Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02613308 2008-06-25
A METHOD AND APPARATUS TO DETECT AND LOCATE DAMAGE AND
BREACHES IN ROOF MEMBRANES
The present invention relates to a system for testing roof membranes
for damage to and breaches in roof membranes by detection and location of
moisture penetration. It has particular application to testing the integrity
of low-slope
and flat roofs of residential and commercial buildings.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The failure to detect, find and correct minor roof deterioration in the
earliest stages is considered the greatest cause of premature roof failure.
This is
particularly true of roofing materials applied on low-slope or flat roofs.
Costly roofing
problems are often the result of design deficiencies or faulty application of
the roof
system. Even when properly designed and applied, all roofing materials
deteriorate
from contraction and expansion of roof decks and natural aging processes.
Several methods have been used to try and locate roof leaks after they
have occurred. Electric capacitance meters identify leaks using a low-
frequency that
measures dielectric constant changes in the roofing material as a result of
moisture
below the membrane. Infrared cameras allow technicians to scan roof surfaces
for
temperature differentials that signify moist areas through changes in thermal
conductivity or evaporation. Electric field vector mapping uses a wire loop
around
the perimeter of the roof surface to introduce an electric potential between
the
structural deck and a selected roof area which is sprayed with water. The
electric
CA 02613308 2008-06-25
2
field potential caused by a conductive path to any roof membrane damage is
then
located using a sensitive voltmeter and a pair of probes.
US Patent 4,565,965 issued Jan 21st 1986 to Geesen discloses an
arrangement for detecting leaks in flat roofs in which electrical pulses are
transmitted
through the moisture in the leak to the roof edge and then the roof is scanned
by a
pulse sensor and hand-held probe rods to find the leak by locating the maximum
amplitude.
The method as described by Geesen requires considerable experience
and careful placement of a wire loop around the perimeter of the area to be
tested.
In particular, metal roof stacks and drains must be isolated by placing
secondary
loops around them to avoid false readings pointing towards these penetrations.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is an object of the present invention to provide an apparatus and
method for testing roof membranes for damage to and breaches in roof membranes
by detection and location of moisture penetration in a flat or low slope roof
construction of the type having an impermeable membrane applied over an
underlying horizontal deck.
According to a first aspect of the invention there is provided a method
of locating a leak site in a roof, where the roof comprises a generally
horizontal roof
support deck with a water impermeable membrane applied onto the upper surface
of
the support deck, the method comprising:
CA 02613308 2008-06-25
3
providing a first conductor arrangement for engaging the roof above
the membrane;
providing a return conductor arrangement for electrical connection to
the support deck;
generating an electrical potential between the first and return
conductor arrangements;
mounting the first conductor arrangement on a carriage which can be
moved over the roof so as to scan the first conductor arrangement over
selected
areas of the roof while the first conductor arrangement remains in contact
with the
roof as the carriage is moved;
sensing the current flowing from the roof support deck to the first
conductor arrangement;
and detecting the changes in current as the first conductor
arrangement is scanned over the selected areas of the roof to locate the leak
in the
] 5 membrane.
Preferably the carriage is mounted on roller wheels for carrying the
carriage in rolling movement over the roof_ However a sliding action without
wheels
is possible or other transport devices such as rollers may be used.
Preferably the carriage includes a handle such that the carriage can be
manually rolled across the roof. However the device may be propelled by other
arrangements including robotically.
CA 02613308 2008-06-25
4
Preferably the first conductor arrangement comprises at least one
conductive component arranged for engaging the roof and for sliding over the
roof
while in contact therewith. This may be a conductive brush with conductive
flexible
bristles but other flexible conductive members may be used.
Such a member may include a vertically floating support to maintain
intimate contact with the roof while accommodating variances in the roof
surface.
Preferably the first conductor arrangement includes first and second
conductor members which are electrically isolated each other. Preferably the
circuit
includes first and second circuit sections arranged to independently sense the
i0 current flowing from the roof support deck to the first and second
conductor
members and to detect the changes in current as the first conductor
arrangement is
scanned over the selected areas of the roof to locate the leak in the
membrane.
Preferably the circuit includes two independent leakage current detection
components sharing a common power supply source.
Preferably the first conductor member is an inner member and the
second member is a perimeter outer member such that both the first inner
member
and the second outer member engage the roof with the outer member peripherally
surrounding the inner member. The outer member can be formed from four brushes
in the form of an outer rectangle and the inner conductor may be one or more
inner
brushes contained within the outer periphery.
Preferably the circuit includes variable sensitivity of the changes and
an output display for providing a visual indication of the changes to an
operator.
CA 02613308 2008-06-25
According to a second aspect of the invention there is provided a
method of locating a(eakage site in a roof, where the roof comprises a
generally
horizontal roof support deck with a water impermeable membrane applied onto
the
upper surface of the support deck, the method comprising:
5 providing a first conductor arrangement for engaging the roof above
the membrane;
providing a return conductor arrangement for electrical connection to
the roof support deck;
wherein the first conductor arrangement includes first and second
conductor members which are electrically isolated from each other;
wherein the first conductor member is an inner member and the
second member is an outer shielding member at least partly surrounding the
first
inner member;
generating an electrical potential between the first conductor member
of the first conductor arrangement and the roof support deck;
generating an electrical potential between the second conductor
member of the first conductor arrangement and the roof support deck;
scanning the first conductor arrangement over selected areas of the
roof such that both the first inner member and the second outer member engage
the
roof as the first conductor arrangement is scanned;
independently sensing the current flowing from the roof support deck to
the first and second conductor members of the first conductor arrangement;
CA 02613308 2008-06-25
6
and locating the leakage site by:
detecting changes in the sensed current received by the second outer
conductor member at a distance from the a leakage site with the second outer
conductor member shielding the first inner conductor member to reduce
communication of current thereto from the leakage site;
and detecting the changes in the sensed current received by the first
inner conductor member when the first inner conductor member is over the
leakage
site and the second outer shielding conductor member acts as a shield around
the
leakage site.
Preferably the circuit includes variable sensitivity of the changes and
an output display for providing a visual indication of the changes to an
operator so
that the operator can detect the presence of a leak in the area of the device
and an
audible alert for indicating when the inner conductor member is over the
leakage
site.
According to a third aspect of the invention there is provided an
apparatus for locating a leak in a roof, where the roof comprises a generally
horizontal roof support deck with a water impermeable membrane applied onto
the
upper surface of the support deck, the apparatus comprising:
a conductor arrangement for engaging the roof above the membrane
including first and second conductor members which are electrically isolated
each
other;
CA 02613308 2008-06-25
7
a carriage carrying the first and second conductor members which can
be moved over the roof so as to scan the members over selected areas of the
roof;
wherein the first conductor member is an inner member and the
second member is an outer shielding member at least paEtly surrounding the
first
inner member with both the first inner member and the second outer member
engaging the roof;
and a circuit arranged to sense current flowing from the roof support
deck to each of the first and second members, the circuit including two
independent
current detection components respectively for the first and second conductor
members;
the circuit being arranged to detect changes in current as the
conductor members are moved over the roof.
The device is used in a method in which a power supply potential is
applied between the roof deck and the two sets of conductive brushes so that
any
] 5 leakage path through the roof membrane to the roof deck will be detected
by the first
set of conductive brushes at distance from the leak and by the second set of
conductive brushes when directly over the leakage site. Usually the selected
area to
be tested is wetted while reading the outer perimeter display and then
sweeping the
platform in a covering pattern over the wetted area if the outer perimeter
brush
detection circuit indicates a leak. The sweeping process is halted and the
area
directly under the platform examined when the inner brush circuit indicates a
leakage by a visual and/or audible response.
CA 02613308 2008-06-25
8
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
One embodiment of the invention will now be described in conjunction
with the accompanying drawings in which:
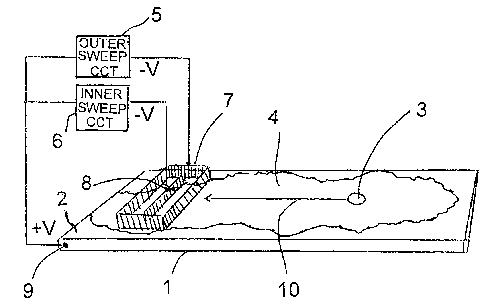
Figure 1 is an isometric view of a roof membrane on a roof deck
including a basic illustration of the sensor brushes and measurement circuits.
Figure 2 is a circuit schematic.
Figures 3A, 3B and 3C show respectively a top plan view, a bottom
plan view and a front view of a carriage and sensing system for use in the
general
method of Figure 1.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFFERED EMBODIMENT
Referring now to the drawings, the overall arrangement of the subject
roof membrane moisture detection system can best be seen with reference to
Figure
1. A roof membrane 2 is illustrated which is applied as a direct covering
layer over a
concrete roof deck 1. The deck is typically of concrete but can be of any
suitable
material to provide the necessary structural strength and can be steel or
wood. The
membrane is an impervious material such as plastics and is sealed at any
joints to
provide a continuous water barrier over the roof deck. This barrier is
intended to
provide the leak prevention and any penetration therein caused by a puncture
or
faulty seal or by wear can allow the moisture to penetrate to the deck where
it can
cause damage or can continue into the structure to cause damage to internal
structures.
CA 02613308 2008-06-25
9
The membrane may be covered by a layer of an aggregate material for
heat insulation and protection. If used, the aggregate may be loose or may
contain
a binder such as asphalt. The arrangement described herein can be used with
various roof constructions they can range from directly adhered membranes with
no
ballast (aggregate) to fully built up roofs with gardens.
The basic operation is shown in Figure 1. A typical concrete deck I
over which the non-conducting water proof membrane 2 is applied is
illustrated. A
defect in the membrane 3 allows water 4 to intrude and forms a conductive path
to
the roof deck. The conductive outer 7 brushes and inner 8 brush are placed on
the
top surface of the membrane 2 with the outer perimeter conductive brushes 7
surrounding the inner brush 8. The brush sets are positioned so as to be in
intimate
contact with the wetted surface 4 of the test area. The outer sweep detection
circuit
5 and inner sweep detection circuit 6 which share a common power supply are
connected to the outer brush set 7 and inner brush set 8 respectively with the
common positive side of both connected to a grounding point 9 on the deck.
A DC potential is applied between the roof deck 1 and the wetted area
4. At the membrane damage site 4 there is a conductive path through the
membrane and a leakage current 10 travels through the damage point and back to
the outer conductive brush 7. The return current picked up by the outer
brushes is
measured and displayed on the outer sweep circuit 5. As the outer brush
perimeter
surrounds the inner brush sensor, very little of the return current reaches
the inner
brush 8. The sweep system is then moved forward over the membrane towards the
CA 02613308 2008-06-25
defect and when the outer brush passes over the damage site, the inner brush
picks
up the return current and provides a visual and audible alarm. The damage site
is
thereby located.
A detailed schematic of the detector circuit is shown in Figure 2. The
5 roof deck connection 9 is connected to the ground terminal 13 which ties the
connecting cable from roof deck to the positive supply 17 of the circuit. The
connecting lead from the inner brush 8 is connected to the negative summing
input
of a first stage Amplifier 14. Diodes DI and D2 provide input protection. The
gain of
the first stage is set by Resistors R2 and R3 while Capacitor Cl filters out
any
10 unwanted noise. The output of Amplifier 14 is tied to the input of a second
Amplifier
through Resistor R4. Resistors R4, R5 set the gain of the second stage
Amplifier
to unity. The positive summing input of Amplifier 15 is tied to common through
Resistor R6.
A voltage to frequency converter 21 has an input which is connected to
15 the output of Amplifier 15. The output of the voltage to frequency
converter is
applied to the input of audio Amplifier 23 through volume control 22. The
audio
output of Amplifier 23 is connected to a speaker 24. The output of Amplifier
15 is
applied to voltage divider defined by Resistors R7 and R8 which scales the
signal
level and applies it to the input of a display driver 19. The display driver
19 is
connected to and drives an LED level display 20 of the inner brush.
The entire first and second stage input circuit 18 is duplicated in a
second sensing system schematically indicated at 27. The connecting lead from
the
CA 02613308 2008-06-25
11
outer brushes 8 is connected to the input of the second amplifier circuit 27
as
indicated at 25. The output of the circuit 27 is applied to display driver 28
which
drives a LED level display 29 of the outer brush.
The mechanical arrangement of the apparatus is illustrated in Figure 3.
A horizontal platform or carriage 30 with a flat top wall and a depending side
wall 35
forming four sides of a rectangular carriage. The carriage is carried on four
swivel
wheels or casters 31 attached to the top plate by mountings 36. The carriage
supports an outer brush assemblies defined by two parallel front and rear
brushes
32 and two parallel side brushes 37, thus defining a rectangular outer area
just
inside the outside wall of the carriage. Inside the outer rectangular area is
provided
a single transverse brush defining an inner brush 33. Vertically floating
brackets 34
position the outer brushes and allow vertical movement of the brushes as the
platform travels over the membrane surface. Similar brackets 38 carry the
inner
brush. The brushes are formed as a strip from conductive bristles carried on a
base
so that the base can float upwardly and downwardly from pressure of the roof
against the tips of the bristles so that a constant electrical contact is
maintained with
the roof.
A simple manually graspable handle assembly 40 is attached to
brackets 39 on the top plate of the carriage. The sweep circuits are mounted
in a
housing 41 and attached to the handle 40 assembly at a position below a top
hand
rail of the handle assembly.