Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02626626 2008-03-18
FLAME-RESISTANT HIGH VISIBILITY TEXTILE FABRIC
FOR USE IN SAFETY APPAREL
BackQround of the Invention
[0001] The present invention relates generally to textile fabrics suitable for
use in safety
apparel. More particularly, the present invention relates to such fabrics
which are flame
resistant and also have an affinity for high visibility dyes meeting
established standards for
such.
[0002] Workers in many occupations are exposed to various personal safety
hazards which
can be mitigated by wearing safety apparel which provides selected properties
such as flame
resistance and high visibility. Such safety apparel has wide-spread
applications across many
varied occupations, such as in particular within the construction and
manufacturing
industries.
[0003] To date, governmental organizations have not promulgated defined
minimum
standards for such safety apparel. However, private organizations, such as the
Airiet-ican
National Standards Institute (ANSI), the Safety Equipment Association (ISEA)
and the
American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), have published certain
standards for
safety apparel. For example, ANSI in conjunction with ISEA has established a
standard for
the minimum conspicuity of safety apparel used in certain occupational
activities so as to be
deemed "high visibility", such standard commonly designated as ANSI/ISEA-107.
ASTM
has similarly developed a standard for minimum flame resistant in safety
apparel, designated
as standard ASTM F-1506.
[0004] Until recently, the textile industry considered such standards to be
essentially
incompatible as the vast majority of textile fiber materials suitable for
apparel fabrication
which meet the ASTM F-1506 flame resistant standard are incapable of being
dyed to a
luminescence sufficient to meet the ANSI/ISEA-107 standard for high visibility
and, visa-
versa, the vast majority of textile fiber materials suitable for apparel
fabrication which have a
sufficient affinity for luminescent dyeing to meet the ANSI/ISEA-107 standard
would not
provide flame resistance properties meeting the ASTM F-1506 standard.
CA 02626626 2008-03-18
[0005] However, it has been discovered that modacrylic fibers have a dye
affinity and flame
resistance characteristics capable of satisfying both standards and,
accordingly, in recent
years, textile fabrics have been developed which are composed entirely or
predominantly of
modacrylic fibers for use in fabricating safety apparel to meet each standard.
Representative
examples of such fabrics are disclosed in U.S. Patent Nos. 6,706,650;
6,787,228; and
6,946,412, and U.S. Patent Application Publication No. 20040192134.
[0006] While such modacrylic fabrics satisfy the aforementioned flame
resistance and high
visibility standards, safety apparel made from such fabrics has thus far
achieved only limited
acceptance within the apparel industry because such fabrics are stiff,
abrasive and otherwise
very uncomfortable when worn, particularly when in contact with a wearer's
skin.
Accordingly, there is a recognized and yetunmet need within the relevant
safety apparel
industry for an alternative fabric providing apparel-like hand and comfort
properties while
still meeting the relevant flame resistance and high visibility standards.
Summary of the Invention
[0007] It is accordingly an object of the present invention to provide a
textile fabric which
provides flame resistance and high visibility properties so as to be suitable
for use in safety
apparel but also provides a comfortable hand suitable for direct contact with
a wearer's body.
[0008] The present invention addresses this objective by forming a textile
fabric of two
different types of yarns integrated into the textile fabric such that one yarn
having flame
resistance and high visibility properties is disposed predominantly at bne
face of the fabric
while the other yarn having a hand suitable for comfortable body contact with
a user's skin is
disposed predominantly at the opposite face of the fabric, whereby the fabric
can be
fashioned into safety apparel with the first-mentioned face disposed outwardly
for flame
resistance and high visibility protection and with the other face disposed
inwardly towards
the wearer's body to promote comfort by buffering the user's skin from the
outer face of the
fabric.
[0009] While inany varied embodiments of the fabric utilizing differing yarns
and differing
fabric constructions are contemplated to be possible, it is considered
advantageous that the
first yarn or yarns comprise a sufficient content of modacrylic fibers to
provide the outer face
of the fabric with the requisite flame resistance and affinity for high
visibility dyeing so as to
meet the currently established standards, ANSI/ISEA-107 and ASTM F-I 506, and
the other
2
CA 02626626 2008-03-18
yarn should have a sufficient content of conventional apparel-suitable fibers,
e.g., cellulosic,
animal hair, silk, polyester, polyamide, acrylic, rayon, and polyimide fibers,
so as to provide
a comfortable hand to the inner face of the fabric.
[0010] For example, but without limitation, it is contemplated that the first
yarn appearing at
the one outer face of the fabric may preferably have a content of modacrylic
fibers ranging
between twenty percent (20%) and one hundred percent (100%), while the second
yarn
appearing predominantly at the opposite inner face of the fabric may
preferably have an
apparel fiber content of at least about fifty percent (50%) and may also
optionally include
modacrylic fibers. In one particular embodiment of the present fabric, the one
outer face yarn
comprises approximately ninety percent (90%) modacrylic fibers and
approximately ten
percent (10%) polyester fibers, while the other inner face yarn comprises
approximately fifty
percent (50%) cotton fibers and approximately fifty percent (50%) modacrylic
fibers.
[0011] The fabric may be formed of any suitable construction by which the
first yarns
offering flame resistance and high visibility properties are disposed
predominantly at the one
outer face of the fabric and the second yarns offering comfort properties are
disposed
predominantly at the opposite inner face of the fabric. One particularly
embodiment
contemplated by the present invention is a knitted fabric wherein the two
yarns are formed in
plated relationship, e.g., by circular kilitting presenting the first yarn at
one fabric face and
the second yarn at the opposite fabric face. While such a plated knit fabric
construction is
presently preferred, the present invention also contemplates various other
textile fabric
construction methodologies such as a plated warp knitted fabric construction,
a so-called bi-
ply knitted fabric construction, a so-called spacer-type warp knitted fabric
construction, a
two-ply woven fabric construction or an alternative woven fabric construction
of a pattern
presenting warp and weft yarns predominantly at opposite faces of the fabric,
such as a twill
fabric construction.
[0012] Other features, characteristics and advantages of the present invention
are described
more fully hereinafter.
Brief Description of the Drawings
3
CA 02626626 2008-03-18
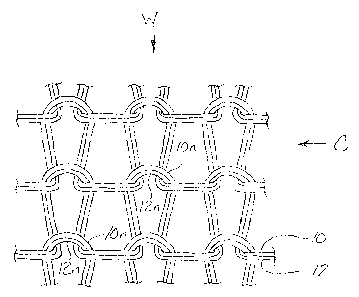
[0013] Figure 1 depicts diagrammatically in elevation the knitted structure of
a textile fabric
according to one preferred embodiment of the present invention; and
(0014] Figure 2 depicts diagrammatically in cross-section the knitted
structure of the textile
fabric of Figure 1, as viewed along section line 2-2 thereof.
Detailed Description of the Preferred Embodiments
[0015] Referring now to the accompanying drawings of Figures 1 and 2, a
fragmentary
portion of a textile fabric according to the present invention is shown at 10
in a representative
embodiment fabricated by circular knitting on a circular knitting inachine
which may be of
any suitable type the fabrication and construction of which is commonly known
within the
industry and therefore need not be fully described herein.
[0016] Such knitting machines basically include a rotatable needle cylinder
with axial needle
slots formed at a spacing from one another about the outer circumferential
surface of the
cylinder. A plurality of knitting needles, typically latch-type needles each
having a yarn
receiving hook and a closeable latch assembly, are reciprocably disposed
within the axial
cylinder slots. Stationary needle-actuating cams are positioned outwardly
about and adjacent
to the needle cylinder. Typically, the knitting machine has multiple knitting
stations at which
yarn feeding fingers or other feeding instruments are positioned for yarn
feeding disposition
adjacent the upper end of the needle cylinder to feed yarn to the needles
thereat.
[0017] For the knitting of the fabric 10 according to the present invention,
the knitting
machine is set up at each knitting station to deliver simultaneously two yarns
12, 14,
described more fully hereinafter, to each needle,via the yarn feeding
instruments. As the
needle cylinder rotates during operation, the needles are operatively
manipulated within the
respective slots of the cylinder by the adjacent stationary cams to receive
and stitch the yarns
12, 14 into interknitted loops extending in circumferential courses and axial
wales. The
knitting of the fabric 10 proceeds in this fashion for a predetermined number
of successive
revolutions of the knitting machine sufficient to progressively knit the yarns
12, 14 into a
continuous seamless length of tubular fabric 10 of a desired length. The
simultaneous
delivery of both yarns 12, 14 to each needle at each knitting station thusly
forms the yarns in
plated relationship in a single jersey stitch construction throughout the
entirety of the fabric
10.
4
CA 02626626 2008-03-18
[0018] As will thus be understood, the resultant knitted structure of the
fabric 10 is shown
schematically in an enlarged form in the drawings of Figures I and 2. As
indicated, each yarn
12, 14 is formed identically in plated needle loops 12n, 14n extending
circumferentially about
the fabric 10 in courses C and aligned lengthwise along the fabric 10 in
perpendicular wales
W. In the drawing of Figure 1, the plated relationship of the yarns 12, 14 is
depicted
diagrammatically and schematically by showing the yarns side by side in the
same plane, but
those persons skilled in the art will recognize and understand that, within
the three
dimensional structure of the actual fabric 10, the yarns 12, 14 are actually
formed in
overlying relationship with the yarn 12 disposed predoininantly at one face of
the fabric 10
while the yarn 14 is disposed predominantly at the opposite face of the fabric
10, as shown in
the cross-sectional view of Figure 2.
[0019] In accordance with the present invention, the yams 12, 14 incorporated
into the
fabrication of the textile fabric 10 are selected to achieve differing,
physical and chemical
properties in the fabric 10 at the opposite faces of the fabric. Specifically,
the yarn 12
appearing at one face of the fabric is selected to have a sufficiently high
content of a flame
resistant material to impart to such face of the fabric flame resistance
properties which will
comply with prevailing flame resistance standards observed within the textile
industry,
particularly standard ASTM F-1506 established by the American Society for
Testing and
Materiais. By contrast, the yarn 14 appearing at the opposite face of the
fabric is a material
of the type ordinarily utilized in apparel fabric to impart to such face of
the fabric 10 a
satisfactory hand, e.g., non-abrasive, flexible and not stiff, and essentially
soft, to be suitable
for direct body contact with the skin of a person wearing safety apparel. In
this manner, the
fabric 10 can be fabricated into safety garments with the face of the fabric
predominantly
comprised of the yarn 12 as outward face of the garment and with the opposite
face of the
fabric predominantly comprised of the yarn 14 as the inner face of the
gannent.
[0020] Various yarns are deeined to be suitable for these purposes.
Specifically, the yarn 12
can be selected from any fibrous material exhibiting satisfactory flame
resistance or fire
retardant properties. The yarns presently considered most preferable for use
in safety apparel
applications of the fabric 10 are yarns having a modacrylic fiber content,
because modacrylic
fibers are known to exhibit flame resistant properties and also to have an
affinity to receive
dyes which will provide high fluorescence and optimally will meet established
standards for
minimuin high visibility conspicuity, such as standard ANSI/ISEA-107
established by the
CA 02626626 2008-03-18
American National Standard Institute. The yarn 14 appearing at the inner face
of the fabric
may be selected from any known apparel fiber, whether natural or synthetic in
origin, and
including by way of example but without limitation cotton, other natural
cellulosic fibers
such as flax, animal hair (wool, alpaca, cashmere, etc.), silk, polyester,
polyamide (nylons),
acrylic, rayon and polyimide fibers. Cotton is considered to have the most
widespread
potential application in the yarn 14, as it is widely available, relatively
inexpensive, and is
well established to provide a soft comfortable hand pleasing to the vast
majority of apparel
wearers.
[00211 Importantly, the yarn 12 does not necessarily have to be formed
entirely of a flame
resistant fiber such as modacrylic, nor does the yarn 14 necessarily need to
be formed entirely
of an apparel fiber. For example, for safety apparel applications intended to
meet both flame
resistance and high visibility standards, it is only necessary that the total
content of the fabric,
including both yarns 12 and 14, offers sufficient flame resistance to meet
such criteria and
that the yarn 12 have a sufficient content of fiber having an affinity for
high visibility dyes so
as to meet such standards. As will be understood, greater flexibility in the
selection of yarns
and the yarn content will be available in fabrics intended for safety apparel
that is not
necessarily to be used in applications requiring high visibility dyeing. By
way of example,
but without limitation, in fabrics wherein modacrylic fibers are utilized to
impart the requisite
flame resistance properties, the yarn 12 may have a modacrylic content as low
as
approximately twenty percent (20%) up to as high as one hiuldred percent
(100%), while the
yarn 14 may have an apparel fiber content from one hundred percent (100%) down
to as low
as approximately fifty percent (50%) with the other fiber content being
modaerylic or an
alternative fiber, including another flame resistant fiber. One particularly
suitable
embodiment of the present fabric 10 is fabricated of a blended staple fiber
spun yarn as the
yarn 12 comprised of approximately ninety percent (90%) modacrylic fibers and
approximately ten percent (10%) polyester fibers (which may be a flame
resistant polyester),
and blended staple fiber spun yarn as the yarn 14 comprised of approximately
fifty percent
(50%) cotton and approximately fifty percent (50%) modacrylic fibers.
[0022] Advantageously, the present invention accordingly provides a fabric 10
having one
face which will offer both a high level of flame resistance capable of meeting
the ASTM F-
1506 standard and also having an affinity for dyeing by high visibility
fluorescent dyes
capable of meeting the ANSI/ISEA-107 standard, while the yarn 12 which impart
these
6
CA 02626626 2008-03-18
properties are separated from the body of a wearer by the yarn 14
predominantly forming
inner face of the fabric 10 which by contrast impart a hand comparable to
normal apparel and
avoiding the stiffness and abrasiveness of modacrylic fibers. As such, the
fabric 10 of the
present invention overcotnes the disadvantages of known safety apparel fabrics
and is
expected to achieve a much wider acceptance and use in the safety apparel
industry.
[0023] It will therefore be readily understood by those persons skilled in the
art that the
present invention is susceptible of a broad utility and application. Many
embodiments and
adaptations of the present invention other than those herein described, as
well as many
variations, modifications and equivalent arrangements will be apparent from or
reasonably
suggested by the present invention and the foregoing description thereof,
without departing
from the substance or scope of the present invention. Accordingly, while the
present
invention has been described herein in detail in relation to its preferred
embodiment, it is to
be understood that this disclosure is only illustrative and exemplary of the
present invention
and is made merely for purposes of providing a full and enabling disclosure of
the invention.
The foregoing disclosure is not intended or to be construed to limit the
present invention or
otherwise to exclude any such other embodiment, adaptations, variations,
modifications and
equivalent arrangements, the present invention being limited only by the
claims appended
hereto and the equivalents thereof.
7