Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02582587 2007-04-05
WO 2006/044924 PCT/US2005/037501
FINISHING MATERIAL STANDOFF
MEMBER FOR A STRUCTURAL SUPPORT
AND INSTALLATION METHOD THEREFOR
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to the finishing of structural supports. In
particular, this invention relates to structural support finishing components
and
a method of installing the structural support finishing components so that
finishing material such as wallboard may be affixed to the structural
supports.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The construction of commercial and residential structures often
requires the use of structural supports such as metal load bearing supports.
These structural supports are typically sturdy rectangular, square, and/or
planar members having dimensions which are often several inches in width
and which incorporate substantially surfaces meeting at right angles. The
structural supports are commonly constructed of such materials as steel,
aluminum, iron, and/or alloys of such metals. In one application, the
structural
supports are typically intended to receive a compressive load on one end and
transmit the compressive load to a second end of the structural support with
insignificant lateral deflection. In another application, these structural
supports as designed to carry horizontal loads. Conventionally these
structural supports exist in almost any commercial or residential setting and
include columns, struts, posts, I-beams, and/or other common structures such
as spandrel beams, joists, girders, trusses, and rafters.
It is well known that exposed structural supports introduce several
potential problems. For instance, the exposed structural supports often do not
mesh or blend into the aesthetic design flow of the building into which they
are
incorporated. In addition, unprotected structural supports, when composed
mainly of metal, may be subject to corrosion from salts and moisture.
Furthermore, the structural supports are often formed of extremely heavy,
dense, and thick metals and/or concrete that prevent finishing material
1
CA 02582587 2007-04-05
WO 2006/044924 PCT/US2005/037501
fasteners from embedding into the structural supports. For at least this
reason, the sealing, coating, covering, and/or encasing of these structural
supports is a labor intensive and expensive operation.
Conventionally, finishing material such as wallboard, paneling,
fireproofing, insulation, and/or other materials are installed with the use of
intermediate framing elements to cover the surfaces of structural supports.
The framing elements are installed to provide a surface that finishing
material
fasteners can easily embed in. However, the framing element typically used
to mount the finishing material to the structural supports is a full-length
steel
stud. A full-length steel stud is often several feet in length and is
relatively
expensive. The full-length steel studs, because of their sizable dimensions,
require a number of man-hours to install in a typical building project. In
addition, since the typical full-length steel stud is configured to be a load
bearing structure, the use of steel studs for the purpose of merely attaching
finishing material to the structural supports is wasteful and inefficient.
Furthermore, the full-length steel studs, due to their large dimensions, often
waste valuable interior room space due to the void they create between the
finishing material and the structural supports.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
Briefly stated, the present invention in a preferred form is generally
directed toward fastenable standoff members and a method of installing
fastenable standoff members for use in attaching finishing material to
structural supports. The fastenable standoff member includes a structural
support mating surface which is transversely spaced from a finishing material
mating surface. The structural support mating surface has a fastening portion
through which a fastener may be projected into the structural support for the
purpose of securing the fastenable standoff member to the structural support.
The structural support mating surface may also be associated with a bonding
adhesive or double sided adhesive tape element configured to provide
adhesion between the structural support mating surface and the structural
support.
The present invention also encompasses, in a preferred form, a
method of installation and/or utilization of a fastenable standoff member
which
2
CA 02582587 2007-04-05
WO 2006/044924 PCT/US2005/037501
includes a structural support mating surface and a transversely spaced
finishing material mating surface wherein the fastenable standoff member is
fixed to a structural support. The fastenable standoff member is fixed to the
structural support by driving a fastener through a fastening portion of the
fastenable standoff member. The structural support mating surface may also
include a bonding adhesive or double sided adhesive tape between the
structural support mating surface and the structural support.
The fastenable standoff member is configured to provide a finishing
material mating surface which is transversely spaced from the structural
support by a desired distance. Multiple finishing material mating surfaces can
be employed for the efficient attachment of finishing material to the exterior
surface of multiple structural supports. In addition, the exterior of a
structural
support may be converted from a channeled or fluted surface to a
substantially square or rectangular shape.
Thus, among other things, the present invention provides a new and
improved structural support finishing component to facilitate the covering
and/or attaching of a structural support with a finishing material,
particularly in
a cost effective manner.
The present invention also provides a new and improved method of
installing and utilizing a standoff member for attachment of finishing
material
to a structural support in an efficient, safe and cost effective manner.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Other objects and advantages of the invention will be evident to one of
ordinary skill in the art from the following detailed description with
reference to
the accompanying drawings, in which:
Figure 1 is a side view of a fastenable standoff member with
associated fasteners in accordance with the present invention.
Figure 2 is a side view of a fastenable standoff member with
associated fasteners attached to a structural support, shown in section, in
accordance with the present invention.
Figure 3 is a side view of an alternative embodiment of a fastenable
standoff member with associated fasteners attached to a structural support,
shown in section, support in accordance with the present invention.
3
CA 02582587 2007-04-05
WO 2006/044924 PCT/US2005/037501
Figure 4 is top view, partly in phantom, of the fastenable standoff
member of Figure 3 in accordance with the present invention.
Figure 5 is top view, partly in phantom, of the fastenable standoff
member of Figure 1 in accordance with the present invention.
Figure 6 is a top view of another alternative embodiment of the
fastenable standoff member in accordance with the present invention.
Figure 7 is a side view, partly in phantom, of the fastenable standoff
member of Figure 6 in accordance with the present invention.
Figure 8 is a side view, partly in phantom, of the fastenable standoff
member of Figure 6 associated with a structural support and finishing material
in accordance with the present invention.
Figure 9 is a side view, partly in phantom, of the fastenable standoff
member of Figure 2 associated with a structural support and finishing
material, both shown in section, in accordance with the present invention.
Figure 10 is a fragmentary elevated view, partly in phantom, showing a
possible installation of fastenable standoff members associated with
structural
supports and finishing material in accordance with the present invention.
Figure 11 is a cut away side view of the fastenable standoff member of
Figure 8 associated with a channeled structural support and finishing
material,
both shown in section, in accordance with the present invention.
Figures 12A-12B show, respectively, a side view, partly in phantom,
and a top view, partly in phantom, of an embodiment of a fastenable standoff
member utilizing double sided adhesive tape in accordance with the present
invention.
Figures 12C-12D show, respectively, a side view and an end view of a
channel insert present in the fastenable standoff member of Figure 12A-12B.
Figures 13A-13C show, respectively, a side view, partly in phantom
and a top view and bottom view, partly in phantom, of an embodiment of a
fastenable standoff member utilizing a fastening portion in accordance with
the present invention. Figures 14A-14B show, respectively, a side view and an
end view of a
channel insert present in the fastenable standoff member of Figures 13A-13C.
Figures 15A-15C show, respectively, a bottom view, a top view, partly
in phantom, and a side view, partly in phantom, of an embodiment of a
4
CA 02582587 2007-04-05
WO 2006/044924 PCT/US2005/037501
fastenable standoff member utilizing a fastening portion accessible through an
opening in the finishing material mating surface in accordance with the
present invention.
Figures 15D-15E show, respectively, an end view and a side view of a
channel insert present in the fastenable standoff member of Figures 15B-15C.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
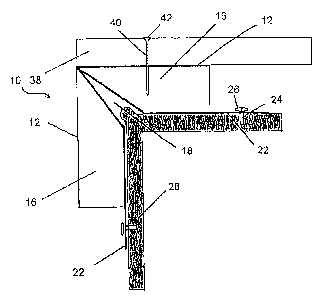
With reference to the drawings wherein like numerals represent like
parts throughout the several Figures, a fastenable standoff member or
framing bracket in accordance with the present invention is generally
designated by the numeral 10. The fastenable standoff member 10, as shown
in Figures 1 and 5, includes a finishing material mating surface 12. The
finishing material mating surface 12 is transversely spaced apart from a
structural support mating surface 14. Between the finishing material mating
surface 12 and the structural support mating surface 14 is a finishing
material
fastener intrusion zone 16. The fastenable standoff member 10 may be
formed from sheet metal such as galvanized or stainless steel sheets, and/or
from plastic such as glass filled fiber reinforced plastics. In one
embodiment,
the standoff member 10 is manufactured from 25 gauge galvanized steel.
The fastenable standoff member 10 may also be cast, milled, or extruded
using materials such as ferrous and non-ferrous metals, plastics, ceramics
and/or polymeric materials. The fastenable standoff member 10 may have a
substantially seamless construction.
In one embodiment of the invention, the finishing material mating
surface 12 is transversely spaced apart from a structural support mating
surface 14 by a side wall 13. The structural support mating surface 14 and
side wall 13 preferably has a cutout 18 which allows portions (x, y) of the
structural support mating surface 14 to be movably adjusted relative to each
other. Portions (x, y) of the structural support mating surface may be
adjusted
manually to form a variety of angles relative to one another. For example, the
portions (x, y) may be bent to form an angle between about 600 and about
270 . It should be understood that angles greater than about 180 can be
employed in an inside corner formed by a structural support(s). The
orientations (x, y) of the structural support mating surface may be adjusted
5
CA 02582587 2007-04-05
WO 2006/044924 PCT/US2005/037501
through bending a hinge 20 of the fastenable standoff member 10. The hinge
20 is formed adjacent the cutout 18 on the finishing material mating surface
12. In one example, the standoff member or framing bracket is dimensioned
so that portions x and y have a length of 3 inches (7.62 cm) and the spacing
between surfaces 12 and 14 is 0.825 inches (2.10 cm). The height along
hinge 20 is approximately 2.5 inches (6.35 cm).
The fastenable standoff member 10 includes a fastening tab 22 which
functions as an easily accessible fastening plate. The fastening tab 22, in
one
embodiment of the invention, is approximately 0.75 inches (1.91 cm) may be
formed from a portion of the structural support mating surface 14 that extends
laterally beyond the side wall 13 and the finishing material mating surface
12.
A fastener 24 is driven through the fastening tab 22. The fastener 24 includes
a head 26 which prevents the fastener 24 from passing entirely through the
fastening tab 22. The fastener head-26 provides a retentive bearing surface
that holds the structural support mating surface 14 against a structural
support
28, as shown in Figure 2.
In one embodiment of the invention, as shown in Figure 2, the
fastenable standoff member 10 is fixed to a structural support 28 by the
fastener 24. The fastener 24 extends through the fastening tab 22 and into
the structural support 28. A variety of fasteners may be used for fixing the
fastenable standoff member 10 to the structural support 28. For example, the
fastener 24 may be a screw, a rivet, a bolt, or a pin. The fastener 24 may be
driven by a powder actuated device. For example, a pin having a length
between about 0.5 inches (1.27 cm) to about 3 inches (7.62 cm), with or
without a washer, may be driven through the fastening portion 22 and into the
structural support 28 by a .27 caliber (6.8mm) cartridge load (not shown).
Other sized powder loads such as .22 caliber (5.6mm) and powder loads
having different relative driving powers may also be used. Pneumatic and
mechanical drivers can also be used to drive the fastener 24.
The cutout 18, in one embodiment of the invention may be configured
to accommodate a nub 30 which is often present on the corner of a structural
support 28. The nubs 30 more frequently occur in concrete columns. In
some cases, the nub 30 is an artifact of the process of cold or hot forming
the
structural support 28. The cutout 18 receives the nub 30 such that the
6
CA 02582587 2007-04-05
WO 2006/044924 PCT/US2005/037501
structural support mating surface 14 can make substantially flush and
uninterrupted contact with the sides of the structural support 28. The hinge
20
allows the relative size of the cutout 18 to be adjusted such that a good fit
is
made between the structural support mating surface 14 and the structural
support 28. In addition, the cutout 18 adjustment also assures that the hinge
20 is substantially adjacent a true corner 32 of the structural support 28.
This
alignability allows numerous fastenable standoff members 10 to be installed
along a length of a structural support 28, as shown in Figure 10, such that
the
hinge 20 of each fastenable standoff member 10 is in substantial alignment.
This allows finishing material 38 to be installed without deflection of the
finishing material 38 between two or more structural supports 28 and without
misalignment of edges of the finishing material 38 at, for example, corners
and butt joints.
In one embodiment of the invention, as shown in Figures 3 and 4, the
fastenable standoff member 10A has a fastening portion 22a that is located
within the perimeter of an access opening 34 in the finishing material mating
surface.
In one embodiment of the invention, as shown in Figures 6 and 7, the
fastenable standoff member 10B may have an opening 34a in the finishing
material mating surface 12b that provides access to the fastening portion 22b.
A secondary finishing material mating surface 12a may be present which is
located adjacent to the structural support mating surface 14a. A ledge 36
may be present near the intersection of the auxiliary finishing material
mating
surface 12a and the structural support mating surface 14a. In use, as shown
in Figure 8, the finishing material mating surface 12b and/or the auxiliary
finishing material mating surface 12a may be associated with a finishing
material 38. For example, the finishing material 38 may be drywall, foam,
wood, metal, and/or any composite material that provides the desired
isolation, protection and/or aesthetic properties. The finishing material 38
may be fixed to the fastenable standoff member 10b by a fastener 40 which
extends through the finishing material 38 and the auxiliary finishing material
mating surface 12a and extends into the fastener intrusion zone 16.
With reference to Figure 9, in one embodiment of the invention, the
finishing material 38 may be fixed to the fastenable standoff member 10 with a
7
CA 02582587 2007-04-05
WO 2006/044924 PCT/US2005/037501
fastener 40. For example, a wall board screw may be used to fasten a panel
of wall board to the fastenable standoff member 10. The wall board is
retained by the head 42 of the fastener.
With reference to Figure 11, in one embodiment of the invention, the
structural support may be an I-beam having channels 50. The fastenable
standoff member 10B may be attached inside and/or outside the channel such
that finishing material 38 can be fixed to the finishing material mating
surface
12b and/or the auxiliary finishing material mating surface 12a. This allows
the
structural support channels 50 and/or the sides of the structural support 28
to
be covered.
In one embodiment of the invention, as shown in Figures 12A-12D, the
fastenable standoff member 10C may be constructed from a piece of sheet
metal which has been bent into a channel shape. A cut is made either prior to
bending or after bending the cutout 18 is formed. On either side of the cutout
18 a channel module 15, as shown in Figures 12B and 12C, is fixed. The
channel module 15 may be fixed to the channel shape by spot welds 17,
clinches, etc. The channel module includes the structural support mating
surface 14 and a portion of side wall 13. The channel shape includes the
finish material mating surface 12.
In one embodiment of the invention, as shown in Figures 12A and 12B,
adhesive may be used to attach the fastenable standoff member 10C to the
structural support 28. For example, double-sided adhesive tape 52 may be
fixed to the structural support mating surface 14 such that an adhesive
surface of the tape 52 may contact and bind to a structural support.
In one embodiment of the invention, as shown in Figures 13A-13C, the
fastenable standoff member 10D may be constructed from a piece of sheet
metal which has been bent into a channel shape. A cutout 18 is formed either
prior to bending or after forming the channel shape. On either side of the
cutout 18 a channel module 15a, as shown in Figures 14A and 14B is fixed.
The channel module 15a may be fixed to the channel shape by spot welds 17.
The channel module includes the structural support mating surface 14, a
fastening portion 22, and a portion of side wall 13. The channel shape
includes the finish material mating surface 12.
8
CA 02582587 2007-04-05
WO 2006/044924 PCT/US2005/037501
In one embodiment of the invention, as shown in Figures 15A-15C, the
fastenable standoff member 10E is constructed from a piece of sheet metal
which has been bent into a channel shape. A cut is made either prior to
bending or after forming the channel shape. On either side of the cutout 18 a
channel module 15b, as shown in Figures 15D and 15E is fixed. The channel
module 15 may be fixed to the channel shape by spot welds 17. The channel
module includes the structural support mating surface 14, and a portion of
side wall 13. The channel shape includes the finish material mating surface
12, and an access opening 34.
In one embodiment of the invention, an adhesive 54, as shown in
Figure 3, is applied to the structural support mating surface 14 to replace or
augment the fastener 24. The adhesive 54 may be, for example, a thermoset,
a thermoplast, a latex or an alkyd adhesive, examples of which are epoxies,
acrylics, urethanes and silicones. For instance, hot melt adhesives, spray
adhesives, glues, or other construction adhesives well known in the art or
combinations thereof may be used. Thus, the adhesive 54 may be a latex
based construction adhesive having quick set properties and a high bonding
strength. The adhesive 54 may render the fastenable standoff member 10A
substantially immovable within 15 minutes and may be fully cured within 24
hours. An example of such an adhesive is the available commercially made
Loctite Power GrabTM construction adhesive distributed by Henkel Consumer
Adhesives, Inc. A suitable hot melt adhesive may include the Henkel
Corporation 7804 FRM HV hot melt adhesive which has flame retardant
properties and has a high viscosity.
The invention also encompasses a construction method wherein the
fastenable standoff member 10, 10A, 10B, 10C, 10D, 10E is employed for
finishing a structural support 28. The fastenable standoff member 10, 10A,
10B, 10C, 10D, 10E is attached to the structural support by a fastener 24
and/or an adhesive 54 to the structural support at various pre-selected
vertical
or horizontal positions depending on, for example, the finishing material 38
to
be utilized. This attachment is accomplished, for example, as shown in Figure
9, by extending a fastener through the fastening portion 22, and/or by coating
the structural support mating surface 14 and/or coating a portion of the
structural support with the adhesive 54 (Figure 3). The adhesive 54 may be
9
CA 02582587 2007-04-05
WO 2006/044924 PCT/US2005/037501
subjected to activation through additional procedures, for example the
application of heat, mixing the adhesive with a catalyst, or by allowing the
coated adhesive time to become tacky or otherwise ready for use. A pre-
applied double side tape 52 may also be utilized. The adhesive coated
structural support mating surface 14 is then bonded to the structural support
28.
A hot melt adhesive can be utilized by placing it between the structural
support mating surface 14, 14a and the structural support 28.
The fastenable standoff member 10, 10A, 10B, 10C, 10D, 10E may
then be selectively heated with, for example, a torch such that the thermal
set
adhesive deforms or flows. The heat is then removed and the fastenable
standoff member 10, 10A, 10B, 10C, 10D, 10E becomes bonded to the
structural support member 28. If required, the standoff member 10, 10A, 10B,
10C, 10D, 10E can be repositioned by reheating the adhesive.
Depending on the application desired, the steps of mounting further
fastenable standoff members 10, 10A, 10B, 10C, 10D, 10E to the structural
support 28 at other locations is efficiently accomplished. The finishing
material mating surface 12, 12a, 12b of each fastenable standoff member 10,
10A, 10B, 10C, 10D, 10E can be arranged to form co-planar framing
members so that the finishing material 38 may be aligned and fastened in
place. The finishing material 38 is preferably mounted to the fastenable
standoff members 10, 10A, 10B, 10C, 10D, IOE by fastening with, for
example, a screw 40 which extends through the finishing material 38 and the
finishing material mating surface 12, 12a, 12b such that the distal shaft
portion
of the fastener enters and is fully received in the fastener intrusion cavity
16.
The fastenable standoff members 10, 10A, 10B, 10C, 10D, IOE have
sufficient structural rigidity so they are not crushed during the wallboard
fastening.
In one preferred installation, standoff members or framing brackets 10
are spaced at a maximum of 48 inches (121.92cm) on center and are located
on all four corners of a tubular steel column. The brackets 10 were fastened
to the corners with half-inch (1.27 cm) powder actuated fasteners driven
through the center of the tabs 22. Chips and board was then attached to the
brackets by one inch Phillips head self-drilling, self-tapping fine thread
screws
CA 02582587 2007-04-05
WO 2006/044924 PCT/US2005/037501
which are spaced 48 inches (121.92cm) on center. It will be appreciated that
for tube columns with a four-inch dimension (10.16 cm), the standoff members
or framing brackets can be installed vertically offset by the weight of the
bracket. For tube columns greater than the four-inch dimensions (10.16 cm),
suitably dimensioned standoff members or framing brackets 10 can be
located at the same horizontal level on all four corners.
While various preferred embodiments have been illustrated to describe
the invention, various modifications, alternatives and adaptations may be
made thereto without departing from the spirit and the scope of the invention.
Accordingly, it is to be understood that the present invention has been
described by way of illustration and not limitation.
11