Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02665618 2009-05-07
Rotary lifting table
The present invention relates to a rotary lifting table
according to the preamble of claim 1.
Rotary lifting tables for processing planar articles,
in particular printed products, such as printed sheets,
newspapers, magazines, etc., are generally known. They
are equipped with a rotatable and/or liftable and
lowerable rotary lifting table plate, on which or above
which the planar articles come to lie. Rotary lifting
tables have as a rule associated ejection means, by
means of which the planar articles lying on the rotary
lifting table plate can be pushed out in a selected
ejection direction.
The rotatability of the rotary lifting table plate is
advantageous in particular when forming stacks of
folded printed products. Thus, to increase the
stability of such stacks, partial stacks rotated
relative to one another in each case by 180 relative
to a rotation axis oriented at right angles to the
rotary lifting table plate are alternately arranged in
layers one above the other. In this way, thicker
regions on the fold side and thinner regions of the
free side edges of printed products of successive
partial stacks in each case come to lie alternately one
above the other, such that differences in height of the
individual partial stacks on account of their different
thicknesses in certain regions are compensated for.
Rotary lifting table plates are preferably liftable and
lowerable in order to specifically reduce, for example,
drop heights for printed products or partial stacks
formed therefrom or, for the purpose of compressing
stacks, in order to be able to press said stacks
against pressing elements arranged above the rotary
lifting table plate.
CA 02665618 2009-05-07
- 2 -
It is not absolutely necessary in every case to form
both the rotatability and the liftability and
lowerability of the rotary lifting table plate. On the
contrary, the claimed rotary lifting table described
below can also be used in a completely analogous manner
with restricted functionality, that is to say when used
as a rotary table or lifting table, or even only as a
stacking table.
A rotary lifting table for supporting printed products
is described, for example, in EP-A-1852379. In this
case, a rotary lifting table plate is arranged on a
rotary lifting cylinder, said rotary lifting table
plate being equipped on two opposite sides with
ejection devices which have ejection means for ejecting
the printed products arranged in a stack. A movement,
displacing the printed products, of the ejection means
over the rotary lifting table plate defines an ejection
device in this case. The rotary lifting table plate has
a supporting surface arched convexly upward and having
a transverse ridge region, the longitudinal extent of
which runs at least virtually at right angles to the
ejection direction. The planar articles lying one above
the other in the stack are adapted to the arched
supporting surface on account of their sheet-like
formation and their dead weight and give the stack
increased stability due to their profiling.
In particular during the ejection of the stacks of
planar products, the problem arises that the
dimensional stability of the stack and the intactness
of the planar products may be impaired during the
ejection.
It is therefore the object of the present invention to
improve the dimensional stability and intactness of the
stacks of planar articles during their removal from a
rotary lifting table.
CA 02665618 2009-05-07
- 3 -
This object is achieved by a rotary lifting table as
claimed in claim 1. Especially preferred embodiments
are provided with the features stated in the dependent
claims.
The rotary lifting table according to the invention is
equipped with a rotary lifting table plate for
supporting planar articles, in particular printed
products. A stacking shaft is bounded at the bottom at
least partly by the rotary lifting table plate, said
stacking shaft being defined by two opposite ejection
devices, and the planar articles being collected in
said stacking shaft in order to form a stack. The
ejection devices, by means of which the stacked planar
articles can be removed in at least one ejection
direction, are mounted on a turntable connected to the
rotary lifting table plate in a rotationally fixed
manner.
According to the invention, the rotary lifting table is
equipped with at least one sliding plate which has air
discharge openings. During removal of the stack of
planar articles, low-friction sliding from the stacking
shaft in the ejection direction is made possible by air
being forced from the air discharge nozzles, such that
an air cushion is formed between the lowermost planar
article of the stack and the sliding plate. Due to the
low-friction sliding from the stacking shaft, there is
less risk of the planar articles being damaged or of
the stack being deformed or collapsing. At the same
time, a lower expenditure of force is required by the
ejection devices when pushing the stack out of the
stack space.
In especially preferred embodiments, the rotary lifting
table plate engages in the sliding plate during the
ejection of the stack. In a further preferred
CA 02665618 2009-05-07
4 -
embodiment, the sliding plate is fixed on the
turntable.
An especially preferred embodiment of the rotary
lifting table according to the invention is described
in detail below with reference to drawings, in which,
purely schematically and in detail:
fig. 1 shows a rotary lifting table according to the
invention in a side view with partial sectional
illustration, having a rotary lifting table
plate in a lowered and a raised position (dot-
dash line) and laterally arranged sliding
plates;
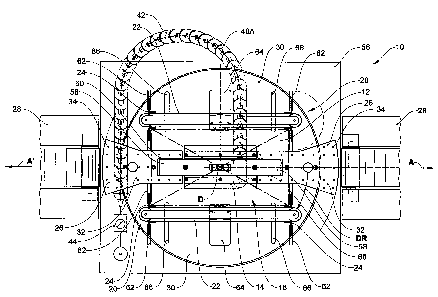
fig. 2 shows, in a plan view, the rotary lifting table
shown in fig. 1, in a basic rotary position with
the laterally arranged sliding plates and
assigned outfeed conveyors; and
fig. 3 shows, in a plan view, the rotary lifting table
shown in fig. 1 and fig. 2, in an end rotary
position.
The rotary lifting table 10 according to the invention
shown in fig. 1, which is intended for planar articles
12, in particular for printed products, such as
magazines, newspapers, paper sheets, etc., has a rotary
lifting table plate 14 for supporting the planar
articles 12, a stacking shaft 16 being bounded at least
partly at the bottom by said rotary lifting table plate
14. The rotary lifting table plate 14 is shown in fig.
1 in a lowered basic lifting position and in a raised
position (dot-dash lines). The rotary lifting table
plate 14 is mounted centrally on a rotary spindle
device 18 which ensures the liftability and
lowerability of the rotary lifting table plate 14. The
rotary spindle device 18 is part of a lifting means
CA 02665618 2009-05-07
-
which can preferably be operated electrically,
hydraulically or pneumatically.
The stacking shaft 16 is defined by two ejection
5 devices 20 which are located opposite one another and
of which only one can be seen in fig. 1. The ejection
devices 20 are described in detail, for example, in EP-
A-1445224. They are equipped with ejection means which
are fastened to transport means 22 and are in the form
of angle profiles 24. The angle profiles 24 define the
stacking shaft 16 laterally and permit the spatially
defined formation of stacks of planar articles 12.
To eject the planar articles 12 which are then arranged
in a stack, the angle profiles 24 are moved in the
ejection directions A, A', likewise defined by the
ejection devices 20, and the stacks are pushed to
assigned conveyors, in particular outfeed conveyors 28,
in a sliding manner via sliding plates 26 designed
according to the invention. A section through one of
the sliding plates 26 is shown in fig. 1 in the partial
sectional illustration.
The sliding plates 26 are fixedly arranged on a
turntable 30 which rotates with the rotary lifting
table plate 14. They have a top sliding surface 32 with
air discharge openings 34, from which pressurized air
can escape, such that, when a stack of planar articles
12 is being pushed out, an air cushion forms between
the lowermost planar article 12 of the stack and the
sliding surface 32. The stack of planar articles 12
which is "floating" on this air cushion is pushed in
one of the ejection directions A, A' to the respective
outfeed conveyor 28 for ejecting by the angle profiles
24 of the ejection devices 20.
In the interior, the sliding plates 26 have a cavity
36, to which the pressurized air is directed via air
feed connections 38, said pressurized air then
CA 02665618 2009-05-07
- 6 -
discharging from the cavity 36 through the air
discharge openings 34. In this case, the air discharge
openings 34 can preferably widen from the cavity 36 in
the direction of the top sliding surface 32. The cross
sections of the air discharge openings 34 may of course
be adapted to the respective application.
The air feed connections 38 are fluidically connected
to a reservoir (not depicted) of pressurized air via
air feed lines 40, which are shown by dashed lines in
fig. 1. In the embodiment shown here, the two air feed
connections 38 of the two sliding plates 26 are
connected to one another via a T piece, and a common
air feed line 40A which is directed along the rotary
spindle device 18 enters a movable trailing cable 42
via an end arranged fixedly relative to the turntable
30 on the side of the rotary lifting table. Inside the
movable trailing cable 42, the preferably flexible
common air feed line 40A is directed to a pressure-
regulating device 44, shown in fig. 2 and fig. 3, and
is connected via the latter to the reservoir.
The pressure-regulating device 44 forms a control
device for establishing the pressure of the air
escaping from the air discharge openings 34 of the
sliding plates 26. The air pressure is in this case
preferably established as a function of the weight of
the supported planar articles and/or of the
rotary/lifting state of the rotary lifting table plate
14. It may be noted at this point that the air medium
may of course also be replaced by another gaseous
medium.
The essentially circular-disk-shaped turntable 30 is
rotatably mounted on a table frame 50 via a bell-shaped
support 46 by means of a ball bearing 48. The rotary
spindle device 18, which extends essentially at right
angles to the turntable 30, is arranged coaxially in
the interior of the bell-shaped support 46. A rotary
CA 02665618 2009-05-07
- 7 -
movement of the turntable 30, which is connected to the
rotary lifting table plate 14 in a rotationally fixed
manner, is driven by a belt drive (not depicted), the.
belt or toothed belt of which rests on the outer
circumferential surface of a hub element 52 of the
bell-shaped support 46.
The belt drive is operated, for example, by means of an
electric motor (not depicted).
The table frame 50 is connected in a rotationally fixed
manner to a rotary lifting table housing 54, which has
a fixed base plate 56 on the top side.
The stacking shaft 16, formed by the ejection devices
20, and the ejection directions A, A', in which the
associated outfeed conveyors 28 follow, can be seen
especially well in the plan view in fig. 2 of the
rotary lifting table 10 according to the invention. As
can be seen from the figure, in which the rotary
lifting table 10 is shown in a basi-c rotary position,
tongue-like extensions 58 of the rotary lifting table
plate 14, which are formed thereon on the wide side,
are in engagement with associated, U-shaped apertures
60 of the sliding plate 26. The sliding plates 26
arranged fixedly on the turntable 30 rotate, during a
rotation of the turntable 30, about a rotation axis D
defined by the longitudinal axis of the rotary spindle
device and in the process sweep over the base plate 56
with their radially outer end regions.
During the ejection of a stack of planar articles 12
from the stacking shaft 16, the stack of planar
articles 12, in the lowered state of the rotary lifting
table plate 14, is pushed by the angle profiles 24 of
the two ejection devices 20, which are each driven
synchronously, over the rotary lifting table plate 14
in a low-friction, sliding manner via the sliding
surfaces 32 of the sliding plates 26 in one of the
CA 02665618 2009-05-07
- 8 -
ejection directions A, A' onto the directly opposite
outfeed conveyor 28.
As can also be seen from fig. 2, the angle profiles 24,
in the free end regions of their legs projecting from
the transport means 22, are provided with profile
extensions 62 of U-shaped cross section. These profile
extensions 62 are preferably formed from an elastic
plastic material and reduce the risk of damage to the
planar articles 12 when the stack of planar articles 12
is being pushed out.
The opposite ejection devices 20 are each provided,
centrally with respect to their longitudinal axis, with
format adaptation elements 64 on the outer side
opposite the stacking shaft 16. These format adaptation
elements 64 permit a displacement of the ejection
devices 20 in the longitudinal direction of elongated
holes 66 formed in the turntable 30. Further format
adaptation can be carried out via a displacement of the
angle profiles 24 along the transport means 22 of the
ejection device 20.
As can likewise be seen from fig. 2, the air discharge
openings 34 of the sliding plates 26 are arranged in a
repetitive pattern, preferably in a regularly
distributed manner at least in sections. In this way,
an air cushion is formed as evenly as possible under
the stack of the planar articles 12. In the process,
too rapid an escape of air from the air cushion is
reduced by outer end regions of the planar articles 12,
lying flat one on top of the other, being arched
downward in the direction of the turntable 30 or the
base plate 56.
In the basic rotary position, shown in fig. 2, of the
rotary lifting table 10, as is assumed, for instance,
when ejecting a stack of planar articles 12, the
movable trailing cable 42, in which the common air feed
CA 02665618 2009-05-07
- 9 -
line 40A is guided, describes an essentially U-shaped
bend. During a rotation about the rotation axis D in a
direction of rotation DR, as indicated in fig. 2 by an
arrow, through 1800, the end rotary position shown in
fig. 3 is assumed.
In this end rotary position, the movable trailing cable
42 together with the common air feed line 40A is
rearranged in a worm shape. During the changeover from
the basic rotary position into the end rotary position,
the sliding plates 26 are each moved toward the outfeed
conveyor 28 arranged opposite in the basic rotary
position. During the rotation of the stack of planar
articles 12, the ejection directions A, A' are
therefore oriented toward the respective other outfeed
conveyors 28.
Fig. 3 indicates how the stack of planar articles 12 is
moved from the rotary lifting table plate 14 via the
sliding plate 26 to the assigned outfeed conveyor 28 by
synchronous movement of the angle profiles 24 together
with their profile extensions 62 in the ejection
direction A'.
The specific form of the sliding plates 26 and of their
sliding surfaces 32 may of course be adapted to the
specific requirements. It is thus possible, as in the
exemplary embodiment described, for the sliding plates
26 to extend into the stacking shaft 16 or to first be
arranged outside the stacking shaft.
In addition, it is possible to also provide the rotary
lifting table plate 14 with air discharge openings 34
like the sliding plates 26, pressurized air escaping
from said air discharge openings 34 to produce an air
cushion under the stack of planar articles 12. Contrary
to a rotationally fixed arrangement of the sliding
plates 26 on the turntable 30, as in the exemplary
embodiment described above, it is also conceivable to
CA 02665618 2009-05-07
-
fasten the sliding plates 26 to the base plate 56 of
the rotary lifting table housing 54 in a fixed
position. In addition to the flat sliding surfaces 32,
running essentially horizontally in the exemplary
5 embodiment described, of the sliding plates 26,
inclined or profiled sliding surfaces 32 are of course
also conceivable.
In all these cases, however, as in the exemplary
10 embodiment described, low-friction sliding of the stack
from the stacking shaft 16 in the ejection directions
A, A' to associated outfeed conveyors 28 is made
possible by means of the air cushion produced under the
stack of planar articles 12.