Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02712442 2010-07-16
PatXML 1/17 PWO07XO4P
Description
SUCTION PUMP FOR A DISPENSER UNIT AND DISPENSER UNIT
Technical Field
[0001] The invention relates to a suction pump which is constructed in
particular
as a bellows pump and is provided for a dispenser unit for the delivery of
medium in paste, foam or liquid form, in particular of a liquid soap, a skin
protection cream or another liquid cleansing- or care product for the skin.
The suction pump has fastening means here for its sealed fastening to a
storage container for the liquid medium and has a pumping chamber, hav-
ing an elastic wall, able to be compressed elastically as a result of a pump-
ing force in a pumping direction, which is connected fluidically directly or
indirectly on the one hand with intercalation of an outlet valve with a deliv-
ery means to deliver a defined quantity of the medium, and on the other
hand is able to be connected fluidically directly or indirectly with the stor-
age container with intercalation of an inlet valve.
[0002] The invention further relates to a dispenser unit for the delivery of a
me-
dium in liquid, paste or foamed form, wherein the medium is provided in
particular in liquid or paste form in the storage container. These dispenser
units have a dispenser housing into which a filling insert is able to be
placed. The filling insert preferably consists of a storage container pro-
duced by a blow moulding process and the suction pump which is
mounted thereon. Such filling inserts are mostly inserted into the dispenser
housing after opening up a housing cover, such that the suction pump is
gripped with its head region through the insertion movement by a mount-
ing device, often constructed in the form of a so-called "catcher clip" and is
thus coupled with the actuating device. This actuating device can be a
mechanical press button, for example a so-called "push button", which is
connected with the mounting device via a lever. Alternatively, a contact-
less actuation can also be provided, in which the user triggers a sensor
which in turn causes an electrical actuator to actuate the suction pump.
Prior Art
CA 02712442 2010-07-16
PatXML 2/17 PWO07XO4P
[0003] Dispenser units of this type are known from EP 1711094 A. Suction
pumps of the above-mentioned type are, moreover, generally known under
the term bellows pump. The bellows pumps have a pumping chamber,
delimited by the rubber wall, which is generally compressed manually by
squeezing together, with the medium situated in the pumping chamber
being hereby pressed out. Such bellows pumps have the advantage that
they are able to be produced particularly easily and at a favourable price.
[0004] The disadvantage of the known bellows pumps consists, however, in that
they are only moderately suitable for use in delivery devices, because the
squeezing movement which is able to be carried out in a simple manner by
the human hand is only able to be converted mechanically with difficulty
and with additional guide elements, in order for example to avoid a lateral
migration of the delivery opening. The use of bellows pumps is also prob-
lematical when a precise quantity of a medium must be delivered in a de-
fined manner, because usually the pumping chamber can not be fully
compressed, to avoid damage to the elastic wall, and the volume of the
delivery can be dependent on the deformation geometry of the elastic wall.
[0005] A further disadvantage of the bellows pumps consists in that in
connection
with dispenser units, the insertion of the filling inserts, which are formed
from a storage container and the suction pump connected therewith, is
only able to be carried out with difficulty. When a filling insert is pushed
into the unfolded dispenser housing, the mounting device presses against
a functional element of the pump, in order for example to produce the con-
nection, via the "catcher clip", between the actuating device or the actuator
and the pumping means. This insertion movement must lead reliably to the
mechanical coupling of the pump with the actuating device or with the ac-
tuator, even when it is not carried out very carefully, because otherwise
the dispenser would remain without function.
[0006] With the use of bellows pumps, the problem now exists that owing to the
elastic wall, the lower pump part can evade the grasp of the "catcher clip".
It can therefore happen that the pump places itself "transversely" and by
actuation of the dispenser the elastic wall is indeed compressed but the
medium is delivered into the dispenser housing transversely to the actually
CA 02712442 2010-07-16
PatXML 3/17 PWO07XO4P
intended delivery direction. An only partially successful mounting is of
course also possible. It is obvious that in both cases, a malfunction of the
dispenser is the result.
Representation of the invention
[0007] It is therefore an object of the invention, with regard to the suction
pump,
to provide a suction pump with an elastic wall, which can be used in a de-
livery device, in particular a dispenser unit, with as great a freedom from
error as possible, with, at the same time, a simple and favourably priced
construction. With regard to the dispenser unit, it is an object of the inven-
tion to provide a dispenser unit in which a suction pump with an elastic
pumping chamber is able to be used as free from error as possible.
[0008] The object with regard to the suction pump is solved according to the
in-
vention in that guide means are provided which are arranged such that
they are able to eliminate a migration of the elastic wall of the pumping
body transversely to the pumping direction during the compression of the
pumping body.
[0009] The object with regard to the dispenser is solved according to the
inven-
tion in that the housing has a mounting device which is constructed and ar-
ranged such that by the insertion of the filling insert into the final
position,
the head region of the suction pump, cooperating with the actuating de-
vice, is automatically held by the mounting device during the insertion, with
a bending of the elastic pumping chamber by the guide means being pre-
vented.
[0010] Through the suction pump according to the invention, the advantage of a
conventional piston/cylinder pump can be combined with a bellows pump.
Through the provision of the guide means, the compression movement is
limited to a preferred direction of the pumping movement. In a conven-
tional dispenser, for example, this is the vertical direction, with the
storage
container then being mounted with the suction pump downwards into the
dispenser housing, and the guide means being constructed such that de-
spite the elastic wall a migration into one of the horizontal directions is
prevented. The pumping body can therefore only be compressed in a ver-
tical direction, so that even the friction force on applying the mounting de-
}
CA 02712442 2010-07-16
PatXML 4/17 PWO07XO4P
vice onto a head region of the suction pump can not lead to the head re-
gion being displaced in a transverse direction.
[0011] In a particularly simple development of the suction pump, the pumping
chamber is formed by the elastic wall and head- and a base region. The
base region is arranged at the top with the filling insert standing on the
head and has the inlet valve. This inlet valve is constructed so that on de-
compression of the pumping chamber, medium is able to be drawn out of
the storage container into the pumping chamber and closes on compres-
sion of the pumping chamber. In the head region, in turn, the outlet valve
is arranged, which delivers the medium on compression of the pumping
chamber and closes on decompression of the pumping chamber. In par-
ticular in the head region, but possibly also in the base region, further func-
tional elements can be provided, in particular for foaming the medium or
for preventing dripping.
[0012] In a preferred development of the invention, the guide means act at
least
on the movable head region, and the base region is secured relative to the
dispenser housing. Here, the guide means ensure that the head region is
only movable relative to the secured base region in the preferred pumping
direction.
[0013] In order to ensure a first protection from malfunctions, it can also be
suffi-
cient to provide guide means which apply a guiding force only in one direc-
tion. In the case of the above-mentioned dispenser unit, for instance a pro-
tection from migration as a reaction to the insertion movement can already
be sufficient, so that here the guidance is "only" produced by an abutment
which is opposed to the insertion movement. For this, the guide means
must prevent the head region of the bellows pump from being movable in
the direction of the rear wall of the housing in the case of an insertion of
the filling insert directed from the front in the direction of the rear wall
of
the housing. To increase the functional reliability, however, preferably a
more extensive, preferably complete guidance of the head region will take
place over the entire range of movement. The guidance therefore then
takes place over the entire displacement path of the head region in all di-
rections transversely to the preferred pumping direction.
CA 02712442 2010-07-16
PatXML 5/17 PWO07XO4P
[0014] The head region of the suction pump can be provided with a rim
projecting
outwards in the manner of a flange which, on insertion into the dispenser
housing, is grasped by the mounting device, in particular by the "catcher
clip". This rim is, for example, embodied in a plate shape and is arranged
so that the mounting device can not damage the elastic wall. Depending
on the embodiment of the wall, the head region can itself be constructed in
a plate shape or can have a section constructed in a plate shape, which is
connected for example by a spacer with the part of the head region adjoin-
ing the elastic wall.
[0015] The guide means can be constructed both as inner and also as outer
guide means. In the case of the outer guide means, the suction pump has
a pumping body on which the pumping chamber is arranged. In the sim-
plest case, the pumping body can be formed by the base region from
which the guide means, for example in the form of guide rods, extend in
the direction of the head region, where they can penetrate bearing eyes,
for example, which are arranged in the head region, to form the guide.
[0016] Alternatively, of course, the guide means can also be formed by a wall
of
the pumping body, which can be pushed together like a concertina in the
manner of a telescope rod. Finally, it is possible for the head region to
have a rim projecting outwards in the manner of a piston, which is guided
in the preferred pumping direction in the pumping body, which is then em-
bodied in the manner of a cylinder, with a further part of the head region,
for connection to the actuating device, adjoining the piston-like region, fac-
ing away from the pumping chamber, which further part projects out from
the cylindrical region in all positions of the head region. For example, this
can be a delivery tube with a plate-like rim projecting laterally in the lower
region, onto which the mounting device can be applied.
[0017] Alternatively, the head region can also have a cylindrical wall
section, pro-
jecting upwards in the direction of the base region, which is connected with
a plate-like region which, in turn, is connected with the elastic wall of the
pumping chamber. The cylindrical wall region of the head region can, in
turn, then be either guided on the pumping body or else on the base re-
gion.
CA 02712442 2010-07-16
PatXML 6/17 PWO07XO4P
[0018] To secure the suction pump during transportation, the base region can
be
constructed in this embodiment so that it can be moved into a transporta-
tion position. Here, the height of the cylindrical ring corresponds at least
to
the height of the pumping chamber, so that the base region can be dis-
placed onto the upper rim of the ring, so that the entire pumping chamber
is arranged within the cylindrical ring.
[0019] An alternative embodiment of a suction pump with transportation
security
has a base region which extends in the manner of a bell in the direction of
the head region, wherein the elastic wall of the pumping chamber adjoins
the lower region of the bell-like side region of the base part. To form the
transportation security, the entire elastic part of the wall of the pumping
chamber together with the head region can then be turned inwards, so that
the head and base regions lie substantially against each other and the
pump is put out of function.
[0020] The mounting aid can be embodied here so that through the insertion
movement not only is a rim of the head part grasped and the latter is thus
coupled with the actuating device, but also at the same time the transpor-
tation security is deactivated by the insertion, and the mounting aid, with
pushing in for the first time, brings about a coverage of such a large dis-
tance of the head region that the elastic wall region of the pumping cham-
ber is turned outwards again.
[0021] Alternatively or in addition to an outer guidance, the guide means can
also
be arranged in the interior of a pumping chamber. For this, the head region
can for example be connected with the base region via guide rods con-
structed in the manner of telescope rods, which are arranged inside the
elastic wall. These guide means can be arranged for example centrally in-
side the pumping chamber, so that the telescope rod is constructed as a
hollow rod or tube and has a lateral inlet for the medium which is to be
pumped. On compression of the pumping chamber, the medium is then
firstly driven through this lateral inlet of the telescope rod and then
through
the hollow telescope rod itself outwards. The valve of the head region can
still remain here in the actual head region, or else in the region of the lat-
CA 02712442 2010-07-16
PatXML 7/17 PW007XO4P
eral opening of the telescope rod. Alternatively or in addition, further guide
rods can also be provided in the outer region of the pumping chamber.
[0022] A particularly advantageous embodiment of the invention uses the push
rods of the inlet valve and/or of the outlet valve to form the guide means.
For this, the respective valve is provided with a push rod which has the
valve means, i.e. for example the sealing membrane. The push rod is ex-
tended beyond the region of the valve means and has a guide section in
this extended region which is guided with guide means which are arranged
on the pumping body or, depending on which valve has the guiding push
rod, are arranged on the head region or the base region. For this, the re-
spective part of the guide preferably has bearing eyes in which the guide
section is mounted so as to be movable in the preferred pumping direction.
[0023] A further preferred embodiment uses a shared push rod for both valves.
This shared push rod is preferably constructed as a central push rod pene-
trating the pumping chamber, wherein on the side of one of the valves the
switching element is securely connected with the push rod and on the side
of the other valve the switching element is movably mounted on the push
rod. Here, for example, on the side of the outlet valve the switching valve
can be securely connected with the push rod, whereas the switching ele-
ment on the side of the inlet valve is movably guided on the push rod, so
that both valves can operate in a pressure-controlled manner independ-
ently of each other. On compression of the bellows valve, the push rod will
then extend into the storage container or into an intermediate region ar-
ranged between the suction pump and the storage container.
[0024] The above-mentioned embodiment can be produced for example in that
the switching element of the inlet valve has a sleeve-like part, through
which the push rod is guided in a longitudinally movable manner. The mo-
bility of the switching element can be limited relative to the push rod in
both directions by stops, whereby then at the same time also the com-
pression movement of the bellows pump as a whole is established. This
can, for example, prevent damage to the elastic wall material by deforma-
tions which are too extreme. In this embodiment, the mounting of the push
rod is preferably realized by the valve seat of one or both valves, i.e. of
the
CA 02712442 2010-07-16
PatXML 8/17 PWO07XO4P
inlet valve and of the delivery valve. Alternatively or in addition, the push
rod can also be mounted movably inside or outside the pumping chamber
in the preferred pumping direction to form an (additional) guide.
[0025] In all embodiments, the outlet valve can be provided with a pusher
which
extends in the direction directed away from the pumping chamber and in
the lower region has a plate region which is able to be coupled with the ac-
tuating device of the dispenser. This does not necessarily have to be a
plate region; the coupling can also be produced by any other mechanical
device.
[0026] In connection with the present invention, all forms of valve actuating
de-
vices come into consideration as the actuating device, in particular a me-
chanical push button or else an electrical actuator which can be triggered
via a sensor arrangement. The push rod of the outlet valve, extending
away from the pumping chamber, is preferably constructed in a hollow cy-
lindrical shape, so that through this push rod the medium can be conveyed
for delivery. Here, the push rod therefore forms the delivery duct for the
medium. To form an additional drip protection, an additional seal or an ad-
ditional valve means can be provided in the delivery duct, irrespective of
whether this is formed by the push rod or is constructed as a separate
duct, wherein here for instance a membrane seal comes into considera-
tion.
[0027] The dispenser unit according to the invention comprises a housing into
which the filling insert is able to be inserted. This filling insert
comprises,
as already described above, the storage container and the suction pump
arranged therein. The suction pump, in turn, is constructed as a bellows
pump and has a head region which is movable in the direction of a base
region to transfer an actuating force, irrespective of whether this is applied
via an electrical actuator or a "push button", wherein the suction pump has
guide means which ensure a guidance of the head region in the preferred
pumping direction. Usually, the filling insert with the suction pump is in-
serted downwards in the housing, so that the preferred pumping direction
is the downwardly directed vertical direction and the delivered medium can
CA 02712442 2010-07-16
PatXML 9/17 PWO07XO4P
therefore drip directly from the delivery site for example onto the user's
hand.
[0028] The dispenser unit preferably has a mounting device which can be con-
structed in the form of a "catcher clip". This clip is a U-shaped clip with
rounded or bent arms which on insertion of the filling insert engage behind
a rim of the movable part of the suction pump, in particular a rim of the
head region, wherein the mounting device is, in turn, functionally coupled
with the mechanism of the housing in such a way that a movement of the
actuating device brings about a movement of the rim of the suction pump
which is coupled with the mounting device. Hereby, in the present case,
the elastic pumping chamber is compressed and the medium is driven out
from this pumping chamber in the preferred pumping direction.
[0029] If the suction pump has the transportation security described above,
the
dispenser unit can have an additional mounting aid which cooperates with
a further mounting element on the movable part of the suction pump. This
additional mounting aid can bring about the first path for deactivation of the
transportation security, i.e. for example the outward turning of the elastic
wall of the pumping chamber, in which through the insertion movement the
additional mounting element slides along a guide surface of the further
mounting aid and hereby brings about the corresponding displacement of
the head region into the position of use.
[0030] Alternatively, the additional mounting aid can also be arranged
upstream
of the first mounting aid, in which for example the "catcher clip" has arms
which are bent very intensively in the preferred pumping direction.
[0031] The suction pump can, finally, have a drip protection which is arranged
behind the pumping chamber. Such a drip protection can be formed by a
membrane seal which can be constructed for example in the manner of a
heart valve with several, for example, three sails, with the sails being
folded to a closed circle in the state of rest and on the occurrence of a
pressure driving out the medium, are pressed apart in the delivery direc-
tion. For this, the sails are connected with the rims, respectively facing
away from the other sails, with the wall of the delivery duct and preferably
overlap each other in the state of rest with the respectively other rims.
CA 02712442 2010-07-16
PatX M L 10/17 PW 007X04 P
[0032] If medium is now pressed through this seal, the flap-like sails open in
the
direction of the wall and the medium can flow through. With decreasing
pressure, on the other hand, the sails close again owing to the elastic re-
storing forces. Through this movement, directed contrary to the flow direc-
tion, the medium is thereby sucked back into the delivery duct again, so
that a dripping can be avoided.
[0033] Of course, other steps can also be provided to form a drip protection
or a
similar function. These can, for example, be siphon-like reversals of the
flow direction in the delivery duct or valves or flaps, for example loaded by
a spring in the closing direction and able to be switched by the pumping
pressure.
[0034] Further features and advantages of the invention will become apparent
from the sub-claims and from the following description of preferred exam-
ple embodiments with the aid of the drawings.
Brief description of the drawings
[0035] In the drawings:
[0036] Fig. 1 shows a side view of a dispenser unit according to the
invention,
[0037] Fig. 2 shows a simplified illustration of a suction pump according to
the
invention, in section, and
[0038] Fig. 3 shows a further development of a suction pump according to the
invention.
Best way to carry out the invention
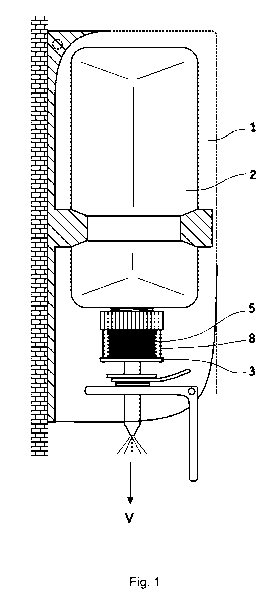
[0039] In Figure 1 a dispenser unit with a dispenser housing 1 is illustrated,
which
is able to be filled via a filling insert. The filling insert is formed by a
suction
pump and by a storage container 2, onto which the suction pump is ap-
plied. The suction pump, in turn, is constructed as a bellows pump which
has a head region 3, a base region 4 and an elastic wall 5 arranged there-
between.
[0040] In Figure 2 a first development of the suction pump is reproduced dia-
grammaticaly in an enlarged illustration. This suction pump is constructed
as a bellows pump and has a head region 3 which is held so as to be
movable relative to the dispenser housing 1. The head region 3 is con-
nected with the base region 4 via the elastic wall 5. In order to prevent a
CA 02712442 2010-07-16
PatXML 11/17 PWO07XO4P
lateral migration of the movable head region 3, the head region 3 is addi-
tionally guided via guide means 8, with the guide means 8 being con-
structed here as external guide means 8, which are connected on the one
hand with the base region 4 and on the other hand are guided through
bearing eyes of the head region 3. In this way, the head region 3 is pre-
vented from migrating in the insertion direction on insertion of the filling
in-
sert into the dispenser housing 1, so that a secure mounting is possible
and thereby a malfunction of the bellows valve can be prevented.
Way(s) to carry out the invention
[0041] Figure 3 shows a further development of a bellows valve, in which the
guide means 8 are constructed as internal guide means 8. For this, the
inlet valve and the outlet valve have a shared push rod 6, wherein the
valve means of one of the two valves, here that of the inlet valve of the
bellows pump, are arranged on a sleeve which is mounted movably on the
shared pusher 6, so that both valves can fulfil their respective function in-
dependently of each other.
[0042] The bellows pump which is illustrated here has in addition a push rod
6,
which is constructed in a hollow cylindrical shape, and has a lateral inlet
opening in the region of the pumping chamber. Through this, the medium
situated in the pumping chamber 7 can be driven out, on compression of
the elastic wall 5, passing the lateral opening and the push rod 6 con-
structed as a hollow rod, in the preferred pumping direction V.
[0043]
[0044] List of reference numbers:
[0045] 1 dispenser housing
[0046] 2 storage container
[0047] 3 head region
[0048] 4 base region
[0049] 5 elastic wall
[0050] 6 shared pusher of the inlet and outlet valves
[0051] 7 pumping chamber
[0052] 8 guide means
[0053] V preferred valve direction