Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02673941 2009-06-26
SELF-PROPELLED CABLE SYSTEM FOR TRANSPORTING PERSONS,
INTENDED FOR AERIAL PANORAMIC ENVIRONMENTAL OBSERVATION
TECHNICAL FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The technical field of the invention is that of vehicles, devices, structures
and
installations used for the transportation of persons by cable that are self-
driven
and may serve to observe the scenery (environment) in a (aerial) panoramic way
with recreation and/or scientific purposes.
BACKGROUND TO THE INVENTION
There are different ways to make aerial panoramic observations of the
environment with recreation and/or scientific purposes, however, most of these
require very costly and sophisticated mechanical equipment, i.e., Airplanes,
helicopters, cableways, lift-cars, etc., and the intervention of highly
trained third
parties who are dedicated to operate the said equipment, so that their use is
limited to a few persons.
There are different cable transportation systems for people, however the great
majority are not self-driven and require special rails or lanes so that the
cost of
installation, maintenance and operation, increases.
There are other cheaper ways like the use of cables set at an angle so there
is a
level difference between the starting and ending points, through which the
user
slides using his own weight and gravity as the driving force. The user hangs
from
the cable through a pulley to which he is attached using straps, hooks and a
harness; these methods are inconvenient as they can only be used one way
(downwards), there is no real control of the speed, nor is it possible to stop
to
1
CA 02673941 2009-06-26
make detailed observations. In addition, the user must stop at the points of
cable
anchorage which must be fitted with a platform, remove his weight from the
cable, separate himself from the pulley and/or cable to re-attach again to the
same after the anchorage in order to be able to continue in his descending
tour.
In some cases, the same system is used in level stretches wherein the user
pulls
himself along the cable with his arms, which is not very practical as he is
using
the same to provide the driving force instead of having his arms ready to
observe
the environment with binoculars, take notes or pictures, in addition to the
quick
tiredness of the arms of any users, so the level stretch must be very short.
The problem to overcome is: How to attain a cable transportation device for
persons that allows for the aerial panoramic observation over any type of
terrain,
that is easy and cheap to build and maintain, and which will allow, in
addition,
any person with no prior training or specialized equipment to use it?
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FIGURES
Figure 1. General view of the self-driven cable transportation system for
persons
used for the aerial panoramic observation of the environment.
Figure 2. Detailed view of the vehicle of the self-driven cable transportation
system for persons used for the aerial panoramic observation of the
environment.
Figure 3. Detail view of the safety mechanism and the grooved wheels of the
self-driven cable transportation vehicle system for persons used for the
aerial panoramic observation of the environment.
Figure 4. Detail view of the mechanism to mount the self-driven cable
transportation vehicle system for persons used for the aerial panoramic
observation of the environment.
2
CA 02673941 2009-06-26
Figure 5. Front perspective view of the side-support bracket.
Figure 6. Front perspective view of the opposed support bracket.
Figure 7. Detail of (A) showing the tab coupling flange for the cable used in
the
brackets.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
The self-driven cable transportation system for persons used for the aerial
panoramic observation of the environment described herein, will allow for the
economic installation and operation of suspended cable through rough terrain
like mountains, jungles, ravines, rivers, forests, etc., with which a great
number of
people will be able to make observations, investigation and pictures of the
environment from an aerial panoramic perspective in a safe and comfortable
manner, without requiring any prior training and/or the use of costly
mechanized
equipment.
The system is essentially a cable suspended over the ground using special
brackets through which vehicles driven by the a user's feet run, through the
use
of these vehicles the user moves about in a safe and comfortable manner
through the line in order to observe the environment and transport himself
from
one place to the other of the line without having to stop at the cable's
anchoring
points.
The user has full control of the vehicle's speed, being able to accelerate,
break
and stop at will, having at all times both hands free to be able to take
notes,
snapshots, etc.
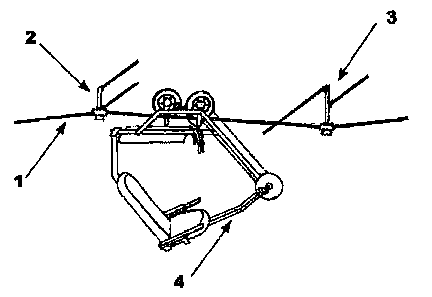
The self-driven cable transportation system for persons used for the aerial
panoramic observation of the environment is made up by a cable (1), which
3
CA 02673941 2009-06-26
allows the user to transport himself through any type of ground over which the
same is suspended. The journey, extension, level gradient and the way of
setting the route will vary according to the design of its path and the
different
variables of the ground over which it will be installed. The route is made up
mainly of a cable, preferably of steel, which is run along the route of the
desired
path using brackets which support and provide the tension. Two types of
brackets have been used: the side -support bracket (2) and the opposed-
support
bracket (3), which are fixed to any natural element available like trees,
rocks,
etc., or if necessary, to any type of artificial element, like poles, towers,
constructions, etc.. These brackets allow the system's vehicle (4) to run
freely
along the route without need for stopping or making transfers in the places of
the
cable anchoring (Figure 1).
The cable (1), once installed over the ground using the brackets (2, 3) may be
used by several vehicles (4) at the same time, having to limit their number
according to the resistance of the natural or artificial elements to which the
brackets have been fixed and with the resistance specifications of the
materials
used in the construction of same.
The vehicle (4) in which the user travels driving it with his legs and feet
along the
cable, has among its main elements: A frame made of a rigid material like
welded
metal (5) with a hook-shaped arm of the top (20) made of the same material; a
seat with backrest (6), wherein the user may sit comfortably and recline his
back.
This seat may be adjusted by sliding horizontally and vertically within the
frame
of the vehicle in order to fit the sizes of the different users. This seat has
safety
straps which fasten the user to the vehicle avoiding accidental falls; A top
(roof)
(7), designed to protect the user against possible impacts, from the rain and
the
sun, in addition to forming a barrier to avoid accidental contact of his head
or
hands with the cable and the grooved blocks (13). This top may have different
shapes and be made of different materials; Two grip bars, a lower one (8)
placed
at the seat, and a higher one (9) fixed to the frame, which the user may take
4
CA 02673941 2009-06-26
momentarily to stabilize or break if he so desires, without this being
necessary for
the operation of the vehicle; A traction mechanism (11) with pedals,
sprockets,
chain and the grooved wheels, driven by the user's legs and feet, which
provides
the drive force that moves the vehicle through the cable route, the pedals may
have elements allowing them to be fixed to the user's feet, and a braking
system
installed at the grooved wheels (13) which its actuated by a handle (10)
located
on the higher handgrip (Figure 2).
The vehicle (4) hangs from the cable line through a hook - shaped arm (20),
where the grooved wheels (13) and the hanging mechanisms are (14); these
elements, along with the vehicle frame (5) form a safety system to keep the
same
from being removed from the cable line while in use. However, this versatile
safety system allows the vehicle to be easily removed from the cable whenever
the user is not in the same. In order to remove it, it is necessary to take
the
vehicle, lift it and maintain it parallel to the cable (1) push it to the
front a few
centimeters, with which the vehicle will be released from the cable. This is
possible because it has an open side (12) and precise distances in relation to
the
grooved blocks (13), to the hanging system (14) and to the vehicle's frame
(5);
this mechanism allows the vehicle to run freely through the brackets, but in
case
of jumping out of the grooves, the angle created by the vehicle with respect
to the
cable (1) is sufficient for the vehicle assisted by gravity to seize or lock
to the
cable (Figure 3).
The vehicle displaces through the cable by means of two grooved wheels(13)
with a rolling surface lined in rubber. One of them is idle, while the other
provides the traction using a chain and sprockets mechanism driven by the
user's
feet (11).
The vehicle has a mechanism to hang properly from the cable, consisting in a
set
of "V" shaped guides (14), which align the grooved wheels of the vehicle (13)
with the cable (1) in case of incorrect alignment or jumping out of track,
this
CA 02673941 2009-06-26
mechanism is found at the bottom and at each side of the grooved wheels. This
mechanism forms a "V" which allows the vehicle to keep the optimal alignment
with the cable without using moving parts. This mechanism is also designed to
allow the free passage of the vehicle through the brackets (Figure 4).
The "L" shaped brackets, supporting and providing tension to the cable route
(1),
are made of a rigid material which is strong enough to support the weight of
the
cable and of the vehicles like for example, welded metal. The brackets, at
their
lower open side have a ledge with a tab coupling flange (15) to support the
cable
(1).
Brackets are fixed by means of two cables to any type of natural element
available like trees, rocks, etc., or if necessary, to any type of artificial
element,
such as poles, towers, constructions, etc. the system uses two different types
of
brackets, chosen depending on the direction in which the cable route (1) is to
be
laid-out.
The bracket with side support (2) is connected to the tensor cable (16) and to
the
positioning cable (17) in its closed side, that is, on the outer part of the
long side
of the "L", which allows pulling the cable route (1) toward the closed side of
the
bracket, making the cable route turn in that direction. This is achieved by
pulling
the lateral tensor cable (16). Once the said cable has been fixed, the
positioning
cable (17) allows adjustment of the bracket so that it stays straight, thus
allowing
passage of the vehicle (Figure 5).
The opposed support bracket (3) is connected to the opposed tensor cable (18)
at the open side or internal part of the long side of the "L", and the
positioning
cable (17) is connected to its closed side, that is, that the external part of
the long
side of the "L", which allows pulling the cable line (1) toward the open side
of the
bracket, and making the cable route tum in that direction. This is achieved by
pulling the opposed tensor cable (18). Once the said cable is fixed, the
positioning cable (17) allows adjusting the bracket so that it remains
straight, thus
6
CA 02673941 2009-06-26
allowing passage of the vehicle (Figure 6).
At their open side, brackets have a ledge with a tab coupling flange allowing
them to support the cable (1). This coupling flange surrounds the cable and
fixes
it to the bracket with screws (19). This tab coupling flange allows for the
brackets
to be installed and removed from the cable easily and quickly, making it
possible
to maintain and repair the cable route in an efficient and economic manner
(Figure 7).
The brackets, the safety mechanism, and the mechanism for proper hanging are
designed in such a way that they allow the vehicle to displace safely and
continuously along the cable. The brackets support the cable on the side
allowing the vehicle to pass. The mechanism to ensure proper hanging passes
above the bracket, while the vehicle frame passes below the same (Figure 4).
From the aforesaid, it can be affirmed that the features of the self-driven
cable
transportation system for persons used for the aerial panoramic observation of
the environment, are unique and exclusive of same, as these have not been
achieved by any other similar existing artifact.
7