Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02669155 2009-05-11
WO 2008/065240 PCT/F12007/050598
Method and device in a fibre-web reeler
The invention relates to a method in a reeler of a fibre web according to the
pre-
amble of claim 1.
The invention also relates to a device in a reeler of a fibre web according to
the
preamble of claim 5.
The present invention relates to a method and a device in reeling a fibre web,
such
as a paper or board web, into a machine reel i.e. a reel corresponding to the
full-
width of the web. The width of machine reels is usually 2.0-10.0 m and the
diame-
ter 2.0-4.5 m naturally depending on the dimensioning of the paper or board ma-
chine.
As known from prior art, the machine reelers of a paper or board web are
usually
located at the end of the manufacturing line of the paper or board web and
with
them the completed fibre web is reeled into a machine roll around a reeling
shaft
i.e. a so-called spool. This is often followed by on-line or off-line
finishing appa-
ratuses by means of which customer rolls according to customer requirements
are
manufactured of the paper or board web. In reeling-up taking place in machine
reelers, a reeling drum arranged in a nip contact with the reeling shaft and
the web
roll forming around it is usually utilised. A problem in connection with the
ma-
chine reelers of a fibre web is that, when reeling fibre-web types having poor
air
permeability at high speeds, air is carried along inside the machine roll from
a nip
between the forming web roll and the reeling drum. Air inside the roll, again,
de-
creases the friction between the web layers in the roll, which can cause
different
reeling problems, such as reel falling, telescoping, edge displacement,
flagging,
wrinkles etc. With fibre-web types having poor air permeability, air can exit
the
roll / air can be removed from the roll principally only through the ends of
the
CA 02669155 2009-05-11
WO 2008/065240 PCT/F12007/050598
2
roll, which is problematic, because due to the deflections of the rolls and
the load-
ing of the reeling drum and the machine roll done from the ends of the reeling
shaft, the nip pressure profile is usually smiling i.e. the pressure is
greater in the
end areas of the roll than in the middle of the roll.
As known from prior art, one has tried to minimise above-described problems by
making onto the surface of the reeling drum a low groove which rises towards
the
edges and guides the air in the machine roll towards the edges of the roll. A
dis-
advantage of this arrangement is that the surface of the machine roll is not
always
even but can include rises and valleys, whereby, when a groove and a valley en-
counter, the nip pressure can be lower and thus at such a point a lot more air
can
penetrate the machine roll compared with other points. Furthermore, removing
air
from the edges is difficult as the nip load in the edge areas is higher than
in the
middle.
DE patent publication 199 27 897 describes a roll adjustable in its bow used
as a
contact or transfer roll. A contact roll is e.g. a roll used in reeling, which
is partly
covered by the web and which is in pressure contact with the forming web roll
and which prevents air from penetrating into the forming web roll especially
dur-
ing high reeling speeds. It is possible to us higher pressure in the middle of
the
contact roll compared to the pressure used at the ends in order to press the
air
travelling with the web to the sides.
US patent 6,604,703 shows a reeling cylinder using a reeling cylinder
adjustable
on its bow. In addition to the reeling cylinder a separate pressure roll can
be used,
which is pressed against the forming web roll before the reeling nip is
opened.
The separate press roll forms a roll nip after the reeling nip with the
forming web
roll and the aim of the roll nip is to prevent air from penetrating into the
web roll
when the reeling nip is opened.
CA 02669155 2009-05-11
WO 2008/065240 PCT/F12007/050598
3
EP patent publication 369 977 shows a reeler using a deflection compensated
reel-
ing shaft and a deflection compensated reeling cylinder. The idea of the
deflection
compensated reeling cylinder is to keep the nip pressure as even as possible
in the
reeling nip.
A roll adjustable in its bow is described in FI patent applications 20031384
and
20041287 which describe a roll for paper, board or fmishing machines in which
the outer shell of the roll is supported from its ends to the frame structures
of the
machine by means of an adjustable bearing so that both the direction and
amount
of the deflection of the outer shell can be controlled i.e. the bow of the
outer shell
of the roll can be adjusted for compensating the tightness differences between
the
edge and middle areas of the web. The roll consists of two parts supported to
each
other in the middle area of the roll, an inner tube and an outer shell. The
nominal
stiffness of the production material of the inner tube of the roll can be
substan-
tially greater than the nominal stiffness of the production material of the
outer
shell of the roll. A roll of this type with two shells, supported from the
middle,
adjustable of its bow, of equal diameter, a so-called T roll has been used
e.g. in
calenders as a fly roll.
An object of the present invention is to provide a method and a device in
reeling a
fibre web in which the above-described disadvantages and problems of arrange-
ments known from prior art have been eliminated or at least minimised.
A special object of the invention is thus to create a novel type of an
arrangement
by means of which the structure of the web roll can be affected.
To achieve the above-mentioned objects and those which come out later, a
method according to the invention is mainly characterised by what is presented
in
the characterising part of claim 1.
CA 02669155 2009-05-11
WO 2008/065240 PCT/F12007/050598
4
Again, a device according to the invention is mainly characterised by what is
pre-
sented in the characterising part of claim 5.
In the method and the device in reeling a fibre web according to the
invention, it
has been realised to affect the structure of the web roll by a separate roll
adjust-
able of its bow, by means of which is provided peripherical force affecting
the
forming web roll from the surface of the roll as surface draw different from
the
thoughts related to the reeling of machine rolls known from prior art in which
peripherical force has been typically provided by means of central force.
According to an embodiment of the invention, in reeling a fibre web for
affecting
the structure of the web roll, in connection with the reeler there is a
separate roll
adjustable of its bow which is used substantially for the whole time of
reeling and
by means of which a roll nip is provided at the forming web roll. The bow of
the
roll is advantageously adjusted so that the pressure in the roll nip between
the roll
and the forming web roll does not increase, advantageously decreases towards
the
ends of the reel, whereby e.g. it is easier to remove air from the structure
of the
web roll towards lower pressure. Then, the nip pressure profile of the roll
nip be-
tween the separate roll adjustable on its bow and the forming web roll is
substan-
tially even or lowers towards the edge areas (a sad profile).
According to an advantageous embodiment of the invention, the roll nip between
the separate roll adjustable of its bow and the forming web roll is
advantageously
located after the reeling nip advantageously as close as possible before the
start of
the next web layer. In this embodiment, also the reeling drum can be a roll
adjust-
able of its bow.
In the roll adjustable of its bow utilised in the method and the device
according to
the invention, the direction of the bow is advantageously adjustable, whereby
against the rotation direction of the forming web roll is provided a plough
effect
CA 02669155 2009-05-11
WO 2008/065240 PCT/F12007/050598
which facilitates the removal of air from the reel, because air exits the reel
in its
natural travel direction.
In connection with the invention, the bow and the direction of the bow of the
roll
5 adjustable of its bow are adjustable during run, whereby also the tightness
profile
of the forthcoming web can be affected.
By means of the equal-diameter roll adjustable of its bow utilised in
connection
with the invention, which thus advantageously substantially corresponds the
type
of a roll described in FI specifications 20031384 and 20041287 of its
structure, is
achieved as an advantage compared with crowned rolls according to prior art
that,
when using a roll according to the invention, no speed and thus tightness
differ-
ences of the cross direction of the web caused by diameter difference, e.g.
further
loosening of loose edges, will be created.
By means of the invention is provided minimising the total amount of air in
reel-
ing, because in the reeling nip between the reeling drum and the forming web
roll
the access of air into the web roll is prevented and in the roll nip between
the
separate roll adjustable of its bow and the web roll to be formed the air
possibly
remaining in connection with the web roll is removed.
The roll adjustable of its bow utilised in connection with the method and the
de-
vice according to the invention is advantageously covered with a suitable soft
cover, such as polyurethane or rubber, whereby the roll adapts to
irregularities
possibly on the surface of the machine reel, the air permeance of the web
being
reeled being low.
According to an advantageous additional characteristic of the invention, onto
the
surface of the roll is made a low groove rising towards the edges for further
en-
hancement of air removal. The spline of the groove can be multiplex.
CA 02669155 2009-05-11
WO 2008/065240 PCT/F12007/050598
6
According to an advantageous additional characteristic of the invention, the
roll is
provided with an electric drive for adapting the speed to the machine reel
speed.
The invention is applicable in connection with reelers utilised in reeling
different
machine reels, particularly advantageously the invention is applicable to be
util-
ised in connection with reelers marketed by the applicant with product names
Op-
tiReel and OptiReelPlus and equivalent types. The advantages achieved with the
invention become particularly evident when reeling fibre-web types having low
air permeability.
In connection with the invention advantageously, the nip force of the roll nip
is
adjusted by measuring the nip force from the ends of the roll with power
sensors
or by implementing to the roll the measuring of nip pressure profile based on
an
electro-magnetic foil or other pressure- or power-sensitive sensor or sensor
strip
directly from the nip. Furthermore, the nip profile can be measured and the
deflec-
tion and bow radius of the roll can be adjusted.
The invention will now be described in more detail with reference to the
figures of
the accompanying drawing, to the details of which the invention is, however,
by
no means intended to be narrowly confined.
Figure 1 schematically shows an embodiment of a roll adjustable of its bow to
be
used in connection with the invention.
Figs. 2-5 schematically show an embodiment of the invention in which the inven-
tion is applied in a reeler which utilises a stationary secondary position.
Fig. 1 schematically shows an embodiment of a roll 40 adjustable of its bow to
be
utilised in connection with the invention, in which an outer shell 42 of the
roll is
supported from its ends to the frame structure of the machine by means of an
ad-
justable bearing 45 so that the direction and amount of the deflection of the
outer
CA 02669155 2009-05-11
WO 2008/065240 PCT/F12007/050598
7
shell can be controlled i.e. the bow of the outer shell of the roll can be
adjusted for
levelling the tightness differences between the edge and middle areas of the
web.
The roll 40 consists of two parts supported to each other in the middle area
of the
roll, an inner tube 41 and the outer shell 42. The roll 40 illustrated in the
figure is
coated with a suitable soft cover 43, such as polyurethane or rubber. Onto the
sur-
face of the roll 40, it is possible to make a low groove (not shown) rising
towards
the ends of the roll 40. Advantageously, the roll 40 is provided with an
electric
drive (not shown). The roll 40 adjustable of its bow utilised in connection
with the
invention is advantageously of the type described in FI specifications
20031384
and 20041287, but also other corresponding types of rolls adjustable of their
bow
are applicable to be used in connection with the invention.
Next in Figs. 2-5, Fig. 2 schematically shows the reeling stage just before
trans-
ferring the reeling from the secondary position to the primary position i.e.
the
change stage; Fig. 3 schematically shows the reeling stage in which there is a
completed reel in the secondary position and the reeling transfers to the
primary
position; Fig. 4 schematically shows the reeling stage in which a completed
reel is
delivered from the secondary position and the reeling from the primary
position is
transferred to the secondary position; and Fig. 5 schematically shows the
reeling
stage in which reeling carriages are transferred to receive the next reeling
shaft,
the reeling continuing in the secondary position. In the figures, the same
designa-
tions are used of parts corresponding each other. In the embodiment shown in
Figs. 2-5 according to the invention, the structure of a web roll 20 is
affected with
a roll nip provided with a roll adjustable of its bow. The roll adjustable of
its bow
is a separate roll 40 arranged in a nip contact with the web roll by means of
which
is provided a roll nip with the web roll in addition to a reeling nip.
According to
an embodiment of the invention, into connection with the web roll is arranged
in
addition to the separate roll adjustable of its bow a reeling drum which is
adjust-
able of its bow.
CA 02669155 2009-05-11
WO 2008/065240 PCT/F12007/050598
8
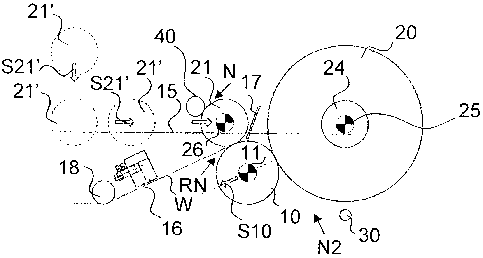
In the situation according to Fig. 2, the web W is reeled into the web roll 20
in the
stationary secondary reeling position. A secondary drive 25 is connected to a
reel-
ing shaft 24. In the vicinity of the secondary position, there is a surface
binding
device 30. During reeling, the reeling drum 10 is in a nip contact with the
forming
web roll 20. The drive of the reeling drum 10 has been referred to with
reference
number 11, and the direction of movement of the reeling drum 10 with reference
number S 10. In the situation described in the figure, the reeling is about to
be
changed around a next reeling shaft 21 which is provided with a primary drive
26
and positioned in reeling carriages (not shown in the figure). The reeling
shaft 21
has been brought to a nip contact with the reeling drum 10 and the change is
per-
formed by means of a water-changing device 16 by cutting the web W and e.g. by
means of an air-blowing device 17 by guiding the web W around the reeling
shaft
21. The roll 40 adjustable of its bow forms during the change the roll nip
assisting
the change and the bow of the roll 40 is adjusted during reeling so that the
nip
pressure profile of the nip between the ro1140 and the forming web roll 22 is
sub-
stantially even or lowering towards the edge areas, whereby the removal of air
towards the lower pressure is easier. The spreader roll of the web W is
designated
with reference number 18. In the embodiment shown in the figure, the reeling
carriages move on reeling rails 15. Dashed lines in the figure also show the
reel-
ing shafts of forthconii.ng reels with reference number 21' and their
direction of
movement in the transfer stage with reference arrows S21'.
In the situation according to Fig. 3, the reeling has transferred around the
new
reeling shaft 21 and the forming web roll has been designated with reference
number 22. The roll 40 adjustable of its bow forms a roll nip with the forming
web rol122 which nip removes air from the web roll. Furthermore, the direction
of
the bow of the roll 40 is advantageously adjustable, whereby against the
rotation
direction of the forming web rol122 is provided a plough effect which
facilitates
the removal of air from the reel, because air exits the reel in its natural
travel di-
rection. As is evident from the figure, the roll nip N between the rol140
adjustable
of its bow and the forming web rol122 is located after the reeling nip RN
advan-
CA 02669155 2009-05-11
WO 2008/065240 PCT/F12007/050598
9
tageously as close as possible before the start of the next web layer, still
typically
in the area of the upper part of the bow of the circle of the web roll 22. The
sur-
face of the completed web roll 20 situated in the secondary position is bound
with
the surface binding device 30 for preventing the loosening of reeling. The
surface
binding device 30 has been transferred by a manner shown with arrow S30 from a
stand-by position to a surface binding position (Fig. 2). In this stage, the
reeling
drum 10 and the forming new web roll 22 are transferred by a manner shown by
arrows S21 and S 10 apart from the web roll 20 in the secondary position.
In the situation shown in Fig. 4, the completed web roll 20' is transferred
away
from the secondary position. This transfer is shown with arrows S20. The
surface
binding device 30 has been detached from the web reel 30 and, in this stage,
the
forming web roll 22 is started to be transferred together with the reeling
drum 10
from the primary position in a manner shown by arrows S21 and S 10 towards the
secondary reeling position and, simultaneously, the roll 40 adjustable of its
bow
moves along the web roll 22 further forming the roll nip. The forthcoming posi-
tion of the forming web roll 22 and the reeling drum 10 in the secondary
position
is shown with dashed lines.
According to what is shown in Fig. 5, when the web roll in reeling has been
trans-
ferred to the secondary position, the web roll being reeled is designated
again with
reference number 20. The reeling carriages are returned, as shown with arrow
SV,
towards the next reeling shaft 21 which is transferred on the reeling rails
towards
the carriages for starting the reeling of the next web reel around the new
reeling
shaft 21, when the reel in the secondary position has grown to a desired
diameter.
The rol140 adjustable of its bow is in the stand-by position and transfers
into con-
nection with the new reeling shaft 21 as the reeling changes onto the new
reeling
shaft for reeling the next web reel.
CA 02669155 2009-05-11
WO 2008/065240 PCT/F12007/050598
The invention was described above only referring to some of its advantageous
embodiments, to the details of which the invention is, however, by no means in-
tended to be narrowly confined.
5