Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
¨ ¨
Title: Baking Oven
Field of the Invention
The invention relates to baking ovens with an input
station, a baking area, an output station, baking
plates, which are arranged along a circulation path
passing through the baking area, and a conveying device
for the baking plates.
Known baking ovens of this type are used for producing
very different products. One product group includes
pancakes, stuffed pancakes etc. Another product group
includes soft waffles, American pancakes, Canadian
pancakes etc. A further product group includes
crunchy/crispy wafers, such as crunchy/crispy wafer
sheets, for example, or crunchy/crispy flat wafers
which contain numerous hollow-body halves. A further
product group comprises packaging parts produced in
accordance with wafer baking technology, such as planar
sheets, cups, trays etc. A further product group
comprises crunchy/crispy wafers, which are produced
from flat wafers which can be plastically deformed in
the warm, baked state, which are shaped into hollow
bodies in the warm, baked state and then are allowed to
solidify as hollow bodies. Such products are rolled
wafer-type cones for ice-cream, deep-drawn wafer cups
for ice-cream or crunchy/crispy wafer rolls etc.
Prior Art
Known baking ovens of this type are usually in the form
of gas-heated baking ovens. In the baking area,
gas-heated infrared radiators or gas flame burners are
arranged along the circulation path of the baking
plates, which infrared radiators or gas flame burners
emit their hot combustion gases into the baking area
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 2 -
while they heat the rear sides of the circulating
baking plates. Long and branched pipelines, which lead
to the gas burners arranged in the baking area, for the
hot gas to be combusted are accommodated in the
framework of these baking ovens. The baking ovens are
provided with large air inlet openings, through which
large quantities of air are sucked into the baking
oven, which large quantities of air are required as
combustion air for the gas burners and for cooling the
hot combustion gases produced thereby.
So-called electrically heated baking ovens are also
known in which heating coils heat the baking plates,
which heating coils are installed in the baking plates
and are in the form of electrical resistance heating.
Each baking plate has been provided with a heating coil
arranged in the baking plate and a current collector,
which protrudes from the rear side of the baking plate.
The heating coil is arranged in the baking plate in a
cavity which is open towards the rear side of the
baking plate. The heating coil is electrically
conductively connected to the current collector in the
interior of the baking plate. The current collector
itself is fixed movably on the rear side of the baking
plate and provided with spring mounting, which pushes
it away from the rear side of the baking plate. The
baking plates, which are provided with electrical
resistance heating, are conveyed by the conveying
device of the baking oven through the baking area. In
said baking area, busbars are arranged along the
circulation path of the baking plates. If the baking
plates enter the baking area, their current collectors
come into engagement with the busbars. In this case,
the current collectors are each pressed against the
rear side of the baking plate and their spring mounting
is compressed. In the baking area, the current
collectors slide along the busbars and, as a result of
their contact with the busbars, draw current from the
CA 02714468 2012-10-23
27363-96
- 3 -
busbars and conduct the current to the heating coil of the
respective baking plate. If the baking plates leave the baking
area, the current collectors are drawn away from the busbars
and their spring mounting is relieved of strain. The current
collectors then spring back into their unloaded initial
position.
Description of the Invention
The object of the invention is to improve baking ovens of the
type mentioned at the outset.
For this purpose, one aspect of the invention proposes a novel
baking oven which is provided with an input station, a baking
area and an output station, in addition with baking plates,
which are arranged along a circulation path passing through the
baking area, and with a conveying device for the baking plates.
With the novel baking oven, the baking plates are in the form
of susceptor plates, which can be heated inductively without
any contact, and a baking zone provided with an induction
heating device is provided in the baking area, in which baking
zone at least one elongated inductor is provided, which is
arranged parallel to the circulation path of the baking plates,
extends along the circulation path over a plurality of baking
plates and produces a large-area, broad magnetic field, which
extends along the circulation path over a plurality of baking
plates and simultaneously inductively heats a plurality of
baking plates in the form of susceptor plates without any
contact.
In accordance with another aspect of the invention, there is
provided a baking oven with an input station, a baking area, an
CA 02714468 2012-10-23
27363-96
- 3a -
output station, baking plates, which are arranged along a
circulation path passing through the baking area, and a
conveying device for the baking plates, wherein the baking
plates are in the form of susceptor plates, which can be heated
inductively without any contact, and in that a baking zone
provided with induction heating is provided in the baking area,
in which baking zone at least one elongated inductor is
provided, which is arranged parallel to the circulation path of
the baking plates, extends along the circulation path over a
plurality of the baking plates and produces a large-area, broad
magnetic field, which extends along the circulation path over
the plurality of the baking plates and simultaneously
inductively heats the plurality of the baking plates in the
form of susceptor plates without any contact.
The novel baking oven has the advantage over the gas-heated
baking ovens that the hot combustion gases produced by the gas
burners in the baking area are no longer present, so that the
baking oven construction can be correspondingly simplified. In
a baking oven according to the invention, neither pipelines
leading
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 4 -
to the gas burners for the hot gas to be combusted are
required nor are large air inlet openings required for
the large quantities of air to be sucked into the
baking oven, which large quantities of air are required
as combustion air for the gas burners or for cooling
the hot combustion gases produced thereby.
The novel baking oven has the advantage over the
abovementioned electrically heated baking ovens that
both the baking plates and the baking oven construction
can be considerably simplified because neither heating
coils installed in the baking plates nor current
collectors protruding from the baking plates are
required in the baking plates and no busbars, which are
in the form of sliding rails for the current
collectors, are required in the baking area.
In the case of the novel baking oven, the process heat
required for the baking process is produced by
contact-free inductive heating of the baking plates,
which are each in the form of susceptor plates. With
the novel baking oven, the elongated inductor, which is
arranged parallel to the circulation path of the baking
plates, extends over a plurality of susceptor plates
arranged one behind the other. This inductor produces a
broad and large-area magnetic field, which extends
along the circulation path over a plurality of
susceptor plates and inductively heats them without any
contact.
In accordance with a further feature of the invention,
it can be provided that the baking plates are arranged
along a circulation path, which passes through two
horizontal transport paths arranged one on top of the
other, and that a baking zone is provided on the two
transport paths, in which baking zone at least one
elongated inductor is provided which is arranged
parallel to the circulation path of the baking plates
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 5 -
and, with its magnetic field, simultaneously
inductively heats a plurality of baking plates in the
form of susceptor plates without any contact.
In accordance with a further feature of the invention,
it can be provided that the baking plates are arranged
along a circular circulation path and are fixed on a
turntable, which is capable of rotating about a
vertical axis of rotation and conveys the baking plates
by means of its rotary movement through the baking
area, and that a baking zone is provided in the baking
area, in which baking zone at least one elongated
inductor is provided which is arranged parallel to the
circular circulation path and extends along the
circular circulation path over a plurality of baking
plates in the form of susceptor plates.
The elongated inductor can be arranged in the baking
zone beneath the circulation path of the baking plates.
The elongated inductor can be arranged in the baking
zone above the circulation path of the baking plates.
A least one elongated inductor can be arranged in the
baking zone both above and below the circulation path
of the baking plates.
In a further configuration of the invention, a novel
baking oven is proposed in which upper and lower baking
plates are provided which are arranged along two
circulation paths passing through the baking area, are
each in the form of susceptor plates and are
accommodated in baking tongs, which are arranged along
a circulation path passing through the baking area and
are conveyed by the conveying device of the baking oven
in the closed state through the baking area. With this
baking oven, at least one baking zone is provided in
the baking area, in which baking zone in each case at
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 6 -
least one elongated inductor is arranged both above and
below the circulation path of the baking tongs, which
inductor, with its magnetic field, simultaneously
inductively heats the susceptor plates of a plurality
of baking tongs without any contact.
With this baking oven, the baked molded products are
produced in the closed baking tongs between the upper
and lower baking plates, which are arranged one above
the other and are in the form of susceptor plates.
In the case of a baking oven which is equipped with
baking tongs, the invention can provide that a
plurality of baking tongs are arranged next to one
another along a circular path and are fixed on a
turntable which is capable of rotating about a vertical
axis of rotation, and that at least one baking zone is
provided in the baking area on the circular path, in
which baking zone in each case at least one elongated,
arcuate inductor is arranged both above and below the
circular path, which inductor, with its magnetic field,
simultaneously inductively heats the susceptor plates
of a plurality of baking tongs without any contact.
In the case of a baking oven equipped with baking
tongs, the invention can furthermore provide that the
baking tongs, which contain the upper and lower baking
plates in the form of susceptor plates, are arranged
along a circulation path, which passes in the baking
area through two horizontal transport paths arranged
one above the other, and that a baking zone is provided
on both transport paths, in which baking zone in each
case at least one elongated inductor is arranged both
above and below the transport path, which inductor,
with its magnetic field, simultaneously inductively
heats the susceptor plates of a plurality of baking
tongs without any contact.
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
,
- 7 -
Furthermore, the invention can provide that in the case
of the baking tongs, the upper tong part is pivotably
connected to the lower tong part via a hinge, and that
the susceptor plates in both tong parts are in each
case arranged between two edge pieces, which laterally
adjoin the susceptor plates, the edge pieces, which are
arranged on the hinge side of the baking tong, of the
two tong parts being connected to one another by the
hinge and the edge piece arranged at the free end of
the upper tong part bearing the control roller for
opening and closing the baking tong.
In accordance with a further feature of the invention,
in the case of the baking tongs the susceptor plates
can be electrically insulated from the edge pieces of
the two tong parts. This design makes it possible to
restrict the inductive heating in both tong parts of
the baking tongs to the baking plates in the form of
susceptor plates.
In accordance with a further feature of the invention,
in the case of the baking tongs a baking tong locking
apparatus can be provided on that side edge of the
baking tong which is remote from the hinge, the locking
elements of said baking tong locking apparatus being
fitted on those edge pieces of the two tong parts which
are arranged on that side edge of the baking tong which
is remote from the hinge, next to the susceptor plates.
In accordance with a further feature of the invention,
in the case of the baking tongs, the two tong parts can
be provided with flat plate frames, in which the
susceptor plates are arranged with exposed rear sides.
According to the invention, the flat plate frames can
have lateral frame parts arranged on both sides of the
susceptor plates, which frame parts are connected to
one another by a front transverse rail, which is
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873 PCT/EP2009/000906
,
- 8 -
arranged along the front edge of the susceptor plate,
and by a rear transverse rail, which is arranged along
the rear edge of the susceptor plate.
According to the invention, the susceptor plates can be
mounted in floating fashion in the flat plate frames or
arranged displaceably, to a limited extent, at right
angles with respect to the plate plane. This design
makes it possible for the dough which is arranged
between the two susceptor plates in the closed baking
tong and which expands at the beginning of the baking
process to raise the susceptor plate, which is arranged
in the upper tong part, despite the fact that the
baking tong is closed.
According to the invention, the susceptor plates can be
arranged in the transverse rails of the flat plate
frames displaceably, to a limited extent, at right
angles with respect to the plate plane.
In the case of the flat plate frames of the upper and
lower tong parts, the two transverse rails can be
electrically insulated from the two lateral frame
parts. This design makes it possible to restrict the
inductive heating to the baking plates, which are
arranged in the flat plate frames and are in the form
of susceptor plates.
In accordance with a further feature of the invention,
the susceptor plates can contain inserts, which are
embedded in them and are in the form of baking mold
halves. In this case, the susceptor plates can be made
of cast iron or steel and the inserts in the form of
baking mold halves are made of aluminum.
In a further configuration of the invention, a novel
baking oven is proposed in which upper and lower baking
plates are provided which are arranged along two
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 9 -
circulation paths passing through the baking area, are
each in the form of susceptor plates and are arranged
in two separate chain conveyors. The two circulation
paths each have a baking section, which passes from the
input station through the baking area to the output
station and is arranged along a baking stretch, and a
return section, which passes from the output station
back to the input station. The susceptor plates, which
are arranged in the baking sections of the two
circulation paths along the baking stretch, are
positioned opposite one another and form baking molds
comprising in each case an upper and a lower baking
plate. At least one baking zone is provided in the
baking area, in which baking zone in each case at least
one elongated inductor is arranged both above and below
the baking molds arranged along the baking stretch,
which inductor, with its magnetic field, simultaneously
inductively heats the susceptor plates of a plurality
of baking molds without any contact.
In the case of this baking oven, the baked molded
products are produced in the baking molds arranged one
behind the other along the baking stretch.
In the case of such a baking oven, the baking sections
of the two circulation paths can be arranged along a
baking stretch, which passes through two horizontal
transport paths, which are arranged one above the
other, in the baking area, on which transport paths in
each case one baking zone is provided, in which in each
case at least one elongated inductor is arranged both
above and below the baking molds, which inductor, with
its magnetic field, simultaneously inductively heats
the susceptor plates of a plurality of baking molds
without any contact.
In accordance with a further feature of the invention,
a baking oven can be provided in which the upper and
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 10 -
lower baking plates in the form of susceptor plates are
arranged along two circulation paths, in which the
baking sections are arranged along a horizontal baking
stretch, and in which a baking zone, which extends
along the horizontal baking stretch, is provided in the
baking area, which baking zone comprises at least one
elongated upper inductor, which is arranged over the
baking molds, and at least one elongated lower
inductor, which is arranged below the baking molds.
In the case of such a baking oven, the invention can
furthermore provide that the upper baking plates are
arranged along an upper circulation path and are
suspended with their baking faces on an upper chain
conveyor in such a way that they point downwards and in
freely pendulous fashion, that the lower baking plates
are arranged along a lower circulation path and are
conveyed by a lower chain conveyor through the baking
stretch, that the upper baking plates are set back from
the upper chain conveyor at the beginning of the baking
stretch on the lower baking plates and are raised from
the lower baking plates at the end of the baking
stretch, and that the lower chain conveyor conveys the
baking molds, which each comprise a lower baking plate
and an upper baking plate positioned thereon, along the
baking stretch through the baking zone.
In the case of a baking oven in which the lower baking
plates are arranged in a circulation path which has a
baking section, which passes from the input station
through the baking area to the output station and is
arranged along a baking stretch, and a return section,
which passes from the output station back to the input
station, the invention can provide that the induction
heating device on the circulation path of the lower
baking plates on the return section provides at least
one additional elongated inductor, which, with its
magnetic field, simultaneously inductively heats the
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
,
- 11 -
susceptor plates of a plurality of lower baking plates
without any contact.
In the case of a baking oven in which the upper baking
plates are arranged in a circulation path which has a
baking section, which leads from the input station
through the baking area to the output station and is
arranged along a baking stretch, and has a return
section, which leads from the output station back to
the input station, the invention can provide that the
induction heating device on the circulation path of the
upper baking plates on the return section provides at
least one additional elongated inductor, which, with
its magnetic field, simultaneously inductively heats
the susceptor plates of a plurality of upper baking
plates without any contact.
In accordance with a further feature of the invention,
in the case of a baking oven in which the upper and
lower baking plates in the form of susceptor plates are
arranged in two separate chain conveyors, at least the
lower baking plates can be electrically insulated from
the chain conveyor, which is arranged along their
circulation path. According to the invention, the upper
baking plates can also be electrically insulated from
the chain conveyor, which is arranged along their
circulation path.
The baking ovens are provided with an induction heating
device. With this induction heating device, the
invention can provide that an elongated inductor is
arranged in each baking zone, which inductor extends
along the circulation path of the baking plates over a
plurality of baking plates and produces a broad
magnetic field, which extends along the circulation
path of the baking plates over a plurality of baking
plates and simultaneously inductively heats a plurality
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 12 -
of baking plates in the form of susceptor plates
without any contact.
According to the invention, the elongated inductor can
comprise two or more inductor bars, which are arranged
next to one another, extend along the circulation path
of the baking plates over a plurality of baking plates
and run parallel to one another.
In accordance with a further feature of the invention,
the elongated inductor can comprise individual inductor
bars, which run parallel to one another and each form a
dedicated inductor loop. With this design, each
inductor bar is connected to the AC generator of the
induction heating device via a dedicated electrical
line.
In accordance with a further feature of the invention,
the elongated inductor can comprise U-shaped inductors,
which are arranged next to one another, each form a
dedicated inductor loop and each have two inductor
bars, which run parallel to one another. With this
design, each U-shaped inductor is connected to the AC
generator of the induction heating device via a
dedicated electrical line.
In accordance with a further feature of the invention,
the elongated inductor can comprise two inductors,
which are arranged next to one another and form in each
case one dedicated inductor loop, and in the case of
which the inductor bars, which run parallel to one
another, are connected at their ends by transverse bars
and together with these form a coil, which is elongated
in the longitudinal direction of the inductor. With
this design, the two inductors which are arranged next
to one another are each connected to the AC generator
of the induction heating device via a dedicated
electrical line.
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 13 -
In accordance with a further feature of the invention,
the elongated inductor can be in the form of an
individual inductor loop, its inductor bars, which run
parallel to one another, being connected at their ends
by transverse bars and together with these forming a
coil, which is elongated in the longitudinal direction
of the inductor. With this design, the elongated
inductor is connected to the AC generator of the
induction heating device via only one electrical line.
In accordance with a further feature of the invention,
the elongated inductor can be in the form of an
individual inductor loop, which contains two half-loops
which are arranged next to one another, in the case of
which the inductor bars, which run parallel to one
another, are connected at their ends by transverse bars
and together with these in each case form a coil, which
is elongated in the longitudinal direction of the
inductor. With this design, the elongated inductor is
connected to the AC generator of the induction heating
device via only one electrical line.
In accordance with a further feature of the invention,
the inductor bars with the transverse bars connecting
them can form a coil running in the clockwise direction
in the case of one half-loop and form a coil running in
the counterclockwise direction in the case of the other
half-loop.
In accordance with a further feature of the invention,
the inductor bars with the transverse bars connecting
them can form coils which run in the same direction in
the case of both half-loops.
In accordance with a further feature of the invention,
the elongated inductor can be in the form of an
individual inductor loop, its inductor bars, which run
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 14 -
parallel to one another, being connected to one another
alternately at their ends by transverse bars and
together with the transverse bars forming a meandering
pattern, in which the meandering loops follow on from
one another transversely with respect to the
longitudinal direction of the inductor.
In accordance with a further feature of the invention,
solid bars, which are each provided with a low,
rectangular full cross section and which face the
baking plates in the form of susceptor plates with
their broad sides, are provided as the inductor bars,
which extend along the circulation path of the baking
plates over a plurality of baking plates.
With the induction heating device according to the
invention, inductor bars are provided which extend
along the circulation path of the baking plates over a
plurality of baking plates. The inductor bars are in
the form of straight bars or in the form of bars which
are curved in the form of arcs, corresponding to the
profile of the circulation path of the baking plates.
A further feature of the invention provides that each
inductor is fixed on the framework of the baking oven
in such a way that it is electrically insulated.
A further feature of the invention provides that each
inductor with its inductor bars is fixed on the
framework of the baking oven in such a way that it is
electrically insulated.
A further feature of the invention provides that each
inductor, which extends along the circulation path of
the baking plates over a plurality of baking plates, is
arranged horizontally in the baking oven and is fixed
on the framework of the baking oven in such a way that
it is vertically adjustable.
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 15 -
A further feature of the invention provides that each
inductor in the baking oven is arranged at a vertical
distance to the circulation path of the baking plates
in the form of susceptor plates which is smaller than
the vertical range of the magnetic field produced by
the inductor.
A further feature of the invention provides that each
inductor is arranged at a distance parallel to the
circulation path of the baking plates in the form of
susceptor plates which is smaller than the range of the
magnetic field produced by the inductor.
The invention will be explained in more detail below
using a few exemplary embodiments with reference to the
drawings.
Brief description of the drawings
Figure 1 shows a baking oven equipped with baking
tongs, from the side,
Figure 2 shows a plan view of the baking oven from
figure 1,
Figure 3 shows a cross section of the baking area of
the baking oven from figure 1,
Figure 4 shows a baking tong of the baking oven from
figure 1 in plan view,
Figure 5 shows the baking tong from figure 4 from the
rear,
Figure 6 shows the left-hand side edge of the baking
tong from figure 4,
Figure 7 shows the central part of the baking tong
from figure 4,
Figure 8 shows the right-hand side edge of the baking
tong from figure 4,
Figure 9 shows the baking tong from figure 4 in a
longitudinal section,
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 16 -
Figure 10 shows an upper inductor, which is fixed on
the oven framework,
Figure 11 shows a fixing apparatus for an inductor bar,
Figure 12 shows a lower inductor, which is fixed on the
oven framework,
Figures 13 to 17 show different designs of inductors in
plan view,
Figure 18 shows a further baking oven equipped with
baking tongs, from the side,
Figure 19 shows a plan view of the baking oven from
figure 18,
Figure 20 shows a cross section of the baking area of
the baking oven from figure 18,
Figure 21 shows the left-hand half of a baking tong of
the baking oven from figure 18,
Figure 22 shows the right-hand half of a baking tong of
the baking oven from figure 18,
Figure 23 shows a further baking oven equipped with
baking tongs, in plan view,
Figure 24 shows a cross section of the baking area of
the baking oven from figure 23,
Figure 25 shows the fixing of the upper inductor in the
baking oven from figure 23,
Figure 26 shows the fixing of the lower inductor in the
baking oven from figure 23,
Figure 27 shows the fixing of an inductor bar in the
baking oven from figure 23,
Figure 28 shows a further baking oven according to the
invention, from the side,
Figure 29 shows a cross section of the baking oven from
figure 28,
Figure 30 shows the left-hand side edge of a baking
mold of the baking oven from figure 28,
Figure 31 shows a detail of the upper baking plate
conveyor of the baking oven from figure 28,
Figure 32 shows a further baking oven according to the
invention, from the side,
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 17 -
Figure 33 shows a baking area of the baking oven from
figure 32, in cross section,
Figure 34 shows a detail of a baking plate conveyor of
the baking oven from figure 33, and
Figure 35 shows a further baking oven according to the
invention, in plan view.
Description of exemplary embodiments
Figures 1 to 12 show a baking oven 1 for producing
baked molded products, which are in the form of round,
soft waffles. The soft waffles are produced from a
liquid waffle dough in baking molds 2, which each
comprise a lower baking mold 2a and an upper baking
mold 2b.
The baking molds 2 are accommodated in the baking tongs
3 of a continuous baking tong chain 4. The baking tong
chain 4 is arranged along a circulation path, which
extends in two horizontal transport paths 5, 6 which
are arranged one above the other, through the baking
oven 1. The baking tong chain 4 is integrated in a
chain conveyor, which is arranged along the circulation
path, conveys the baking tongs 3 through the two
transport paths 5, 6 and deflects them, by means of its
chain wheels which are arranged at the front and rear
end of the baking oven 1, from one transport path into
the other.
The chain conveyor is arranged in the elongated
framework 7 of the baking oven 1 between the two side
walls 8, 9 of the oven framework 7. The baking tongs 3
are arranged in the chain conveyor between two lateral
transport chains 10, 11 and fixed on the chain link
plates 10a, lla thereof. Hinged bolts protrude outwards
from the transport chains 10, 11, on which hinged bolts
running wheels 12, 13 are mounted rotatably, with which
the chain conveyor is supported in both transport paths
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873 PCT/EP2009/000906
,
- 18 -
5, 6 in each case on running rails 14, 15, 16, 17,
which run in the longitudinal direction of the oven and
are fixed on the two side walls 8, 9 of the oven
framework 7.
On the upper transport path 5, an output station 18, an
input station 19 and a device 20 for opening and
closing the baking tongs 3 are arranged in the front
oven half la. In the output station 18, the soft
waffles are removed from the open baking tongs 3. In
the input station 19, liquid waffle dough is introduced
into the open baking tongs 3. Downstream of the input
station 19, the baking tongs 3 are closed by the device
20. The closed baking tongs 3 are conveyed by the chain
conveyor in the upper transport path 5 rearwards
towards the rear end of the baking oven 1 and in the
lower transport path 6 forwards towards the front end
of the baking oven 1.
The baking area 21 of the baking oven 1 is accommodated
in the rear oven half lb. In the baking area 21, an
upper baking zone 22 is arranged on the upper transport
path 5 and a lower baking zone 23 is arranged on the
lower transport path 6.
Figures 4-9 show a baking tong 3 of the baking oven 1.
Each baking tong 3 contains, in its lower tong part, a
lower baking plate, which can be heated inductively
without any contact. Said baking plate is in the form
of a susceptor plate 24 and contains a plurality of
lower baking molds 2a. The susceptor plate 24 is
accommodated in the lower tong part in a flat, lower
plate frame 25. The lower plate frame 25 has two
lateral frame parts 26, 27, between which the susceptor
plate 24 is arranged. The two lateral frame parts 26,
27 are connected to one another by a front transverse
rail 28, which is arranged along the front edge of the
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 19 -
susceptor plate 24, and by a rear transverse rail 29,
which is arranged along the rear edge of the susceptor
plate 24. The susceptor plate 24 is mounted in the
transverse rails 28, 29 of the lower plate frame 25 in
floating fashion or in such a way that it is capable of
moving to a limited extent at right angles with respect
to the plate plane. The bearing arrangement comprises
bolts 30, 31, which protrude horizontally on the front
and, respectively, rear edge of the susceptor plate 24
and are accommodated in the case of the transverse
rails 28, 29 in depressions 32, 33 arranged on the
insides thereof. The edges of these depressions 32, 33
are in the form of guide links for the bolts 30, 31.
Electrically insulating interlayers 34, 35 are arranged
at the lateral ends of the transverse rails 28, 29
between them and the lateral frame parts 26, 27, which
interlayers 34, 35 prevent a metallic contact between
the transverse rails 28, 29 and the lateral frame parts
26, 27. The transverse rails 28, 29 are rigidly
connected at their ends via fixing screws 36, 37 to the
lateral frame parts 26, 27. In the case of each fixing
screw 36, 37, an insert washer 34 is arranged on the
underside of the screw head, and a cylindrical sleeve
35 is arranged around the screw shaft, from which
cylindrical sleeve 35 an annular flange protrudes
outwards, which flange is arranged between the
underside of the transverse rail 28, 29 and the upper
side of the lateral frame part 26, 27. The insert
washers 34 and the sleeves 35 are produced from an
electrically insulating material.
In its upper tong part each baking tong 3 contains an
upper baking plate, which can be inductively heated
without any contact. Said baking plate is in the form
of a susceptor plate 38 and contains a plurality of
upper baking molds 2b. The susceptor plate 38 is
accommodated in the upper tong part in a flat, upper
plate frame 39. The upper plate frame 39 has two
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 20 -
lateral frame parts 40, 41, between which the susceptor
plate 38 is arranged. The two lateral frame parts 40,
41 are connected to one another by a front transverse
rail 42, which is arranged along the front edge of the
susceptor plate 38, and by a rear transverse rail 43,
which is arranged along the rear edge of the susceptor
plate 38. The susceptor plate 38 is mounted in the
transverse rails 42, 43 of the upper plate frame 39 in
floating fashion or in such a way that it is capable of
moving to a limited extent at right angles with respect
to the plate plane. The bearing arrangement comprises
bolts 44, 45, which protrude horizontally at the front
and, respectively, rear edge of the susceptor plate 38
and are accommodated in depressions 46, 47, which are
arranged on the insides of the transverse rails 42, 43.
The edges of these depressions 46, 47 are in the form
of guide links for the bolts 44, 45. Electrically
insulating interlayers 48, 49 are arranged at the
lateral ends of the transverse rails 42, 43 between
them and the lateral frame parts 40, 41, which
interlayers 48, 49 prevent a metallic contact between
the transverse rails 42, 43 and the lateral frame parts
40, 41. The transverse rails 42, 43 are rigidly
connected at their ends via fixing screws 50, 51 to the
lateral frame parts 40, 41. In the case of each fixing
screw 50, 51, an insert washer 48 is arranged on the
underside of the screw head and a cylindrical sleeve 49
is arranged around the screw shaft, from which
cylindrical sleeve 49 an annular flange protrudes
outwards, which flange is arranged between the
underside of the transverse rail 42, 43 and the upper
side of the lateral frame part 40, 41. The insert
washers 48 and sleeves 49 are produced from an
electrically insulating material.
In the case of each baking tong 3, the lower plate
frame 25 is fixed with its two lateral frame parts 26,
27 on chain link plates 10a, 11a of the lateral
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873 PCT/EP2009/000906
,
- 21 -
transport chains 10, 11 of the chain conveyor. The tong
parts are connected to one another pivotably via a
hinge 52. The hinge 52 connects the left-hand, lateral
frame part 26 of the lower plate frame 25 to the left-
hand, lateral frame part 40 of the upper plate frame
39. The upper plate frame 39 bears, on its right-hand,
lateral frame part 41, a control roller 53, with the
aid of which the baking tong 3 is closed and opened by
means of the upper tong part being pivoted. When the
baking tong 3 is closed, the two susceptor plates 24,
38 arranged in the upper and lower tong part are
positioned one above the other, horizontally aligned.
The baking tongs 3 are opened and closed in the front
section of the upper transport path 5 when passing the
device 20. The device 20 provides a guide rod 54 for
the control rollers 53 of the baking tongs 3. The guide
rod 54 is arranged along the upper transport path 5.
The baking tongs 3 are opened and closed by the control
rollers 53, which run along the guide rod 54. The guide
rod 54 provides a rising section for opening the baking
tongs 3, a horizontally running, upper section for
keeping the baking tongs 3 open and a falling section
for closing the baking tongs 3.
The baking oven 1 is provided with an induction heating
device, in which an AC generator 55, which is arranged
next to the front oven half la, is connected to
elongated, upper and lower inductors 59, 60, 61, 62 via
electrical lines 56, 57, 58 and supplies said inductors
with current.
In the upper baking zone 22, an elongated, upper
inductor 59 is arranged above the baking tongs 3 and an
elongated, lower inductor 60 is arranged below the
baking tongs 3. The magnetic field produced by the
upper inductor 59 reaches down as far as the baking
plates, which are arranged on the upper sides of the
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 22 -
baking tongs 3 and are in the form of susceptor plates
38. These susceptor plates 38 are inductively heated by
the magnetic field produced by the upper inductor 59,
without any contact. The magnetic field produced by the
lower inductor 60 reaches upwards as far as the baking
plates which are arranged on the undersides of the
baking tongs 3 and are in the form of susceptor plates
24. These susceptor plates 24 are inductively heated by
the magnetic field produced by the lower inductor 60
without any contact.
In the lower baking zone 23, an elongated, upper
inductor 61 is arranged over the baking tongs 3, and an
elongated, lower inductor 62 is arranged below the
baking tongs 3. The magnetic field produced by the
upper inductor 61 reaches down as far as the baking
plates which are arranged on the upper sides of the
baking tongs 3 and are in the form of susceptor plates
24. These susceptor plates 24 are inductively heated by
the magnetic field produced by the upper inductor 61
without any contact. The magnetic field produced by the
lower inductor 62 reaches upwards as far as the baking
plates which are arranged on the undersides of the
baking tongs 3 and are in the form of susceptor plates
38. These susceptor plates 38 are inductively heated by
the magnetic field produced by the lower inductor 62
without any contact.
The inductors 59, 60, 61, 62 extend in the respective
baking zone 22, 23 along the circulation path of the
baking tongs 3 over a plurality of baking tongs 3
arranged one behind the other. The inductors 59, 60,
61, 62 each produce a broad magnetic field, which
extends along the circulation path of the baking tongs
3 over a plurality of baking tongs 3 arranged one
behind the other and, in the case of the baking tongs 3
arranged one behind the other, inductively heats the
baking plates in the form of susceptor plates 24, 38
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
,
- 23 -
without any contact. The inductors 59, 60, 61, 62 can
have different designs. Some of these designs are
illustrated in figures 13-17.
Figure 13 shows a design of an elongated inductor 63.
Said inductor has elongated inductor bars 64, which are
arranged parallel to one another and are connected at
their ends by transverse bars 65. The inductor bars 64
form, together with the transverse bars 65, an
individual inductor loop. The inductor loop is
connected at its two ends via electrical lines to the
AC generator of the induction heating device. The
inductor loop contains two half-loops, which are
arranged next to one another. In the case of each half-
loop, the inductor bars 64, which run parallel to one
another, are connected at their ends by transverse bars
65. In the case of each half-loop, the inductor bars 64
form, together with the transverse bars 65 connecting
them, a coil, which is elongated in the longitudinal
direction of the inductor 63. In the case of the two
half-loops, the inductor bars 64, together with the
transverse bars 65, form a coil, which runs in the
counterclockwise direction.
Figure 14 shows a design of an elongated inductor 63,
in which likewise elongated inductor bars 64 are
provided which are arranged parallel to one another and
are connected at their ends by transverse bars 65. The
inductor bars 64 form, together with the transverse
bars 65, an inductor loop having two half-loops. In the
case of the lower half-loop in figure 14, the inductor
bars 64, together with the transverse bars 65
connecting them, form a coil, which is elongated in the
longitudinal direction of the inductor 63 and runs in
the counterclockwise direction. In the case of the
upper half-loop in figure 14, the inductor bars 64
form, together with the transverse bars 65 connecting
them, a coil, which is elongated in the longitudinal
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 24 -
direction of the inductor 63 and runs in the clockwise
direction.
Figure 15 shows a further design of an elongated
inductor 63, in which elongated inductor bars 64, which
are arranged parallel to one another, are connected at
their ends by transverse bars 65 and, together with the
transverse bars 65, form an individual inductor loop.
In the case of the inductor in figure 15, all of the
inductor bars 64 arranged next to one another, together
with the transverse bars 65 connecting them, form a
single coil, which is elongated in the longitudinal
direction of the inductor 63 and runs in the clockwise
direction.
Figure 16 shows a further design of an elongated
inductor 63. In the case of this inductor 63, the
inductor bars 64, which run parallel to one another,
are connected to one another at their ends alternately
by transverse bars 65. The inductor bars 64 form,
together with the transverse bars 65, a meandering
pattern, in which the meandering loops follow on from
one another transversely with respect to the
longitudinal direction of the inductor, from the bottom
up in figure 16.
Figure 17 shows a further design of an elongated
inductor 63. In the case of this inductor 63, a
plurality of U-shaped inductors 66 are provided which
are arranged next to one another and each form a
dedicated inductor loop. Each U-shaped inductor 66 has
two inductor bars 67, which are arranged parallel to
one another and are connected at one end via two
electrical lines to the AC generator of the induction
heating device and are connected to one another at the
other end by a transverse bar.
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873 PCT/EP2009/000906
,
- 25 -
An elongated inductor can also comprise a plurality of
inductor bars, which are arranged parallel to one
another, which each form a dedicated inductor loop and
which are connected at both ends via an electrical line
to the AC generator of the induction heating device.
In order to fix the inductors on the oven framework,
supports are provided in the two baking zones 22, 23,
which supports are arranged at relatively large
distances one behind the other and run in the
transverse direction of the oven and on which the
inductors are fixed, in each case in an electrically
insulating manner, with their inductor bars running in
the oven longitudinal direction. Upper transverse
supports 68, which are each arranged above the upper
and lower transport paths 5, 6 are provided for the
upper inductors 59, 61, and lower transverse supports
69, which are each arranged below the upper and lower
transport paths 5, 6, are provided for the lower
inductors 60, 62. Solid bars, which are provided with a
small, rectangular full cross section, are provided as
the inductor bars. These bars are aligned horizontally
and are arranged, with their broad sides facing the
respective transport paths 5, 6, above or below the
closed baking tongs 3, which are arranged in the
transport path 5, 6.
Figure 10 shows an upper inductor 71, which is arranged
above the rear side of a susceptor plate 70. Said
inductor 71 has eight inductor bars 71a, which are
arranged next to one another and are fixed, in each
case in such a way that they are vertically adjustable,
on an upper transverse support 68 of the oven framework
7 via electrically insulating fixing apparatuses 72.
The flat inductor bars 71a, which are arranged below
the transverse support 68, are arranged at the lower
ends of the fixing apparatuses 72 and are fixed to the
horizontally arranged, lower limbs of L-shaped fixing
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
,
- 26 -
clips 74 via vertical fixing screws 73, which fixing
clips 74 are fixed with their vertically arranged,
upper limbs on the support 68 in each case in such a
way that they are vertically adjustable. In each case a
plurality of electrically insulating intermediate
pieces 75 are arranged between the fixing screws 73 and
the lower limbs of the fixing clips 74.
Figure 12 shows a lower inductor 77, which is arranged
below the rear side of a susceptor plate 76, with eight
inductor bars 77a, which are arranged next to one
another and are fixed, in each case in such a way that
they are vertically adjustable, via electrically
insulating fixing apparatuses 78 on a lower transverse
support 69 of the oven framework 7. The flat inductor
bars 77a, which are arranged above the lower transverse
support 69, are arranged at the upper ends of the
fixing apparatuses 78 and are fixed, via vertical
fixing screws 79, to the horizontally arranged, upper
limbs of L-shaped fixing clips 80, which are fixed, in
each case in such a way that they are vertically
adjustable, with their vertically arranged, lower limbs
on the lower support 69. In each case a plurality of
electrically insulating intermediate pieces 81 are
arranged between the fixing screws 79 and the upper
limbs of the fixing clips 80.
Figures 18-22 show a baking oven 82 for producing baked
molded products, which are in the form of rectangular,
crunchy/crispy wafer sheets, which are produced from a
liquid wafer dough in baking molds formed by two baking
plates.
The baking molds are accommodated in the baking tongs
83 of a continuous baking tong chain 84. The baking
tong chain 84 is arranged along a circulation path,
which extends in two horizontal transport paths 85, 86,
which are arranged one above the other, through the
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 27 -
baking oven 82. The baking tong chain 84 is integrated
in a chain conveyor, which is arranged along the
circulation path, conveys the baking tongs 83 through
the two transport paths 85, 86 and, via its chain
wheels arranged on the front and rear end of the baking
oven 82, deflects them from one transport path into the
other.
The chain conveyor is arranged in the elongated
framework 87 of the baking oven 82 between the two oven
side walls 88, 89. The baking tongs 83 are arranged in
the chain conveyor between two lateral transport chains
90, 91 and are fixed on the chain link plates 90a, 91a
thereof. Hinged bolts protrude outwards from the
transport chains 90, 91, on which hinged bolts running
wheels 92, 93 are mounted rotatably, with which the
chain conveyor is supported in both transport paths 85,
86 in each case on running rails 94, 95, 96, 97, which
run in the oven longitudinal direction and are fixed on
the two side walls 88, 89 of the oven framework 87.
Figures 21 and 22 show a baking tong 84 of the baking
oven 82.
In the case of each baking tong 83, a lower baking
plate in the form of a susceptor plate 98 is arranged
in the lower tong part between a left-hand and a right-
hand, lateral edge piece 99, 100 of the lower tong
part. The lower tong part is connected at its two edge
pieces 99, 100 via horizontal bolts to the chain link
plates 90a, 91a of the lateral transport chains 90, 91
of the chain conveyor. A hinge 101, which pivotably
connects the lower tong part to the upper tong part, is
fitted to the left-hand edge piece 99 of the lower tong
part. In the upper tong part, an upper baking plate in
the form of a susceptor plate 102 is arranged between a
left-hand and a right-hand lateral edge piece 103, 104
of the upper tong part. The left-hand edge piece 103 of
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 28 -
the upper tong part is connected to the hinge 101 and a
control roller 105 is fitted on the right-hand edge
piece 104 of the upper tong part, with the aid of which
control roller 105 the baking tong 83 is opened and
closed by the upper tong part being pivoted. The two
susceptor plates 98, 102 each have a rear side, which
is arranged on the outside of the baking tong 83 and
via which they can be inductively heated without any
contact, and a front side, which is arranged in the
interior of the baking tong 83 and on which the baking
face of the upper or lower baking plate is arranged.
When the baking tong 83 is closed, the two susceptor
plates 98, 102 are positioned one above the other in
such a way that they are aligned horizontally, and the
baking faces arranged on their front sides face one
another.
The baking tongs 83 are each provided with a baking
tong locking apparatus 106. The apparatus 106 provides
a rigid locking element, which is formed by a bolt 107,
which is fitted on the right-hand edge piece 104 of the
upper tong part and protrudes beyond the front side of
the upper tong part. The apparatus 106 provides a
movable locking element, which is formed by a pivotable
hook 108. The hook 108 in the case of the right-hand
edge piece 100 of the lower tong part is arranged on
the underside next to a through-opening, which passes
through the edge piece 100, for the bolt 107. A control
roller 108a protrudes downwards from the hook 108, with
the aid of which control roller 108a the hook 108 can
be pivoted about its pivot axis, which is arranged at
right angles with respect to the edge piece 100. When
the baking tong 83 closes, the upper tong part pivots
towards the lower tong part and the bolt 107 is
inserted into the through-opening in the right-hand
edge piece 100 of the lower tong part. At the end of
the closing movement, the bolt 107 is arranged
vertically and the free bolt end 109 protrudes
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 29 -
downwards beyond the rear side of the right-hand edge
piece 100 of the lower tong part. The hook 108 is
pivoted with the aid of the control roller 108a about
its pivot axis, which is parallel to the bolt 107. The
hook 108 is pivoted with its hook head 110 towards the
bolt 107 until the hook head 110 engages in a lateral
circumferential groove of the bolt 107. Before the
baking tong 83 opens, the hook 108 is pivoted away from
the bolt 107 with its hook head 110 and the bolt 107 is
released.
In the front oven half 82a, an output station 111, an
input station 112, a device 113 for opening and closing
the baking tongs 83 and an actuating apparatus 114 for
the baking tong locking apparatuses 106 of the baking
tongs 83 are arranged on the upper transport path 85.
In the output station 111, baked, crispy/crunchy wafer
sheets are removed from the open baking tongs 83. In
the input station 112, liquid wafer dough is introduced
into the open baking tongs 83. Downstream of the input
station 112, the baking tongs 83 are closed by the
device 113. The device 113 provides a guide rod, which
is arranged along the upper transport path 85 and along
which the baking tongs 83 run with their control
rollers 105 and are opened and closed by the control
rollers 105.
The actuating apparatus 114 for the baking tong locking
apparatuses 106 provides a stationary, sloping rod,
which protrudes into the path of the control roller
108a of the hook 108 of the baking tong locking
apparatus 106. In the case of each closed baking tong
83 which runs past the actuating apparatus 114, the
control roller 108a of the hook 108 of the baking tong
locking apparatus 106 comes into engagement with the
sloping rod of the actuating apparatus 114. As a result
of this engagement, the hook 108 is pivoted via the
control roller 108a and the baking tong locking
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
,
- 30 -
apparatus 106 is locked. The chain conveyor conveys the
closed and locked baking tongs 83 rearwards towards the
rear end of the baking oven 82 in the upper transport
path 85 and, in the lower transport path 86, forwards
towards the front end of the baking oven 82. In the
front oven half 82a, a second actuating apparatus 115
for the baking tong locking apparatuses 106 of the
baking tongs 83 is arranged on the lower transport path
86. The second actuating apparatus 115 provides a
sloping rod, which protrudes into the path of the
control roller 108a and, in the case of each closed and
locked baking tong 83, which runs past it, comes into
engagement with the control roller 108a of the hook 108
of the baking tong locking apparatus 106, pivots the
hook 108 and unlocks the baking tong locking apparatus
106.
The baking oven 82 is provided with an induction
heating device. The baking area 116 is accommodated in
the rear oven half 82b. In the baking area 116, an
upper baking zone 117 is arranged on the upper
transport path 85 and a lower baking zone 118 is
arranged on the lower transport path 86. Elongated,
upper and lower inductors 119, 120, 121, 122 are
provided in the two baking zones 117, 118 and are
connected, via electrical lines 123, to an AC generator
124, which is arranged next to the front oven half 82a
and supplies the inductors 119, 120, 121, 122 with
current. The inductors 119, 120, 121, 122 are arranged
in the two baking zones 117, 118 in each case above or
below the closed baking tongs 83. They produce in each
case one large-area, broad and elongated magnetic
field, which extends over a plurality of baking tongs
83, which are arranged one behind the other.
In the upper baking zone 117, an elongated, upper
inductor 119 is arranged over the baking tongs 83 and
an elongated, lower inductor 120 is arranged below the
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 31 -
baking tongs 83. The magnetic field produced by the
upper inductor 119 reaches downwards as far as the
baking plates, which are arranged on the upper sides of
the baking tongs 83 and are in the form of susceptor
plates 102. These susceptor plates 102 are inductively
heated by means of the magnetic field which is produced
by the upper inductor 119 without any contact. The
magnetic field produced by the lower inductor 120
reaches upwards as far as the baking plates which are
arranged on the undersides of the baking tongs 83 and
are in the form of susceptor plates 98. These susceptor
plates 98 are inductively heated by the magnetic field
produced by the lower inductor 120 without any contact.
In the lower baking zone 118, an elongated, upper
inductor 121 is arranged over the baking tongs 83 and
an elongated, lower inductor 122 is arranged below the
baking tongs 83. The magnetic field produced by the
upper inductor 121 reaches downwards as far as the
baking plates which are arranged on the upper sides of
the baking tongs 83 and are in the form of susceptor
plates 98. These susceptor plates 98 are inductively
heated by the magnetic field produced by the upper
inductor 121 without any contact. The magnetic field
produced by the lower inductor 122 reaches upwards as
far as the baking plates which are arranged on the
undersides of the baking tongs 83 and are in the form
of susceptor plates 102. These susceptor plates 102 are
inductively heated by the magnetic field produced by
the lower inductor 122.
The inductors 119, 120, 121, 122 extend in the
respective baking zone 117, 118 along the circulation
path of the baking tongs 83 over a plurality of baking
tongs 83 arranged one behind the other. The inductors
119, 120, 121, 122 each produce a broad magnetic field,
which extends along the circulation path of the baking
tongs 83 over a plurality of baking tongs 83 arranged
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 32 -
one behind the other and, in the case of the baking
tongs 83 arranged one behind the other, inductively
heats the baking plates which are in the form of
susceptor plates 98, 102, without any contact. The
inductors 119, 120, 121, 122 can have different
designs. They can have the designs illustrated in
figures 13-17. The fixing of the inductors 119, 120,
121, 122 in the framework 87 of the baking oven 82
corresponds in each case to the fixing explained above
in connection with figures 10-12.
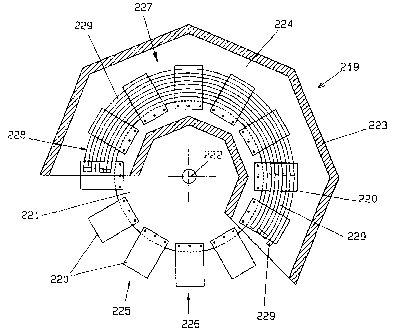
Figures 23 to 27 show a baking oven 125, in which a
plurality of baking tongs 127 are arranged next to one
another along a circular path on a horizontal, round
turntable 126 and are conveyed along the circular path
through the baking oven by means of the rotary movement
of the turntable 126. The turntable 126 can be rotated
about a vertical axis of rotation 128. The baking oven
125 has an annular or polygonal housing 129, which
extends along the circular path and in which the baking
area 130 of the baking oven 125 is arranged. The
housing 129 is arranged on a lower framework 131. The
housing 129 is designed to be open at the front side of
the baking oven 125. The input station and the output
station of the baking oven 125 are arranged in the open
region of the housing 129. A guide rod 132, which is
arranged along the circular path and along which the
baking tongs 127 run with their control rollers 133 and
are opened and closed by the control rollers 133, is
provided in the open region of the housing 129.
Each baking tong 127 has a lower tong part 134, which
is fixed on the turntable 126 and is connected
pivotably to an upper tong part 136 via a hinge 135,
which upper tong part 136 bears the control roller 133
at its free end. A lower baking plate in the form of a
susceptor plate 137 is arranged in the lower tong part
134 and an upper baking plate in the form of a
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 33 -
susceptor plate 138 is arranged in the upper tong part
136. The two susceptor plates 137, 138 each have a rear
side, which is arranged on the outside of the baking
tong 127 and via which they can be inductively heated
without any contact, and a front side, which is
arranged in the interior of the baking tong 127 and on
which the baking face of the upper or lower baking
plate is arranged. When the baking tong 127 is closed,
the susceptor plates 137, 138 are positioned one above
the other in such a way that they are aligned
horizontally and the baking faces, which are arranged
on their front sides, face one another.
The baking tongs 127 are conveyed by the rotary
movement of the turntable 126 along the circular path
through the baking area 130. A baking zone, which runs
along the circular path, is provided in the baking area
130. In said baking zone, an elongated, arcuate, upper
inductor 139 is arranged above the circular path and an
elongated, arcuate, lower inductor 140 is arranged
below the circular path. The two inductors 139, 140
produce a large-area, broad, elongated, arcuate
magnetic field, which extends along the circular path
over a plurality of baking tongs 127 arranged next to
one another. The magnetic field produced by the upper
inductor 139 reaches therefrom downwards as far as into
the upper tong parts of the baking tongs 127, in which
the upper baking plates in the form of susceptor plates
138 are inductively heated without any contact. The
magnetic field produced by the lower inductor 140
reaches therefrom upwards as far as into the lower tong
parts of the baking tongs 127, in which the lower
baking plates in the form of susceptor plates 137 are
inductively heated without any contact.
The upper inductor 139 is arranged in the housing 129
just above the upper baking plates, which are in the
form of susceptor plates 138, of the closed baking
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873 PCT/EP2009/000906
,
- 34 -
tongs 127. It is fixed in the housing 129 on an upper
support 141, which runs transversely with respect to
the circular path. It has four inductor bars 139a
arranged next to one another. Said inductor bars 139a
are in the form of flat, solid bars, which have a low,
rectangular full cross section. The flat inductor bars
139a are fixed on the upper support 141 via
electrically insulating fixing apparatuses 142. The
fixing apparatuses 142 provide L-shaped fixing clips
143, which are fixed with their vertically arranged,
upper limbs on the support 141 in such a way that they
are vertically adjustable. The flat inductor bars 139a
are arranged on the lower ends of the fixing
apparatuses 142 and are fixed on the horizontally
arranged, lower limbs of the fixing clips 143 via
vertical fixing screws 144. In each case a plurality of
electrically insulating intermediate pieces 145 are
arranged between the fixing screws 144 and the lower
limbs of the fixing clips 143 (figure 25).
The lower inductor 140 is arranged in the housing 129
just below the lower baking plates, which are in the
form of susceptor plates 137, of the closed baking
tongs 127. It is fixed in the housing 129 on a lower
support 146, which runs transversely with respect to
the circular path. It has four inductor bars 140a,
which are arranged next to one another. Said inductor
bars 140a are in the form of flat, solid bars, which
have a low, rectangular full cross section. The flat
inductor bars 140a are fixed on the lower support 146
via electrically insulating fixing apparatuses 147. The
fixing apparatuses 147 provide L-shaped fixing clips
148, which are fixed with their vertically arranged,
lower limbs on the support 146 in such a way that they
are vertically adjustable. The flat inductor bars 140a
are arranged at the upper ends of the fixing
apparatuses 147 and are fixed to the horizontally
arranged, upper limbs of the fixing clips 148 via
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
,
- 35 -
vertical fixing screws 149. In each case a plurality of
electrically insulating intermediate pieces 150 are
arranged between the fixing screws 149 and the lower
limbs of the fixing clips 148 (figure 26).
Figures 28 to 31 show a baking oven 151 for producing
baked molded products, in baking molds, which each
comprise two baking plates 152, 153 arranged one above
the other. These baking molds are arranged one behind
the other in the baking area 154 along a horizontal
baking stretch. The baking stretch extends from the
input station 155 of the baking oven 151 through a
baking zone 156 arranged in the baking area 154 to the
output station 157 of the baking oven 151. Portions of
dough are applied to the lower baking plates 152 of the
baking mold in the input station 155. At the beginning
of the horizontal baking stretch 158, the upper baking
plates 153 are lowered onto the lower baking plates 152
and as a result the baking molds are closed. In the
output station 157, the upper baking plates 153 are
lifted off from the lower baking plates 152 and the
baked molded products are output from the baking molds
opened thereby.
A lower chain conveyor 159 is arranged in the baking
oven 151 below the horizontal baking stretch 158, which
chain conveyor 159 bears the lower baking plates 152,
which are arranged along a lower circulation path. The
lower circulation path extends in two horizontal
transport paths 160, 161, which are arranged one above
the other, through the lower part of the baking oven
151. The transport path 160 on the upper side of the
chain conveyor 159 is arranged along the horizontal
baking stretch 158 and forms the baking section of the
chain conveyor 159. The transport path 161 on the
underside of the chain conveyor 159 forms the return
section of the chain conveyor 159. The chain conveyor
159 conveys its baking plates 152 through the two
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 36 -
transport paths 160, 161 and deflects them at its front
and rear end via chain wheels from one transport path
to the other.
The chain conveyor 159 is arranged in the elongated
framework 162 of the baking oven 151 between the two
side walls 163, 164 of the oven framework 162 in the
lower part of the baking oven 151. The chain conveyor
159 has two lateral transport chains 165, 166, between
which the lower baking plates 152 are arranged. The
transport chains 165, 166 are provided with laterally
protruding hinged bolts, on which in each case running
wheels 167, 168 are mounted rotatably, with which the
chain conveyor 159 in the case of the two transport
paths 160, 161 is supported on running rails 169, which
run in the oven longitudinal direction and are fixed on
the side walls 163, 164. The transport chains 165, 166
are in the form of plate link chains. The lower baking
plates 152 are fixed with their lateral edge pieces on
the chain link plates 165a, 166a of the two transport
chains 165, 166. The lower baking plates 152 are in the
form of susceptor plates which can be inductively
heated via their exposed rear sides without any contact
and whose front sides bear the baking faces of the
lower baking plates 152. Electrically insulating
interlayers 170, which prevent metallic contact between
the chain link plates 165a, 166a and the lower baking
plates 152, are arranged between the chain link plates
165a, 166a and the lower baking plates 152.
In the baking oven 151, an upper chain conveyor 171 is
arranged above the horizontal baking stretch 158 and
bears the upper baking plates 153, which are arranged
along an upper circulation path. The upper circulation
path extends in two horizontal transport paths 172,
173, which are arranged one above the other, through
the upper part of the baking oven 151. The transport
path 172 on the underside of the chain conveyor 171 is
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 37 -
arranged along the horizontal baking stretch 158 and
forms the baking section of the chain conveyor 171. The
transport path 173 on the upper side of the chain
conveyor 171 forms the return section of the chain
conveyor 171. The chain conveyor 171 conveys its baking
plates 153 through the two transport paths 172, 173 and
deflects them at its front and rear end via chain
wheels from one transport path to the other.
The upper chain conveyor 171 has two lateral transport
chains 174, 175. The upper baking plates 153 are
arranged between the two transport chains 174, 175 and
are suspended in freely pendulous fashion on bolts bl,
b2, which protrude inward from the transport chains
174, 175. The baking faces are arranged on the
downwardly pointing front sides of the upper baking
plates 153. The upper baking plates 153 bear, on their
lateral edge pieces, upwardly protruding suspension
means gl, g2, with which they are suspended in freely
pendulous fashion on the bolts bl, b2 of the transport
chains 174, 175. The upper baking plates 153 are held
in their position with the baking faces pointing
downward by means of the force of gravity. The upper
baking plates 153 are in the form of susceptor plates
which can be inductively heated via their upwardly
pointing rear sides without any contact. Electrically
insulating interlayers 176, which prevent metallic
contact between the suspension means gl, g2 and the
upper baking plates 153, are arranged between the
susceptor plates and the suspension means gl, g2 of the
upper baking plates 153. The transport chains 174, 175
are provided with outwardly protruding hinged bolts, on
which in each case running wheels 176, 177 are mounted
rotatably, with which the chain conveyor 171, in the
case of the two transport paths 172, 173, is supported
on running rails 178, which run in the oven
longitudinal direction and are fixed on the side walls
163, 164 of the oven framework 162.
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 38 -
The baking oven 151 is provided with an induction
heating device. The induction heating device provides,
in the baking zone 156, an elongated, upper inductor
179, which produces a large-area, broad and elongated
magnetic field, which extends over a plurality of
baking molds arranged one behind the other. The upper
inductor 179 is arranged just above the baking molds
arranged along the horizontal baking stretch 158. The
upper baking plates 153, which are arranged on the
upper sides of the baking molds and are in the form of
susceptor plates, are inductively heated by the
magnetic field produced by the upper inductor 179
without any contact. The induction heating device
provides, in the baking zone 156, an elongated, lower
inductor 180, which produces a large-area, broad and
elongated magnetic field, which extends over a
plurality of baking molds arranged one behind the
other. The lower inductor 180 is arranged just below
the baking molds arranged along the horizontal baking
stretch 158. The lower baking plates 152, which are
arranged on the undersides of the baking molds and are
in the form of susceptor plates, are inductively heated
by the magnetic field produced by the lower inductor
179 without any contact.
The induction heating device furthermore provides
additional inductors 181, 182, which are arranged on
the return sections 171, 173 of the two chain conveyors
159, 171.
In the case of the return section 161 of the lower
chain conveyor 159, an additional inductor 181 is
provided, which produces a large-area, broad and
elongated magnetic field, which extends over a
plurality of lower baking plates 152 arranged one
behind the other. This additional inductor 181 is
arranged above the upwardly pointing rear sides of the
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 39 -
lower baking plates 152. The lower baking plates 152,
which are arranged in the return section 161 and are in
the form of susceptor plates, are inductively heated by
the magnetic field produced by the additional inductor
181 without any contact.
In the case of the return section 173 of the upper
chain conveyor 171, a further additional inductor 182
is provided, which produces a large-area, broad and
elongated magnetic field, which extends over a
plurality of upper baking plates 153 arranged one
behind the other. This additional inductor 182 is
arranged above the upwardly pointing rear sides of the
upper baking plates 153. The upper baking plates 153,
which are arranged in the return section 173 and are in
the form of susceptor plates, are inductively heated by
the magnetic field produced by the additional inductor
182 without any contact.
The inductors 179, 180 and the additional inductors
181, 182 each extend along the path of the upper and,
respectively, lower baking plates 152, 153 over a
plurality of upper and, respectively, lower baking
plates 152, 153 arranged one behind the other. The
inductors 179, 180, 181, 182 in each case produce a
broad magnetic field, which extends along the
circulation path of the baking plates 152, 153 over a
plurality of baking plates 152, 153 arranged one behind
the other and inductively heats a plurality of baking
plates 152, 153, which are arranged one behind the
other and are in the form of susceptor plates, without
any contact. The inductors 179, 180, 181, 182 can have
different designs. They can have the designs
illustrated in figures 13-17. The
fixing of the
inductors 179, 180, 181, 182 in the framework 162 of
the baking oven 151 corresponds in each case to the
fixing explained above in connection with figures 10 to
12.
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 40 -
Figures 32 to 34 show a baking installation 183 for
producing flat molded products which are baked on both
sides. The baking installation 183 provides a first
baking oven 184, in which flat dough cakes are produced
and are baked on the underside. A turning apparatus 185
adjoins the first baking oven 184. In said turning
apparatus 185, the dough cakes which are baked on the
underside are turned with the upper side down and then
transferred to a second baking oven 186 with the upper
side down, in which baking oven 186 the dough cakes are
baked on the other side.
In the first baking oven 184, planar baking plates 187
are arranged along a circulation path, which extends
along two horizontal transport paths 188, 189 arranged
one above the other through the baking oven 184. The
input station 190 is arranged on the lower transport
path 189. In the input station 190, the flat dough
cakes are produced. For this purpose, a liquid baking
dough is applied to the upwardly pointing baking faces
of the baking plates 187. The output station 191 is
arranged at the rear end of the baking oven 184 on the
upper transport path 188. In the output station 191,
the dough cakes which are baked on the underside are
removed from the upwardly pointing baking faces of the
baking plates 187 and transferred to the turning
apparatus 185.
The baking oven 184 has a chain conveyor 192, which is
arranged along the circulation path of the planar
baking plates 187 and circulates in the clockwise
direction. The chain conveyor 192 conveys its baking
plates 187 through the two transport paths 188, 189 and
deflects them at its front and rear end via chain
wheels from one transport path to the other. The chain
conveyor 192 has two lateral transport chains 193, 194.
These are each in the form of plate link chains, in
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 41 -
which the hinged bolts protrude laterally on the inside
and on the outside. The baking plates 187 are arranged
between the two transport chains 193, 194 and are
suspended in freely pendulous fashion on those sections
of the hinged bolts 195, 196 which protrude inwards in
each case from the transport chains. The baking faces
are arranged on the upwardly pointing front sides of
the baking plates 187. The baking plates 187 bear, on
their lateral edge pieces, upwardly protruding
suspension means 197, 198. These suspension means 197,
198 are used to suspend them in freely pendulous
fashion on those sections of the hinged bolts 195, 196
which protrude inwards from the two transport chains
193, 194. The baking plates 187 are held in their
position in which the baking faces point upwards by the
force of gravity. The baking plates 187 are in the form
of susceptor plates which can be inductively heated via
their downwardly pointing rear sides without any
contact. Electrically insulating interlayers 199, which
prevent metallic contact between the suspension means
197, 198 and the baking plates 187, are arranged
between the susceptor plates and the suspension means
197, 198 of the baking plates 187. Running wheels 200,
201 are mounted rotatably on those sections of the
hinged bolts 195, 196 which protrude outwards from the
two transport chains 193, 194, with which running
wheels 200, 201 the chain conveyor 192, in the case of
the two transport paths 188, 189, is supported on
running rails 205, which run in the oven longitudinal
direction and are fixed on the side walls 202, 203 of
the oven framework 204.
In the case of the baking oven 184, two baking zones
are provided in the baking area 206. An upper baking
zone 207 is provided on the upper transport path 188
and a lower baking zone 208 is provided on the lower
transport path 189. The baking oven 184 is provided
with an induction heating device. This provides, in the
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 42 -
case of the upper baking zone 207, an elongated
inductor 209, which produces a large-area, broad and
elongated magnetic field, which extends over a
plurality of baking plates 187, which are arranged one
behind the other and are in the form of susceptor
plates. The inductor 209 is arranged just below the
baking plates 187 which pass through the upper
transport path 188. The induction heating device
provides, in the case of the lower baking zone 208, an
elongated inductor 210, which produces a large-area
broad and elongated magnetic field, which extends over
a plurality of baking plates 187, which are arranged
one behind the other and are in the form of susceptor
plates. The inductor 210 is arranged just below the
baking plates 187 which pass through the lower
transport path 188.
The inductors 209, 210 can have different designs. They
can have the designs illustrated in figures 13-17. The
inductors 209, 210 differ from the inductors in these
figures by the number of the inductor bars which are
arranged next to one another. In the case of the
inductors 209 and 210, in each case 26 inductor bars
are arranged next to one another. The fixing of the
inductors 209, 210 in the framework of the baking oven
184 corresponds in each case to the fixing explained
above in connection with figures 10-12.
In the second baking oven 186, planar baking plates 211
are arranged along a circulation path, which extends
along two horizontal transport paths 211, 213, which
are arranged one above the other, through the baking
oven 186. The input station 214 is arranged at the
front end of the baking oven 186 on the upper transport
path 212. In the input station 214, the dough cakes
supplied by the turning apparatus 185 are deposited on
the upwardly pointing baking faces of the baking plates
211. The output station 215 is arranged in the center
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 43 -
of the baking oven 186 on the upper transport path 212.
In the output station 215, the dough cakes, which have
been baked on both sides, are removed from the upwardly
pointing baking faces of the baking plates 211 and
output from the baking installation 183.
The second baking oven 186 has a chain conveyor 216,
which is arranged along the circulation path of the
planar baking plates 211 and circulates in the
counterclockwise direction. The chain conveyor 216
corresponds in terms of its structural design to the
chain conveyor 192 of the first baking oven 184. In the
case of the chain conveyor 216, the planar baking
plates 211 are likewise suspended in freely pendulous
fashion on the lateral transport chains of the chain
conveyor 216 and are in the form of susceptor plates,
which can be inductively heated without any contact.
The second baking oven 186 is provided with an
induction heating device, which, on the two transport
paths 212, 213, provides in each case one elongated
inductor 217, 218, which produces a large-area, broad
and elongated magnetic field, which extends over a
plurality of baking plates 211, which are arranged one
behind the other and are in the form of susceptor
plates. The inductors 217, 218 are in each case
arranged just below the baking plates 211, which pass
through the transport paths 212, 213 and are
inductively heated by the magnetic field produced by
the respective inductor 217, 218 without any contact.
The inductors 217, 218 can have different designs. They
can have the designs illustrated in figures 13-17. The
inductors 217, 218 differ from the inductors in these
figures by the number of the inductor bars which are
arranged next to one another. In the case of the
inductors 217, 218, in each case 26 inductor bars are
arranged next to one another. The fixing of the
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 44 -
inductors 217, 218 in the framework of the baking oven
186 in each case corresponds to the fixing explained
above in connection with figures 10-12.
Figure 35 shows a baking oven 219 for producing flat
molded products which are baked on one or both sides.
The baked molded products are produced on baking plates
220, which are arranged next to one another on a
horizontal turntable 221 along a circular path. The
turntable 221 is capable of rotating about a vertical
axis of rotation 222. The baking plates 220 are fixed
on the turntable 221 and protrude radially beyond its
outer edge. The baking plates 220 are moved by the
rotary movement of the turntable 221 through the baking
oven 219. The baking oven 219 has an annular or
polygonal housing 223, which extends along the circular
path of the baking plates 220 and in which a baking
area 224 is arranged. The housing 223 is designed to be
open on the front side of the baking oven 219. The
input station 225 and the output station 226 of the
baking oven 219 are arranged in the open region of the
housing 223. In the input station 225, flat dough cakes
are produced. For this purpose, liquid baking dough is
applied to the upwardly pointing baking faces of the
baking plates 220. The baking plates 220 which have
been provided with the dough cakes are conveyed by the
turntable 221 through the baking area 224. At the
output station 226, the baked dough cakes are removed
from the baking plates 220 and are output from the
baking oven 219 in the form of dough cakes which have
been baked on one side or, when producing dough cakes
.
which are baked on both sides, are turned over with the
upper side down and deposited on the baking plates 220
again in order that they are baked on the other side as
well when they next pass through the baking area 224.
The dough cakes which are baked on both sides pass
through the baking area 224 twice and are only output
CA 02714468 2010-08-06
WO 2009/100873
PCT/EP2009/000906
- 45 -
from the baking oven 219 at the output station 226
after the second time.
The baking plates 220 of the baking oven 219 are in the
form of susceptor plates which can be inductively
heated without any contact. The susceptor plates 220
are inductively heated in the baking area 224 by an
induction heating device 227 without any contact. The
susceptor plates 220 pass the heat produced within them
on to the baking faces arranged on their upper sides by
means of thermal conduction, on which baking faces the
dough cakes are baked.
The induction heating device 227 provides at least one
elongated inductor 228, which is arranged along the
circular path and extends along the circular path over
a plurality of baking plates 220 arranged next to one
another. The inductor 228 has a plurality of inductor
bars 229, which are arranged next to one another
transversely with respect to the circular path, extend
along the circular path and are curved in arcuate
fashion. The inductor 228 produces a broad magnetic
field, which extends along the circular path over a
plurality of baking plates 220 arranged next to one
another and inductively heats them without any contact.
The elongated inductor 228 is preferably arranged below
the circular path and parallel to it. The elongated
inductor 228 can also be arranged above the circular
path. In the baking area 224, such an elongated
inductor 228 can also be arranged above and below the
circular path.
The elongated inductor 228 can have different designs.
It can have one of the designs illustrated in figures
13-17. The fixing of the inductor 228 in the housing
223 of the baking oven 219 corresponds to the fixing
explained above in connection with figures 10-12.