Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
_ ~õ~..,,:.. ...~.....,.~ ~
CA 02596989 2009-10-05
STRUCTURAL PANEL AND MODULAR BUILDING FORMED USING THE PANEL
The present invention relates to a structural panel formed wholly or
primarily from wood which can be used for example to support a modular
building
which can be shipped to an installation site in substantially completed form
to
minimize on-site labour.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The structural panel described and claimed herein is primarily
designed for use in modular buildings and hence the following description
refers
primarily to such constructions. However the same construction can be used in
many other similar and unrelated fields. The modular buildings described
hereinafter are therefore merely examples of end uses.
It is known in the art to fabricate a modular building in sections for later
assembly on a remote site, as in-plant fabrication is known to have a number
of
advantages over on-site construction. In-plant fabrication provides easier
monitoring
of quality and safety issues, improved repeatability and less dependency on
environmental conditions. For many, modular housing may present a desirable
alternative to conventional housing construction due to increasing costs and
waiting
periods. However, when compared to conventional housing, manufactured housing
has been associated in some cases with problems such as noticeable difference
in
appearance, twisting and cracking of materials during travel, low quality wall
construction and insulation, high rate of depreciation and high mortgage down
payments. As a result, there has been a drive to improve the quality of
modular
homes to increase their popularity. Up to now two alternate routes have been
taken
CA 02596989 2009-10-05
2
in view of the twisting or movement of the structure which occurs during
transportation. In one alternative, the quality of finishing of the building
has been
very low to accommodate that twisting. This has prevented this type of
building from
competing in the conventional building market. In the other alternative, much
of the
finishing is carried out after the modules are transported and located, but
this of
course cancels much of the advantage of building in the manufacturing
location.
Canadian Patent No. 1,203,063 (Kaufman) published April 15th 1986
teaches a prefabricated building for installation on a floor-forming
foundation. The
building features completed interior and exterior walls and a roof but no
floor, for
quick and easy on-site installation, but may be limited in size due to its one-
piece
construction. The building uses triple layer framing at the floor rails and
double layer
framing at the ceiling and special comers which are intended to provide a
structure
which is rigid to be lifted onto a foundation which provides the floor.
U.S. Patent No. 4,083,154 (Klink) issued April 11th 1978 teaches a
modular home formed of two similar sections for connection on opposite sides
of a
third section to form an overall shape suggestive of an on-site construction.
Each
section includes its own roof portion and is formed from conventional framing
techniques using floor joists, but from the figures it appears that a
significant amount
of on-site completion may be necessary before the building is ready for
occupation.
Klink does not disclose a structural panel which can be used to form such a
modular
building and discloses no special floor construction.
U.S. Patent Application Publication No. 2005/0252099 (Jenkins)
published November 17th 2005 teaches a modular home made up of two lower
CA 02596989 2009-10-05
3
sections and a third upper roof section, each of which is provided with a
complete
interior to reduce the amount of on-site work necessary after assembly. The
two
lower sections are each covered by a roof portion that cooperates with the
third
section to complete a peaked roof. Installation of an exterior finish is
carried out on-
site and difficulties with transportation of the two lower sections may arise
due to the
significant height added by their respective roof portions, for example,
should
transport between the fabrication and installation sites require passing
beneath a
bridge.
U.S. Patent Application Publication No. 2003/0056446 (Napier)
published March 27th 2003 discloses a building formed of two modules connected
together where a roof piece is added after the modules are brought together.
SUMMARY
It is one object of the present invention to provide a structural panel
which can be arranged to provide a high level of stiffness.
According to a first aspect of the present invention there is provided a
structural panel comprising:
a plurality of parallel joists greater than two so as to form two
outermost joists and a plurality of intermediate joists;
a first pair of parallel perimeter rail members connected across
respective ends of the parallel joists at right angles thereto and arranged to
define
first sides of the panel such that the parallel joists are continuous between
the first
pair of rail members;
the two outermost ones of the parallel joists forming respective ones
CA 02596989 2009-10-05
4
of a second pair of parallel perimeter rail members arranged to define second
sides
of the panel at right angles to the first sides;
the first pair of rail members and the joists having top surfaces lying in
a common top plane and bottom surfaces lying in a common bottom plane;
each of the joists having a first face on a first side thereof connected to
a second face on a second side of a next adjacent one of the joists by a
plurality of
diagonal planar bridge members;
each of the diagonal planar bridge members extending diagonally
between said joist and said next adjacent joist with one end edge of the
diagonal
planar bridge member being fastened to a side face of said joist and an
opposed
end edge fastened to a side face of said next adjacent joist;
the plurality of diagonal planar bridge members extending diagonally
between said joist and said next adjacent joist being arranged in zigzag
manner
back and forth between said joist and said next adjacent joist;
such that the plurality of diagonal planar bridge members form a
plurality of first apexes where two of the bridge members meet along the first
face on
the first side of said joist;
and such that the plurality of diagonal planar bridge members form a
plurality of second apexes where two of the bridge members meet along the
second
face on the second side of said next adjacent joist;
a planar top cover sheet lying in said common top plane and
adhesively bonded to said top surfaces of each of said first pair of said rail
members
and each of said joists;
CA 02596989 2009-10-05
and a planar bottom cover sheet lying in said common bottom plane
and adhesively bonded to said bottom surfaces of each of said first pair of
said rail
members and each of said joists.
Preferably the top cover sheet and the bottom cover sheet each
5 comprise a layer of sheathing boards. They may however be formed from a
single
layer of a fabricated sheet material.
Preferably the ends of the bridge members are adhesively bonded to
the faces of the joists to effectively transfer loads therebetween.
Preferably the top sheet and the bottom sheet span between the top
and bottom cover sheets and are adhesively bonded to top and bottom edges
respectively of the bridge members.
Preferably the butting ends of the bridge members on opposite faces of
the joists are aligned so that loads form one side of the joist are
transferred through
the joist directly to the bridge members butting on the other side of the
joist.
Preferably the bridge members comprise wood sheets such as
plywood or other fabricated wooden structure such as Oriented Strand Board.
However they can also be fabricated members such as aluminum sheets.
Preferably the structural panel is longer in direction between the first
pair so that the joists extend in the longitudinal direction.
Preferably the rail members are of a common construction with the
joists. They can therefore be simple wood members such as 2 x 12 lumber, or
they
can be fabricated joists such as laminated boards or trusses.
In accordance with one important feature there is provided a[ifting
CA 02596989 2009-10-05
6
assembly for lifting the panel comprising a plurality of mounting plates
extending at
right angles to the top cover sheet and fastened to the panel at spaced
positions
thereon with each plate having a captive nut carried thereon and providing an
end of
the nut exposed at the top cover sheet, the lifting assembly including a
plurality of
threaded rods each for fastening to a respective nut so as to extend therefrom
at
right angles outwardly form the top cover sheet.
Preferably the lifting assembly includes a plurality of second mounting
plates extending at right angles to the bottom cover sheet and fastened to the
panel
at spaced positions thereon with each second mounting plate having a captive
nut
carried thereon and providing an end of the nut exposed at the bottom cover
sheet
for receiving a threaded fastener attached thereto.
Preferably the lifting assembly includes a plurality of second mounting
plates extending at right angles to the bottom cover sheet and fastened to the
panel
at spaced positions thereon with each second mounting plate having a captive
nut
carried thereon and providing an end of the nut exposed at the bottom cover
sheet
for receiving a threaded fastener attached thereto.
Preferably respective ones of the mounting plates and respective ones
of the second mounting plates are clamped together through a component of the
panel which extends at right angles to the top and bottom sheets so as to be
fastened to the panel.
Preferably there are four components to which the plates are attached
each of which extends at right angles to the joists and connects between a
joist and
a respective one of the second rail members.
CA 02596989 2009-10-05
7
Preferably the top and bottom sheets are formed from rectangular
sheets having a longer axis and a shorter axis and are arranged with the
longer axis
at right angles to the joists.
According to a second aspect of the present invention there is provided
a structural panel comprising:
a plurality of parallel joists greater than two so as to form two
outermost joists and a plurality of intermediate joists;
a first pair of parallel perimeter rail members connected across
respective ends of the parallel joists at right angles thereto and arranged to
define
first sides of the panel such that the parallel joists are continuous between
the first
pair of rail members;
the two outermost ones of the parallel joists forming respective ones of
a second pair of parallel perimeter rail members arranged to define second
sides of
the panel at right angles to the first sides;
the first pair of rail members and the joists having top surfaces lying in
a common top plane and bottom surfaces lying in a common bottom plane;
each of the joists having a first face on a first side thereof connected to
a second face on a second side of a next adjacent one of the joists by a
plurality of
diagonal planar bridge members;
each of the diagonal planar bridge members extending diagonally
between said joist and said next adjacent joist with one end edge of the
diagonal
planar bridge member being fastened to a side face of said joist and an
opposed
end edge fastened to a side face of said next adjacent joist;
CA 02596989 2009-10-05
8
the plurality of diagonal planar bridge members extending diagonally
between said joist and said next adjacent joist being arranged in zigzag
manner
back and forth between said joist and said next adjacent joist;
such that the plurality of diagonal planar bridge members form a
plurality of first apexes where two of the bridge members meet along the first
face on
the first side of said joist;
and such that the plurality of diagonal planar bridge members form a
plurality of second apexes where two of the bridge members meet along the
second
face on the second side of said next adjacent joist;
a planar top cover sheet lying in said common top plane and
adhesively bonded to said top surfaces of said rail members and said joists;
and a planar bottom cover sheet lying in said common bottom plane
and adhesively bonded to said bottom surfaces of said rail members and said
joists;
wherein the bridge members span between the top and bottom cover
sheets
and wherein the top sheet and the bottom sheet are adhesively
bonded to top and bottom edges respectively of the bridge members.
According to a third aspect of the present invention there is provided a
structural panel comprising:
a plurality of parallel joists greater than two so as to form two
outermost joists and a plurality of intermediate joists;
a first pair of parallel perimeter rail members connected across
respective ends of the parallel joists at right angles thereto and arranged to
define
CA 02596989 2009-10-05
9
first sides of the panel such that the parallel joists are continuous between
the first
pair of rail members;
the two outermost ones of the parallel joists forming respective ones of
a second pair of parallel perimeter rail members arranged to define second
sides of
the panel at right angles to the first sides;
the first pair of rail members and the joists having top surfaces lying in
a common top plane and bottom surfaces lying in a common bottom plane;
each of the joists, with the exception of the second pair of perimeter
rail members, having a first face on a first side thereof connected to an
adjacent face
on an adjacent side of a first next adjacent one of the joists on a first side
by a first
plurality of diagonal planar bridge members;
each of the first diagonal planar bridge members extending diagonally
between said joist and said first next adjacent joist with one end edge of the
first
diagonal planar bridge member being fastened to the first face of said joist
and an
opposed end edge fastened to said adjacent face of said first next adjacent
joist;
the plurality of first diagonal planar bridge members extending
diagonally between said joist and said first next adjacent joist being
arranged in
zigzag manner back and forth between said joist and said first next adjacent
joist;
such that the plurality of first diagonal planar bridge members form a
plurality of first apexes where two of the bridge members meet along the first
face on
the first side of said joist;
and such that the plurality of first diagonal planar bridge members form
a plurality of second apexes where two of the first bridge members meet along
the
CA 02596989 2009-10-05
adjacent face on the adjacent side of said first next adjacent joist;
each of the joists, with the exception of the second pair of perimeter
rail members, having a second face on a second side thereof connected to an
adjacent face on an adjacent side of a second next adjacent one of the joists
on a
5 second side by a second plurality of diagonal planar bridge members;
each of the second diagonal planar bridge members extending
diagonally between said joist and said second next adjacent joist with one end
edge
of the second diagonal planar bridge member being fastened to the second face
of
said joist and an opposed end edge fastened to said adjacent face of said
second
10 next adjacent joist;
the plurality of second diagonal planar bridge members extending
diagonally between said joist and said second next adjacent joist being
arranged in
zigzag manner back and forth between said joist and said second next adjacent
joist;
such that the plurality of second diagonal planar bridge members form
a plurality of third apexes where two of the second bridge members meet along
the
second face on the second side of said joist;
and such that the plurality of second diagonal planar bridge members
form a plurality of fourth apexes where two of the bridge members meet along
the
adjacent face on the adjacent side of said second next adjacent joist;
wherein the first and second diagonal planar bridge members are
arranged in a mirror image relative to said joist such that the second apexes
on the
second side of the joist are located at corresponding locations relative to
the first
_ _ ... ..,~.,~... _ , ..~...~~. _ ~.
CA 02596989 2009-10-05
11
apexes on the first side of the joist;
a planar top cover sheet lying in said common top plane and
adhesively bonded to said top surfaces of said rail members and said joists;
and a planar bottom cover sheet lying in said common bottom plane
and adhesively bonded to said bottom surfaces of said rail members and said
joists.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
In the accompanying drawings, which illustrate exemplary
embodiments of the present invention:
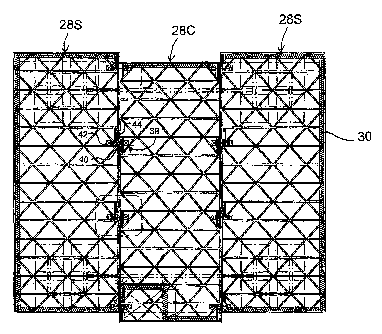
Figure 1 is a top plan view of three structural panels according to the
present invention used as floor structures for assembled sections of a first
embodiment of a modular home, with floor sheathing removed for illustration.
Figure 2 is a top plan view of one of the floor portions of Figure 1
before the installation of floor sheathing.
Figure 3 is a top plan view of the floor portion of Figure 2 with
sheathing installed.
Figure 4 is a top plan view of a structural panel according to the
present invention with top sheathing removed for illustration.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
Figures 2 and 3 show the floor structure 10 of a base section 12 of a
modular home. Figure 1 shows how multiple base sections are assembled to
define
the base of a modular home. As seen in Figure 2, each floor structure is
rectangular
and features a perimeter 14 defined by opposing side walls 16 and opposing end
walls 18. Joists 20 are spaced along the floor structure and extend
thereacross
CA 02596989 2009-10-05
12
parallel to one another between the side walls 16 in a conventional
arrangement.
Where the floor structure differs from the prior art is that bridge members 22
extend
obliquely between adjacent joists, as well as between end walls 18 and end
joists
there adjacent which form a perimeter rail structure, in order to brace
components
against one another to improve the overall rigidity or strength of the floor
structure.
In the figures, the bridge members are arranged in a regular pattern in
that they share the same length and the same angle relative to the joists, for
example approximately 45 degrees, although the angles of adjacent bridge
members relative to a common joist are in opposite ones of clockwise and
counter-
clockwise directions therefrom. Adjacent bridge members between neighboring
joists diverge from a common point or apex 22A along one joist to extend
toward the
other joist. The joist acts like a mirror line in the sense that, at the point
or apex 22A
along the length of the joist where the two adjacent bridge members 22 diverge
from
one side of the joist 20, two adjacent bridge members 22 also diverge from a
corresponding point or apex 22A at the same location on the other side of the
joist
20. The bridge members 22 extending obliquely between adjacent joists extend
the
full space between the side walls 16 of the floor structure perimeter. The
result is
that all space within the perimeter 14 of the floor structure is divided into
triangles by
the joists side walls 16, end walls 18, joists 20 and bridge members 22. The
triangles formed in part by the side walls 16 are half the area of the others.
The
bridge members act as braces between the joists, between the perimeter walls
and
between the joists and perimeter walls, thereby providing a floor structure
with
significantly improved rigidity, strength and stability.
CA 02596989 2009-10-05
13
The perimeter walls, joists and bridge members of the floor structure of
the illustrated embodiment are formed of lumber and are interconnected by
suitable
fasteners known to those of skill in the art. For example, 2 x 12 inch lumber
may be
used for the wooden components with the perimeter walls and joists fastened by
screws and the bridge members and joists fastened by adhesive. It should be
appreciated however, that any one of a number of suitable materials known to
those
of skill in the art may be used to construct the floor structures. As an
example of
possible alternatives to wood, the bridge members may be formed of aluminum.
As shown in Figure 3, the frame work formed by the perimeter walls,
joists and bridge members may be covered on one or both sides by rectangular
sheathing 24. Providing sheathing 24 on both sides of the floor structure
further
improves the rigidity of the structure by adding additional resistance to
relative
movement between the perimeter walls. In the illustrated embodiment, the
sheathing 24 is formed by rectangular plywood sheets arranged end to end
within
rows arranged side by side in order to cover the floor structure. Sheets of a
readily
available standard width, for example 4 foot wide plywood, form two rows 24A
which
cover the majority of the section. A third row 24B features sheets cut to a
reduced
width to cover the remaining area. An end sheet 24C in each row is a suitable
length so as not to extend passed the perimeter of the section. Sheets of
adjacent
rows are staggered such that junctions between sheets in one row do not align
with
junctions between sheets in the next row. In other words, the cut end sheets
of
adjacent rows are disposed at opposite ends of the floor structure so that the
full
length sheets of the adjacent rows are staggered along the floor structure.
This
CA 02596989 2009-10-05
14
particular arrangement of sheets is presented only in an exemplary context,
and like
the other components of the floor structure, the sheathing is not limited to
any
particular dimensions or materials. For example, sheets of metal or composite
materials may be used in place of wood and may be provided in any shapes and
dimensions suitable for collectively covering the floor structure. It is
possible to use
a greater number of smaller sheets, a lesser number of larger sheets and/or
sheets
of different (i.e. non-rectangular) shapes to cover the same area.
Furthermore, it
should be appreciated that more than one layer of sheathing may be applied to
either side of the floor structure. For example, it may be desirable secure a
second
layer of sheathing on top of a first layer fastened to the assembly of
perimeter walls,
joists and bridge members using adhesive or another suitable fastening method
known to those of skill in the art.
The triangular cylinders formed between the top and bottom faces of
the floor structure may be filled with insulation to lessen heat transfer into
and out of
the modular home. Passages for any duct work, venting or plumbing may be
provided in the floor structure by methods known to those of skill in the art.
The floor structure 10 can be used to support a respective wail
structure (not shown) extending partially along the perimeter to form one base
section of the modular building. The building partially illustrated in Figure
1 features
three sections arranged side to side with a center base section 28C
longitudinally
offset from the two longitudinally aligned side base sections 28S disposed on
opposite sides thereof. Such staggering of adjacent sections allows the
peripheral
shape of the building to be varied from a rectangular perimeter while using
only
~. .,~ .,,,~.,,~.....~~,.....,,.
CA 02596989 2009-10-05
rectangular sections of the same size. For example, three sections measuring
approximately 28 by 11 feet can be used to assemble a modular home having the
square footage of an approximately 28 by 33 foot rectangular home without the
blandness of straight exterior walls. The floor structures of the illustrated
5 embodiment measure 28' by 11'-3". As a result, the two wider rows of the
sheathing
each use three 4' x 8' plywood sheets and one end sheet cut to 4' x 4' and the
narrower third row uses three sheets of 8' length cut down to a width of 3'-3"
and
one end sheet cut to 3'-3" x 4. Again, it should be appreciated that these
dimensions are presented in an exemplary context and may be varied.
10 Due to the increased rigidity of the floor structure 10 provided by the
bridge members 22, more weight can be supported without relative movement
between the floor components during transport and the stiffness prevents
cracking of
the finishing caused by distortion of the structure. As a result, the wall
structure (not
shown) can be provided with a finished exterior side (not shown), finished
interior
15 side (not shown) and any necessary elements in-between while still at the
fabrication
plant, as the rigid floor structure should be able to handle the weight
increase. For
example, it may be possible to equip the wall interiors with plumbing,
electrical
components and insulation and apply interior and exterior finishes such as
drywall
and stucco respectively. The rigidity of the floor structure 10 acts to reduce
the
likelihood of shifting in the wall structure (not shown) supported thereon
during
transport and assembly of the base sections, thereby reducing the risk of
cracking,
twisting or other damage that may occur to elements supported in or on a wall
structure supported by a conventional modular building floor framework.
Flooring
CA 02596989 2009-10-05
16
and furnishings (not shown) may even be provided at the fabrication plant to
further
reduce the need for completion of the building at the installation site.
As shown in Figure 1, connectors 38 interconnect the base sections
once they are suitably positioned side by side on a foundation. The connectors
38
extend through the mating perimeter side walls of adjacent floor structures
and
clamp them together to prevent separation. Each connector 38 features a
central
rod 40 extending through the mated perimeter side walls 16 and end members 42
secured to opposite ends of the central rod 40. Spacers 44 are shown as boards
stacked face to face to extend laterally from each perimeter side wall 16 into
the
respective floor structure. Each board is cut to a suitable length and shape
to fit
within the triangular spaces formed in the floor structures due to the bride
members
22, this length varying with the distance from the perimeter side wall at
which the
board is to be stacked in the spacer assembly. Each end member 42 is secured
in
clamping contact with the face of the respective spacer 44 opposite the
perimeter
side wall to block separating motion of the mated perimeter walls.
Different types of foundations on which a modular home can be
supported are known to those of skill in the art, including footers, runners,
slab or
pad, basement and pit-set. Just like prior art modular homes, the base
sections of
the present invention can be supported on each of these foundation types.
When transporting base sections having substantially completed
interiors, which may have flooring, walls finished with paint or panelling and
even
furniture, without the corresponding roof sections installed, each base
section should
CA 02596989 2009-10-05
17
be covered in some way to protect the interior from exposure to rain, dust,
debris,
etc.
Turning now to Figure 4, a modified arrangement of structural panel
includes a first pair of parallel perimeter rail members 18A arranged to
define first
sides of the panel and a second pair of parallel perimeter rail members 18B
arranged to define second sides of the panel at right angles to the first
sides. The
panel is formed also by the parallel joists 20 extending between the first
pair 18A
and parallel to the second pair 18B. Each of the second pair of perimeter rail
members and the joists therebetween are connected to a next adjacent one by a
plurality of diagonal planar bridge members 22 with the diagonal planar bridge
members extending obliquely between said one and said next adjacent one with
one
end edge fastened to a side face of the joist or rail in zigzag manner such
that an
end of one of the bridge members butts an opposed end of a next one of the
bridge
members at a side face. The bridge members are formed of a wooden sheet such
as plywood or aspenite. The structural panel is longer in direction between
the first
pair 18A so that the joists 20 extend in the longitudinal direction and bridge
the ends
18B.
A planar top cover sheet formed by individual sheets of a wood
material lies in a common top plane defined by the joists, rails and bridge
members
and is adhesively bonded to said top surfaces of the rail members and joists
and a
symmetrical planar bottom cover sheet 24A is adhesively bonded to the bottom
surfaces of the rail members, bridge members and joists.
The ends of the bridge members 22 are adhesively bonded at 22A to
CA 02596989 2009-10-05
18
the faces of the joists and the butting ends 22A of the bridge members on
opposite
faces of the joists 20 are aligned.
The panel includes four transverse lifting rails 80 connected between
the rails 18B and the first joist 20 and formed from the same material as the
joists. A
lifting assembly for lifting the panel comprising four pairs of mounting
plates 81
extending at right angles to the top cover sheet and each pair fastened to the
panel
at the lifting rail 80.
The top and bottom sheets are preferably formed from rectangular
sheets having a longer axis and a shorter axis and are arranged with the
longer axis
at right angles to the joists.
The floor structure of each modular base section has sufficient
stiffness alone independently of the stiffness of the walls to provide
stiffness for the
modular base section to allow the modular base section to be transported and
installed with the interior and peripheral wall finished and with the modular
base
section separate from the other modular base sections.
Since various modifications can be made in my invention as herein
above described, and many apparently widely different embodiments of same made
within the spirit and scope of the claims without department from such spirit
and
scope, it is intended that all matter contained in the accompanying
specification shall
be interpreted as illustrative only and not in a limiting sense.