Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02618549 2008-02-08
WO 2007/019947 PCT/EP2006/007330
1
Description
Non-positive Compressor
The invention relates to a compressor with at least one displacer cylinder, in
which an operating
fluid, in particular an ionic fluid, is arranged, which may be brought into
connection with a
suction inlet and a pumped outlet for medium, wherein the operating liquid has
a working
connection to a drive pump embodied as an axial piston pump.
These types of compressors are used for compressing gaseous media. The medium
in this case is
displaced by means of the operating liquid in the displacer cylinder, whereby
these types of
compressors are designated as non-positive compressors. An ionic liquid can be
used as the
operating liquid. However, it is also possible to use liquids with a low vapor
pressure or liquids
with low gas solubility. What these types of liquids have in common is that
they do not dissolve
in the medium and can be separated from the medium without leaving a residue
so that the
compressed medium exhibits a high level of purity.
The operating fluid is pumped in this case into the displacer cylinders by
means of a drive pump
embodied as an axial piston pump and suctioned from the displacer cylinders in
order to convey
the medium from the suction inlet to the pumped outlet and pressurize it. When
using an axial
piston pump as a drive pump, it is necessary for the safe operation of the
compressor that, during
the suction stroke of the axial piston pump, when the operating liquid is
being suctioned from the
displacer cylinder, the pistons of the axial piston machine, which as a rule
are provided with
hydrostatic relief, be kept in contact with a slide path of the axial piston
pump.
To do this, providing the axial piston pump with a mechanical retracting
device, which keeps the
pistons in contact with the slide path, is known. This type of mechanical
retracting device,
however, is associated with a high construction expense.
CA 02618549 2008-02-08
WO 2007/019947 PCT/EP2006/007330
2
A generic non-positive compressor has a high service life because of the lack
of mechanical seals
and the lack of pistons in the displacer cylinders. Adapting an axial piston
pump having a
retracting device to the high service life of the non-positive compressor also
requires a high
construction expense.
The present invention is based on the objective of providing a compressor of
the species cited at
the outset with low construction expense and a long service life.
This objective is attained in accordance with the invention in that the
suction inlet of the
compressor is provided with a pre-compressor. A compressor having an upstream
pre-
compressor can generate, at the suction inlet of the compressor, a minimum
preliminary pressure
of the medium being pumped in a simple manner. This preliminary pressure
generated by the
pre-compressor is also available at the axial piston pump via the operating
liquid, which is in
direct contact with the medium to be pumped, and said preliminary pressure
acts on the pistons
of the axial piston pump during the suction stroke in the direction of the
slide path. As a result,
an inventive pre-compressor makes it possible to achieve a low construction
expense and
guarantee that, in the case of the axial piston pump, the pistons remain in
contact with the slide
path without a mechanical retracting device and/or without modifications to
the retracting
device. This makes it possible to adapt the service life of the axial piston
pump without
appreciable modifications to the retracting device in a simple way to the high
service life of the
non-positive compressor, which makes it possible to achieve a high service
life of the
compressor with low construction expense using a standardized axial piston
pump.
Various designs of compressors and/or pumps can be used as pre-compressors.
There are special
advantages if the pre-compressor is embodied as a screw compressor in
accordance with a
preferred embodiment of the invention. Because of the high service life of a
non-positive
compressor, it is necessary to select a pre-compressor with a correspondingly
high service life in
order to prevent the pre-compressor from being the weakest link in the service
life chain. A
screw compressor does not require any operating seals that have a high level
of seal tightness,
CA 02618549 2008-02-08
WO 2007/019947 PCT/EP2006/007330
3
which results in a standardized screw compressor having a high service life.
In addition, a screw
compressor features low pulsations, which makes it possible to achieve low
noise emissions and
low stress for the compressor on the suction side.
According to an advantageous development of the invention of the pre-
compressor, the pre-
compressor can be lubricated with the operating liquid with special advantage.
Lubricating the
pre-compressor with the operating liquid prevents the to-be-pumped medium from
getting
contaminated due to the use of the pre-compressor. Because of lubrication with
the operating
liquid, the screw compressor only emits the operating liquid already present
in the process,
whereby a negative impact on the functioning of the compressor does not occur.
According to a preferred development of the invention, the pumped outlet of
the compressor is
provided with a separating device for separating operating liquid located in
the pumped medium.
This type of separating device, which can be used to separate operating liquid
emitted into the
pumped medium by the compressor, can also separate the operating liquid
emitted into the
medium by the pre-compressor lubricated with the operating liquid. As a
result, an additional
separating device is not required on the suction side of the compressor in
order to separate any
operating liquid possibly emitted into the to-be-pumped medium by the screw
compressor
lubricated with the operating liquid.
According to a preferred embodiment of the invention, the axial piston pump
has a cylindrical
drum, in which at least one cylinder space is embodied, which is connected to
the displacer
cylinder, wherein a piston is arranged in the cylinder space in a
longitudinally displaceable
manner, which piston is supported on a slide path, in particular an adjustable
diagonal plate. As a
result, it is simple to realize a connection of the displacer cylinder to the
cylinder space and
therefore to the piston in order achieve secure contact of the piston on the
slide path formed by
the diagonal plate with the preliminary pressure generated by the pre-
compressor, during the
suction stroke of the drive pump.
There are special advantages if the displacer cylinders are arranged in a
cylinder block and
attached radially. Because of the radial arrangement of the displacer
cylinders in a rotating
CA 02618549 2008-02-08
WO 2007/019947 PCT/EP20061007330
4
cylinder block, a centrifugal force acts on the operating liquid present in
the displacer cylinders,
which makes a high compressor speed possible. As a result, a high pump output
can be achieved
with a low requirement for construction space for the compressor. In addition,
only a small
quantity of operating liquid is required, whereby the compressor has low
manufacturing costs
and operating costs.
According to a preferred structural embodiment of the invention, the cylinder
block and the
cylindrical drum are coupled in a rotationally synchronous manner or embodied
to be one-piece.
If a pressure of 5-15 bar, in particular a pressure of 8-10 bar, can be
generated by means of the
pre-compressor on the suction inlet, a secure abutment of the piston on the
slide path formed by
the diagonal plate can be guaranteed during compressor operation when using a
standardized
axial piston pump.
The compressor can be embodied for conveying liquids.
There are special advantages if the compressor is embodied for compressing a
gaseous medium,
in particular hydrogen. With an inventive non-positive compressor, in which a
preliminary
pressure of the gaseous medium can be generated on the suction side by means
of a standardized
pre-compressor that is lubricated with the operating liquid, a standardized
axial piston machine
can be used as a drive pump for the operating liquid, which results in lower
manufacturing costs
with a long service life for the non-positive compressor when using
standardized components.
Additional advantages and details of the invention are explained in greater
detail on the basis of
the exemplary embodiment depicted schematically in the figure.
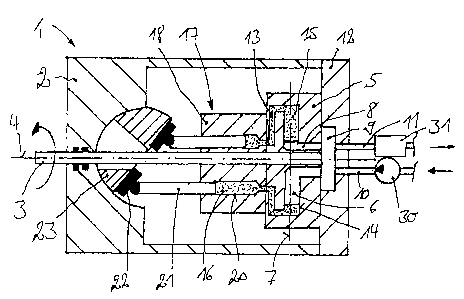
The figure depicts a longitudinal section of an inventive compressor 1. A
drive shaft 3 is
rotatably mounted within a housing 2 around an axis of rotation 4. A
cylindrical drum 5, in
which several displacer cylinders 6 are embodied, is coupled to the drive
shaft 3 in a rotationally
synchronous manner. The displacer cylinders 6 in this case are embodied radial
bores 14
CA 02618549 2008-02-08
WO 2007/019947 PCT/EP2006/007330
arranged in the cylindrical drum 5 and are arranged in a star-shape around the
axis of rotation 4,
whereby the longitudinal axis 7 of the displacer cylinders 6 is arranged
perpendicularly to the
axis of rotation 4 of the drive shaft 3 and thus of the cylindrical drum 5.
In the radial inner region, the displacer cylinders 6 are each connected to a
connecting passage 8,
which is operatively connected to a plate-shaped valve plate 9, whereby the
connection of the
displacer cylinders 6 to a suction inlet 10 as well as to a pumped outlet 11
can be controlled
during rotation of the cylindrical drum 5 by means of the valve plate 9. The
cylindrical drum 5
in this case is supported in the axial direction on the valve plate 9, which
is arranged on a
housing cover 12 fastened to the housing 2.
An operating liquid 15, in particular an ionic liquid, is arranged in the
displacer cylinders 6.
Each displacer cylinder 6 is connected by means of a connecting passage 13 to
a cylinder space
16 of a hydraulic drive pump embodied as an axial piston pump 17 having a
diagonal plate
design. In this case, the drive pump embodied as an axial piston pump 17 has a
cylinder block
18, which is arranged coaxially to the cylindrical drum 5 and is connected to
the cylindrical drum
5 and/or the drive shaft 3 in a rotationally fixed manner. It is also possible
to embody the
cylinder block 18 and the cylindrical drum 5 as a comtnon and therefore one-
piece cylindrical
drum.
The cylinder spaces 16 of the axial piston pump 17 are formed by the
longitudinal bores 20
arranged concentrically in the cylinder block 18, in which bores pistons 21
are respectively
arranged in a longitudinally displaceable manner. The pistons 21 are each
supported by means
of a sliding block 22 on a slide path 23, which is embodied on a diagonal
plate. A spherical
sliding block articulation is embodied between the piston 21 and sliding block
22.
The axial piston machine 17 is embodied as an axial piston machine whose
displacer volume can
be adjusted, whereby the diagonal plate provided with the slide path 23 is
swivel-mounted on the
housing 2 and can be inclined with respect the axis of rotation 4 by means of
a regulating device
(not shown).
CA 02618549 2008-02-08
WO 2007/019947 PCT/EP2006/007330
6
However, it is also possible to embody the axial piston machine with a fixed
displacer volume,
whereby the diagonal plate can be embodied directly on the housing 2.
In this case, the cylindrical drum 5 and the drive pump 17 are arranged in the
common housing.
According to the invention, the suction inlet 10 of the compressor 1 is
provided with a pre-
compressor 30. The pre-compressor 30 is embodied as a screw compressor and is
lubricated
with the operating liquid 15.
In this case, the pre-compressor 30 generates a preliminary pressure of the
medium of approx. 8-
bar at the suction inlet 10. Via the operating liquid 15 present in the
displacer cylinders 6, the
connecting passages 13 and the cylinder bores 16, which is in direct contact
with the medium,
the preliminary pressure of the medium acts on the pistons 21 in the direction
of the slide path 23
embodied on the diagonal plate. This results in a secure abutment of the
pistons 21 on the slide
path 23 during the suction stroke of the axial piston pump 17.
The pumped outlet 11 is provided with a separating device 31, which can be
used to separate any
operating liquid 15 possibly emitted into the pumped outlet 11 from the pumped
medium. As a
result, a high level of purity of the pumped medium is achieved.
When operating the inventive compressor 1, the drive shaft 3 drives the
cylindrical drum 5 and
the cylinder block 18. The axial piston pump pumps operating liquid 15 from
the cylinder
spaces 16 into the displacer cylinders 6, whereby the medium flowing into the
displacer
cylinders 6 via the suction inlet 10 is compressed by the liquid 15 and
conveyed to the pumped
outlet 11. In this case, the preliminary pressure of the medium at the suction
inlet 10 that is
generated by the pre-compressor 30 guarantees a secure abutment of the pistons
21 of the drive
pump embodied as an axial piston pump 17 on the slide path 23. When the
compressor 1 is in
operation, centrifugal force acts on the liquid 15 due to the radial
arrangement of the displacer
cylinders 6 through the rotation of the cylindrical drum 5, and this
centrifugal force accelerates
CA 02618549 2008-02-08
WO 2007/019947 PCT/EP2006/007330
7
the operating liquid, allowing the liquid column of the operating liquid 15 to
be moved at a great
speed into the displacer cylinders 6 and thus the compressor 1 can be operated
at a great
rotational speed and therefore at a high cycle speed. As a result, high pump
output is achieved
with low construction space for the compressor 1 and a low requirement for
operating liquid 15.
Because of the preliminary pressure of the medium generated by the pre-
compressor 30, a
standardized axial piston pump 17 can be used in this case, which is adapted
to the high service
life of the non-positive compressor 1 without appreciable modifications to the
mechanical
retracting device. The embodiment of the pre-compressor 30 as a standardized
screw
compressor, which is lubricated with the operating liquid 15, makes it
possible to adapt the
service life of standardized pre-compressor 30 to the high service life of the
non-positive
compressor with low construction expense. The operating liquid 15 emitted by
the pre-
compressor 30 into the to-be-pumped medium can be separated in a simple way
from the
pumped medium by means of the separating device 31 allocated to the pumped
outlet 11. All in
all, it is therefore possible to realize a non-positive compressor 1 with low
manufacturing
expense, low construction effort and low operating costs.