Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02509080 2005-06-02
1
STABILIZING MECHANISM FOR A TREE-FELLING HEAD
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention generally relates to the cutting industry and more
particularly concerns a stabilizing mechanism improving the performance of
tree-
felling heads.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Tree-felling heads are well known devices installed at the end of a power
operated
1o boom carried by a forest-going vehicle. Felling heads are usually provided
with a
circular saw rotating in a generally horizontal plane for cutting the trees.
Arms are
provided for grabbing the tree being cut, and subsequently laying it on the
ground.
Multiple arms may be provided for accumulating a number of trees before
putting
them down. An example of such a felling head is shown in Canadian patent No.
is 2,038,784 (GILBERT).
Efforts are being made in the wood cutting industry to increase the cutting
capacity
of tree-felling heads. Such an increase is particularly significant in
regions, such as
Western Canada, where trees are wide, of irregular shape, heavy and measure
20 over 100 feet. Standard tree-felling head having a cutting capacity of 24"
often
need to cut such trees in repetitive steps which increases operational
hazards.
Obtaining a greater cutting capacity may be achieved by either increasing the
saw
diameter, or reducing the size of the surrounding cage ensuring its proper
working.
25 The latter option being difficult to contemplate without affecting the
reliability of the
system, increasing the diameter remains the better option. However, one
important consequence of this expansion is the corresponding increase in the
gyroscopic forces acting on the saw. For example, when the felling head is
angled
forward to put down the cut trees, the saw experiences a sideways tilting
which
30 puts heavy constraints on the saw's driving systems and interferes with its
ability
to resume the desired rotation speed quickly.
CA 02509080 2011-08-24
2
There is therefore a need for a mechanism allowing an increase of the diameter
of
the saw of a tree-felling head without unduly burdening its driving system.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
Accordingly, one aspect of the present invention provides a tree-felling head
having
a frame and a tree-engaging forward direction, comprising:
a center-driven disk saw having left and right sides with respect to said
forward direction, said saw being rotatable within an operative rotation plane
with respect to said frame, the gyroscopic effect inducing a sideways tilting
of
the saw with respect to said operative rotation plane when said saw is angled
in the forward direction; and
a stabilizing mechanism comprising a gyroscopic stop extending slightly
above said saw without contact therewith when said saw rotates within said
operative rotation plane, said gyroscopic stop extending at a position over
one
of said left and right sides of said saw, said position being selected so that
the
gyroscopic stop blocks said sideways tilting.
In cases where the saw rotates clockwise, the gyroscopic stop needs to be
disposed
on the left side. Conversely, when the saw has a counterclockwise rotation,
the
gyroscopic stop needs to be disposed on the right side. In accordance with a
preferred embodiment of the invention, an additional gyroscopic stop may also
be
provided on the opposite side of the saw.
According to another aspect of the invention, there is also provided a
stabilizing
mechanism for a center-driven disk saw of a tree-felling head, said tree-
felling head
having a frame and a tree-engaging forward direction and the saw having left
and
right sides with respect to said forward direction, said saw being rotatable
within an
operative rotation plane with respect to said frame, the stabilizing mechanism
comprising:
CA 02509080 2011-08-24
2a
a gyroscopic stop extending slightly above said saw without contact therewith
when said saw rotates within said operative rotation plane, said gyroscopic
stop
extending at a position over one of said left and right sides thereof, said
position
being selected so that the gyroscopic stop blocks a sideways tilting of the
saw with
s respect to said operative rotation plane induced by the gyroscopic effect
when said
saw is angled in the forward direction.
CA 02509080 2005-06-02
3
Further features and aspects of the present invention will be better
understood
upon reading of preferred embodiments thereof with reference to the appended
drawings.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
FIG. 1 is a perspective view of a tree-felling head according to an embodiment
of
the present invention.
FIG. 2 is an exploded perspective view in partial transparency of the bottom
io portion of the felling head of FIG. 1.
FIG. 3 is a perspective view in partial transparency of a saw provided with a
stabilizing mechanism according to an embodiment of the invention.
FIG. 4 is a side view of the saw of FIG. 3.
FIG. 5 is a front view of the saw of FIG. 3.
FIG. 6 is a top view of the saw of FIG. 3.
FIG. 7 is a cross-sectional side view of a stabilizing mechanism according to
an
aspect of the present invention.
DESCRIPTION OF A PREFERRED EMBODIMENT OF THE INVENTION
The present invention advantageously provides a stabilizing mechanism which
controls the gyroscopic effect on the rotating saw of a tree-felling head.
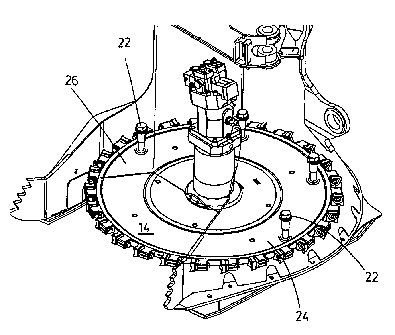
Referring to FIG. 1, there is shown a typical embodiment of a tree-felling
head 10
to which the present invention is applied. The felling head 10 generally
includes a
frame 12 having a boom adapter 13 for attachment to an articulated boom (not
shown). A circular saw 14 is rotationally mounted at the bottom end of the
frame
CA 02509080 2005-06-02
4
12, and is designed to be operated in a generally horizontal plane when
cutting.
The crosswise length 15 of the portion of the saw 14 projecting from the frame
12
determines the cutting capacity of the saw, and the direction in which the
apparatus moves in order to engage the trees is defined herein as the "forward
direction" 16. Clamp arms 18 and accumulating arms 20 typically project
forward
from the upper portion of the frame 12 and are adapted to retain and
accumulate
the trees cut down by felling head 10. It will be understood by one skilled in
the art
that the tree-felling head of FIG. 1 is only one example of the type of
apparatus to
which the present invention pertains and that the invention is in no way
limited to
to such an embodiment.
A rotating object, such as the circular saw of a felling head, has an angular
momentum vector along its rotation axis, in a direction determined by physics'
well
known "right-hand rule". According to this convention, when wrapping the
fingers
of one's right hand around the direction of rotation of the object, the thumb
sticks
out in a direction corresponding to the angular momentum vector. Angular
momentum being a conserved quantity, any rotating object tends to resist a
change of direction of its angular momentum vector, such as created when its
rotation axis is tilted from its original orientation, and tries to compensate
by
adding the necessary component to its new angular momentum. This creates a
sideways tilting of the rotation plane, in a direction depending on the
direction of
rotation.
By way of example, let us suppose a circular saw as described above rotating
counterclockwise in a horizontal plane. Using the right-hand rule, it can be
seen
that its angular momentum vector points upward. Now let us suppose that the
saw
in angled forward, therefore changing the direction of its angular momentum in
the
same direction. In order to bring it back in its original vertical direction,
a rearward
component is missing, which the system will try to add. Using again the right-
hand
3o rule, it can be seen that a rearward pointing angular momentum vector
CA 02509080 2005-06-02
corresponds to a rotation of the saw around the rearward-forward axis, towards
the left; the saw therefore tends to tilt downwardly on its left side.
Referring to FIGs. 2 to 7, in accordance with the present invention, there is
5 provided a stabilizing mechanism to control the gyroscopic effects described
above. This mechanism includes a gyroscopic stop 22 extending slightly above
the
saw 14, at a position over either its left or right side 24 or 26, in order to
block the
sideways tilting of the saw 14. Following the reasoning above, it can be seen
that if
the saw 14 rotates counterclockwise, it will tend to tilt towards the left 24;
the
1o corresponding gyroscopic stop 22 will therefore be placed above the right
side 26
of the saw 14. Similarly, for a clockwise rotating saw 14, the gyroscopic stop
22
will be placed above the left side 24. The "left" and "right" designations
used herein
are determined with respect to the forward direction 16 of the felling head,
that is,
from the point of view of its operator.
According to a preferred embodiment of the invention, an additional gyroscopic
stop may be provided on the opposite side of the saw 22. For a saw rotating in
a
given direction, the second gyroscopic stop will prevent tilting under the
gyroscopic
effect when the saw is angled in the rearward direction, and generally
increase
stability.
It will be understood that the gyroscopic stops 22 need not be at a precise
location
on the corresponding side of the saw. In the illustrated embodiment, it can be
seen
that the gyroscopic stops 22 are generally located in alignment with the
rotation
axis 28 of the saw, at a right angle with the forward direction 16. The
gyroscopic
saw may however be displaced forward of backward, and the distance between
the gyroscopic stops 22 and the edge of the saw may vary, as long as they are
in
a position to provide the leverage effect necessary to stop the tilting of the
saw on
its other side. In addition, more than one gyroscopic stop may be provided on
one
side of the saw in order to prevent its gyroscopic induced tilting.
CA 02509080 2005-06-02
6
The gyroscopic stops 22 extend above the saw 14 at a distance from its top
surface sufficient to efficiently block the tilting of the saw without
interfering with its
general operation. In the preferred embodiment, this distance is of about 3,2
mm
to 4,8 mm.
Referring more particularly to FIG. 7, the construction of a gyroscopic stop
according to a preferred embodiment of the invention is explained in more
details.
Typical tree felling heads casings usually include a plate 30 which extends
above
io the saw 14, generally in parallel therewith. In order to install the
gyroscopic stops
22 of the present invention, the plate 30 is preferably provided with openings
32
therethrough, at locations directly over the positions where the gyroscopic
stops
22 interact with the saw 14. Each gyroscopic stop is preferably embodied by a
bolt
33, which has a threaded pin 34 extending through the corresponding opening
32,
generally perpendicularly to the saw 14. The head 36 of the bolt abuts on the
top
surface of the plate 30. A threaded bore 38 is preferably rigidly affixed
underneath
the plate 30 in alignment with each opening 32, for example by welding. The
pin
34 is threadedly engaged in the bore 38 so that the vertical movement of the
bolt
33 is prevented. Alternatively, a nut could be threaded on the pin 34
underneath
the plate 30 to maintain the bolt 33 into place.
It will be readily understood by one skilled in the art that the present
invention is
not limited to the particular form and mounting arrangement of the gyroscopic
stops described above. The gyroscopic stops could take any other appropriate
shape which would allow them to block the sideways tilting of the saw under
the
gyroscopic effect. Any appropriate part of the saw casing could be used to
mount
the gyroscopic stops instead of the plate described above, and additional
components could be added for this purpose. In an alternate embodiment, the
stops could be mounted from a side structure instead of from above.
CA 02509080 2005-06-02
7
The wear of the bottom of the pin 34 will constantly increase the distance
between
it and the surface of the saw. In order to keep this distance in the proper
interval,
such as from 3,2 mm to 4,8 mm as explained above, the gyroscopic stops 22 are
preferably provided with one or more spacers 42 between the head 36 of the
bolt
and the top surface of the plate 30. These spacers 42 will initially raise the
bolt 32
with respect to the saw. As the extremity 40 of the pin 34 is worn out,
spacers may
be gradually removed to lower the bolt 33, and consequently bring back the
extremity 40 of the pin 34 within the desired distance interval from the saw
14. The
spacer may be embodied by washers. Such spacers 42 are better seen in the
io exploded view of FIG. 2.
Referring back to FIGs. 2 and 6, it can be seen that the gyroscopic stops 22
according to the present invention may advantageously be used in combination
with back stops 44 as are well known in the art. Back stops 44 are used to
prevent
damage to the saw 14 when it hits the ground, and are usually provided in
pairs on
the rearward portion of the saw 14 on each of its sides. It will be noted that
the
back stops 44 are used to prevent the saw from tilting forward on impact, and
that
their function has nothing to do with gyroscopic motion. As a matter of fact,
the
back stops 44 are positioned too far rearwardly of the saw to efficiently
prevent its
sideways tilting as with the gyroscopic stops of the present invention.
As will easily be appreciated by one skilled in the art, the provision of a
stabilizing
mechanism according to the present invention allows an increase of the
diameter
of the saw without putting undue constraints on its driving system. Industry
standards currently use felling head saws having a maximum of 57 inches, with
very few models going up to 60 inches, with a cutting capacity of 24 inches.
With
the present invention, the saw diameter has been successfully increased to 66
inches, providing a cutting capacity of 28 inches, a 16% increase on the
closest
prior art. Additionally, reducing the gyroscopic tilting of the saw has the
advantage
of improving its ability to resume its desired rotation speed quickly, as well
as
ensuring a better protection of the components of the felling head,
particularly the
CA 02509080 2005-06-02
8
saw itself and its surrounding frame. Finally, the stabilizing mechanism
according
to the present invention allows reducing the thickness of the saw, and
therefore
reducing its kerf. This further increases the cutting capacity of the felling
head, as
less material needs to be eliminated from the tree.
Of course, numerous modifications could be made to the embodiments above
without departing from the scope of the present invention as defined in the
appended claims.