Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02507110 2011-06-10
25771-1046
1
CARBAMIC ACID ESTERS WITH AN ANTICHOLINERGIC ACTION
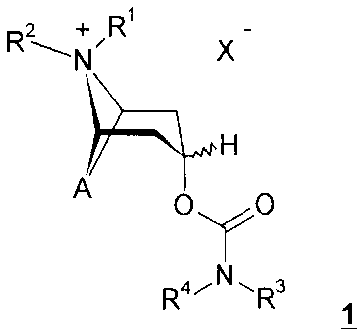
The present invention relates to new carbamic acid esters of general formula
1
R\+/R
N X
A H
O YO
R4iNl~ R3
wherein X - and the groups A, R1, R2, R3 and R4
are defined below, processes for preparing them and
their use as pharmaceutical compositions, particularly as pharmaceutical
compositions with an anticholinergic activity.
Description of the invention
The present invention relates to compounds of general formula 1
R2\+/R' -
N X
H
A O YO
R4i N "R3
wherein
A denotes a double-bonded group selected from among
\ / \ /
C - C =C and
H2 H2 H H H 0 H H CH2H
X - denotes an anion with a single negative charge, preferably an
anion selected from the group consisting of chloride, bromide,
iodide, sulphate, phosphate, methanesulphonate, nitrate,
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
2
maleate, acetate, citrate, fumarate, tartrate, oxalate, succinate,
benzoate and p-toluenesulphonate;
R1 and R2 which may be identical or different, denote Ci-CS-alkyl, which
may optionally be substituted by a group selected from the group
consisting of -C3-C6-cycloalkyl, hydroxy or halogen,
or
R1 and R2 together denote a C3-C5-alkylene bridge;
R3 and R4 which may be identical or different, denote
hydrogen, or
C,-C5-alkyl, which may optionally be mono- or polysubstituted by
one or more groups selected from the group consisting of
hydroxy, halogen, CF3 and -OC1-C4-alkyl, or
a C2-C5-alkenyl or C2-C5-alkynyl group, which may optionally be
mono- or polysubstituted by one or more groups selected
from the group consisting of hydroxy, halogen, CF3, -OC1-C4-
alkyl, phenyl and phenyl which may be mono- or
polysubstituted by methyl, halogen, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy,
or
C6-C1o-aryl, which may optionally be substituted by one or more
groups selected from the group consisting of Ci-C4-alkyl,
hydroxy, halogen, CF3, -OC1-C4-alkyl, phenyl and phenyl
which may be mono- or polysubstituted by methyl, halogen,
hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
C6-C1o-aryl, which is substituted by a 5- or 6-membered
heteroaryl ring, which may optionally be mono- or
polysubstituted by methyl, halogen, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy,
or
C6-C1o-aryl-Cl-C4-alkylene, which may optionally be substituted
at the aryl group by one or more groups selected from the
group consisting of C1-C4-alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, CF3, -0C1-
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
3
C4-alkyl, phenyl and phenyl which may be mono- or
polysubstituted by methyl, halogen, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy,
or
C6-C1o-aryl-C,-C4-alkylene, which is substituted at the aryl group
by a 5- or 6-membered heteroaryl ring, which may optionally
be mono- or polysubstituted by methyl, halogen, hydroxy, CF3
or methoxy, or
C6-C1o-aryl-C1-C4-alkylene, which may optionally be substituted
at the alkylene group by one or more groups selected from
the group consisting of C1-C4-alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, CF3, -
OC1-C4-alkyl and phenyl, or
a 5- or 6-membered saturated or unsaturated ring which may
contain one, two or three heteroatoms selected from the
group consisting of nitrogen, oxygen or sulphur and which
may optionally be mono- or polysubstituted by one or more
groups selected from the group consisting of C1-C4-alkyl
hydroxy, halogen, CF3, phenyl, benzyl and -OC1-C4-alkyl, or
a 5- or 6-membered saturated or unsaturated ring which may
contain one, two or three heteroatoms selected from the
group consisting of nitrogen, oxygen or sulphur and which is
substituted by a 5- or 6-membered heteroaryl ring, which may
optionally be mono- or polysubstituted by methyl, halogen,
hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
C3-C6-cycloalkyl, which may optionally be substituted by one or
more groups selected from the group consisting of C1-C4-
alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, CF3, -OC1-C4-alkyl, phenyl and
phenyl which may be mono- or polysubstituted by methyl,
halogen, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
C3-C6-cycloalkyl, which is substituted by a 5- or 6-membered
heteroaryl ring, which may optionally be mono- or
polysubstituted by methyl, halogen, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy,
or
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
4
a group of formula
B
wherein B denotes -CH2, -NH, -S or -0-, which may optionally
be mono- or polysubstituted by one or more groups selected
from the group consisting of C,-C4-alkyl, hydroxy, halogen,
CF3 and -OC1-C4-alkyl, or
a group of formula
wherein B' denotes CH or N, which may optionally be mono-
or polysubstituted by one or more groups selected from the
group consisting of C1-C4-alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, CF3 and -
OC,-C4-alkyl, or
a group of formula
II[CLLII1 /
wherein B denotes -CH2, -NH, -S or -0-, which may optionally
be mono- or polysubstituted by one or more groups selected
from the group consisting of C1-C4-alkyl, hydroxy, halogen,
CF3 and -OCR-C4-alkyl, or
a group of formula
R'
B
wherein B denotes -CH2, -NH, -S or -0-,
R' may represent hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, hydroxymethyl,
ethyl, -CF3, CHF2 or halogen, and which may optionally be
mono- or polysubstituted by one or more groups selected
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
from the group consisting of Ci-C4-alkyl, hydroxy, halogen,
CF3 and -OC1-C4-alkyl, or
R3 and R4 together with the nitrogen atom form a 5- or 6-membered
saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic ring which may optionally
contain one or two more heteroatoms selected from the group
consisting of nitrogen, oxygen or sulphur and which may
optionally be mono- or polysubstituted by one or more groups
selected from the group consisting of Ci-C4-alkyl hydroxy,
halogen, CF3, phenyl, benzyl and -OC1-C4-alkyl, or
R3 and R4 together with the nitrogen atom form a 5- or 6-membered
saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic ring which is substituted by
a 5- or 6-membered heteroaryl ring, which may optionally be
mono- or polysubstituted by methyl, halogen, hydroxy, CF3 or
methoxy,
optionally in the form of the individual enantiomers or diastereomers,
mixtures
of the enantiomers or diastereomers and optionally in the form of the
racemates, and optionally in the form of the pharmacologically acceptable
acid addition salts, solvates and hydrates thereof.
Preferred are compounds of general formula 1 wherein
A denotes a double-bonded group selected from among
C JC/ and
H H H 0 H H CH2H
X - denotes an anion with a single negative charge, preferably an
anion selected from the group consisting of chloride, bromide,
methanesulphonate and p-toluenesuIphonate, preferably
bromide;
R1 and R2 which may be identical or different, denote C1-C3-alkyl, which
may optionally be substituted by a group selected from the group
consisting of C3-C5-cycloalkyl, hydroxy, or fluorine,
or
R1 and R2 together denote a C3-C4-alkylene bridge;
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
6
R3 and R4 which may be identical or different, denote
hydrogen, or
Cj-C5-alkyl, which may optionally be substituted by a group
selected from the group consisting of hydroxy, fluorine, CF3
and methoxy, or
a phenyl or naphthyl group which may optionally be substituted
by one, two or three groups selected from the group
consisting of methyl, ethyl, hydroxy, fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, CF3, methoxy, phenyl and phenyl which may be
mono-, di- or trisubstituted by methyl, fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
a phenyl or naphthyl group which is substituted by a heteroaryl
ring selected from the group consisting of furan, thiophene,
pyrrole, imidazole, pyridine and pyrimidine, which may
optionally be mono- or disubstituted by methyl, fluorine,
chlorine bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
a benzyl or phenylethyl group which may optionally be
substituted at the phenyl ring by one, two or three groups
selected from the group consisting of methyl, ethyl, hydroxy,
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, CF3, methoxy, phenyl and phenyl
which may be mono-, di- or trisubstituted by methyl, fluorine,
chlorine, bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
a benzyl or phenylethyl group which is substituted at the phenyl
ring by a heteroaryl ring selected from the group consisting of
furan, thiophene, pyrrole, imidazole, pyridine and pyrimidine,
which may optionally be mono- or disubstituted by methyl,
fluorine, chlorine bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
a benzyl or phenylethyl group which may optionally be
substituted at the alkylene bridge by one or two, preferably
one group selected from the group consisting of methyl, ethyl,
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
7
hydroxy, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, CF3, methoxy and
phenyl, or
a 5- or 6- membered saturated or unsaturated ring which may
contain one, two or three heteroatoms selected from the
group consisting of nitrogen, oxygen or sulphur and which
may optionally be mono-, di- or trisubstituted by one or more
groups selected from the group consisting of methyl, ethyl,
hydroxy, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, CF3, phenyl, benzyl and
methoxy, or
a 5- or 6- membered saturated or unsaturated ring which may
contain one, two or three heteroatoms selected from the
group consisting of nitrogen, oxygen or sulphur and which is
substituted by a heteroaryl ring selected from the group
consisting of furan, thiophene, pyrrole, imidazole, pyridine and
pyrimidine, which may optionally be mono- or disubstituted by
methyl, fluorine, chlorine bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy,
or
a cyclopentyl or cyclohexyl group which may optionally be
substituted by one, two or three groups selected from the
group consisting of methyl, ethyl, hydroxy, fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, CF3, methoxy, phenyl and phenyl which may be
mono-, di- or trisubstituted by methyl, fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
a cyclopentyl or cyclohexyl group which is substituted by a
heteroaryl ring selected from the group consisting of furan,
thiophene, pyrrole, imidazole, pyridine and pyrimidine, which
may optionally be mono- or disubstituted by methyl, fluorine,
chlorine bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
a group of formula
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
8
I I \
B
wherein B denotes - CH2, -NH, -S or -0-, which may
optionally be mono-, di- or trisubstituted by one or more
groups selected from the group consisting of methyl, fluorine,
chlorine, bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
a group of formula
wherein B' denotes CH or N, which may optionally be mono-,
di- or trisubstituted by one or more groups selected from the
group consisting of methyl, fluorine, chlorine, bromine,
hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
a group of formula
wherein B denotes -CH2, -NH, -S or -0-, which may optionally
be mono-, di- or trisubstituted by one or more groups selected
from the group consisting of methyl, fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
a group of formula
R'
~ I I \
B
wherein B denotes -CH2, -NH, -S or -0-,
R' may represent hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, hydroxymethyl,
ethyl, -CF3, CHF2 or fluorine, and which may optionally be
mono-, di- or trisubstituted by one or more groups selected
from the group consisting of methyl, fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
9
R3 and R4 together with the nitrogen atom form a 5- or 6-membered
saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic ring which may optionally
contain one or two more heteroatoms selected from the group
consisting of nitrogen, oxygen or sulphur and which may
optionally be mono-, di- or trisubstituted by one or more groups
selected from the group consisting of methyl, fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, hydroxy, phenyl, CF3 or methoxy, or
R3 and R4 together with the nitrogen atom form a 5- or 6-membered
saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic ring which may optionally
contain one or two more heteroatoms selected from the group
consisting of nitrogen, oxygen or sulphur, which is substituted by
a heteroaryl ring selected from the group consisting of furan,
thiophene, pyrrole, imidazole, pyridine and pyrimidine, which
may optionally be mono- or disubstituted by methyl, fluorine,
chlorine bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy,
optionally in the form of the individual enantiomers or diastereomers,
mixtures
of the enantiomers or diastereomers and optionally in the form of the
racemates, and optionally in the form of the pharmacologically acceptable
acid addition salts, solvates and hydrates thereof.
Particularly preferred are compounds of general formula 1 wherein
A denotes a double-bonded group selected from among
C and
H H H H p H H CH2H
X denotes an anion with a single negative charge, preferably an
anion selected from the group consisting of chloride, bromide,
methanesulphonate and p-toluenesulphonate, preferably
bromide;
R1 and R2 which may be identical or different, denote a methyl or ethyl
group which may optionally be substituted by cyclopropyl,
hydroxy or fluorine,
or
R1 and R2 together denote a C3-C4-alkylene bridge;
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
R3 denotes hydrogen or Ci-C3-alkyl, which may optionally be
substituted by a group selected from the group consisting of
hydroxy, fluorine or CF3;
R4 denotes C1-C3-alkyl, which may optionally be substituted by a
group selected from the group consisting of hydroxy, fluorine or
CF3;
R4 denotes a phenyl group which may optionally be substituted by
one or two, preferably one group selected from the group
consisting of furyl, thienyl, phenyl and phenyl which may be
mono-, di- or trisubstituted by methyl, fluorine, chlorine, bromine,
hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
R4 denotes a benzyl group which may optionally be substituted at
the phenyl ring by one, two or three, preferably one group
selected from the group consisting of methyl, ethyl, hydroxy,
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, CF3, methoxy, furyl, thienyl and
phenyl, or
R4 denotes a benzyl group which may optionally be substituted at
the methylene bridge by one, two or three, preferably one group
selected from the group consisting of methyl, ethyl, hydroxy,
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, CF3, methoxy and phenyl, or
R4 denotes a group of formula
wherein B' denotes CH, which may optionally be mono- or
disubstituted by one or more groups selected from the group
consisting of methyl, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or
methoxy,
optionally in the form of the individual enantiomers or diastereomers,
mixtures
of the enantiomers or diastereomers and optionally in the form of the
racemates, and optionally in the form of the pharmacologically acceptable
acid addition salts, solvates and hydrates thereof.
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
11
Also of particular interest are compounds of general formula 1 wherein
A denotes a double-bonded group selected from among
C and
H H H p H H CH2H
X_ denotes an anion with a single negative charge selected from
the group consisting of chloride, bromide, methanesulphonate
and p-toluenesulphonate, preferably bromide;
R1 and R2 which may be identical or different, denote a methyl or ethyl
group which may optionally be substituted by cyclopropyl,
hydroxy or fluorine,
or
R' and R2 together denote a C3-C4-alkylene bridge;
R3 denotes hydrogen or C,-C3-alkyl, which may optionally be
substituted by a group selected from the group consisting of
hydroxy, fluorine or CF3;
R4 denotes C,-C3-alkyl, which may optionally be substituted by a
group selected from the group consisting of hydroxy, fluorine or
CF3;
R4 denotes a phenyl group which may optionally be substituted by
phenyl, which may optionally be mono- or disubstituted by
methyl, fluorine, hydroxy or CF3, or
R4 denotes a benzyl group which may optionally be substituted at
the phenyl ring by one or two, preferably one group selected
from the group consisting of methyl, ethyl, hydroxy, fluorine, CF3,
and phenyl, or
R4 denotes a benzyl group which may optionally be
monosubstituted at the methylene bridge by phenyl, or
R4 denotes a group of formula
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
12
\ I ( /
wherein B' denotes CH, which may optionally be mono- or
disubstituted by one or more groups selected from the group
consisting of methyl, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or
methoxy,
optionally in the form of the individual enantiomers or diastereomers,
mixtures
of the enantiomers or diastereomers and optionally in the form of the
racemates, and optionally in the form of the pharmacologically acceptable
acid addition salts, solvates and hydrates thereof.
Of the abovementioned compounds of general formula 1 particular
importance is attached to those wherein X - denotes bromide or
methanesulphonate, most preferably bromide, optionally in the form of the
individual enantiomers or diastereomers, mixtures of the enantiomers or
diastereomers and optionally in the form of the racemates, and optionally in
the form of the pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts, solvates and
hydrates thereof.
Also particularly preferred according to the invention are those of the
abovementioned compounds of formula 1 wherein R' and R2 have the same
meaning and denote methyl, optionally in the form of the individual
enantiomers or diastereomers, mixtures of the enantiomers or diastereomers
and optionally in the form of the racemates, and optionally in the form of the
pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts, solvates and hydrates
thereof.
Also of particular importance according to the invention are those of the
abovementioned compounds of formula 1, wherein R3 denotes hydrogen or
methyl, optionally in the form of the individual enantiomers or diastereomers,
mixtures of the enantiomers or diastereomers and optionally in the form of
the racemates, and optionally in the form of the pharmacologically acceptable
acid addition salts, solvates and hydrates thereof.
Also of particular importance are all the compounds of general formula 1
wherein the group R4 denotes biphenyl, benzhydryl, fluorenyl or
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
13
biphenylmethyl, optionally in the form of the individual enantiomers or
diastereomers, mixtures of the enantiomers or diastereomers and optionally
in the form of the racemates, and optionally in the form of the
pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts, solvates and hydrates
thereof.
Of outstanding importance according to the invention are compounds of
general formula 1 wherein
A denotes a double-bonded group selected from among
C and
H H H O H H CH2H
X - denotes an anion with a single negative charge, preferably an
anion selected from the group consisting of bromide and
methanesuIphonate, preferably bromide;
R1 and R2 denote methyl;
R3 denotes hydrogen or methyl;
R4 denotes biphenyl, benzhydryl, fluorenyl or biphenylmethyl,
optionally in the form of the individual enantiomers or diastereomers,
mixtures
of the enantiomers or diastereomers and optionally in the form of the
racemates, and optionally in the form of the pharmacologically acceptable
acid addition salts, solvates and hydrates thereof.
The alkyl groups used, unless otherwise stated, are branched and
unbranched alkyl groups having 1 to 5 carbon atoms. Examples include:
methyl, ethyl, propyl or butyl. The groups methyl, ethyl, propyl or butyl may
optionally also be referred to by the abbreviations Me, Et, Prop or Bu. Unless
otherwise stated, the definitions propyl and butyl also include all possible
isomeric forms of the groups in question. Thus, for example, propyl includes
n-propyl and iso-propyl, butyl includes iso-butyl, sec. butyl and tent.-butyl,
etc.
The alkylene groups used, unless otherwise stated, are branched and
unbranched double-bonded alkyl bridges with 1 to 5 carbon atoms. Examples
include: methylene, ethylene, n-propylene or n-butylene.
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
14
The alkyloxy groups used, unless otherwise stated, are branched and
unbranched alkyl groups with 1 to 4 carbon atoms which are linked via an
oxygen atom. The following may be mentioned, for example: methyloxy,
ethyloxy, propyloxy or butyloxy. The groups methyloxy, ethyloxy, propyloxy or
butyloxy may optionally also be referred to by the abbreviations MeO, EtO,
PropO or BuO. Unless otherwise stated, the definitions propyloxy and
butyloxy also include all possible isomeric forms of the groups in question.
Thus, for example, propyloxy includes n-propyloxy and iso-propyloxy, butyloxy
includes iso-butyloxy, sec. butyloxy and tert.-butyloxy, etc. The word alkoxy
may also possibly be used within the scope of the present invention instead of
the word alkyloxy. The groups methyloxy, ethyloxy, propyloxy or butyloxy may
optionally also be referred to as methoxy, ethoxy, propoxy or butoxy.
Within the scope of the present invention halogen denotes fluorine, chlorine,
bromine or iodine. Unless otherwise stated, fluorine and bromine are the
preferred halogens.
The alkenyl groups used are branched and unbranched hydrocarbon groups
with 2 to 5 carbon atoms, preferably 2 to 3 carbon atoms, provided that they
have at least one double bond. Examples include vinyl, propenyl, iso-
propenyl, butenyl, butadienyl, pentenyl.
The alkynyl groups used are hydrocarbon groups with 2 to 5 carbon atoms,
provided that they have at least one triple bond, for example ethynyl,
propargyl, butynyl, pentynyl.
The term aryl denotes an aromatic ring system with 6 to 10 carbon atoms.
Preferred aryl groups are phenyl or naphthyl.
By 5-or 6-membered heteroaryl rings are meant, within the scope of the
present invention, aromatic ring systems which contain one or two
heteroatoms selected from the group consisting of oxygen, nitrogen and
sulphur and may optionally be substituted as defined hereinbefore. Examples
include furan, thiophene, pyrrole, pyrazole, imidazole, pyridine, pyrimidine,
triazine, oxazole, isoxazole, thiazole, isothiazole, oxadiazole and
pyrazolidine,
while the heterocycle may be substituted as specified in the definitions.
Particularly preferred 5- or 6-membered heterocyclic rings within the scope of
the present invention are furan, thiophene, pyrrole, imidazole, pyridine and
pyrimidine, while furan and thiophene are particularly important.
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
The term arylalkylene denotes aromatic ring systems with 6 to 10 carbon
atoms which are linked via an alkylene bridge with 1-4 carbon atoms.
Examples of arylalkylene groups include benzyl or phenylethyl.
Examples of 5- or 6-membered saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic rings
which may contain nitrogen, oxygen or sulphur as heteroatoms include furan,
tetrahydrofuran, 2-methyltetrahydrofuran, 2-hydroxymethylfuran,
tetrahydrofuranone, y-butyrolactone, a-pyran, y-pyran, dioxolan,
tetrahydropyran, dioxane, thiophene, dihydrothiophene, thiolan, dithiolan,
pyrrole, pyrroline, pyrrolidine, pyrazole, pyrazoline, imidazole, imidazoline,
imidazolidine, triazole, tetrazole, pyridine, piperidine, pyridazine,
pyrimidine,
pyrazine, piperazine, triazine, tetrazine, morpholine, thiomorpholine,
oxazole,
isoxazole, oxazine, thiazole, isothiazole, thiadiazole, oxadiazole,
pyrazolidine,
while the heterocyclic group may be substituted as in the definitions.
Particularly preferred 5- or 6-membered heterocyclic rings within the scope of
the present invention are furan, thiophene, pyrrole, imidazole, pyridine,
piperidine, pyrimidine, morpholine, oxazole and oxadiazole, while the furan,
thiophene, pyrrole, imidazole, pyridine and piperidine rings are particularly
important according to the invention.
Examples of cycloalkyl groups with 3 - 6 carbon atoms include for example
cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl or cyclohexyl.
Examples of 5-, 6- or 7-membered saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic rings
which may be formed by the groups R3 and R4 together with the nitrogen
include: pyrrole, pyrroline, pyrrolidine, 2-methylpyrrolidine, 3-
methylpyrrolidine, piperidine, piperazine, N-methylpiperazine, N-
ethylpiperazine, N-(n-propyl)-piperazine, N-benzylpiperazine, morpholine,
thiomorpholine, imidazole, imidazoline, imidazolidine, pyrazole, pyrazoline,
pyrazolidine, preferably morpholine, N-benzylpiperazine, piperazine, and
piperidine, while the abovementioned heterocycles may be substituted as in
the definitions. Particularly preferred rings in this context are: pyrrole,
piperidine, piperazine, N-methylpiperazine, N-benzylpiperazine, morpholine,
imidazole, imidazoline, imidazolidine, pyrazole, pyrazoline, pyrazolidine,
preferably morpholine, N-benzylpiperazine, piperazine and piperidine, while
the abovementioned heterocycles may be substituted as in the definitions.
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
16
By pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts are meant for example
the salts selected from the group consisting of hydrochloride, hydrobromide,
hydroiodide, hydrosulphate, hydrophosphate, hydromethanesulphonate,
hydronitrate, hydromaleate, hydroacetate, hydrocitrate, hydrofumarate,
hydrotartrate, hydrooxalate, hydrosuccinate, hydrobenzoate and hydro-p-
toluenesulphonate, preferably hydrochloride, hydrobromide, hydrosulphate,
hydrophosphate, hydrofumarate and hydromethanesulphonate.
The compounds according to the invention may in some cases be prepared
analogously to the methods known from the prior art, as explained hereinafter.
Diagram 1 illustrates the method of synthesising compounds of formula 1
wherein R3 denotes hydrogen.
R2 +
NR R-N=C=O N~ Nf~ X
3 R? X
A OH A O A O~
R4'N ~-I R4,N H
2 4 (R3= H) 1 (R 3 = H)
Diagram 1:
These compounds may be obtained starting from the alcohols of formula 2 by
reacting with the isocyanates of formula 3. The isocyanates of formula 3 are
known in the prior art or may be prepared using methods of synthesis known
from the prior art. If desired, the isocyanates of formula 3 may be generated
in
situ using methods known from the prior art and used in the reaction without
any further isolation. The compounds of formula 2 are also known in the prior
art. The reaction of the compounds 2 with the isocyanates 3 is preferably
carried out in an aprotic organic solvent, particularly preferably in an
aprotic
polar solvent selected, for example, from the group consisting of
acetonitrile,
tetrahydrofuran and dioxane, preferably acetonitrile, at temperatures from 0-
100 C, preferably at about 10-50 C , most preferably at ambient temperature
(about 23 C). The working up of the reaction mixture and the purification of
the intermediate product 4 are carried out using conventional methods.
Compounds of formula 4 wherein R3 denotes hydrogen are partly known from
the prior art. In connection with this reference is made to the publications
WO
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
17
97/34892, Aberle et al. (Tetrahedron Letters 42 (2001) 1975-1977) as well as
Polonovski et al. (Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr. <4> 43, 1928, 596).
The compounds of formula 1 wherein R3 does not represent hydrogen may be
obtained as shown in Diagram 2.
N N N X-
R' R3-L R1 R2\+ R~
R2 -X
A O 1'e A O A O
R 4 IN 'H Ra,1 ~3 R4 I,3
4 (R3=H) 4 1
Diagram 2:
For this, a compound of formula 4 wherein R3 denotes hydrogen, is reacted
with the compound 5 in a suitable organic solvent in the presence of a strong
base. In compound 5 R3 may have the above meanings. L denotes a leaving
group, preferably a leaving group selected from chlorine, bromine, iodine,
mesylate, triflate, benzenesulphonate or tosylate. According to the invention,
alkali metal hydrides are preferably used as bases. The hydrides of sodium,
lithium and potassium are preferred. Suitable solvents are preferably selected
from dimethylformamide, dimethylacetamide, methylene chloride and
tetrahydrofuran. The reaction mixture is reacted for 0.5 to 4 days, preferably
1
to 2 days at ambient temperature, optionally also at elevated temperature.
The working up of the reaction mixture and purification of the product 4 are
carried out by conventional methods.
The compounds of formula 4 obtained according to Diagram I or Diagram 2
may be converted into the target compounds of formula 1 by reacting with the
compounds R2-X, wherein R2 and X may have the above meanings. This
synthesising step may also be carried out analogously to the examples of
synthesis disclosed in WO 92/16528. In the event that R1 and R2 together
form an alkylene bridge, there is no need to add the reagent R2-X, as will be
apparent to anyone skilled in the art. In this case the compounds of formula 4
have a suitably substituted group R1 (-C3-C5-alkylene-X) corresponding to the
abovementioned definitions and the compounds of formula 1 are prepared by
intramolecular quatemisation of the amine.
CA 02507110 2011-08-29
25771-1046
18
As can be seen from Diagram 1, the intermediate products of general formula 4
are of central
importance. Accordingly, in another aspect, the present invention relates to
the
intermediates of formula 4
R1
N~
H
A O
R4A.R3
4
wherein
A denotes a double-bonded group selected from among
H H and
H 0 H H CH2H
R1 denotes C,-C5-alkyl, which may optionally be substituted by a group
selected from the group consisting of C3-C6-cycloalkyl or hydroxy, or
R' denotes -C3-C5-alkylene-X, wherein X denotes chloride, bromide, iodide,
sulphate, phosphate, methanesulphonate, nitrate, maleate, acetate, citrate,
fumarate,
tartrate, oxalate, succinate, benzoate and p-toluenesulphonate;
R3 and R4 which may be identical or different, denote
hydrogen, or
C,-C5-alkyl, which may optionally be mono- or polysubstituted by one or more
groups selected from the group consisting of hydroxy, halogen, CF3 and -OC1-C4-
alkyl, or
a C2-C5-alkenyl or C2-C5-alkynyl group, which may optionally be mono- or
polysubstituted by one or more groups selected from the group consisting of
hydroxy,
halogen, CF3, -OC1-C4-alkyl, phenyl and phenyl which may be mono- or
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
19
polysubstituted by methyl, halogen, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy,
or
C6-C1o-aryl, which may optionally be substituted by one or more
groups selected from the group consisting of C1-C4-alkyl,
hydroxy, halogen, CF3, -OC1-C4-alkyl, phenyl and phenyl
which may be mono- or polysubstituted by methyl, halogen,
hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
C6-C1o-aryl, which is substituted by a 5- or 6-membered
heteroaryl ring, which may optionally be mono- or
polysubstituted by methyl, halogen, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy,
or
C6-C1o-aryl-C,-C4-alkylene, which may optionally be substituted
at the aryl group by one or more groups selected from the
group consisting of C1-C4-alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, CF3, -OC--
C4-alkyl, phenyl and phenyl which may be mono- or
polysubstituted by methyl, halogen, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy,
or
C6-C1o-aryl-C1-C4-alkylene, which is substituted at the aryl group
by a 5- or 6-membered heteroaryl ring, which may optionally
be mono- or polysubstituted by methyl, halogen, hydroxy, CF3
or methoxy, or
C6-C1o-aryl-C1-C4-alkylene, which may optionally be substituted
at the alkylene group by one or more groups selected from
the group consisting of C1-C4-alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, CF3,
-OCR-C4-alkyl and phenyl, or
a 5- or 6-membered saturated or unsaturated ring which may
contain one, two or three heteroatoms selected from the
group consisting of nitrogen, oxygen or sulphur and which
may optionally be mono- or polysubstituted by one or more
groups selected from the group consisting of C,-C4-alkyl
hydroxy, halogen, CF3, phenyl, benzyl and -OC1-C4-alkyl, or
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
a 5- or 6-membered saturated or unsaturated ring which may
contain one, two or three heteroatoms selected from the
group consisting of nitrogen, oxygen or sulphur and which is
substituted by a 5- or 6-membered heteroaryl ring, which may
optionally be mono- or polysubstituted by methyl, halogen,
hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
C3-C6-cycloalkyl, which may optionally be substituted by one or
more groups selected from the group consisting of C1 -C4-
alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, CF3, -OC1-C4-alkyl, phenyl and
phenyl which may be mono- or polysubstituted by methyl,
halogen, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
C3-C6-cycloalkyl, which is substituted by a 5- or 6-membered
heteroaryl ring, which may optionally be mono- or
polysubstituted by methyl, halogen, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy,
or
a group of formula
wherein B denotes -CH2, -NH, -S or -0-, which may optionally
be mono- or polysubstituted by one or more groups selected
from the group consisting of C1-C4-alkyl, hydroxy, halogen,
CF3 and -OC1-C4-alkyl, or
a group of formula
wherein B' denotes CH or N, which may optionally be mono-
or polysubstituted by one or more groups selected from the
group consisting of Cl-C4-alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, CF3 and
-Ci-C4-alkyl, or
a group of formula
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
21
i I
~ B
wherein B denotes -CH2, -NH, -S or -0-, which may optionally
be mono- or polysubstituted by one or more groups selected
from the group consisting of C1-C4-alkyl, hydroxy, halogen,
CF3 and -OC1-C4-alkyl, or
a group of formula
d R'
~ I
~ B
wherein B denotes -CH2, -NH, -S or -0-,
R' may represent hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, hydroxymethyl,
ethyl, -CF3, CHF2 or halogen, and which may optionally be
mono- or polysubstituted by one or more groups selected
from the group consisting of Cl-C4-alkyl, hydroxy, halogen,
CF3 and -OCR-C4-alkyl, or
R3 and R4 together with the nitrogen atom form a 5- or 6-membered
saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic ring which may optionally
contain one or two more heteroatoms selected from the group
consisting of nitrogen, oxygen or sulphur and which may
optionally be mono- or polysubstituted by one or more groups
selected from the group consisting of CI-C4-alkyl hydroxy,
halogen, CF3, phenyl, benzyl and -OC1-C4-alkyl, or
R3 and R4 together with the nitrogen atom form a 5- or 6-membered
saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic ring which is substituted by
a 5- or 6-membered heteroaryl ring, which may optionally be
mono- or polysubstituted by methyl, halogen, hydroxy, CF3 or
methoxy,
optionally in the form of the individual enantiomers or diastereomers,
mixtures
of the enantiomers or diastereomers and optionally in the form of the
racemates, and optionally in the form of the acid addition salts, solvates and
hydrates thereof, with the proviso that if
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
22
A denotes
C=C
H H
R1 denotes methyl and
R3 denotes hydrogen,
R4 cannot denote phenyl, pentafluorophenyl, 2-chloro-4-
trifluorom ethyl-phenyl, 3-chloro-4-methoxyphenyl or
cyclopentyl;
and with the proviso that if
A denotes
H 0 H
R1 denotes methyl and
R3 denotes hydrogen,
R4 cannot denote phenyl.
Preferred are intermediates of general formula 4 wherein
A denotes a double-bonded group selected from among
C =C and
H H H p H H CH2H
R' denotes C1-C3-alkyl, which may optionally be substituted by a
group selected from the group consisting of C3-C5-cycloalkyl,
hydroxy or fluorine, or
R1 denotes C3-C4-alkylene-X, wherein X may represent chloride,
bromide, methanesulphonate or p-toluenesulphonate;
R3 and R4 which may be identical or different, denote
hydrogen, or
C,-C5-alkyl, which may optionally be substituted by a group
selected from the group consisting of hydroxy, fluorine, CF3
and methoxy, or
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
23
a phenyl or naphthyl group which may optionally be substituted
by one, two or three groups selected from the group
consisting of methyl, ethyl, hydroxy, fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, CF3, methoxy, phenyl and phenyl which may be
mono-, di- or trisubstituted by methyl, fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
a phenyl or naphthyl group which is substituted by a heteroaryl
ring selected from the group consisting of furan, thiophene,
pyrrole, imidazole, pyridine and pyrimidine, which may
optionally be mono- or disubstituted by methyl, fluorine,
chlorine bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
a benzyl or phenylethyl group which may optionally be
substituted at the phenyl ring by one, two or three groups
selected from the group consisting of methyl, ethyl, hydroxy,
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, CF3, methoxy, phenyl and phenyl
which may be mono-, di- or trisubstituted by methyl, fluorine,
chlorine, bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
a benzyl or phenylethyl group which is substituted at the phenyl
ring by a heteroaryl ring selected from the group consisting of
furan, thiophene, pyrrole, imidazole, pyridine and pyrimidine,
which may optionally be mono- or disubstituted by methyl,
fluorine, chlorine bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
a benzyl or phenylethyl group which may optionally be
substituted at the alkylene bridge by one or two, preferably
one group selected from the group consisting of methyl, ethyl,
hydroxy, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, CF3, methoxy and
phenyl, or
a 5- or 6- membered saturated or unsaturated ring which may
contain one, two or three heteroatoms selected from the
group consisting of nitrogen, oxygen or sulphur and which
may optionally be mono-, di- or trisubstituted by one or more
groups selected from the group consisting of methyl, ethyl,
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
24
hydroxy, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, CF3, phenyl, benzyl and
methoxy, or
a 5- or 6-membered saturated or unsaturated ring which may
contain one, two or three heteroatoms selected from the
group consisting of nitrogen, oxygen or sulphur and which is
substituted by a heteroaryl ring selected from the group
consisting of furan, thiophene, pyrrole, imidazole, pyridine and
pyrimidine, which may optionally be mono- or disubstituted by
methyl, fluorine, chlorine bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy,
or
a cyclopentyl or cyclohexyl group which may optionally be
substituted by one, two or three groups selected from the
group consisting of methyl, ethyl, hydroxy, fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, CF3, methoxy, phenyl and phenyl which may be
mono-, di- or trisubstituted by methyl, fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
a cyclopentyl or cyclohexyl group which is substituted by a
heteroaryl ring selected from the group consisting of furan,
thiophene, pyrrole, imidazole, pyridine and pyrimidine, which
may optionally be mono- or disubstituted by methyl, fluorine,
chlorine bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
a group of formula
wherein B denotes -CH2, -NH, -S or -0-, which may optionally
be mono-, di- or trisubstituted by one or more groups selected
from the group consisting of methyl, fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
a group of formula
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
0):
1 10
wherein B' denotes CH or N, which may optionally be mono-,
di- or trisubstituted by one or more groups selected from the
group consisting of methyl, fluorine, chlorine, bromine,
hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
a group of formula
B
a
wherein B denotes -CH2, -NH, -S or -0-, which may optionally
be mono-, di- or trisubstituted by one or more groups selected
from the group consisting of methyl, fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
a group of formula
CiB
wherein B denotes -CH2, -NH, -S or -0-,
R' may represent hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, hydroxymethyl,
ethyl, -CF3, CHF2 or fluorine, and which may optionally be
mono-, di- or trisubstituted by one or more groups selected
from the group consisting of methyl, fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
R3 and R4 together with the nitrogen atom form a 5- or 6-membered
saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic ring which may optionally
contain one or two more heteroatoms selected from the group
consisting of nitrogen, oxygen or sulphur and which may
optionally be mono-, di- or trisubstituted by one or more groups
selected from the group consisting of methyl, fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, hydroxy, phenyl, CF3 or methoxy, or
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
26
R3 and R4 together with the nitrogen atom form a 5- or 6-membered
saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic ring which may optionally
contain one or two more heteroatoms selected from the group
consisting of nitrogen, oxygen or sulphur, which is substituted by
a heteroaryl ring selected from the group consisting of furan,
thiophene, pyrrole, imidazole, pyridine and pyrimidine, which
may optionally be mono- or disubstituted by methyl, fluorine,
chlorine bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy,
optionally in the form of the individual enantiomers or diastereomers,
mixtures
of the enantiomers or diastereomers and optionally in the form of the
racemates, and optionally in the form of the acid addition salts, solvates and
hydrates thereof, with the proviso that if
A denotes
C=C
H H
R1 denotes methyl and
R3 denotes hydrogen,
R4 cannot represent phenyl, 2-chloro-4-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl, 3-chloro-4-methoxyphenyl or cyclopentyl;
and with the proviso that
if A denotes
H 0 H
R1 denotes methyl and
R3 denotes hydrogen,
R4 cannot represent phenyl.
Particularly preferred are intermediates of general formula 4 wherein
A denotes a double-bonded group selected from among
C and
H H H p H H CH2H
R1 denotes a methyl or ethyl group which may optionally be
substituted by cyclopropyl, hydroxy or fluorine, or
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
27
R1 denotes C3-C4-alkylene-X, wherein X may represent chloride,
bromide, methanesulphonate or p-toluenesulphonate;
R3 denotes hydrogen or C,-C3-alkyl, which may optionally be
substituted by a group selected from the group consisting of
hydroxy, fluorine or CF3;
R4 denotes Cl-C3-alkyl, which may optionally be substituted by a
group selected from the group consisting of hydroxy, fluorine or
CF3, or
R4 denotes a phenyl group which may optionally be substituted by
one or two, preferably one group selected from the group
consisting of furyl, thienyl, phenyl and phenyl which may be
mono-, di- or trisubstituted by methyl, fluorine, chlorine, bromine,
hydroxy, CF3 or methoxy, or
R4 denotes a benzyl group which may optionally be substituted at
the phenyl ring by one, two or three, preferably one group
selected from the group consisting of methyl, ethyl, hydroxy,
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, CF3, methoxy, furyl, thienyl and
phenyl, or
R4 denotes a benzyl group which may optionally be substituted at
the methylene bridge by one, two or three, preferably one group
selected from the group consisting of methyl, ethyl, hydroxy,
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, CF3, methoxy and phenyl, or
R4 denotes a group of formula
wherein B' denotes CH, which may optionally be mono- or
disubstituted by one or more groups selected from the group
consisting of methyl, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or
methoxy,
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
28
optionally in the form of the individual enantiomers or diastereomers,
mixtures
of the enantiomers or diastereomers and optionally in the form of the
racemates, and optionally in the form of the acid addition salts, solvates and
hydrates thereof, with the proviso that if
A denotes
C =C or
H H H 0 H
R1 denotes methyl and
R3 denotes hydrogen,
R4 cannot represent phenyl.
Also of particular interest are intermediates of general formula 4 wherein
A denotes a double-bonded group selected from among
C and
H H H p H H CH2H
R1 which may be identical or different, denotes a methyl or ethyl
group which may optionally be substituted by cyclopropyl, hydroxy or fluorine,
or
R1 denotes C3-C4-alkylene-X, where X denotes chloride, bromide,
methanesuIphonate and p-toluenesulphonate;
R3 denotes hydrogen or C,-C3-alkyl, which may optionally be
substituted by a group selected from the group consisting of
hydroxy, fluorine or CF3;
R4 denotes C1-C3-alkyl, which may optionally be substituted by a
group selected from the group consisting of hydroxy, fluorine or
CF3, or
R4 denotes a phenyl group which may optionally be substituted by
phenyl, which may optionally be mono- or disubstituted by
methyl, fluorine, hydroxy or CF3, or
R4 denotes a benzyl group which may optionally be substituted at
the phenyl ring by one or two, preferably one group selected
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
29
from the group consisting of methyl, ethyl, hydroxy, fluorine, CF3,
and phenyl, or
R4 denotes a benzyl group which may optionally be
monosubstituted by phenyl at the methylene bridge, or
R4 denotes a group of formula
cxa wherein B' denotes CH, which may optionally be mono- or
disubstituted by one or more groups selected from the group
consisting of methyl, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, hydroxy, CF3 or
methoxy,
optionally in the form of the individual enantiomers or diastereomers,
mixtures
of the enantiomers or diastereomers and optionally in the form of the
racemates, and optionally in the form of the acid addition salts, solvates and
hydrates thereof, with the proviso that if
A denotes
C / or
H H H O H
R1 denotes methyl and
R3 denotes hydrogen,
R4 cannot represent phenyl.
Of exceptional importance according to the invention are intermediates of
general formula 4 wherein
A denotes a double-bonded group selected from among
C and
H H H O H H CH2H
R' denotes methyl;
R3 denotes hydrogen or methyl;
R4 denotes biphenyl, benzhydryl, fluorenyl or biphenylmethyl,
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
optionally in the form of the individual enantiomers or diastereomers,
mixtures
of the enantiomers or diastereomers and optionally in the form of the
racemates, and optionally in the form of the acid addition salts, solvates and
hydrates thereof.
By acid addition salts are meant salts selected from the group consisting of
the hydrochloride, hydrobromide, hydroiodide, hydrosulphate,
hydrophosphate, hydromethanesulphonate, hydronitrate, hydromaleate,
hydroacetate, hydrocitrate, hydrofumarate, hydrotartrate, hydrooxalate,
hydrosuccinate, hydrobenzoate and hydro-p-toluenesulphonate, preferably
hydrochloride, hydrobromide, hydrosulphate, hydrophosphate, hydrofumarate
and hydromethanesulphonate.
The present invention also relates to the use of the abovementioned
intermediates of formula 4 for preparing the compounds of formula 1.
The examples of synthesis described below serve to illustrate the present
invention still further. However, they are to be regarded as only examples of
the procedure, as further illustration of the invention, without restricting
the
invention to the object described below by way of example.
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
31
Example 1: tropenol biphen-2-ylcarbamate methobromide
Me\+,,Me Br -
N
H
Oy0
NH
1.1.: tropenol biphen-2-ylcarbamate
5.0 g (0.026 mol) 2-biphenylisocyanate are placed in 10 ml acetonitrile, a
solution of 3.619 g (0.026 mol) tropenol in 5 ml acetonitrile is added
dropwise,
then stirred for 24 hours at ambient temperature. The solution is concentrated
by evaporation and the residue is distributed between dichioromethane and
water. The organic phase is dried over sodium sulphate and evaporated to
dryness.
Yield: 7.4 g yellowish-orange oil (= 85% of theory).
1.2.: tropenol biphen-2-ylcarbamate methobromide
1.00 g (0.003 mol) tropenol biphenyl-2-ylcarbamate and 1.709 g (0.009 mol)
50% methyl bromide solution in acetonitrile are placed in 70 ml acetonitrile
and left to stand for 3 days at ambient temperature in a sealed container and
in the dark. The mixture is evaporated down to the residue. Purification is
carried out by recrystallisation first from ethanol / diethyl ether. Yield:
0.38 g
white crystals (= 29% of theory); melting point: 244 -245 C.
Example 2: scopine biphen-2-ylcarbamate methobromide
-
Me\+, Me Sr
N
O H
Or
NH
2.1.: scopine biphen-2-ylcarbamate -hydrochloride
2.5 g (0.013 mol) 2-biphenyl-isocyanate are placed in 7 ml acetonitrile, a
solution of 0.99 g (0.013 mol) scopine in 7 ml acetonitrile is added dropwise
at
ambient temperature. After 3 hours' reaction the solution is concentrated by
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
32
evaporation and the residue is distributed between dichloromethane and
water. The organic phase is dried over sodium sulphate and evaporated to
dryness. The residue is dissolved in dichloromethane, precipitated by the
addition of ethereal HCI, then dissolved in water and washed with diethyl
ether. The aqueous phase is made basic using 10% sodium carbonate
solution and extracted with dichloromethane. Then the hydrochloride is
precipitated. Yield: 1.57 g (= 31 % of theory); melting point: 154 -155 C.
2.2.: scopine biphen-2-ylcarbamate methobromide
From 1.56 g (0.004 mol) scopine biphen-2-ylcarbamate hydrochloride the free
base is prepared by mixing with 10% sodium carbonate solution and
subsequently extracting with methylene chloride. After drying over magnesium
sulphate the extract is evaporated to dryness, dissolved in 40 ml acetonitrile
and 20 ml dichloromethane, combined with 3.5 g (0.012 mol) of approx. 50%
methyl bromide solution in acetonitrile and left to stand 6 days at ambient
temperature in a sealed container in the dark. The solution is evaporated to
dryness. Purification is carried out by recrystallisation from ethanol.
Yield: 1.33 g (= 75% of theory); melting point: 216 -217 C.
Example 3: tropenol biphen-2-yl-methyl-carbamate methobromide
Me\+ Me Br
N
H
O1O
N, Me
1
3.1.: scopine biphen-2-yl-methyl-carbamate hydrochloride
2.5 g (0.007 mol) tropenol biphenyl-2-ylcarbamate are dissolved at ambient
temperature in 40 ml of tetrahydrofuran, combined with 0.45 g (0.011 mol)
sodium hydride and stirred for 0.5 hours at ambient temperature. Then 1.06 g
(0.007 mol) methyl iodide are added dropwise and the reaction mixture is
stirred for 24 hours at ambient temperature. The suspension obtained is
evaporated to dryness and distributed between dichloromethane and water.
The organic phase is washed with water mixed with acetic acid (2 drops of
glacial acetic acid to 100 ml of water), dried over magnesium sulphate and
evaporated to dryness. The residue is dissolved in dichloromethane,
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
33
precipitated using ethereal HCI and recrystallised from isopropanol / diethyl
ether.
Yield: 0.23 g (= 9% of theory); melting point: 192 -194 C.
3.2.: scopine biphen-2-yl-methyl-carbamate methobromide
From 0.2 g (0.001 mol) scopine biphenyl-2-yl-methyl-carbamate hydrochloride
the free base is prepared by combining with 10% sodium carbonate solution
and subsequently extracting with methylene chloride. The residue is dissolved
in 50 ml acetonitrile and 30 ml dichloromethane and combined with 0.596 g
(0.003 mol) approx. 50% methyl bromide solution in acetonitrile. The solution
is left to stand for 4 days in a sealed container in the dark at ambient
temperature, then the solvent is distilled off under reduced pressure.
Purification is carried out by recrystallisation from acetonitrile.
Yield: 0.06 g (= 14% of theory); melting point: 228 -229 C.
Example 4: tropenol benzhydryl-carbamate methobromide
Me,+ Me Br -
N
H
Oy0
NH
4.1.: tropenol benzhydryl-carbamate
2.5 g (0.012 mol) diphenylmethylisocyanate are placed in 7 ml acetonitrile, a
solution of 1.67 g (0.012 mol) tropenol in 5 ml acetonitrile is added
dropwise.
The solution is stirred for 24 hours at ambient temperature, after 10 minutes
a
white precipitate is formed. After the end of the reaction time the suspension
is cooled and the precipitate is suction filtered. Yield: 2.28 g (= 55% of
theory); melting point: 140 -142 C.
4.2.: tropenol benzhydryl-carbamate methobromide
1.2 g (0.003 mol) tropenol benzhydryl-carbamate are dissolved in 40 ml
acetonitrile and 30 ml dichloromethane, 1.789 g (0.009 mol) approx. 50%
methyl bromide solution in acetonitrile are added and the mixture is left to
stand for 4 days in a sealed container at ambient temperature. The solution is
concentrated by evaporation and the residue recrystallised from acetonitrile.
Yield: 0.76 g (= 57% of theory); melting point: 243 -244 C.
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
34
Example 5: tropenol 9H-fluoren-9-yl-carbamate methobromide
Me\+ Me Br -
N
H
/ 0y0
NH
5.1.: tropenol 9H-fluoren-9-yl carbamate
1.95 g (0.009 mol) 9-fluorene-9-isocyanate are suspended in 20 ml
acetonitrile, a solution of 1.253 g (0.009 mol) tropenol in 4 ml acetonitrile
is
added dropwise at ambient temperature, then stirred for 24 hours at this
temperature. The reaction mixture is concentrated by evaporation in vacuo
and distributed between dichloromethane and water. The organic phase is
dried over magnesium sulphate and evaporated to dryness. The residue is
dissolved in dichloromethane, precipitated by the addition of ethereal HCI,
then dissolved in water and washed with diethyl ether. The solid obtained is
dissolved in water, combined with 10% sodium carbonate solution, extracted
with dichloromethane, dried over magnesium sulphate, evaporated to dryness
and recrystallised from acetonitrile.
Yield: 0.32 g (= 10% of theory); melting point: 143 -144 C.
5.2.: tropenol 9H-fluoren-9-yl -carbamate methobromide
0.32 g (0.001 mol) tropenol 9H-fluoren-9-yl -carbamate are dissolved in 3D ml
acetonitrile and 50 ml dichloromethane, and 0.596 g (0.003 mol) of approx.
50% methyl bromide solution in acetonitrile are added. The solution is left to
stand in a sealed container for 4 days at ambient temperature, then
evaporated down to the residue and recrystallised from acetonitrile.
Yield: 0.16 g (= 36% of theory); melting point: 226 -227 C.
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
Example 6: tropenol biphen-2-ylmethyl-carbamate methobromide
Mew+"Me Br -
N
H
Oro
NH
6.1.: tropenol biphen-2-ylmethyl-carbamate
3.67 g (0.02 mol) 2-phenylbenzylamine are placed in 250 ml saturated sodium
bicarbonate solution and 250 ml dichloromethane. At 0 C 52.9 ml (0.10 mol)
20% phosgene-toluene solution are added under the surface of the
dichloromethane. The mixture is vigorously stirred for 30 minutes. The two
phases are separated, the organic phase is dried over sodium sulphate and
evaporated to dryness.
The residue is dissolved in 20 ml acetonitrile and 4.18 g (0.03 mol) tropenol
in
10 mI acetonitrile are added dropwise, whereupon a precipitate is formed. It
is
stirred for 12 hours at ambient temperature. The precipitate is suction
filtered
and the mother liquor evaporated to dryness. The residue is dissolved in
dichloromethane and washed with water, water mixed with acetic acid (2
drops of glacial acetic acid to 100 mI of water) and 10 % sodium carbonate
solution. The organic phase is dried and evaporated to dryness. Yield: 2.85 g
(= 41 % of theory).
6.2.: tropenol biphen-2-ylmethyl-carbamate methobromide
2.8 g (0.008 mol) tropenol biphenyl-2-ylmethyl-carbamate are dissolved in 10
ml acetonitrile and combined with 2.27 g (0.024 mol) 50% methyl bromide
solution. The solution is left to stand for 4 days in a sealed container in
the
dark at ambient temperature. The solvent is concentrated by evaporation and
the foamy residue is triturated with acetone until crystallisation is
complete.
Yield: 2.78 g (= 78% of theory); melting pointl 80 C-181 C (decomp.).
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
36
Example 7: scopine biphen-2-ylmethyl-carbam ate methobromide
Me,+ Me Br -
N
H
Or
QNH
7.1.: scopine biphenyl-2-ylmethyl-carbam ate
3.67 g (0.02 mol) 2-phenylbenzylamine are placed in 250 ml saturated sodium
bicarbonate solution and 250 ml dichloromethane. At 0 C 52.9 ml (0.10 mol)
20% phosgene-toluene solution are added under the surface of the
dichloromethane. It is stirred vigorously for 30 minutes. The two phases are
separated, the organic phase is dried over sodium sulphate and evaporated to
dryness.
The residue is dissolved in 20 ml acetonitrile and 4.66 g (0.03 mol) of
scopine
in 10 ml acetonitrile are added dropwise, whereupon a precipitate is formed.
It
is stirred for 12 hours at ambient temperature. The precipitate is suction
filtered and the mother liquor evaporated to dryness. The residue is dissolved
in dichloromethane, washed with water and then extracted with dilute
hydrochloric acid (approx. 0.05 mol/L). The acidic aqueous phase is made
basic with sodium carbonate and extracted with dichloromethane. The
resulting organic phase is dried over sodium sulphate and evaporated to
dryness. Yield: 2.85 g (= 33% of theory)
7.2.: scopine biphen-2-ylmethyl-carbamate methobromide
1.2 g (0.003 mol) scopine biphenyl-2-ylmethyl-carbamate are dissolved in 5
ml acetonitrile and combined with 1.709 g (0.009 mol) 50% methyl bromide
solution. The solution is left to stand for 4 days in a sealed container in
the
dark at ambient temperature. The solvent is concentrated by evaporation and
the foamy residue is triturated with acetone until crystallisation is
complete.
Yield: 1.04 g (= 76% of theory); melting pointl75 C-176 C.
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
37
Example 8: 9-methyl-9-aza-tricyclo[3.3.1.0*2.4*lnon-7-yl biphen-2-
ylcarbamate methobromide
Me \+ Me Br - 11 N
H
O
NH
8.1.: 9-methyl-9-aza-tricyclo[3.3.1.0*2.4*lnonan-7-ol
35 ml (0.349 mol) 40% aq. KOH was covered with 100 ml diethyl ether and
cooled in the ice bath, 23.64 g (0.101 mol) N-methyl-N-nitrosourea was added
batchwise, then the mixture was stirred for 10 min. Then the ether phase was
decanted off, again combined with diethyl ether, swirled round and decanted
off. The combined org. phases were dried over solid KOH while cooling with
an ice bath and the solution obtained was further used. 25 ml of the
diazomethane solution prepared above and then 53.4 mg (0.000139 mol) of
bis(benzonitrile)dichloro-palladium(ll) were added to a solution of 4.01 g
(0.028 mol) tropenol in 25 ml diethyl ether and 5 ml of methanol while cooling
with an ice bath. A further 8 ml of the diazomethane solution were added, then
two lots of 10 ml of diazomethane solution, each after 30 min, and the mixture
was then stirred for another 30 min.. The solvent was concentrated by
evaporation, extracted with hot hexane, filtered hot, evaporated to dryness.
Yield: 4.25 g of slightly yellowish crystals (= 96% of theory).
8.2.: 9-methyl-9-aza-tricyclo[3.3.1.0*2.4*lnon-7-yl biphen-2-ylcarbamate
hydrochloride
2.15 g 9-methyl-9-aza-tricyclo[3.3.1.0*2.4*]nonan-7-ol in acetonitrile were
added dropwise to a solution of 2.5 g biphenyl-2-isocyanate in acetonitrile.
The solution was stirred overnight at ambient temperature, diluted with 200 ml
dichloromethane and washed with water and water mixed with acetic acid (2
drops of glacial acetic acid to 100 ml of water). The organic phase was dried
over magnesium sulphate, filtered and concentrated by rotary evaporation.
The yellow oil obtained was dissolved in dichloromethane, converted into the
hydrochloride by the addition of ethereal HCI and recrystallised from
acetonitrile/ether. Yield: 0.35g white crystals (= 7% of theory).
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
38
8.3.: 9-methyl-9-aza-tricyclo[3.3.1. 0*2.4*lnon-7-yl biphenyl-2-ylcarbamate
methobromide
0.35 g 9-methyl-9-aza-tricyclo[3.3.1.0*2.4*]non-7-yl biphenyl-2-ylcarbamate
hydrochloride were dissolved in water, made basic with 10% sodium
carbonate solution and extracted with dichloromethane. The organic phase
was dried over magnesium sulphate, filtered and evaporated to dryness. The
residue was dissolved in 10 ml acetonitrile, and after the addition of 1.2 g
of
50% methyl bromide solution in acetonitrile stirred for 30 days at 75 C in a
sealed pressure vessel. The solution was evaporated to dryness and the
residue was recrystallised from acetonitrile.
Yield: 0.16g white crystals (= 39% of theory); melting point: 142-144 C.
It was found that the compounds of formula I according to the invention are
antagonists of the M3 receptor (Muscarinic Receptor subtype 3). The
compounds according to the invention have Ki values of less than 1000nM in
terms of their affinity for the M3 receptor. These values were determined by
the method described below.
Chemicals
3H-NMS was obtained from Messrs Amersham of Braunschweig, with a
specific radioactivity of 3071 GBq/mmol (83 Ci/mmol). All the other reagents
were obtained from Serva of Heidelberg and Merck of Darmstadt.
Cell membranes:
We used cell membranes from CHO (Chinese hamster ovary) cells which
were transfected with the corresponding genes of the human muscarinic
receptor subtypes hml to hm5 (BONNER). The cell membranes of the
desired subtype were thawed, resuspended by hand with a glass
homogeniser and diluted with HEPES buffer to a final concentration of 2-30
mg of protein/mi.
Receptor binding studies:
The binding assay was carried out in a final volume of 200 pI and consisted of
50 pl of unlabelled substance in various concentrations, 50 pl of radioligand
(3H-N-methylscopolamine 2 nmol/L (3H-NMS), 100 pl of membrane
preparation in TRIS buffer (50 mmol/L TRIS, 10 mmol/L MgCI2, 100 mmol/L
NaCl, adjusted with 1 mol/L NaOH to pH 7.4).
CA 02507110 2011-06-10
25771-1046
39
The non-specific binding was determined by displacement with 10 pmol/I of
atropine.
The preparation was incubated for 1 hour at ambient temperature in 96-well
TM
microtitre plates (Beckman, polystyrene, No. 267001) as a double
measurement. The incubation was ended by filtering using a Skatron Cell
TM
Harvester (type IH 110) through Whatman GF/C filters. The filters were
washed with 3 ml of ice-cooled TRIS buffer. The filters were then transferred
into scintillation vials (Zinsser 5ml), 4 ml of scintillation liquid were
added
(Zinsser: Quickszint 2000 or Beckmann Ultima Gold) and the vials were
shaken end over end for 1 hour.
Determining the radioactivity:
The radioactivity of the filters was measured using a scintillation counter
(Beckmann or LKB).
Evaluation:
The Ki values were calculated using implicit equations which were derived
directly from the mass-action law, with the model for the 1 receptor 2 ligand
reaction (SysFit software, SCHITTKOWSKI).
Literature:
BONNER TI, New subtypes of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 10, Suppl.: 11-15 (1989); SCHITTKOWSKI K
Parameter estimation in systems of nonlinear equations Numer Math. 68:
129-142 (1994).
The compounds of formula 1 according to the invention are characterised by
their range of uses in the therapeutic field.
Particular mention should be made of those applications for which the
compounds of formula 1 according to the invention may preferably be used on
the basis of their pharmaceutical activity as anticholinergics. These are for
example the treatment of asthma or COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease). The compounds of general formula 1 may also be used to treat
vagally induced sinus bradycardia and to treat heart rhythm disorders.
Generally, the compounds according to the invention may also be used
therapeutically to treat spasms, for example, in the gastrointestinal tract .
They may also be used to treat spasms in the urinary tract and also to treat
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
menstrual pain, for example. Of the ranges of indications mentioned above,
the treatment of asthma and COPD with the compounds of formula I
according to the invention is of particular importance.
The compounds of general formula 1 may be used on their own or in
conjunction with other active substances of formula 1. The compounds of
general formula 1 may optionally also be used in combination with other
pharmacologically active substances. These may be, in particular,
betamimetics, antiallergics, PAF antagonists, PDE-IV inhibitors, leukotriene
antagonists, p38 kinase inhibitors, EGFR kinase inhibitors and corticosteroids
as well as combinations of active substances thereof.
Examples of betamimetics which may be used according to the invention in
conjunction with the compounds of formula 1 include compounds selected
from among bambuterol, bitolterol, carbuterol, clenbuterol, fenoterol,
formoterol, hexoprenaline, ibuterol, pirbuterol, procaterol, reproterol,
salmeterol, sulphonterol, terbutaline, tolubuterol, 4-hydroxy-7-[2-{[2-{[3-(2-
phenylethoxy)propyl]sulphonyl}ethyl]-amino}ethyl]-2(3H)-benzothiazolone, 1-
(2-fluoro-4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-[4-(1-benzimidazolyl)-2-methyl-2-
butylam ino]ethanol, 1-[3-(4-methoxybenzyl-am ino)-4-hydroxyphenyl]-2-[4-(1-
benzimidazolyl)-2-methyl-2-butylamino]ethanol, 1-[2H-5-hydroxy-3-oxo-4H-
1,4-benzoxazin-8-yl]-2-[3-(4-N, N-dimethylaminophenyl)-2-methyl-2-
propylamino]ethanol, 1-[2H-5-hydroxy-3-oxo-4H-1,4-benzoxazin-8-yl]-2-[3-(4-
m ethoxyphenyl)-2-methyl-2-propylamino]ethanol, 1-[2H-5-hydroxy-3-oxo-4H-
1,4-benzoxazin-8-yl]-2-[3-(4-n-butyloxyphenyl)-2-methyl-2-
propylamino]ethanol, 1-[2H-5-hydroxy-3-oxo-4H-1,4-benzoxazin-8-yl]-2-{4-[3-
(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl]-2-methyl-2-butylamino]ethanol, 5-
hydroxy-8-(1-hydroxy-2-isopropylaminobutyl)-2H-1,4-benzoxazin-3-(4H)-one,
1 -(4-am i no-3-ch loro-5-trifl uormethylphenyl)-2 -tert. -buty lam ino)ethano
I and 1-
(4-ethoxycarbony lam ino-3-cyano-5-fluorophenyl)-2-(tert.-butylam ino)ethanol,
optionally in the form of the racemates, the enantiomers, the diastereomers
and optionally the pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts, the
solvates and/or the hydrates thereof. Most preferably, the betamimetics used
as active substances in conjunction with the compounds of formula 1
according to the invention are selected from among fenoterol, formoterol,
salmeterol, 1-[3-(4-methoxybenzyl-amino)-4-hydroxyphenyl]-2-[4-(1-
benzimidazolyl)-2-methyl-2-butylamino]ethanol, 1-[2H-5-hydroxy-3-oxo-4H-
1,4-benzoxazin-8-yl]-2-[3-(4-N, N-dimethylam inophenyl)-2-methyl-2-
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
41
propylamino]ethanol, 1-[2H-5-hydroxy-3-oxo-4H-1,4-benzoxazin-8-yl]-2-[3-(4-
methoxyphenyl)-2-methyl-2-propylam ino]ethanol, 1-[2H-5-hydroxy-3-oxo-4H-
1,4-benzoxazin-8-yl]-2-[3-(4-n-butyloxyphenyl)-2-methyl-2-
propylamino]ethanol, 1-[2H-5-hydroxy-3-oxo-4H-1,4-benzoxazin-8-yl]-2-{4-[3-
(4-m ethoxyphenyl)-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl]-2-methyl-2-butylamino}ethanol,
optionally in the form of the racemates, the enantiomers, the diastereomers
and optionally the pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts and the
hydrates thereof. Of the betamimetics mentioned above the compounds
formoterol and salmeterol are particularly preferred, optionally in the form
of
the racemates, the enantiomers, the diastereomers and optionally the
pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts thereof, and the hydrates
thereof. According to the invention, the acid addition salts of the
betamimetics
selected, for example, from among the hydrochloride, hydrobromide,
sulphate, phosphate, fumarate, methanesuIphonate and xinafoate are
preferred. Particularly preferred in the case of salmeterol are the salts
selected from among the hydrochloride, sulphate and xinafoate, of which the
xinafoate is particularly preferred. Particularly preferred in the case of
formoterol are the salts selected from among the hydrochloride, sulphate and
fumarate, of which the hydrochloride and fumarate are particularly preferred.
According to the invention, formoterol fumarate is of exceptional importance.
Within the scope of the present invention, the corticosteroids which may
optionally be used in conjunction with the compounds of formula 1 may be
compounds selected from among flunisolide, beclomethasone, triamcinolone,
budesonide, fluticasone, mometasone, ciclesonide, rofleponide, GW 215864,
KSR 592, ST-126 and dexamethasone. Preferably, within the scope of the
present invention, the corticosteroids are selected from among flunisolide,
beclomethasone, triamcinolone, budesonide, fluticasone, mometasone,
ciclesonide and dexamethasone, while budesonide, fluticasone, mometasone
and ciclesonide are important and budesonide and fluticasone are particularly
important. In some cases, within the scope of the present patent application,
the term steroids is used on its own instead of the word corticosteroids. Any
reference to steroids within the scope of the present invention includes a
reference to salts or derivatives which may be formed from the steroids.
Examples of possible salts or derivatives include: sodium salts,
sulphobenzoates, phosphates, isonicotinates, acetates, propionates,
dihydrogen phosphates, palmitates, pivalates or furoates. In some cases the
corticosteroids may also occur in the form of their hydrates.
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
42
Examples of PDE-IV inhibitors which may be used according to the invention
as a combination with the compound of formula 1 include compounds
selected from among enprofylline, roflumilast, ariflo, Bay-198004, CP-
325,366, BY343, D-4396 (Sch-351591), V-1 1294A and AWD-12-281.
Preferred PDE-IV inhibitors are selected from among enprofylline, roflumilast,
ariflo and AWD-12-281, while AWD-12-281 is particularly preferred as the
combination partner with the compound of formula 1 according to the
invention. Any reference to the abovementioned PDE-IV inhibitors also
includes, within the scope of the present invention, a reference to any
pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts thereof which may exist. By
the physiologically acceptable acid addition salts which may be formed by the
abovementioned PDE-IV inhibitors are meant, according to the invention,
pharmaceutically acceptable salts selected from among the salts of
hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid,
methanesulphonic acid, acetic acid, fumaric acid, succinic acid, lactic acid,
citric acid, tartaric acid and maleic acid. According to the invention, the
salts
selected from among the acetate, hydrochloride, hydrobromide, sulphate,
phosphate and methanesuiphonate are preferred in this context.
Within the scope of the present invention, the term dopamine agonists, which
may optionally be used in conjunction with the compounds of formula 1,
denotes compounds selected from among bromocriptine, cabergolin, alpha-
dihydroergocryptine, lisuride, pergolide, pramipexol, roxindol, ropinirol,
talipexol, tergurid and viozan. It is preferable within the scope of the
present
invention to use, as combination partners with the compounds of formula 1,
dopamine agonists selected from among pramipexol, talipexol and viozan,
pramipexol being of particular importance. Any reference to the
abovementioned dopamine agonists also includes, within the scope of the
present invention, a reference to any pharmacologically acceptable acid
addition salts and hydrates thereof which may exist. By the physiologically
acceptable acid addition salts thereof which may be formed by the
abovementioned dopamine agonists are meant, for example,
pharmaceutically acceptable salts selected from among the salts of
hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid,
methanesulphonic acid, acetic acid, fumaric acid, succinic acid, lactic acid,
citric acid, tartaric acid and maleic acid.
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
43
Examples of antiallergic agents which may be used according to the invention
as a combination with the compound of formula 1 include epinastin, cetirizin,
azelastin, fexofenadin, levocabastin, loratadine, mizolastin, ketotifen,
emedastin, dimetinden, clemastine, bamipin, cexchloropheniramine,
pheniramine, doxylamine, chiorophenoxamine, dimenhydrinate,
diphenhydramine, promethazine, ebastin, desloratidine and meclizine.
Preferred antiallergic agents which may be used within the scope of the
present invention in combination with the compounds of formula 1 according
to the invention are selected from among epinastin, cetirizin, azelastin,
fexofenadin, levocabastin, loratadine, ebastin, desloratidine and mizolastin,
epinastin and desloratidine being particularly preferred. Any reference to the
abovementioned antiallergic agents also includes, within the scope of the
present invention, a reference to any pharmacologically acceptable acid
addition salts thereof which may exist.
Examples of PAF antagonists which may be used according to the invention
as a combination with the compounds of formula 1 include
4-(2-chlorophenyl)-9-methyl-2-[3-(4-morpholinyl)-3-propanon-1-yl]-
6H-thieno-[3,2-f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4.3-a][1,4]diazepine, 6-(2-chlorophenyl)-8,9-
dihydro-1-methyl-8-[(4-morpholinyl)carbonyl]-4H,7H-cyclo-penta-
[4.5]thieno-[3,2-f][1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a][1,4]diazepine.
Examples of EGFR kinase inhibitors which may be used as a combination
with the compounds of formula I according to the invention include, in
particular, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-7-[4-((R)-6-methyl-2-oxo-
morpholin-4-yl)-butyloxy]-6-[(vinylcarbonyl)amino]-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-
fluoro-phenyl)amino]-7-[4-((S)-6-methyl-2-oxo-morpholin-4-yl)-butyloxy]-6-
[(vinylcarbonyl)amino]-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-7-(2-
{4-[(S)-(2-oxo-tetrahydrofuran-5-yl)carbonyl]-piperazin-1-yl}-ethoxy)-
6-[(vinylcarbonyl)amino]-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-7-[2-
((S)-6-methyl-2-oxo-morpholin-4-yl)-ethoxy]-6-[(vinylcarbonyl)amino]-
quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)amino]-6-[(4-{N-[2-(ethoxycarbonyl)-
ethyl]-N-[(ethoxycarbonyl)methyl]am ino}-1 -oxo-2-buten-1 -yl)am ino]-7-
cyclopropylmethoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(R)-(1-phenyl-ethyl)amino]-6-{[4-
(morpholin-4-yl)-1-oxo-2-buten-1-yl]amino}-7-cyclopropylmethoxy-quinazoline
and 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)amino]-6-[3-(morpholin-4-yl)-propyloxy]-7-
methoxy-quinazoline. Any reference to the abovementioned EGFR kinase
inhibitors also includes, within the scope of the present invention, a
reference
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
44
to any pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts thereof which may
exist. By the physiologically or pharmacologically acceptable acid addition
salts thereof which may be formed by the EGFR kinase inhibitors are meant,
according to the invention, pharmaceutically acceptable salts selected from
among the salts of hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, sulphuric acid,
phosphoric acid, methanesulphonic acid, acetic acid, fumaric acid, succinic
acid, lactic acid, citric acid, tartaric acid and maleic acid. The salts of
the
EGFR kinase inhibitors selected from among the salts of acetic acid,
hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid and
methanesulphonic acid are preferred according to the invention.
Particularly preferred examples of p38 kinase inhibitors which may be used as
a combination with the compounds of formula 1 according to the invention
include 1-[5-tert-butyl-2-p-tolyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl]-3-[4-(2-morpholin-4-yl-
ethoxy)naphthalin-1-yl]-urea; 1-[5-tert-butyl-2-p-tolyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl]-3-[4-
(2-
(1-oxothiomorpholin-4-yl)ethoxy)naphthalin-1-yl]-urea; 1-[5-tent-butyl-2-(2-
methylpyridin-5-yl)-2H-pyrazol-3-yl]-3-[4-(2-pyridin-4-yl-ethoxy)naphthalin-1-
yl]-urea; 1-[5-tent-butyl-2-(2-methoxypyridin-5-yl)-2H-pyrazol-3-yl]-3-[4-(2-
morpholin-4-yl-ethoxy)naphthalin-1-yl]-urea or 1-[5-tert-butyl-2-methyl-2H-
pyrazol-3-yl]-3-[4-(2-morpholin-4-yl-ethoxy)naphthalen-1-yl]-urea. Any
reference to the abovementioned p38 kinase inhibitors also includes, within
the scope of the present invention, a reference to any pharmacologically
acceptable acid addition salts thereof which may exist. By the physiologically
or pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts thereof which may be
formed by the p38 kinase inhibitors are meant, according to the invention,
pharmaceutically acceptable salts selected from among the salts of
hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid,
methanesulphonic acid, acetic acid, fumaric acid, succinic acid, lactic acid,
citric acid, tartaric acid and maleic acid.
If the compounds of formula I are used in conjunction with other active
substances, the combination with steroids, PDE IV inhibitors or betamimetics
is particularly preferred, of the categories of compounds mentioned above.
The combination with betamimetics, particularly with long-acting
betamimetics, is of particular importance. The combination of the compounds
of formula 1 according to the invention with salmeterol or formoterol is
particularly preferred.
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
Suitable preparations for administering the salts of formula 1 include for
example tablets, capsules, suppositories and solutions, etc. Administration of
the compounds according to the invention by inhalation is of particular
importance according to the invention (particularly for treating asthma or
COPD). The content of the pharmaceutically active compound(s) should be in
the range from 0.05 to 90 wt.-%, preferably 0.1 to 50 wt.-% of the
composition as a whole. Suitable tablets may be obtained, for example, by
mixing the active substance(s) with known excipients, for example inert
diluents such as calcium carbonate, calcium phosphate or lactose,
disintegrants such as corn starch or alginic acid, binders such as starch or
gelatine, lubricants such as magnesium stearate or talc and/or agents for
delaying release, such as carboxymethyl cellulose, cellulose acetate
phthalate, or polyvinyl acetate. The tablets may also comprise several layers.
Coated tablets may be prepared accordingly by coating cores produced
analogously to the tablets with substances normally used for tablet coatings,
for example collidone or shellac, gum arabic, talc, titanium dioxide or sugar.
To achieve delayed release or prevent incompatibilities the core may also
consist of a number of layers. Similarly the tablet coating may consist of a
number or layers to achieve delayed release, possibly using the excipients
mentioned above for the tablets.
Syrups or elixirs containing the active substances or combinations thereof
according to the invention may additionally contain a sweetener such as
saccharine, cyclamate, glycerol or sugar and a flavour enhancer, e.g. a
flavouring such as vanillin or orange extract. They may also contain
suspension adjuvants or thickeners such as sodium carboxymethyl cellulose,
wetting agents such as, for example, condensation products of fatty alcohols
with ethylene oxide, or preservatives such as p-hydroxybenzoates.
Solutions are prepared in the usual way, e.g. with the addition of isotonic
agents, preservatives such as p-hydroxybenzoates or stabilisers such as
alkali metal salts of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, optionally using
emulsifiers and/or dispersants, while if water is used as diluent, for
example,
organic solvents may optionally be used as solubilisers or dissolving aids,
and
the solutions may be transferred into injection vials or ampoules or infusion
bottles.
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
46
Capsules containing one or more active substances or combinations of active
substances may for example be prepared by mixing the active substances
with inert carriers such as lactose or sorbitol and packing them into gelatine
capsules.
Suitable suppositories may be made for example by mixing with carriers
provided for this purpose, such as neutral fats or polyethyleneglycol or the
derivatives thereof.
Excipients which may be used include, for example, water, pharmaceutically
acceptable organic solvents such as paraffins (e.g. petroleum fractions),
vegetable oils (e.g. groundnut or sesame oil), mono- or polyfunctional
alcohols (e.g. ethanol or glycerol), carriers such as e.g. natural mineral
powders (e.g. kaolins, clays, talc, chalk), synthetic mineral powders (e.g.
highly dispersed silicic acid and silicates), sugars (e.g. cane sugar, lactose
and glucose), emulsifiers (e.g. lignin, spent sulphite liquors,
methylcellulose,
starch and polyvinylpyrrolidone) and lubricants (e.g. magnesium stearate,
talc,
stearic acid and sodium lauryl sulphate).
For oral use the tablets may obviously contain, in addition to the carriers
specified, additives such as sodium citrate, calcium carbonate and dicalcium
phosphate together with various additional substances such as starch,
preferably potato starch, gelatin and the like. Lubricants such as magnesium
stearate, sodium laurylsulphate and talc may also be used to produce the
tablets. In the case of aqueous suspensions the active substances may be
combined with various flavour enhancers or colourings in addition to the
abovementioned excipients.
For administering the compounds of formula 1 for the treatment of asthma or
COPD it is particularly preferred according to the invention to use
preparations or pharmaceutical formulations which are suitable for inhalation.
Inhalable preparations include inhalable powders, propellant-containing
metering aerosols or propellant-free inhalable solutions Within the scope of
the present invention, the term propellant-free inhalable solutions also
includes concentrates or sterile inhalable solutions ready for use. The
formulations which may be used within the scope of the present invention are
described in more detail in the next part of the specification
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
47
The inhalable powders which may be used according to the invention may
contain 1 either on its own or in admixture with suitable physiologically
acceptable excipients.
If the active substances 1 are present in admixture with physiologically
acceptable excipients, the following physiologically acceptable excipients may
be used to prepare these inhalable powders according to the invention:
monosaccharides (e.g. glucose or arabinose), disaccharides (e.g. lactose,
saccharose, maltose), oligo- and polysaccharides (e.g. dextrans),
polyalcohols (e.g. sorbitol, mannitol, xylitol), salts (e.g. sodium chloride,
calcium carbonate) or mixtures of these excipients. Preferably, mono- or
disaccharides are used, while the use of lactose or glucose is preferred,
particularly, but not exclusively, in the form of their hydrates. For the
purposes
of the invention, lactose is the particularly preferred excipient, while
lactose
monohydrate is most particularly preferred.
Within the scope of the inhalable powders according to the invention the
excipients have a maximum average particle size of up to 250 pm, preferably
between 10 and 150 pm, most preferably between 15 and 80 pm. It may
sometimes seem appropriate to add finer excipient fractions with an average
particle size of 1 to 9 pm to the excipient mentioned above. These finer
excipients are also selected from the group of possible excipients listed
hereinbefore. Finally, in order to prepare the inhalable powders according to
the invention, micronised active substance 1, preferably with an average
particle size of 0.5 to 10 m, more preferably from 1 to 5 m, is added to the
excipient mixture. Processes for producing the inhalable powders according
to the invention by grinding and micronising and finally mixing the
ingredients
together are known from the prior art. The inhalable powders according to the
invention may be administered using inhalers known from the prior art.
The inhalation aerosols containing propellant gas according to the invention
may contain the compounds I dissolved in the propellant gas or in dispersed
form. The compounds 1 may be contained in separate formulations or in a
common formulation, in which the compounds 1 are either both dissolved,
both dispersed or in each case only one component is dissolved and the other
is dispersed. The propellant gases which may be used to prepare the
inhalation aerosols are known from the prior art. Suitable propellant gases
are selected from among hydrocarbons such as n-propane, n-butane or
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
48
isobutane and halohydrocarbons such as fluorinated derivatives of methane,
ethane, propane, butane, cyclopropane or cyclobutane. The abovementioned
propellant gases may be used either on their own or in mixtures thereof.
Particularly preferred propellant gases are halogenated alkane derivatives
selected from TG134a and TG227 and mixtures thereof.
The propellant-driven inhalation aerosols may also contain other ingredients
such as co-solvents, stabilisers, surfactants, antioxidants, lubricants and pH
adjusters. All these ingredients are known in the art.
The propellant-driven inhalation aerosols according to the invention
mentioned above may be administered using inhalers known in the art (MDIs
= metered dose inhalers).
Moreover, the active substances 1 according to the invention may be
administered in the form of propellant-free inhalable solutions and
suspensions. The solvent used may be an aqueous or alcoholic, preferably
an ethanolic solution. The solvent may be water on its own or a mixture of
water and ethanol. The relative proportion of ethanol compared with water is
not limited but the maximum is up to 70 percent by volume, more particularly
up to 60 percent by volume and most preferably up to 30 percent by volume.
The remainder of the volume is made up of water. The solutions or
suspensions containing I are adjusted to a pH of 2 to 7, preferably 2 to 5,
using suitable acids. The pH may be adjusted using acids selected from
inorganic or organic acids. Examples of particularly suitable inorganic acids
include hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, nitric acid, sulphuric acid
and/or
phosphoric acid. Examples of particularly suitable organic acids include
ascorbic acid, citric acid, malic acid, tartaric acid, maleic acid, succinic
acid,
fumaric acid, acetic acid, formic acid and/or propionic acid etc. Preferred
inorganic acids are hydrochloric and sulphuric acids. It is also possible to
use
the acids which have already formed an acid addition salt with one of the
active substances. Of the organic acids, ascorbic acid, fumaric acid and
citric
acid are preferred. If desired, mixtures of the above acids may be used,
particularly in the case of acids which have other properties in addition to
their
acidifying qualities, e.g. as flavourings, antioxidants or complexing agents,
such as citric acid or ascorbic acid, for example. According to the invention,
it
is particularly preferred to use hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH.
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
49
The addition of editic acid (EDTA) or one of the known salts thereof, sodium
edetate, as stabiliser or complexing agent may optionally be omitted in these
formulations. Other embodiments may contain this compound or these
compounds. In a preferred embodiment the content based on sodium edetate
is less than 100 mg/100ml, preferably less than 50mg/100ml, more preferably
less than 20mg/100ml. Generally, inhalable solutions in which the content of
sodium edetate is from 0 to 10mg/100mI are preferred.
Co-solvents and/or other excipients may be added to the propellant-free
inhalable solutions according to the invention. Preferred co-solvents are
those which contain hydroxyl groups or other polar groups, e.g. alcohols -
particularly isopropyl alcohol, glycols - particularly propyleneglycol,
polyethyleneglycol, polypropyleneglycol, glycolether, glycerol,
polyoxyethylene alcohols and polyoxyethylene fatty acid esters. The terms
excipients and additives in this context denote any pharmacologically
acceptable substance which is not an active substance but which can be
formulated with the active substance or substances in the physiologically
suitable solvent in order to improve the qualitative properties of the active
substance formulation. Preferably, these substances have no
pharmacological effect or, in connection with the desired therapy, no
appreciable or at least no undesirable pharmacological effect. The excipients
and additives include, for example, surfactants such as soya lecithin, oleic
acid, sorbitan esters, such as polysorbates, polyvinylpyrrolidone, other
stabilisers, complexing agents, antioxidants and/or preservatives which
guarantee or prolong the shelf life of the finished pham-iaceutical
formulation,
flavourings, vitamins and/or other additives known in the art. The additives
also include pharmacologically acceptable salts such as sodium chloride as
isotonic agents.
The preferred excipients include antioxidants such as ascorbic acid, for
example, provided that it has not already been used to adjust the pH, vitamin
A, vitamin E, tocopherols and similar vitamins and provitamins occurring in
the
human body.
Preservatives may be used to protect the formulation from contamination with
pathogens. Suitable preservatives are those which are known in the art,
particularly cetyl pyridinium chloride, benzalkonium chloride or benzoic acid
or
benzoates such as sodium benzoate in the concentration known from the
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
prior art. The preservatives mentioned above are preferably present in
concentrations of up to 50 mg/100 mI, more preferably between 5 and 20
mg/100 ml.
Preferred formulations contain, in addition to the solvent water and the
active
substance 1, only benzalkonium chloride and sodium edetate. In another
preferred embodiment, no sodium edetate is present.
The dosage of the compounds according to the invention is naturally highly
dependent on the method of administration and the complaint which is being
treated. When administered by inhalation the compounds of formula 1 are
characterised by a high potency even at doses in the pg range. The
compounds of formula 1 may also be used effectively above the pg range.
The dosage may then be in the gram range, for example.
Particularly when administered by routes other than by inhalation the
compounds according to the invention may be administered in higher doses
(for example, but not restrictively, in the range from 1 to 1000 mg).
The following examples of formulations illustrate the present invention
without
restricting its scope:
Examples of pharmaceutical formulations
A) Tablets per tablet
active substance 1 100 mg
lactose 140 mg
corn starch 240 mg
polyvinylpyrrolidone 15 mg
magnesium stearate 5 mg
500 mg
The finely ground active substance, lactose and some of the corn starch are
mixed together. The mixture is screened, then moistened with a solution of
polyvinylpyrrolidone in water, kneaded, wet-granulated and dried. The
granules, the remaining corn starch and the magnesium stearate are
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
51
screened and mixed together. The mixture is compressed to produce tablets
of suitable shape and size.
B) Tablets per tablet
active substance 1 80 mg
lactose 55 mg
corn starch 190 mg
microcrystalline cellulose 35 mg
polyvinylpyrrolidone 15 mg
sodium-carboxymethyl starch 23 mg
magnesium stearate 2 mg
400 mg
The finely ground active substance, some of the corn starch, lactose,
microcrystalline cellulose and polyvinylpyrrolidone are mixed together, the
mixture is screened and worked with the remaining corn starch and water to
form a granulate which is dried and screened. The sodium carboxymethyl
starch and the magnesium stearate are added and mixed in and the mixture is
compressed to form tablets of a suitable size.
C) Ampoule solution
active substance 1 50 mg
sodium chloride 50 mg
water for inj. 5 ml
The active substance is dissolved in water at its own pH or optionally at pH
5.5 to 6.5 and sodium chloride is added to make the solution isotonic. The
resulting solution is filtered to remove pyrogens and the filtrate is
transferred
under aseptic conditions into ampoules which are then sterilised and heat-
sealed. The ampoules contain 5 mg, 25 mg and 50 mg of active substance.
CA 02507110 2005-05-24
52
D) Metering aerosol
active substance 1 0.005
Sorbitan trioleate 0.1
Monofluorotrichloromethane and
Difluorodichloromethane 2 : 3 ad 100
The suspension is transferred into a conventional aerosol container with
metering valve. Preferably 50 pl suspension are released on each actuation.
The active substance may also be released in higher doses if desired
(e.g. 0.02 wt.-%).
E) Solutions (in mg/100ml)
active substance 1 333.3 mg
formoterol fumarate 333.3 mg
benzalkonium chloride 10.0 mg
EDTA 50.0 mg
HCI (1 n) ad pH 3.4
This solution may be prepared in the usual way.
F) Inhalable powder
active substance 1 8 pg
formoterol fumarate 6 pg
lactose monohydrate ad 25 mg
The inhalable powder is prepared in the usual way by mixing the individual
ingredients.
G) Inhalable powder
active substance 1 9 pg
lactose monohydrate ad 5 mg
The inhalable powder is prepared in the usual way by mixing the individual
ingredients.