Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02563178 2006-10-05
Profiled rail system for covering joints
The innovation relates to a profiled rail system for
covering joints between floor and/or wall coverings, in
order to obtain smooth transitions even when adjacent
floor coverings have different heights. Joint bridges
of this type are known from the prior art. Although
such arrangements are already capable of being adapted
to predetermined height tolerances, it is nevertheless
desirable to extend the adaptability even further, so
that even large joint depths or pronounced depth
variations can be dealt with by means of a single
product design. Such a requirement is demanded, in
particular, by the trade, so that there is no need to
keep in stock too many different types. Another
requirement in this context is that the connection
should have a good hold and be adaptable to all
situations. For example, EP 1 403 444 discloses a
profiled rail system, in which a profiled shank with a
holding head, onto which the covering rail is placed,
is plugged in the base rail. The plug connection of a
shank in a longitudinal groove has lateral instability,
particularly when the connection is held pivotably with
respect to the covering rail put in place.
The object of the innovation is, therefore, to provide
a profiled rail system for covering joints, in which a
firm, secured connection between the base rail and
covering rail is made, which can be used both for small
and for very large joint heights.
The object is achieved, according to the innovation, by
means of the features of claim 1. Due to the upstanding
fixed holding head on the web of the base rail, the
interposed holding part has a good hold in spite of the
rotational moveable retention. The selected rotational
CA 02563178 2006-10-05
- 2 -
moveability can readily have a generous angular
deflection if the clamping and holding effect is
sufficiently taut. The design of the interposed holding
part in the form of a U-rail is particularly
advantageous, because the holding elements can be
accommodated protectively and in a space-saving way
inside the U-rail, the entire width of the U-rail can
be utilized for the pivoting region and the covering
rail put in place can be retained with its two webs on
the outer walls of the U-rail with a sufficient
clamping effect . Here, too, the height position can be
adapted and readjusted in a known way. Thus, a U-rail
is compact and stable and easily withstands any tensile
and compressive forces.
So that the holding part can be supported rotationally
moveably on the base rail, the holding head of the web
of the base rail has a cross section of circular
design. This rounded end extends over the entire length
of the web. Such a shape can be produced preeminently
and cost-effectively by the extrusion method. Through
the slender web and the large rounded closing-off head,
the holding part put in place can be pivoted on both
sides overeat least 10°. It is also intended to provide
the surface of the circular head with a structure or
with a longitudinally running flute, in order to give
the retention part a better hold and to find the
central orientation for the covering rail. It need not
be mentioned that the holding part should have a
corresponding elevation.
In order to secure the holding part on the holding head
favorably to the base rail, there are several
possibilities. The features of claim 3 have proved
highly advantageous. The spring element is a part which
is produced from an elastic and resilient material and
which projects from the upper transverse wall into the
inner space of the U-rail and is supported with its
outwardly bent-up ends on the sidewalls of the U-rail.
CA 02563178 2006-10-05
- 3 -
The special shaping and mounting give the spring head a
good and firm hold on the holding head of the web, the
tension of which remains stable due to the lateral
support of the bent-up ends. The strip material claimed
refers merely to the fact that the spring element is
thin-walled. It could, for example, be manufactured in
one piece with the U-rail if both are produced from the
same material.
A holding part with a spring element would also be
highly advantageous if it were equipped with the
features of claim 4. The spring element is admittedly
preferably produced from sheet steel. A plastic part
would, however, also be conceivable, because there are
also types of plastic which have good spring
properties. In this version according to claim 4, the
spring element is a loose part which is pressed into
the inner space of the U-rail and clamped. The free,
outwardly directed ends engage into the structure of
the inner sidewalls with such firmness that there is no
fear of any independent release. The desired bracing is
brought about by the pressure of the spring heads
against the upper transverse wall. The manufacture of
the rail system becomes more versatile due to the
individual production of the springs. Above all, the
spring elements can also be used individually at
intervals, depending on the length of the U-rail or of
the covering rail.
It has also proved to be highly advantageous to equip
the holding part to be interposed with the features of
claim 5. This manufacture may take place both in
plastic and in metal. In the case of plastic,
corresponding molds would have to be produced. Where
metal is concerned, the walls of the U-rail would be
partially indented and bent into their spring shape. It
would also be possible, however, to manufacture the
spring element separately and to hold it at intervals
by means of thin webs, whereupon the U-rail is then
CA 02563178 2006-10-05
- 4 -
cast and the web are at the same time encased, so that
the spring element are interposed between the U-rail
portions. In this version, too, the spring head
covering more than 180° affords a sufficient hold for a
rotationally moveable connection on the holding head of
the base rail. The free ends of the spring are secured
to the lower edge of the U-rail, so that the spring
possesses sufficient tension. The shorter the portions.
of the spring elements and of the U-rail portions are,
the more this profiled rail system can be produced in a
more versatile and more cost-saving way.
A further and advantageous securing of the interposed
holding part is possible if the features of claim 6 are
utilized. The integrally formed webs preferably consist
of plastic in the same way as the U-rail itself. For
the snapping onto the holding head of the base rail,
three webs distributed in the rounding are the most
beneficial. Their elasticity makes it possible that
they can receive the holding head securely between them
as a rotary bearing and that the U-rail can be angled
in the required region. High angular freedom is
achieved when two webs are arranged on one side at a
short interval and the third web is arranged opposite
the two. However, even more webs for support are
possible. This U-rail with the integrally formed webs
can be produced highly cost-effectively by the
extrusion method.
There is no difficulty in allowing the webs to extend
over the length of the U-rail, particularly when the
rail is produced by the extrusion method. This ensures
that the holding part, over its entire length, retains
the base rail.
It is highly advantageous, furthermore, if the features
of claim 8 are utilized. It goes without saying that
the covering rail must extend over the entire length of
the joint. By contrast, it is entirely sufficient if
CA 02563178 2006-10-05
- 5 -
this covering rail is secured at intervals only to the
base rail. This saves a large amount of material and is
cost-effective, as demanded by the trade.
When the holding pieces are used at intervals, it is
necessary, as an alternative, that the features of
claim 9 are adopted. In this version, there is high
variability, since the U-rail, which serves as a
holding part for the covering rail, may consist both of
plastic and of metal. The same applies to the spring
segment which is required for securing to the base
rail. And because the two individual parts are first
assembled to form a unit, only the shaping is important
in the case of the individual parts so as to ensure
that they are effectively connected to one another. The
material is in this case unimportant. It is necessary
merely to have the required properties of strength and
elasticity. Since the parts are beneficially produced
as mass production parts, the entire profiled rail
system is highly cost-effective.
As regards the use of portions, another variant is also
possible, for which the features of claim 10 are
utilized. If the portion consists of metal, the U-rail
is indented vertically in the sidewalls and a part
region of the wall is shaped into a spring. The
portions can even more beneficially be produced from
plastic in a mold. Both the spring element and the rail
segment immediately having the desired shape by which
they can fulfill their tasks. These parts, too, are
mass production parts which can be produced
beneficially by permanent mold casting.
It has provided favorable, in practice, if the features
of claim 11 are utilized. Plastic parts are not subject
to corrosion, and because both the base rail and the
interposed holding part are always covered completely,
the visual appearance of these parts is entirely
unimportant. Plastic possesses the required mechanical
CA 02563178 2006-10-05
- 6 -
properties of strength, elasticity, breaking strength
and resistance, and therefore its use affords nothing
but advantages. Moreover, it can be processed
beneficially by the injection molding or extrusion
method.
Finally, it is particularly advantageous for the
profiled rail system if the features of claim 12 are
used. Owing to the profiling, which may be Braining,
fluting or a row of sawteeth, the overengaging webs
have a good hold, above all when they themselves are
also provided with a corresponding structure. Owing to
a very slight angling of the webs, the have a prestress
when they engage over the outer walls of the U-rail,
and the clamping grip is a secure hold.
Exemplary embodiments of the innovation are described
in more detail below with reference to the drawings in
which:
fig. 1 shows a profiled rail system in the
assembled state in which floor coverings
of equal thickness are held;
fig, 2 shows the same profiled rail system in an
installation with floor coverings of
different thickness and with an angularly
adapted covering rail;
fig, 3 shows the profiled rail system according
to fig. 1 in an exploded illustration so
that the individual parts can be seen
more clearly;
fig. 4 shows an interposed holding part which is
used in fig. 2;
fig. 5 shows a further holding part in another
version;
fig. 6 shows a further-modified holding part,
and
fig. 7 shows a further version of a holding
part.
CA 02563178 2006-10-05
_ 7 _
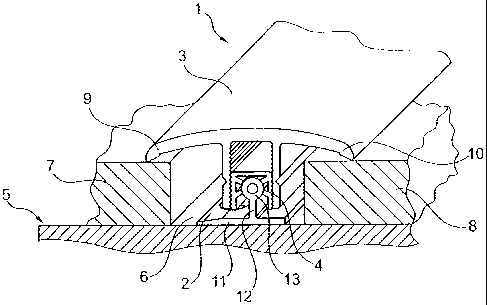
The profiled rail system 1 illustrated in fig. 1
consists of a base rail 2 and of a covering rail 3
which are connected to an interposed holding part 4.
The base rail 2 is secured by adhesive bonding or by
means of screws, not illustrated, to the floor 5 in a
groove or joint 6 which occurs between floor coverings
7, 8 adjacent to one another at an interval. The
covering rail 3 secured to the base rail 2 by means of
the holding part 4 bridges with its covering wings 9,
10 the groove 6 and is supported on the ends of the
floor coverings 7, 8 so that these are held down. If
the floor coverings 7, 8 are of equal thickness, as
illustrated in fig. 1, the covering rail 3 sits
completely straight on the interposed holding part 4.
Often, however, two floor coverings 7,8 of different
thickness butt against one another. In order, even in
this case, to have a smooth transition in which the
covering wings 9, 10 butt onto the floor coverings 7, 8
on both sides, the covering rail 3 has to be angled. As
may be gathered from fig. 2, the covering rail 3
together with the interposed holding part 4 can be
brought jointly into an oblique position by being
rotated on the holding head 13.
So that the individual parts can be seen more clearly
in terms of their configuration and functioning, the
rail system 1 is illustrated in fig. 3 as an exploded
drawing. The lowest part shown is the base rail 2 with
a baseplate 11 in which a bore for possible securing by
means of screws in indicated. A web 12 extends upright
from the baseplate 11. This web 12 has at its free end
a reinforcement of circular cross section which is
designed as a holding head 13 for a holding part 4.
This holding head 13 is preferably made hollow in order
to save material. It extends over the entire length of
the base rail 2.
CA 02563178 2006-10-05
Located above the base rail 2 is the holding part 4
which is designed as a downwardly open U-rail 14. In
the inner space 15 of the U-rail 14, holding elements
in the form of webs 16 are provided, which are
integrally formed on the inner sidewalls 17 of the
U-rail 14. In the present case, two webs 16, which are
directed toward the center of the inner space 15, are
provided at an interval on each sidewall 17. These webs
16 extend into the inner space 15 to an extent such
that they firmly grip between them with their free ends
the holding head 13 of the base rail 2, although said
holding head remains rotationally moveable. Since the
webs 16 are directed into the center only from the
sidewalls, the necessary space remains from below in
order to press the holding head 13 between the free
ends of the webs 16 which have the required elasticity
for this purpose. Preferably, the U-rail 14 together
with the integrally formed webs 16 is manufactured from
plastic having a Shore hardness of 74° to 76°. With
this material strength, the holding head 13 is
surrounded from outside to an extent such that it
cannot automatically jump out of the mounting. The webs
16 extend over the entire length of the U-rail 14. They
consequently have a firm, but rotationally moveable
grip on the holding head 13.
Fig. 3 illustrates as the uppermost attachment part the
covering rail 3. The latter consists of the cover plate
18 with the lateral covering wings 9, 10 which may be
designed with a different width. It is also to known to
draw the cover plate 18 on one side when it is used as
a lateral closure. Two integrally formed webs 19, 20
extend from the underside of the cover plate 18 which
are arranged at an interval with respect to one another
which corresponds to the width of the U-rail 14. These
webs 19, 20 are provided on their inside, in the
longitudinal direction, with a fluting 21 of sawtooth
form which cooperates with a fluting 22 on the outer
sidewall 17 of the U-rail 14 with a holding effect when
CA 02563178 2006-10-05
- g _
the covering rail 3 is pressed onto the holding part 4.
Any other surface structure, such as, for example, a
Braining, could also be conceivable. The surfaces lying
on one another have to have a good hold against
possible slipping out of place. As can be seen on the
outsides of the webs 19, 20, in each case a
longitudinal notch 22, 23 is provided as a
predetermined breaking point. The lower ends 24, 25 of
the webs 19, 20 are broken off at this notch 22, 23 if
the floor covering 7, 8 has only a small thickness and
the webs 19, 20 run the risk of sitting on the
baseplate 11 of the base rail 3 before the covering
wings 9, 10 press onto the floor covering 7, 8. The
covering rail 3 is preferably produced from a
wood/plastic mixture. The material could also be wood,
metal or even plastic.
The holding part 4 used for securing the covering rail
3 to the base rail 2 may even be equipped only with
three webs 16 in the inner space 15 of the U-rail, as
may be gathered from fig. 2 and 4. Even three webs 16
offer the required firm grip on the holding head 13 of
the base rail 2. It is important in this case that the
3-point mounting on the holding head 13 is maintained.
It is sufficient if two webs 16 run toward the center
of the inner space 15 at an interval from one inner
sidewall 17 and the third web 16 is directed from the
other inner sidewall 17 toward the center between the
two webs 16, and the holding head 13 fits between the
free ends of the webs 16 of the base rail 2. The three-
point mounting of the U-rail 14 on the holding head 13
ensures both the desired pivotability and the firm
holding grip, as may be gathered from fig. 2, where the
covering rail 3 is angled on account of the floor
coverings 7, 8 of different thickness, in order to lie
on the floor covering 7, 8 in each case with the
covering wings 9, 10. During the mounting of the
covering rail 3, specifically when its downwardly
directed webs 19, 20 are push over the U-rail 14, the
CA 02563178 2006-10-05
- 10 -
U-rail 14 rotates into the required oblique position as
soon as a covering wing 9, 10 sits on the floor
covering 7, 8.
In the case of a further holding part, which is
designed as a U-rail 14, another holder holding element
is provided, as shown in fig. 5. A spring element 27 is
inserted into the inner space 15 of the U-rail 14. This
spring element 27 has a head 28 which is shaped as an
arc of a circle of somewhat more than 180° and with
which said spring element presses on the inside against
the upper transverse wall 29 of the U-rail 14. The two
ends 30, 31 of the spring element 27 are bent obliquely
outward after the head arc 28 and engage into a fluting
32 of the inside of the sidewall 17 of the U-rail 14.
The spring element 27 is shaped as an independent
individual piece and is pressed into the inner space 15
of the U-rail 14 and anchored in the fluting 32, the
pressure by means of the head 28 against the upper
transverse wall 29 contributing to the required bracing
and consequently ensuring reliable securing. The spring
elements 27 are preferably short pieces of sheet steel
or plastic with a Shore hardness of 74° to 76°, which
are inserted at intervals in the U-rail. In a few
instances, a continuous spring element 27 is also
inserted. Its head arc 28 corresponds to the holding
head 13 of the base rail 2, onto which the head 28 is
placed in the assembled state, and provides the
rotationally moveable connection between the covering
rail 3 and base rail 2. The inner surface of the head
28 may be provided with a fine structure and/or a
slight narrow elevation in the longitudinal direction,
which engages into a corresponding structure and/or
into a thin longitudinal flute on the holding head 13.
Fig. 6 shows another holding part 4 in which a spring
element 27 is inserted between two U-rail pieces. This
part may be produced from metal. In this case, the
sidewall 17 and part of the upper transverse wall 29
CA 02563178 2006-10-05
11
are indented, and the cut-free portion is bent to form
the spring element 27 with the head arc 28 and with
outwardly set ends 30, 31. The ends 30, 31 are then
anchored laterally to the U-rail 14. On the other hand,
these parts are also injection-molded from plastic. The
ends 30, 31 of the spring element 27 form a unit with
the lower edge of the sidewalls 17. The head 28 of the
spring element 27 serves in each case as a rotationally
moveable connection between the holding part 4 and the
base rail 2, the connection between the holding part
and the covering rail 3 being achieved by means of the
webs 19, 20 of the latter which engage over the U-rail.
14 and grip its sidewalls 17.
Finally, fig. 7 also shows a U-rail 14 as a holding
part 4, in which, in the inner space 15, a spring
element 27 is integrally formed, the side ends 30, 31
of which can be seen through the cut-out windows 33 in
the sidewalls 17. Both the insides and the outsides of
the sidewalls 17 are provided with a fluting 22
preferably in the form of a sawtooth profile. This
holding part 4 may be manufactured both from metal and
from plastic. It is preferably placed as a short part
at intervals on the holding head 13 of the base rail in
order to serve as a connection part for the covering
rail 3 which is to held pivotably.
CA 02563178 2006-10-05
- 12 -
List of reference symbols
1 profiled rail system 23 longitudinal notch
2 base rail 24 longitudinal notch
3 covering rail 25 lower end
4 holding part 26 lower end
floor 27 spring element
6 groove 28 head
7 floor covering 29 transverse wall
8 floor covering 30 end of the spring
element
9 covering wing 31 end of the spring
element
covering wing 32 fluting of the inner
wall
11 baseplate 33 window
12 web of the base rail
13 holding head
14 U-rail
inner space
16 webs of the U-rail
17 sidewall
18 coverplate
19 web of the covering
rail
web of the covering
rail
21 fluting of the webs
22 fluting of the holding
part