Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02693757 2010-02-19
This application is a divisional of Canadian Patent Application No. 2,515,252
filed March 12, 2004.
INFORMATION STORAGE MEDIUM STORING A PLURALITY OF TITLES,
REPRODUCING APPARATUS AND METHOD THEREOF
Technical Field
The present invention relates to reproduction of audio/video (AV) data, and
more
particularly, to an information storage medium on which AV data and data
providing a
navigation function such as a search function are recorded, and an apparatus
and
method of reproducing the data.
Background Art
Video titles are composed of AV data which is recorded on a Digital Video Disc
(DVD)-Video disc. Additionally, navigation data which enables a user to select
superimposed dialogues or search for scenes is also recorded on the DVD-Video
disc
reproducing the video titles.
However, there is a demand for more interaction with users and more efficient
reproduction of the AV data.
Disclosure of the Invention
The present invention provides an information storage medium with a data
structure in which audio/vid.eo (AV) data can be efficiently reproduced and a
navigation
function can be efficiently performed, and a reproducing apparatus and method
of
reproducing titles as motion pictures.
The present invention further provides an information storage medium with a
data structure through which various applications can be provided, and a
reproducing
apparatus and method of providing the various applications.
According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided an
information
storage medium including: a plurality of titles which are reproduced as motion
pictures;
1
CA 02693757 2010-02-19
and a plurality of units of attribute information, which correspond to the
titles and
indicate whether a user can control a title to be reproduced.
The titles may be recorded with core mode data which includes audio/video data
and navigation data reproducing the audio/video data.
Each of the titles may include at least one navigation object, and the at
least one
navigation object may include a navigation command which provides a command to
a
playlist corresponding to the title.
The title may include core mode data, which includes audio/video data and
navigation data reproducing the audio/video data; and full mode data, which
includes
program data that enables interaction with a user and browsing data that
enables
Internet browsing, or the title may include a navigation object, and at least
one of a
browsing object that enables web browsing and a program object that enables
interaction with a user.
Additional aspects and/or advantages of the invention will be set forth in
part in
the description which follows and, in part, will be obvious from the
description, or may
be learned by practice of the invention.
According to another aspect of the invention, there is provided an information
storage medium including: a plurality of titles which are reproduced as moving
pictures;
and title access type information which corresponds to the titles and
indicates whether a
corresponding title can be searched for by a user operation.
The title access type information may further include title number display
type
information indicating whether a title number of the corresponding title is
displayed.
According to another aspect of the present invention, a reproducing apparatus
includes a reader, which reads a plurality of titles to be reproduced as
motion pictures
and a plurality of units of title information that correspond to the titles; a
buffer, which
buffers the data read by the reader; and a decoder, which interprets the title
information
2
CA 02693757 2010-02-19
to indicate an entry point of a title and reproduces the title, wherein the
decoder
interprets attribute information contained in the title information to
indicate whether a
user can control the title to be reproduced.
The decoder may reproduce the titles, which are recorded with core mode data
that includes audio/video data and navigation data reproducing the audio/video
data,
execute at least one navigation object that is indicated by the entry point of
the title, or
execute a navigation object that includes a navigation command that provides a
command to reproduce a playlist corresponding to the title.
The decoder may reproduce the title which includes: core mode data, which
includes audio/video data and navigation data reproducing the audio/video
data; and full
mode data, which includes program data that enables interaction with a user
and
browsing data that enables Internet browsing, execute at least one of a
navigation
object corresponding to the title, a browsing object that enables web
browsing, and a
program object that enables interaction with a user, or execute the navigation
object
implemented as a command program which provides a command to reproduce the
playlist, the browsing object implemented as a file, which is recorded with a
markup
language and an executing script language, and the program object implemented
as a
specific program file.
The decoder may determine that the title can be searched for by the user
operation if access type information as the attribute information represents
the title as
"normal title", and the title cannot be searched for by the user operation if
the access
type information represents the title as "hidden title". If the access type
information
represents the title as "hidden title", the decoder may display a title number
of the title
when the title is reproduced according to information which is contained in
the attribute
information that indicates whether the title number of the title is displayed.
According to still another aspect of the present invention, there is provided
a
reproducing method including: reading a plurality of titles that are
reproduced as motion
pictures and a plurality of units of title information that correspond to the
titles; and
3
CA 02693757 2010-02-19
interpreting attribute information included in the title information that
indicates whether a
user operation can search for a corresponding title, interpreting the title
information to
indicate an entry point of the title, and reproducing the title.
The information interpreting and title reproducing may include reproducing the
titles that are recorded with core mode data that includes audio/video data
and
navigation data for reproducing the audio/video data, executing at least one
navigation
object that is indicated by the entry point of the title, or executing a
navigation object
that includes a navigation command that provides a command to reproduce a
playlist
corresponding to the title.
The information interpreting and title reproducing may include reproducing the
title which includes: core mode data, which contains audio/video data and
navigation
data for reproducing the audio/video data; and full mode data, which contains
program
data that enables interaction with a user and browsing data that enables
Internet
browsing, executing at least one of a navigation object corresponding to the
title, a
browsing object that enables web browsing, and a program object that enables
interaction with a user, or executing the navigation object implemented as a
command
program which provides a command to reproduce the playlist, the browsing
object
implemented as a file, which is recorded with a markup language and an
executing
script language, and the program object implemented as a specific program
file.
The information interpreting and title reproducing may include determining
that
the title can be searched for by the user operation if access type information
as the
attribute information represents the title as "normal title", and the title
cannot be
searched for by the user operation if the access type information represents
the title as
"hidden title". If the access type information represents the title as "hidden
title", the
information interpreting and title reproducing step may include displaying a
title number
of the title when the title is reproduced according to information which is
contained in the
attribute information that indicates whether the title number of the title is
displayed.
Brief Description of the Drawings
4
CA 02693757 2010-02-19
These and/or other aspects and advantages of the invention will become
apparent and more readily appreciated from the following description of the
embodiments, taken in conjunction with the accompanying drawings of which:
FIGS. 1A, 1 B, and 1 C are diagrams illustrating various kinds of data
recorded on
a disc 100 according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2A is a diagram illustrating the relationship between reproduction modes
of
the disc 100 of FIG. 1A or 1 B.
FIG. 2B is a diagram illustrating the relationship among reproduction modes of
the disc 100 of FIG. 1C.
FIG. 3A is a block diagram of a reproducing apparatus which supports both a
core mode and a full mode according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 3B is a detailed block diagram of the reproducing apparatus of FIG. 3A.
FIG. 4A is a diagram explaining a method of reproducing core mode data
recorded on the disc 100 of FIG. 1A or 1 B.
FIG. 4B is a diagram explaining a method of reproducing core mode data and
full
mode data recorded on the disc 100 of FIG. 1C.
FIG. 5A is a diagram illustrating a data structure of a title #i which is unit
information of title information according to the present invention.
FIG. 5B is a diagram illustrating a data structure of a hidden title #i which
is unit
information of the title information according to the present invention.
Best mode for carrying out the Invention
Reference will now be made in detail to the embodiments of the present
invention,
examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings, wherein like
reference
numerals refer to the like elements throughout. The embodiments are described
below
to explain the present invention by referring to the figures. .
FIGS. 1 A, 1 B, and 1 C are diagrams illustrating various kinds of data
recorded on
a disc 100 according to an embodiment of the present invention. Data having
the same
function are given the same reference numerals. However, although the data are
given
CA 02693757 2010-02-19
the same reference numerals, the data may be different from one another with
respect
to the contents and structure.
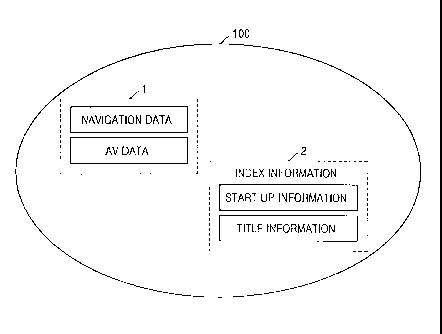
Referring to FIG. 1A, core mode data 1 and index information 2 are stored on
the
disc 100. The core mode data 1 comprises audio/video (AV) data that includes a
plurality of titles and navigation data which has a plurality of navigation
commands
navigating the AV data, similar to a conventional digital video disc (DVD)-
Video disc.
The structure of the core mode data meets the requirements of the DVD-Video
standards.
The index information 2 is system data, which enables a user to search for the
core mode data 1 or reproduce the core mode data 1. The index information 2
designates reproduction paths of the plurality of titles that are recorded in
the core mode
data 1 according to a disc manufacturer's intentions. More particularly, the
index
information 2 comprises start up information and title information. The start
up
information indicates the initial AV data of a title that is to be reproduced
when the disc
100 is inserted into a reproducing apparatus. The title information indicates
the initial
AV data of the plurality of titles to be reproduced and attribute information,
which are
referred to when reproducing the plurality of titles stored in the disc 100.
The attribute
information indicates whether a user can directly control a title to be
reproduced. If the
user cannot directly control the title to be reproduced, the attribute
information may
further contain information which indicates whether a title number of the
title is displayed.
A mode in which the start up information contained in the index information 2
is
reproduced is referred to as a start up mode. A mode in which the core mode
data 1 is
reproduced is referred to as a core mode or movie mode and the core mode is
performed in the same manner as in the conventional DVD-Video disc.
Referring to FIG. 1 B, core mode data 1 and index information 2 are stored on
the
disc 100, similarly to FIG. 1A. However, the index information 2 shown in FIG.
1 B
comprises start up information, title information, and menu information.
6
CA 02693757 2010-02-19
The core mode data 1 comprises AV data that includes a plurality of titles and
navigation data which has a plurality of navigation commands navigating the AV
data,
similar to the conventional DVD-Video disc.
The start up information has the entry point that indicates the initial AV
data of a
title that is to be reproduced when the disc 100 is inserted into a
reproducing apparatus.
The title information has the entry point that indicates the initial AV data
of the plurality of
titles to be reproduced and attribute information, which are referred to when
reproducing
the plurality of titles stored in the disc 100. The attribute information
indicates whether a
user can directly control a title to be reproduced. If the user cannot
directly control the
title to be reproduced, the attribute information further contains information
which
indicates whether a title number of the title is displayed. This information
is referred to
as title number display type information.
The menu information displays a list of titles that can be selected and
reproduced
by the user among the plurality of titles that are recorded with the AV data,
such that the
user can select one of the titles.
Referring to FIG. 1 C, core mode data 1, index information 2, and full mode
data 3
are stored on the disc 100. The full mode data 3 comprises program data that
enables
interaction with the user, and browsing data that enables Internet browsing.
Java
applications that provide various functions for interaction with users can be
included in
the program data. The browsing data includes a markup document that is
recorded with
a markup language such as Extensible Markup Language (XML), a markup document
that includes or links a script code such as a European Computer
Manufacturers'
Association (ECMA) script code, a script file, and a resource file including
at least one
image, graphic, and sound referred to by a markup document.
The full mode data 3 and the core mode data 1 can communicate with each other
using an Application Program Interface (API).
7
CA 02693757 2010-02-19
The titles include several different mode data. In other words, the titles
include at
least part of the AV data which is included in the core mode data 1 and the
browsing
data and the program data which are included in the full mode data 3. For
example,
while a movie is being displayed, a quiz relating to a scene can be displayed,
or an
Internet page giving the latest information about actors and actresses
appearing in the
scene can be displayed.
The index information 2 is system data, which enables the user to more
conveniently search for or reproduce the core mode data 1 and the full mode
data 3.
The index information 2 designates reproduction paths of the plurality of
titles that are
comprised of the core mode data 1 and the full mode data 3 according to the
disc
manufacturer's intentions. More particularly, the index information 2
comprises start up
information, title information, and menu information, similarly to the index
information
described with reference to FIG. 1 B. The title information indicates the
initial AV data of
the plurality of titles to be reproduced and attribute information, which is
referred to
when reproducing the plurality of titles stored in the disc 100. The attribute
information
indicates whether the user can directly control a title to be reproduced. If
the user
cannot directly control the title to be reproduced, the attribute information
may further
contain information which indicates whether a title number of the title is
displayed.
Similar to the modes described with reference to FIGS. 1A and 1 B, a mode in
which the start up information and the menu information are reproduced is
referred to as
a start up mode, a mode in which the core mode data is reproduced is referred
to as a
core mode, a mode in which program data is reproduced is referred to as a
program
mode, and a mode in which the browsing data is reproduced is referred to as a
browsing mode.
When the disc 100 is reproduced, the reproducing apparatus first reads the
start
up information and searches for data indicated by the start up information to
reproduce
the data. If the start up information provides instructions to reproduce the
core mode
data, the reproducing apparatus is set to the core mode, if the start up
information
8
CA 02693757 2010-02-19
provides instructions. to reproduce the program data, the reproducing
apparatus is set to
the program mode, and if the start up information provides instructions to
reproduce the
browsing data, the reproducing apparatus is set to the browsing mode.
For example, the AV data shown in FIGS. 1A, I B, and 1 C is recorded as an AV
stream file that is encoded using a Motion Picture Experts Group (MPEG)-II
encoding
method. A continuous AV stream file is called a clip stream file. A clip
information file
corresponds to each clip stream file. Reproduction control information
regarding the clip
stream file, for example, mapping information which maps a reproduction time
and a
recording position, is stored in the clip information file. The clip
information file that
corresponds to the clip stream file is referred to as a clip.
A playlist indicates at least a part of one of the clips. In other words, the
playlist
is a unit of reproduction, and corresponds to one clip, a part of one of the
clips, a
plurality of the clips, or parts of a plurality of the clips. The playlist can
be reproduced
via the API as an object in the browsing mode and the program mode. A playlist
is a
unit of reproduction described from a player's point of view while a title is
a unit of
reproduction described from the user's point of view. That is, a title
corresponds to at
least one playlist.
The navigation data is typically stored in the form of a binary code table. In
an
embodiment of the present invention, the navigation data includes a plurality
of
commands including commands reproducing a predetermined playlist and commands
reproducing another playlist during the reproduction of the predetermined
playlist.
FIG. 2A is a diagram illustrating the relationship between reproduction modes
of
the disc of FIG. 1A or 1 B. Referring to FIG. 2A, after the disc 100 of FIG. 1
A or 1 B is
loaded into the reproducing apparatus, the reproducing apparatus reads the
start up
information and determines the location from which the initial AV data of a
title is to be
reproduced so as to initiate the reproduction of the title. For example, the
start up
information can be implemented using a navigation command that provides
instructions
9
CA 02693757 2010-02-19
to reproduce'a specific playlist that should be reproduced. After the start up
mode is
completed, the mode is changed into core mode.
FIG. 2B is a diagram illustrating the relationship among reproduction modes of
the disc 100 of FIG. 1C. Referring to FIG. 2B, after the disc 100. of FIG. IC
is loaded
into the reproducing apparatus, the reproducing apparatus reads the start up
information and determines the location of the initial AV data of a title
which is to be
reproduced so as to initiate the reproduction of the title. For example, the
start up
information can be implemented using a navigation command which gives
instructions
to reproduce a specific playlist that should be reproduced. After the start up
mode is
completed, the mode is changed into the core mode.
Because some reproducing apparatuses can reproduce only the core mode data,
both core start up information and full start up information must be included
in the start
up mode. If the core start up information does not exist, a reproducing
apparatus that
can reproduce only the core mode data cannot operate. Particularly, when a
disc in
which the start up information only provides instructions to reproduce the
full mode data,
it is impossible to initiate reproduction. For this reason, both the core
start up
information and the full start up information are provided in the start up
mode, so that
the reproducing apparatus that can reproduce only the core mode data can
initiate
reproduction using the core start up information.
If the start up information contains commands to initially reproduce core mode
data 1, the start up mode is converted into the core mode. If the start up
information
contains commands to initially reproduce the full mode data, the start up mode
is
converted into the full mode.
FIG. 3A is a block diagram of a reproducing apparatus which supports both the
core mode and the full mode according to an embodiment of the present
invention.
Referring to FIG. 3A, the reproducing apparatus reproduces the AV data in the
core mode or the full mode by using the core mode data 1 and/or the full mode
data 3
CA 02693757 2010-02-19
stored in the'disc 100. The reproducing apparatus includes a reader 10, a
buffer 20,
and a decoder 30.
The reader 10 reads the necessary data from the disc 100. The buffer 20
buffers
the data read by the reader 10. The decoder 30 decodes and outputs the data
buffered
by the buffer 20.
FIG. 3B is a detailed block diagram of the reproducing apparatus of FIG. 3A.
Referring to FIG. 3B, the buffer 20 includes a browsing data buffer 21 which
buffers the browsing data, a program data buffer 22 which buffers the program
data, a
navigation data buffer 23 which buffers the navigation data, an AV data buffer
which
buffers the AV data, and an index information buffer 25 which buffers the
index
information.
The decoder 30 includes a browsing engine 31 which interprets the browsing
data and executes browsing commands, a program engine 32 which interprets the
program data and executes program commands, a navigation engine 33 which
interprets the navigation data and executes navigation commands, and a
presentation
engine 34 which decodes the AV data. These engines can transmit information to
one
another via the API.
In particular, the decoder 30 includes an application manager 35 which
interprets
the index information. The application manager 35 selects and reproduces a
title which
is to be first reproduced according to an entry point indicated by the start
up information
contained in the index information, and informs the engine corresponding to
the entry
point according to mode conversion during the reproduction. Further, the
application
manager 35 receives a user's input and transmits the input to the engine that
corresponds to the user's input mode.
FIG. 4A is a diagram explaining a method of reproducing the core mode data
stored in the disc 100 of FIG. 1A or 1B.
11
CA 02693757 2010-02-19
Referring to FIG. 4A, the title information comprises a plurality of units of
information, each of which designates a navigation object. The unit
information is
implemented as a title #i or a hidden title #j. The title #i can be reproduced
in response
to a user. The hidden title #j cannot be reproduced by the user. That is, the
hidden title
#j is reproduced only in the order predetermined by a manufacturer of the disc
100. In
other words, allowing reproduction control allows the titles to be searched
for by a user
initiated operation.
When a specific title is selected through a title search in the disc 100 of
FIG. 1A
or the menu information is reproduced and one of the titles shown in the menu
is
selected from the disc 100 of FIG. 1B, the title information indicates an
entry point where
data is to be initially executed or reproduced, that is, a navigation object.
The
navigation object is implemented as an executable navigation command program.
In
other words, the navigation object is an upper layer of the playlist that is a
unit of
reproduction, and includes the navigation command that initiates the
reproduction of the
specific playlist.
For example, if the user selects a first title #1, the first title #1 includes
title
information that designates a first navigation object #1, thereby executing
the first
navigation object #1. The first navigation object #1 includes a navigation
command.
When the navigation command is executed, a predetermined playlist is
reproduced.
After the playlist is reproduced according to the first navigation object #1,
the first
navigation object #1 indicates a first hidden title #1, and a third navigation
object #3
designated by the first hidden title #1 is executed. Here, a hidden title is
not directly
selected by the user to be reproduced. The hidden title is only reproduced in
the order
predetermined by the disc manufacturer. For example, a moving picture
including an
official announcement about a copyright, a moving picture of a trailer
broadcasted after
a movie ends, etc. can be a hidden title. Because these moving pictures are
searched
by the user operation and need little be reproduced separately, these moving
pictures
are set to hidden titles and are reproduced only in the order determined by
the
navigation command.
12
CA 02693757 2010-02-19
If the user selects a second title #2, the second title #2 designates a second
navigation object #2, thereby executing the second navigation object #2. The
second
navigation object #2 also includes a navigation command for reproducing a
predetermined playlist. The predetermined playlist is reproduced when the
navigation
command is executed. After the playlist is reproduced according to the second
navigation object #2, the second navigation object #2 indicates a second
hidden title #2,
and a fifth navigation object #5 designated by the second hidden title #2 is
executed.
FIG. 4B is a diagram explaining a method of reproducing the core mode data and
the full mode data stored in the disc 100 of FIG. 1C.
Referring to FIG. 4B, the index information includes the start up information,
the
menu information, and the title information. The title information comprises a
plurality of
units of information each of which designates a navigation object. The unit
information
is implemented as a title #i or a hidden title #j. The title #i can be
controlled by the user
to be reproduced and the hidden title #j cannot be controlled by the user to
be
reproduced. That is, the hidden title #j is reproduced only in the order
predetermined by
the manufacturer of the disc.
When the disc 100 is loaded into the reproducing apparatus, a plurality of
navigation objects are reproduced according to the start up information. If
the user calls
a menu, the menu information is reproduced. If the user selects one of the
titles shown
in the menu, the title information indicates an entry point where data is to
be initially
executed or reproduced, that is, an object.
In an embodiment of the present invention, the object is divided into a
navigation
object corresponding to the core mode data, a browsing object corresponding to
the
browsing data, and a program object corresponding to the program data. The
navigation object is implemented as a command program that provides a command
to
reproduce the core mode data, and the browsing object is implemented as a file
that is
recorded with the browsing data, for example, with a markup language and an
13
CA 02693757 2010-02-19
executing script language, and has a file name as an entry point. The program
object is
implemented as a specific program file which has a file name as an entry
point.
One object belonging to a predetermined mode can be connected to another
object belonging to another mode so as to be reproduced. When objects
belonging to
the same mode are connected to one another, mode conversion is not required.
However, mode conversion is required when objects belonging to different modes
are
connected to one another. The mode conversion is carried out using the hidden
title
information contained in the title information. That is, the title information
indicates an
entry point for title search and an entry point for reproduction of a
predetermined title,
and the hidden title information indicates an entry point for mode conversion
among the
core mode, the browsing mode, and the program mode.
After the disc 100 of FIG. 1 C is loaded, the reader 10 of the reproducing
apparatus reads the index information 2 and transmits the read index
information 2 to
the application manager 35. The application manager 35 provides instructions
from the
start up information to indicate a title which is to be initially reproduced.
Alternatively, if
the user calls a menu and selects a title among the titles shown in the menu,
the
application manager refers to an entry point of the selected title and
transmits an object
designated by the selected title to the engine corresponding to the selected
title.
According to an embodiment of the present invention, because the initial title
to be
reproduced as instructed by the start up information is a navigation object,
in operation
1, an entry point of the navigation object is transmitted to the navigation
engine 33. The
navigation engine 33 commences the reproduction of the core mode data by
transmitting a navigation command contained in the navigation object to the
presentation engine 34. In operation 2, another navigation object designated
by a first
title #1 is reproduced after the navigation object is first executed in the
core mode. The
navigation object reproduced in operation 2 may be reproduced in operation 3
through a
title search. In the same manner, second and third titles #2 and #3 are
respectively
connected to the browsing object and the program object in operation 4 and 5,
and the
titles can be reproduced when the user provides a command to reproduce them.
14
CA 02693757 2010-02-19.
In operation 6, the navigation object designated by the first title #1 is
connected
to the browsing object via a first hidden title #1. In other words, the mode
conversion is
performed with reference to the first hidden title #1. In this case, the
navigation engine
33 transfers control to the application manager 35. The application manager 35
provides instructions to the browsing engine 31 to reproduce the browsing
object
designated by the first hidden title #1. In this way, the hidden title cannot
be directly
accessed by the user. Because a title can include data in a variety of modes
through
the mode conversion with reference to the hidden title, the user can reproduce
the title
without regard to the mode conversion.
FIG. 5A is a diagram illustrating a data structure of a title #i according to
an
embodiment of the present invention.
Referring to FIG. 5A, the title #i includes access type information that acts
as
attribute information. The title #i also indicates an entry point of a title.
The access type
information indicates whether the user can directly control the title to be
reproduced.
Since the title #i permits the user's direct access, the access type
information
represents the title #i as "normal title".
FIG. 5B is a diagram illustrating a data structure of a hidden title #i
according to
an embodiment of the present invention.
Referring to FIG. 5B, the hidden title #j also includes access type
information that
acts as attribute information, and indicates an entry point of a title. The
access type
information indicates whether the user can directly control the title to be
reproduced.
Because the hidden title #j prohibits the user's direct access, the access
type
information represents the title #ji as "hidden". The access type information
further
contains information that indicates whether a title number of the "hidden"
title is
displayed to the user. That is, the access type information displays the title
number
when the title number is allotted to the hidden title and does not display the
title number
when the title number is not allotted to the hidden title.
CA 02693757 2010-02-19
For example, assuming that the access type information is represented in a
binary form, if the value of 1 bit of the access type information is "1 ", the
title is a hidden
title that is used only as a bridge point for mode conversion, while if the
value of the
access type information is "0", the title is a normal title that can also be
used as an
access point for title search.
Table 1 shows a case where only title access type information of 1 bit is
included
in the attribute information and Table 2 shows a case where title access type
information
and title display information are included in the attribute information,
respectively. Here,
the attribute information may be index table information.
Table I
Title
Result
access type
0 Title search is allowable by a user
1 Title search is not allowable by a user
Table 2
Title
Result
access type
00 Title search is allowable by a user and a title number is
displayed
01 Title search is allowable by a user and a title number is not
displayed
Title search is not allowable by a user and a title number is
16
CA 02693757 2010-02-19
displayed
11 Title search is not allowable by a user and a title number is not
displayed
Referring to Table 2, a first bit of the title access type indicates whether a
corresponding title can be searched for directly by a user operation or
whether the
corresponding title can be searched for only by a navigation command. A second
bit of
the title access type indicates whether the title number is displayed to a
user.
The present invention may be embodied in a general purpose digital computer by
running a program from a computer usable medium, including but not limited to
storage
media such as magnetic storage media (e.g., ROMs, RAMs, floppy discs, hard
discs,
etc.), optically readable media (e.g., CD-ROMs, DVDs, etc.) and carrier waves
(e.g.,
transmissions over the Internet). The computer readable recording medium can
be
dispersively installed in a computer system connected to a network, and stored
and
executed as a computer readable code in a distributed computing environment.
As described above, because attribute information indicates whether a
plurality of
titles are hidden titles or not, a disc manufacturer can produce contents with
which
various applications can be made. That is, because the titles are divided into
titles that
can be accessed directly and titles that can only be accessed in a
predetermined order
determined by the manufacturer of the disc, contents suitable for the disc
manufacturer's intentions can be produced. Accordingly, various applications
can be
provided to users.
Although a few embodiments of the present invention have been shown and
described, it would be appreciated by those skilled in the art that changes
may be made
in this embodiment without departing from the principles and spirit of the
invention, the
scope of which is defined in the claims and their equivalents.
17