformatting the content in accordance with the device characteristics and
browser utilized by the new device.
Therefore, whether the content being viewed is a report, dashboard,
alert, indicator, email, task or calendar item, multi-modal navigation
provides the ability to view analytical content on one device and then
continue the viewing session on another device, with the system
remembering the point in the content at which the switch from one device
to the other occurred.
This is possible through the highly integrated, server-centric
architecture, which provides data to all devices. The build-once view-
anywhere concept of maintaining content separate from the presentation
format allows for dynamic device support. The ability,to keep content
separate from the presentation format also allows users to seamlessly
switch between mobile interfaces without losing their place in the content.
To summarize, the writing discloses an
analytics deliv ery platform for providing a user interface,
dynamic device support, and seamless multi-modal navigation for any
number of devices. The dynamic device support is capable of efficiently
supporting analysis of content on a plurality of devices. The multi-modal .
navigation provides users with the ability to analyze content on one device
5
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
and then seamlessly switch to analyzing the same content on a second
device. All the while the user interface is replicated across the various
devices, in accordance with the characteristics of the particular device.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The present disclosure is illustrated by way of example and not by way
of limitation, in the figures of the accompanying drawings and in which
like reference numerals refer to similar elements and in which:
Figure 1 shows a diagram of an electronic analytics delivery platform
in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention.
1p Figure 2 shows a diagram of an analytics delivery platform in
accordance with another embodiment of the present invention.
Figure 3 shows a diagram of a possible embodiment of a analytics
content engine in accordance with the present invention.
Figure 4 shows a diagram of a possible embodiment of a user
15 interface in accordance with the present invention.
Figure 5 shows a possible user login in accordance with the present
invention.
6
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
Figure 6 shows a possible user content request in accordance with
the present invention.
Figure 7 shows a possible user launch function in accordance with
the present invention.
Figure 8 shows a possible system alert function in accordance with
the present invention.
7
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
Reference will now be made in detail to the embodiments of the
invention, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying
drawings. While the invention will be described in conjunction with the
preferred embodiments, it will be understood that they are not intended to
limit the invention to these embodiments. On the contrary, the invention is
intended to cover alternatives, modifications and equivalents, which may be
included within the spirit and scope of the invention as defined by the
appended claims. Furthermore, in the following detailed description of the
present invention, numerous specific details are set forth in order to
provide a thorough understanding of the present invention. However, it
will be obvious to one of ordinary skill in the art that the present invention
may be practiced without these specific details. In other instances, well-
known methods, procedures, components, and circuits have not been
described in detail as not to unnecessarily obscure aspects of the present
invention.
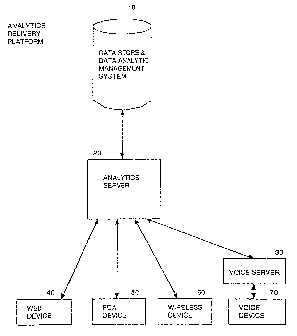
Referring now to Figure 1, a diagram of an analytics delivery
platform in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention is
shown. As depicted in Figure 1, the analytics delivery platform includes a
combination of a data store and data analytic management system 10
communicatively coupled to an analytics server 20.
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
The combination of a data store and data analytic management
system 10 may be a data warehouse, data mart, operation database,
relational database, or the like database, and any combination thereof.
The analytics sewer 20 is also communicatively coupled to a plurality
of user devices 40, 50 , 60, 70. The user devices may include web devices 40,
hand held personal computer (PDA) devices 50 , wireless devices 60 , voice
devices 70; computers, terminals, monitors, WEB-TV, printers, facsimile
machines, wired phones, wireless phones, cordless phones, analog cell
phones, digital phones, PCS phones, intern et and email capable phones,
WAP-enabled phones, satellite phones, video phones, email, and other like
devices. It is also contemplated that user devices may include virtual
devices, such as instant messaging functions.
In the case of the voice devices 70, the analytics server 20 is
communicatively connected to the voice device via a voice server 30_ The
voice server 30 provides voice-to-text and text-to-voice conversion between
the awalytics server 20 and the voice device 70, via a conventional wired or
wireless telephone system.
The analytics server 20 receives a request for content from a
requesting device (say a PDA device 50)_ The analytics server 20 translates
the request into instructions for manipulation of the data store by the data
analytic management system 10_ The data analytic management system,
upon manipulation of the data store, returns a result set to tine analytics
server 20.
9
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
The analytics server 20 stores the result set in a "device agnostic"
report; that is, the result set is stored in a manner that is independent of
the
downstream (end-user) device. The analytics server 20 has the ability to
determine the characteristics of the user device, and the browser the device
is utilizing from the communication protocol, such as hypertext transfer
protocol (http), that the device uses. This enables the analytics server 20 to
reformat the device agnostic report in a format that is optimal for display on
the particular device. The optimally formatted report is then output to the
requesting device (e.g. the PDA device 50).
Figure 2 shows an analytics delivery platform in accordance with an
embodiment of the present invention. An analytics server 110 includes a
analytics content engine 120, a launch and alert engine 130, and a plurality
of plug-ins 140, 150, 160. The analytics content engine 120 is
communicatively coupled to a data store and data analytic management
system 100.
Each plug-in 140, 150, 160 provides 'a launcher and a viewer. The
viewer of each plug-in 140, 150, 160 is communicatively coupled to the
analytics content engine 120 and the launch and alert engine 120. The
launcher of each plug-in 140, 150, 160 is communicatively coupled to the
launch and alert engine 130. The viewer of each plug-in 140, 150, 160 is also
communicatively coupled to a user device 170, 180, 190. The plug-in
constitutes a one-to-one relationship between it and the device it supports.
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
The plug-in aspect of the architecture allows for scalability. As new
devices come along, a new plug-in is built to support the capabilities,
limitations and nuances of the new device. The plug-in resides in the
analytics server 110. In accordance with the present invention, each new
viewer can be easily created because the result set is in a standard format
with a standard interface. The result set is sent to each viewer in a device
agnostic format, which represents the standard format that the data is
received in by each viewer.
The viewer of the plug-in 140, 150, 160 receives a request for content
from the associated user device 170, 1~0, 190. From the request the viewer is
able to determine the identity of the device, its characteristics, and the
browser utilized by the device. The viewer passes the request for content to
the analytics content engine 120. The analytics content engine I20 is
eapable of controlling the manipulation of the data store by the data analytic
management system 100, in accordance with the request. The analytics
content engine 120 receives back a result set. The analytics content engine
120 stores the results set in a device agnostic report. The analytics content
engine also passes the device agnostic report to the requesting viewer 140,
150, 160.
The viewer 140, 150, 160 uses the information about the identity of the
device, its characteristics, and browser utilized by the device to reformat
the
device agnostic report in accordance with the device's capabilities,
limitations, and nuances.
11
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
Figure 3 shows a analytics content engine in accordance with an
embodiment of the present invention. The analytics content engine
includes a translator 210, a formatter 240, and a storage capacity 260. The
analy-tics content engine receives a report request from a viewer 220. The
translator 210 translates the request received from the viewer into an
instruction set for manipulating a data store. The translator outputs the
instruction set to a data analytic management system 200. The data
analytic management system returns a result set 230 to the formatter. The
formatter 240, formats the result set into a device agnostic report. The
device agnostic report is maintained in the storage capacity 260 of the
analytics content engine. Furthermore, the formatter 240 outputs the
device agnostic formatted report to the requesting viewer 250.
The analytics device platform, according to any of the embodiments of
the present invention, also provides a user interface to each device. The
user interface may be either a graphical user interface for data capable
devices, or an audio user interface for voice capable devices. Figure 4, is an
embodiment of a user interface in accordance with one embodiment of the
present invention. The graphical user interface contains alerts 300,
indicators 310, shortcuts to reports 320, shortcuts to shared documents 330,
and launching function 340.
In one embodiments the alerts, indicators, reports, shared
documents, and launching functions may constitute a group of alert icons,
a group of reports icons, a group of report shortcut icons, a group of shared
document icons, and a group of launcher function icons, respectively. All
12
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
of the icons for each group are capable of being configured lay the user, and
constitute a user-defined dashboard or cockpit.
Figure 5 illustrates a possible process flow that an analytics delivery
platform, according to an embodiment of the present invention, is capable of
performing. A user login is shown in Figure 5. In step 400, a user Iogs into
the analytics delivery platform. An analytics server determines the device
and browser configuration that the user is utilizing, from the device's
communication protocol (step 410). The communication protocol may be a
standard protocol such as http. The analytics server then initiates a
session between the device and a corresponding plug-in (step 420). The
plug-in implements a viewer and a launcher configured according to the
device characteristics and the device's browser, or browser like
functionality. The viewer stores the device and browser configuration for
further use. The viewer passes a user interface to the device (step 430). The
user interface is configured for the device, in accordance with the device's
characteristics and browser configuration, and is passed to the device (step
440).
The login provides the analytics delivery platform with the ability to
personalize the user interface to the user. Furthermore, the login can also
be used to define permissions for viewing content.
Figure 6 illustrates a second possible process flow that an analytics
delivery platform, according to an embodiment of the present invention, is
capable of performing. A request for content by a user device is shown in
13
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
Figure 6. The request for content illustrates one possible advantage of the
build-once view-anywhere feature of the present invention.
In step 500, a user enters a request for content via a device. A viewer
passes the content request to a analytics content engine (step 5I0). The
analytics content engine translates the request for content into structured
query language (SQL) instructions, or a like instruction set, for
manipulating a data store (step 520). The analytics content engine passes
the SQL instructions to the data store (step 530). The data store
manipulates a plurality of data according to the SQL instructions, and
IO returns a result set back to the analytics content engine (step 540). The
analytics content engine stores the result set in a device agnostic format
(step 550). The analytics content engine also passes the device agnostic
format to the viewer (step 560). The viewer reformats the device agnostic
format (step 570). The reformatting is performed in accordance with the
device characteristic and browser configuration of the device. The
reformatted result set is thus appropriate for viewing on the device. The
viewer passes the reformatted result set to the device (step 580).
Figure 7 illustrates a third possible process flow that an analytics
delivery platform, in accordance with an embodiment of the present
invention, is capable of performing. A user-initiated launch is shown in
Figure 7. The user initiated launch represent one possible form of
seamless handoff between user devices. The user initiated launch also
illustrates another possible advantage of the build-once view-anywhere
feature of the present invention.
I4
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
In step 660, a user enters a launch request and specifies a requested
destination device. A viewer, associated with the originating device,
creates a resource locator containing for example the identity of the
requested destination device, the identity of a content currently being
analyzed, and the location of the analysis within the content (step 610). The
viewer passes the launch request along with the resource locator to a
launch and alert engine (step 620). The launch and alert engine activates a
launcher associated with the requested destination device (step 630). The
launch and alert engine passes the resource locator to the launcher
associate with the requested destination device (step 640). The launcher
activates a viewer, associated with the requested destination device (step
650). The launcher passes information about the content and location of
analysis within the content to the viewer, associated with the destination
device (step 660). The viewer, associated with the destination device,
retrieves the content from a analytics content engine and reformats the
content in accordance with the device characteristics and browser
configuration of the requested destination device (step 670). The viewer,
associated with the destination device, then passes the reformatted content
to the destination device (step 680).
Figure 8 illustrates a fourth-possible process flow that an analytics
delivery platform, in accordance with an embodiment of the present
invention, is capable of performing. A system alert is shown in Figure 8.
The system alert illustrates yet another possible advantage of the build-once
view-anywhere feature of the present invention.
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
In step 700, a launch and alert engine initiates a launch function.
The launch and alert engine passes a resource locator to a launcher
associated with a desired destination device (step 710). The launcher,
associated With a desired destination device, activates a viewer associated
with the desired destination device (step 720). The launcher, associated
with a desired destination device, passes information about the content and
location of analysis within the content to the viewer, associated with the
desired destination device (step 730). The viewer, associated with the
destination device, retrieves the content from a analytics content engine
and reformats the content in accordance with the device characteristics
and browser configuration of the requested destination device (step 740).
The view, associated with the requested destination device, then passes the
reformatted content to the destination device (step 750).
User Interface
An analytics delivery platform, according to an embodiment of the
present invention, provides a user device with a user interface. The user
interface may be graphic or audio, depending upon the characteristics of
the user device.
The user interface is also referred to as a dashboard or cockpit
herein. The dashboard provides the user with alerts, indicators, shortcuts
to commonly used reports, and shared documents. The dashboard also
provides the user with the ability to create reports, and to launch from one
device to another.
16
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
An alert on the dashboard is a visual indicator that the user can set.
The user sets a threshold value for monitoring a key bit of data. For
example, the user can set a threshold value for sales of a particular item.
The alert will go off if the sales for that particular item fall below the
threshold quantity. The user in this example needs to know if a top
performing product's sales falls off. However, they do not want to have to
constantly monitor the sales number for each product of interest. Instead
the user just needs to know as soon as such an event occurs. The user can
then check his or her reports for more details, once the threshold is reached
and an alert is triggered.
An indicator on the dashboard represents a business measure for
monitoring key data. For example, indicators may be key performance
indicators such as: top ten product sales figures, profitability of a store,
or
the like. Such indicators may be aggregate sales, average profit on a daily
basis, or the like. The indicators allow the user to monitor the change in
the data of interest.
A shortcut to a report on the dashboard allows the user to quickly
access a commonly used report. A shortcut-to-shared document feature
allows the user to access another type of content such as Word documents,
Excel documents, or the like.
Selecting an alert, indicator, shortcut to report, or shortcut-to-shared
document, allows the used to drill down a level to the underlying report or
other document.
17
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
Thus, the dashboard provides the user with an intuitive view of their
job responsibilities. The dashboard provides easy access to data the user
needs for making decisions. The dashboard also provides a convenient way
for the user to check such things at various times throughout his or her
day.
Dynamic Device Support
Dynamic device support provides the ability for users to simply create a
report, indicator, alert or analytic dashboard once and then view that content
on any web, wireless or voice recognition device without any additional
changes
needing to be made.
The challenge in supporting a wide variety of devices is that the interface
differs significantly from device to device. The interface for each device can
be
defined by the characteristics of the device and the browser utilized by the
device. The characteristics of a device (for example form factor, screen real-
estate available, support for color, resolution, image size, bandwidth and
level
of interactivity possible) varies for each device type and even each model of
a
device type. Likewise the interface of voice recognition devices also differs.
Often when content is created, users are unaware of the differing mobile
technologies available and their specific nuances. Using an analytic delivery
platform of the present invention, content creators do not need to worry how
the
data will be accessed and what format is required by the method of access.
Content creators can just concern themselves with creating superior content.
18
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
With the analytics delivery platform users do not have to even know or be
aware of the fact that others may access the analytic content they are
creating
from data devices and voice recognition devices. Once analytic content is
created it is stored in a device agnostic format. Through an analytics
delivery
platform of the present invention, when users request a pre-created content
from a device, the analytics server determines what is being asked for and
which device it is being requested on. The content is then reformatted
according
to the characteristics of the device and the browser utilized by the device.
The
reformatted content can then effectively be analyzed on the particular device.
In other words, the analytics delivery platform of the present invention
separates the content from the way the content is presented. Such architecture
holds the content in a neutral format and serves it up in a particular device
format depending upon the characteristics of the requesting device and the
browser being utilized by the device.
For example, a PDA device has a touch screen, stylus, possibly even
navigation keys and alphanumeric keys. The screen on the PDA has a certain
physical dimension. The screen has a certain image size, resolution, and may
even support color. Furthermore, the PDA has a certain bandwidth and
discrete amount of memory for receiving and storing data. The viewer of the
related plug-in takes account of these features, limitations, and nuances, and
is able to format the content for optimal presentation on the PDA device.
On the other hand, a cell phone primarily provides a voice link. It may at
best provide some ability to enter alphanumeric characters and have a small
19
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
screen. Therefore, the viewer of the related plug-in will make use of the
voice
server to change the data content into audio content, and to change the audio
navigation instructions received from the user into appropriate text type
instructions. li'urthermore, the plug-in supporting the cell phone will
provide
the discrete elements of the content in serial form that can be best heard and
comprehended by the user.
Thus the analytics delivery platform, of the present invention, provides
for dynamic device support. Content can be created once and served up to any
number of devices for optimal presentation on the particular device.
Multi-modal Navigation
Multi-modal navigation provides the user with the ability to
transition from analyzing content on one device to analyzing the same
content on a second device. The challenge in transitioning between a wide
variety of devices is that the interface differs significantly from device to
device, and that the content being analyzed must be maintained when
switched between devices.
The analytics delivery platform, of the present invention, maintains
content in a device neutral format, which can be presented effectively on
any number of devices. ITpon a request the analytics delivery platform
serves the device neutral format up to another device to provide for
seamless transition between different devices.
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
In other words, the analytics delivery platform of the present
invention separates the content from the way the content is presented.
Such architecture holds the content in a neutral format and serves it up in
a particular device format depending upon a request to change to another
device. Thus the present invention allows the user to analyze content on
different devices as circumstances change.
For example, a user may be analyzing a report on his or her PDA.
The user is navigating the report by tapping away using the PDA's stylus.
The user then gets in his or her car to drive to a meeting. The user wants to
continue analyzing the report. However, driving requires the use of their
hands and eyes. Therefore, the PDA device is no longer a suitable device
while driving.
The user .needs a means for seamlessly switching from analyzing the
report on his PDA to analyzing the same report on his phone. The use of a
phone provides him with the ability to use voice recognition to navigate the
report. Because speech is not used to drive, this method of analysis should
not unduly interfere with his ability to drive.
The user can select the launching function on the dashboard
displayed on his PDA, and specify his or her cell phone number. A
"resource locator" (e.g. a tag) is used to indicate where the use is in the
report (e.g. the page in the report that is being viewed, or perhaps the
particular entry being viewed, bearing in mind that the report is in an
electronic format). In one embodiment, this is accomplished through the
21
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
launchers and viewers of Figure 2. When the user selects the launching
function, the viewer marks the point (using a resource locator) in the report
that is being displayed on the user's device. The resource locator is
forwarded to the launch and alert engine. The launch and alert engine
communicates the resource locator to the device the user is moving to. The
destination launcher can thus access the device-agnostic database (report)
at the point where the user left off. The analytics deliver platform calls the
supplied phone number, and reformats the content into a report and means
of navigation suitable for analysis via speech recognition over the cell
phone. Hence the user is able to continue analyzing the report on a cell
phone, from where he or she left off when they were using the PDA. Note
that the user can also specify the phone number of another person with
whom the report can be shared. The other user can then view an item of
interest that has been, in effect bookmarked by the first user using the
resource locator.
Users also have the ability to forward a report to an email recipient.
For example, the user can invoke the "Email Forwarding" feature. The
analytics server converts the full web-version of the report to a convenient
format (such as PDF, HTML, or Microsoft Word/Excel) and attaches it to an
email message automatically. All that is required from the user is to
specify which report they would like forwarded and the person they would
like to send it to. The analytics server then creates the message, attaches
the report and sends the message to the recipient.
22
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
In another example, a user may be viewing a report on a web-enabled
phone, and may then decide to forward it to a colleague. Ideally the
message should be annotated with a personalized message from the
sender, highlighting why the report is being sent and or what they advise
the recipient to do once received.
In one embodiment, this can be accomplished with the following
steps: open up a mobile browser on a wireless device; locate and view the
analytic content of interest; select "Launch to Voice" feature; when
prompted, enter a phone number to call; hang up and wait; the system calls
the number entered; the user is prompted for a secure, personal account
number (PAN) and personal identification number (PIN); the system then
informs the user of the report they were looking at and asks what to do next;
the user initiates the "email-forwarding" feature by saying "forward
report"; the system asks the user to record a message; the system then asks
the user to find a contact to send the message to. Once the recipient's email
address is located the email is sent with the report attached as a file and
the
recorded voice message attached as a compressed voice (audio) file.
The analytics server retrieves the content, formats the content, and
emails automatically. The mobile user is not required to download the
document to the device, nor do they need to manually attach it to an email
message.
Due to the mobile nature of the wireless and voice devices user,
remote printing is a highly useful feature that allows users to print a web
23
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
version of the report at any fax machine no matter where they may be
located. Whether they are viewing a report on their wireless device or
listening to it through the voice interface, they have the ability to launch
the
remote print feature.
For example, any wireless or voice user can printout a full, web-
version of a report to any fax machine by simply indicating the report and
destination fax number. When initiated the user's mobile device sends a
secure request to the analytics server with the fax number entered by the
user. The analytics server then obtains the full web-version of the same
report, so that any charts or formatting enhancements normally not
viewable on a mobile device are carried through. The analytics server
generates a file (e.g. an Adobe PDF file) of this analytic content. The
analytics server then faxes the file to the specified recipient.
The analytics server also generates a coversheet on the fly and
populates the "To" and "From" fields dynamically based upon the senders
profile information and the recipients' details in their address book, such
as Microsoft Outlook. The analytics server attaches the coversheet to the
report and ensures that the fax is sent through successfully.
The analytics server retrieves the content, formats the content, and
faxes automatically. The mobile user is not required to download the
document to the device, nor do they need to manually attach it to a
coversheet message.
24
CA 02476839 2004-08-18
WO 03/073344 PCT/US03/05097
In addition, users can also remote print other document formats
such as hTicrosoft Word or Excel documents, Adobe PDF f les, and text files.
Such content can be either reports or unstructured data. The mobile user
can easily remote print any of these formatted documents by simply
specifying a fax machine number.
Thus the analytics delivery platform, of the present invention,
provides for seamless navigation of content regardless of the device being
used. The user can analyze content on one device and seamlessly
transition to analyzing the same content on another device, as needs
change.
The foregoing descriptions of specific embodiments
have been presented for purposes of illustration and description.
They are not intended to be exhaustive or to limit the invention to the
precise
forms disclosed, and obviously many modifications and variations are
possible in light of the above teaching. The embodiments were chosen and
described in order to best explain the principles of the invention and its
practical application, to thereby enable others skilled in the art to best
utilize the invention and various embodiments with various modifications
as are suited to the particular use contemplated. It is intended that the
scope of the invention be defined by the language herein, the equivalents
of that language and obvious modifications of what is here described.