Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02754411 2011-10-05
ZIP LINE APPARATUS
[01] FIELD OF THE INVENTION
[02] The invention relates to a trolley for guiding a person or an object
using
gravity along an extended cable line suspended between two spaced apart
objects
such as trees or towers, and more specifically relates to a zip line kit or
system
with an easily adjustable seat and handle arrangement which in combination
with
a wheel and braking system for the device facilitates a safe and controllable
descent along the cable line. The trolley is provided with at least two wheels
spaced apart at a suitable distance to increase ride smoothness, provide
sufficient
space to accommodate the braking system and improve operation of the zip line
system along the extended cable.
[03] BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
[04] A zip line system is a work or recreational device which allows a user
to
maneuver or traverse themselves, or another person, object or load by use of a
trolley along a suspended line or cable generally from a higher point of
elevation
to a lower point of elevation using gravity, although the trolley, person,
object or
load may be moved in any direction along the suspended line or cable depending
on the use of different forces, arrangement of the zip line system and
necessity.
The line or cable can be a rope, steel cable, wire or other similar elongate
support,
even a rigid elongate support such as a steel or wooden beam, which can be
extended between two points. The line or cable and zip line system generally
permits travel of the trolley along the vector defined by the cable or line.
The
1
CA 02754411 2011-10-05
trolley has at least a wheel and preferably a plurality of wheels rotatably
supported by the trolley which in turn support the trolley upon the line or
cable.
[05] The trolley may be permanently and/or removably supported by the cable
and will generally include at least a handle, sling, harness or netting
affixed or
suspended from the trolley to support the person, load or object. Commercial
trolleys for instance for mountain climbing and eco-tourism like jungle canopy
tours use a trolley to which a safety harness is secured. The safety harness
is a
support which is merely a set of fabric straps that are adjusted around the
legs and
buttocks of a person with a suspension strap that connects to the trolley or
pulley
system. The person is directly suspended from the trolley system and must hold
onto the suspension strap as they traverse the zip line.
[06] Known zip line systems do not have a seat to comfortably support the
rider during the traverse, nor an adjustment mechanism which makes the seat
easily adjustable for people of different sizes. Usually the rider dangles
within the
harness directly from the trolley system. Known zip line systems also
generally
do not have any type of handle for a rider to hold directly onto the trolley
while
they are also supported by the adjustable seat.
[07] Additionally, known zip line systems do not have any type of braking
system in the trolley itself and the user has little or no ability to slow
themselves
down, or even stop themselves during the traverse. In most current systems a
rubber or cushioned bumper is positioned at the base of the cable to intercept
and
stop the trolley from sliding further down the cable. This provides little
safety or
control to the user and thus there exists a need for an improved zip line
system,
2
CA 02754411 2011-10-05
trolley and seat support for a zip line system as well as a brake safety
device to
slow the descent of the trolley and person, load or object traversing along
the
cable of the zip line system.
[08] OBJECTS AND SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[09] The zip line system of the present invention may be offered as a
completely assembled unit or a kit with various components including for
example the trolley, a braking system, handle, webbing, a seat and a trolley
return
line. Other components of the system could include but are not limited to a
safety
harness, a cable as well as structural accessories, fasteners and tools such
as a
come-along and cable cutters which facilitate constructing and suspending the
cable between two points.
[010] The zip line kit has an improved trolley system that supports at
least one,
and preferably two or more wheels sandwiched between two frame pieces. The
frame pieces can be manufactured of aluminum or other metal, certain rigid
plastics or other stiff durable materials such as carbon fiber could be used
as well.
The frames are affixed to one another sandwiching the wheels therebetween. The
frames can be removably affixed for instance by bolts, screws or other such
fastening devices. The frames can be permanently connected for instance by
rivets or welding or even hingedly connected by a hinge or quick-release and
fastening system which allows the frames to hinge along parallel or non-
parallel
planes with respect to one another. Such a hinge connection may facilitate
taking
the trolley on and off a cable without having to take the cable down or
completely
take the trolley apart.
3
CA 02754411 2011-10-05
[011] In any event the trolley is securely affixed to and supported on the
cable,
line, rope or wire with the cable inserted through, i.e. generally in a planar
relation
between the two frame pieces and below the wheels, so the wheels rest on the
top
of the cable and support the trolley so that it can roll efficiently along and
traverse
the cable. It is to be appreciated that there could be an additional wheel or
wheels
below the cable to facilitate maintaining the trolley tracking along the
cable.
[012] A handle is secured through each of the frame pieces using cushioned
grips, improving the comfort, and grip of the handle for the rider.
Alternatively, a
dual piece handle may be formed by engaging threadable sections which engage
with one another, or which engage directly with frame pieces. The frame pieces
also support fabric webbing, although a cable or rope may also be
contemplated,
that extends from the base of each of the frame pieces to support a seat for
the zip
line rider beneath the trolley. This adjustment allows the seat to be
positioned at a
desired distance below the handle for a rider to comfortably hold the handle
essentially above their head while seated. The seat may be of aluminum,
another
metal or of a plastic composite with an ergonomic shape to allow for a rider
to sit
comfortably.
[013] It is an object of the present invention to provide a trolley for a
zip line
system including a braking system including a brake pad and actuator to
control
the amount of braking desired by the rider as the rider slides along the
cable.
[014] It is another object of the present invention to provide an improved
zip
line system and trolley for traversing a cable with the trolley having an
increased
distance between each wheel to permit the trolley to more efficiently traverse
the
4
CA 02754411 2011-10-05
cable and permit the braking system to be located between the spaced apart
wheels.
[015] It is another object of the present invention to provide a zip line
system
with an easily adjustable seat to more comfortably accommodate riders of
different sizes.
[016] It is still another object of the present invention to secure the
pulley
system of the zip line apparatus within a quick release frame to allow the
apparatus to be easily secured and removed from a cable, rope or wire.
[017] It is yet another object of the present invention to have a braking
system
which a rider activates to slow the descent of the zip line along the cable or
wire.
[018] It is still yet another object of the present invention to have a
braking
system which a rider de-activates to slow the descent of the zip line along
the
cable or wire.
[019] It is a further object of the present invention that the brake pad
has a lining
to increase frictional resistance while reducing wear on the wire or cable.
[020] The present invention is directed to trolley for traversing a zip
line system
comprising a frame including at least two wheels rotatably affixed to the
frame; a
brake affixed to the frame for engaging an object supporting the trolley in
the zip
line system; a handle secured to the frame permitting a user to grasp the
trolley;
an adjustable seat secured to the frame; and wherein the brake is actuated by
the
user while grasping the handle of the trolley to control the descent of the
user and
the trolley along the zip line system.
CA 02754411 2011-10-05
[021] The present invention is also directed to a method of carrying a
person or
object along an extended wire comprising the steps of attaching a pulley
system to
a frame, the pulley system adequate to roll along the wire; attaching a
braking
system to the frame to control the speed of the person or object along the
wire;
attaching a seat using fabric webbing to the frame, the fabric webbing being
adjustable to change the distance of the seat from the frame; and attaching a
handle to the frame.
[022] The present invention is further directed to a kit for a zip line
system
comprising a frame; a pulley system; a braking system; one or more straps of
fabric webbing; an adjustable seat; and a handle.
[023] These and other features, advantages and improvements according to
this
invention will be better understood by reference to the following detailed
description and accompanying drawings.
[024] BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[025] Several embodiments of the present invention will now be described by
way of example only, with reference to the accompanying drawings in which:
[026] FIG. I is a perspective view of an embodiment of the zip line system
of
the present invention;
[027] FIG. 2 is an embodiment of the zip line system kit;
[028] FIGS. 2A ¨ 2 E are views of the components of the zip line system kit
of
the present invention, including a frame, a handle a braking system, a seat
and a
suspension strap, respectively;
6
[29] FIG. 3A is a perspective view of a first embodiment of the frame and
brake assembly for an embodiment of the zip line system of the present
invention;
[30] FIG. 3B is an exploded view of a first embodiment of the frame and brake
assembly
for an embodiment of the zip line system of the present invention;
[31] FIG. 3C is a perspective view of an embodiment of the zip line system
with a
first embodiment of the frame and brake assembly;
[32] FIG. 4 is an exploded view of a second embodiment of the frame and brake
assembly for another embodiment of the zip line system of the present
invention;
[33] FIG. 5A is a perspective view of a second embodiment of the frame and
brake
assembly for another embodiment of the zip line system of the present
invention;
[34] FIG. 5B is an exploded view of a second embodiment of the frame and brake
assembly for another embodiment of the zip line system of the present
invention;
[35] FIG. 5C is a perspective view of another embodiment of the zip line
system
with a second embodiment of the frame and brake assembly;
[36] FIG. 6A - 6B are perspective views of an embodiment of the adjustable
seat for an
embodiment of the zip line system of the present invention;
[37] FIG. 7A - 7B are perspective views of a further embodiment of the
adjustable seat
for an embodiment of the zip line system of the present invention;
[38A] FIG. 8 is a perspective view of an embodiment of the zip line system of
the
present invention with cable and tower.
[38B] FIG. 9 is a perspective view of an embodiment of the zip line system of
the
present invention with cable and tower.
7
CA 2754411 2018-03-28
CA 02754411 2011-10-05
[039] DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
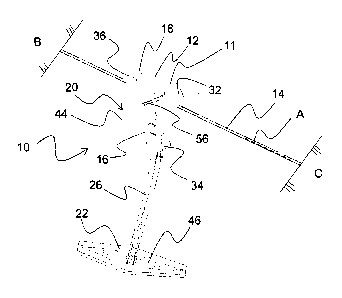
[040] FIG. 1 shows in general a zip line apparatus 10 of the present
invention
including a trolley 11 with a braking system 12 supported on an extended cable
14. The trolley 11 comprises two frame pieces 16 that house one or more wheels
18 for engaging the cable 14. The cable is understood to be in one embodiment
an extended steel cable, but could alternatively be a rope, line, rail or
wire, but for
purposes of description is hereinafter referred to as cable 14. The cable is
fastened at either end between two spaced apart points B-C to generally define
a
longitudinal travel axis A for the trolley. The trolley 11 may also include a
braking system 12, handle 20, a seat 22 and an adjustment mechanism 26
facilitating changing the spacing between the seat 22 and the trolley 11.
[041] A basic zip line kit 30 is shown in FIG. 2 and the components of the
kit 30
are shown in FIGS. 2A ¨ 2E comprising the trolley 11, handle 20, braking
system
12, seat 22, and adjustment mechanism 26, respectfully. The kit 30 could
alternatively include more or less components, for example, the kit might not
contain the braking system 12 if such a braking system where not necessary or
desired in a certain zip line application. The kit could, by way of example,
also
include additional components like the cable 14 and parts for securing and
extending the cable 14 between the points B-C.
[042] The generally triangular shaped frame pieces 16 of the trolley 11 as
shown
in FIG. 2A define a series of pivot points 38, attachment points 39 as well as
other
openings and slots to facilitate the attachment of the wheels 18, secure the
opposing frame pieces 16 together and position the braking system 12, handle
20,
8
CA 02754411 2011-10-05
seat 28 and adjustment mechanism 26. Pivot points 38 are positioned at what
are
defined here as the upper opposing corners of the trolley 11 to rotatably
attach the
wheels 18 between the triangular shaped frame pieces 16. Two wheels 18 are
used
in the preferred embodiment although additional pivot points and wheels may be
configured and overall dimensions of the frame pieces 16 may be altered to
accommodate alternative configurations.
[043] The center portion of the trolley has an opening 40 for the handle 20
to be
inserted through or bolted onto the frame 16, the handle 20 may be a metal,
wood
or other similar rigid material bar or rod, which is inserted through the
opening 40
so as to extend perpendicularly relative to the planar surface 42 of the frame
16 as
shown in FIG. 1. The handle 20 may be round, or other profile such as square
or
rectangular with the opening 40 similarly designed, and be of a various
diameter
or width to comfortably accommodate the hands of a rider 24 gripping the
handle
20 by wrapping their fingers around the handle 20.
[044] The handle 20, as shown in FIG. 2B, may have a removable cushioned
grip 44 that is slid onto or affixed onto the handle 20, providing comfort to
the
rider 24 and helping to secure the handle in the opening 40 where the ends of
the
grips 44 abut against the portion of the frame 16 surrounding the handle
opening
40. In this way, the opening 40 in the frame 16 for the handle 20 may be of a
diameter smaller than an outer circumference of the grip 44 providing for the
grip
44 to maintain the handle 20 in the opening 40 with the trolley 11. The grip
44
may be of a stiff foam or rubber that tightly adheres to the handle 20, but is
9
CA 02754411 2011-10-05
generally manually removable if necessary to remove the handle 20 from the
trolley 11.
[045] One embodiment of a seat 22 and the adjustment mechanism 26 as
flexible
fabric webbing is shown in FIGS. 2D and 2E. The seat 22 may be of any
ergonomical design and material to comfortably and safely support a rider 24.
In
the embodiment of FIG. 2D, the seat is designed to be sat upon by the rider
with
the seat 22 arranged under the user's hamstrings and/or gluteus maximus. The
general diamond shape of the seat 22 here facilitates the rider sitting upon
the seat
and essentially straddling the webbing of the adjustment mechanism 26. The
seat
22 may be other shapes, and may be rigidly formed from a piece of metal, such
as
aluminum, or the seat may be flexible, i.e. a flexible fabric or plastic such
that the
flexible seat conforms to the riders body size and shape. This is an important
safety consideration since a flexible seat would be able to bend around the
body
proportions of any size rider from child to adult, and securing them closely
without changing the size of the seat for different riders. In either a rigid
seat or a
flexible seat, the seat may have cutouts 46, slots 47 or other openings 50,
which
define alternative securing points to allow flexibility in attachment of the
seat 22
to the adjustment mechanism 26.
[046] The adjustment mechanism 26 is in one embodiment fabric webbing 50 of
a reasonable length, generally between for instance 2.44m ¨4.57 (8-15 feet)
long,
to provide sufficient adjustment between the seat and trolley for the size of
the
rider. The critical distance for which the adjustment mechanism 26 is adjusted
is
based on the extension of the rider's arms over their head to grasp the handle
20
CA 02754411 2011-10-05
while sitting on the seat 22 so that their head is entirely below the trolley.
In other
words it is the distance between the handle 20 and the seat 22 which permits
the
rider to sit comfortably on the seat 22 and reach over their head and grasp
the
handle 20 so that they are securely suspended below the trolley 11 and upon
the
seat 22. For a child the webbing would be adjusted to shorten the distance
between the seat and trolley, and for an adult of course the webbing 50 would
be
lengthened to provide a greater distance therebetween.
[047] Although other ways of adjusting the relative seat and trolley
distance are
possible, webbing is a good choice for the adjustment mechanism because of its
flexibility and tensile strength. The flexibility enables the user to easily
adjust the
length of webbing to accommodate a rider. Webbing is inexpensive, strong and
available in a myriad of widths. An appropriate size for the adjustment
mechanism 26 is a width of between about 1.91cm ¨ 3.81cm (3/4" to 1/1/2") and
preferably 1" with a tensile strength of ¨15kN ¨ ¨35kN (-3000 lb. - ¨7000 lb.)
and more specifically a tensile strength of ¨20kN (-4000 lb). The webbing is
preferably resistant to mildew, aging and abrasion. Alternative adjustments
and
attachments of the frame to the seat are discussed in detail below.
[048] The braking system 12 as shown in one embodiment in FIG. 2C is also
supported within the frame 16 of the trolley 11 and generally includes a brake
pad
52 aligned anywhere adjacent the cable 14 for contacting the cable, although
the
most practicable alignment is above or below the cable 14 for contacting the
cable
14 when the braking system 12 is operated by the rider. The brake pad 52 may
have a contact length which depends on the amount of friction desired to be
11
CA 02754411 2011-10-05
generated during braking operations. The contact length of the brake can be
extended to the full length between the wheels 18 or to any desired length to
sufficiently contact the cable 14 and create a frictional resistance to slow
the
trolley system 10 down upon actuation of the braking system. The brake pad 52
may be retained and float above the cable 14 using a tension spring or below
the
cable 14 resting on support or spacer 34 prior to activation. By floating
adjacent
the cable the brake pad 52 may be in light contact with the cable 14 and ride
along
the cable without creating much braking friction until energized by the rider.
The
brake pad 52 may also be provided with a contact surface which is angled or
curved to provide additional frictional contact with the cable 14.
[049] Turning to FIG. 3A, in one embodiment, the two wheels 18 may be
positioned at the upper corners of the trolley 11 providing spacing between
the
pivot points 38 in a range of at least 10.2 cm to 20.3 cm (4" and 8") and more
specifically at a distance c of 11.4 cm to 14 cm (4% "to 5% "). The wheels 18
are
secured in the trolley 11 and thus along the cable 14 at an increased distance
relative to known zip line systems so that rider, load or weight is
distributed along
a greater length and surface area of the cable 14 reducing tension and bending
of
the cable, giving the rider a smoother ride. The wheels 18 are generally
fabricated
of stainless steel, brass or other durable material with sealed, internal or
external
bearings 27 to optimize rolling and rotation of the wheels and trolley along
the
cable 14. Such wheels 18 are often referred to as a sheave which is a wheel or
roller with a groove 32 along its edge for engaging a belt, rope or cable 14.
When
hung between two supports equipped with a belt, rope or cable 14, one or more
12
CA 02754411 2011-10-05
sheaves make up a pulley, or as in this case are embodied as the trolley 11.
The
words sheave and pulley may be sometimes used interchangeably.
[050] Spacers 34 may be positioned between the frame and the connecting
bolts 36 of the frame 16 and additionally at an offset to the pulleys 18 to
act as a
guide for the cable 14 along the pulley 18. Optionally runners or brackets
(not
shown) may also be positioned offset from the pulleys to act as cable guides.
[051] In the embodiment as shown in FIGS. 3A ¨ 3B, a U-shaped brake frame
54 is affixed in the frame 16 by a center connecting pin 36 and the brake
frame 54
supports the brake pad 52 above the cable 14. The brake frame 54 has an
elongate slot 57 in which the center connecting pin 36 permits the brake frame
54
to move linearly up and down. In this embodiment, a leaf spring 58 is
depicted,
although any spring or retention support may be contemplated, to maintain the
brake frame 54 in a disengaged position shown in FIG. 3A. The leaf spring 58
has
one end abutting the handle 20 and another end biasly engaging the brake frame
54 to maintain the brake frame 54 in a normally raised position, holding the
brake
pad 52 above, or in very slight or tenuous contact with the cable 14. The
brake
pad has a cable engaging surface 59 and may be formed from a metal bar of
steel,
aluminum or other metals as shown in FIG. 3A. The cable engaging surface 59
may be flat or it may be angularly formed or rounded to increase the overall
contact area of the brake pad 52 with the cable 14 as shown in FIG. 3B - 3C.
The
brake pad cable engaging surface 59 may have a lining of a heat resistant
material
with a desired durability and coefficient of dynamic friction in a range of
0.35 to
13
CA 02754411 2011-10-05
0.42 meaning a force of 1000kg (or pounds) will result in a brake force close
to
400kg (or pounds).
[052] As shown in an exploded view of the frame 16 and brake system in FIG.
3B, the actuator 56 is coupled to the brake frame 54 and inserted through both
legs of the U-shaped brake frame as shown. A central portion 60 of the
actuator
56 provides a bearing or attachment point for a second end of the leaf spring
58 so
that the leaf spring can directly influence the brake frame 54. Alternatively,
the
second end of the leaf spring 58 can be directly affixed to the brake frame
54.
[053] The actuator 56 is essentially a trigger for the user to actuate the
brake.
The ends of the actuator 56 pass through a brake pin slot 62 in each frame
piece
16, where the slot 62 is located above the handle opening 40 to allow for a
rider
24 to easily grasp the brake actuator 56 with one or more fingers while still
holding the handle 20. In the present embodiment, with their hands grasping
the
handles 20, the rider 24 can easily extend their pointer finger on either side
of the
trolley to engage the actuator 56 while continuing to maintain their grip on
the
handle 20. In this way the rider can compress the actuator 56 to pull down the
brake frame 54 and brake pad 52 against the bias of the leaf spring 58 and so
fully
engage the brake pad 52 with the cable 14. As the brake pad 52 contacts the
cable
14, frictional resistance between the brake pad 52 and cable 14 is increased
creating drag on the cable slowing the trolley 11 along the cable 14.
[054] The actuator 56 inserted through the brake pin slot 62 in the frames
16 of
the trolley 11 as shown in FIG. 3C facilitates easy actuation of the brake.
The
positioning of the actuator immediately above the handle 20 is ergonomically
14
CA 02754411 2011-10-05
=
appropriate even for small or inexperienced riders. The ability for a rider 24
to
grasp the actuator 56 while holding the handle 20 and pull down whenever the
rider feels their speed is too great is critical as it allows the rider to
hold or release
the brake 12 in any desired manner to control their rate of travel, generally
descent, along the cable 14.
[055] In an alternative embodiment as shown in FIG. 4 the brake frame 54 is
supported in the disengaged position by one or more coil springs 64
influencing
the brake frame 54. A spring support 66 may be snapped or clamped on to the
handle 20 or otherwise affixed to the frame 16 or brake frame54. Similar to
the
previous embodiment, the actuator 56 is inserted through the frame 16 and the
brake frame 54 and actuated by pulling down the brake frame 54 and brake pad
52 using the actuator 56 to bring the brake pad 52 into contact with the cable
14.
[056] Different types of springs and biasing devices may be used to bias
the
brake frame and brake pad 52. In an alternative device, the brake pad 52 may
be
positioned below or to the side of the cable 14 with the coil springs 64
holding the
brake frame 54 and brake pad 52 below and/or away from the cable 14. The rider
would then operate the actuator 56 to engage the braking system 12 and slow or
stop the descent of the trolley along the zip line system 10.
[057] In a further embodiment, the braking system 12 may be a simple lever
pin
66 that is affixed to the actuator 56 and pivots on an axis Z around a lever
midpoint, such as the connecting bolt 36 as shown in FIG. 5A. The use of a
smaller spacer 68 would allow the lever to be secured within the frame 16, but
also provide for an axis of rotation of the lever pin 66 about the bolt 36.
The lever
CA 02754411 2011-10-05
pin 66 may have a brake pad 70 that extends along an entire length of the
lever 66
from the actuator 56 to the pulley 18 or as shown in FIGS. 5A ¨ 5C a smaller
surface area that contacts the wire 14 immediately at the pulley to curb
rotation of
the pulley 18 and slow the descent of the zip line system 10. As shown in FIG.
5B, the actuator 56 is inserted through an opening 69 in the lever pin,
allowing the
pin to swing down and pivot around the Z axis and force the opposing end of
the
lever pin 66 having the brake pad 70 to contact the cable 14.
[058] As noted above the lever pin 66 may be positioned below the cable 14
as
shown, or alternatively be positioned above the cable 14 by shortening the
length
of the lever 66 and repositioning the axis point Z perpendicular to a point in
the
center of the frame 16 near the area of the brake pin slot 62. The actuator 56
and
brake pin slot 62 would then be positioned at the opposite end of the lever
brake
pad 70 and be pulled or pushed up to actuate the braking system 12.
[059] The lever pin brake pad may have a heat resistant lining made of a
material with a high coefficient of dynamic friction as described above. In
this
embodiment with a simple lever, a spring may not be necessary if the brake pad
70 is permitted to merely float or glide along the cable 14 in the disengaged
position and operation of the actuator 56 provides a greater frictional force
from
the brake pad 70 to the cable 14.
[060] The present invention is not intended to be limited to only the
braking
systems described above. Other braking system structures could also be used to
slow the trolley 11, for example a braking system where the brake is generally
in
an actuated state, i.e. firmly gripping the cable and the actuation of the
actuator 56
16
CA 02754411 2011-10-05
causes the braking system to essentially release the cable 14. In this way, a
rider
would actively control their descent by releasing the brake a desired amount,
and
if their hands came off the trolley 11 and/or released the brake 12, the
trolley 11
would immediately slow due to the influence of the brake 12 on the cable 14.
[061] The present invention also provides for alternative methods of
attaching
the frame assembly 16 to the seat 22 which supports the rider 24. As shown in
FIGS. 6A and 6B the frame 16 has a series of adjustment openings for linking
and
tightening the support webbing 26 to attach the seat or harness to the frame
16.
The support webbing 26 is first attached to the seat 22 by looping one or more
straps of webbing 26 through one or more slots 47 or openings 50 in the seat
or
around a seat attachment beam 48. A plastic roller 74 may be affixed to or
snapped on to the opening or beam to smooth the surface edge and prevent
cutting
of the seat 22 into the strap 26. The first end of the webbing 26 may be
secured to
the seat 22 or alternatively the strap 26 is looped through and around
therefore
providing two ends of the webbing 26 for attachment to the frame 16.
[062] In a first embodiment, the webbing 26 is inserted through two
attachment
beams 48 and each webbing end 76 is drawn up to each of the two frame pieces
16, with one end being looped through a first upper slot 78 of a first frame
piece
16 and the other end being looped through a first upper slot 78 of the other
frame
piece 16. Each of the webbing ends 76 for each frame piece 16 are then
inserted
through a lower slot 80 having teeth to grip the webbing 26 and secure the
webbing at a specific length and position. As shown in FIG. 6A, by inserting a
longer length of webbing through each slot (78, 80) the distance d from the
seat
17
CA 02754411 2011-10-05
22 to the frame 16 is shortened for a smaller rider 24 as compared to the
distance
D in FIG. 6B. For a taller rider 24with longer arm length, a shorter length of
webbing is inserted through the slots (78, 80) leaving a greater distance
between
the seat and the frame and leaving a shorter length of webbing extending from
the
toothed slot 80. The webbing 26 may be adjusted to any length that is
comfortable
for the rider.
1063] In a further embodiment as shown in FIGS. 7A and 7B, one or more
straps
of webbing 26 may be attached or looped around attachment beams 48 or
openings 50 on either end of the extended end of the seat 22 to form a swing
to
accommodate even smaller riders that may more easily hold onto the straps
rather
than the over head handle 20. A preferred embodiment of the seat with a number
of alternative attachment points using cutouts 46, beams 48 or openings 50 is
shown in FIG. 7B, but numerous seat configurations are contemplated to safely
support and adjust distances of the frame to the seat for comfort of the
rider. In a
further embodiment the number of openings 50 may be increased in number and
size to provide for a leg and buttocks harness to be attached to the seat 22
to
provide additional support and security to the rider. It is to be appreciated
that the
seat may also be a flexible seat 23, such as a playground swing seat,
supported on
both ends and which is pliable enough to form around and hug the rider's body
when the rider 24 sits in the middle of the seat as shown in FIG. 8. The rider
24
may hold on to the straps or alternatively reach around the straps to hold
onto the
handle 20, allowing the pliable seat 23 and straps to curve around and safely
secure the rider 24.
18
CA 02754411 2011-10-05
[064] Actuation of the braking system as shown in FIG. 9, allows the rider
24 to
slow down the zip line system 10, prior to reaching the end of the cable 14.
Alternatively to the above described braking systems or in conjunction
therewith,
the trolley 11 can be stopped at the desired end of descent by a bumper or
stopper
84 of a durable polymeric material such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or
other comparable materials positioned close to the end of the cable 14. The
bumper 84 may be supported on the cable 14 and attached to an anchor point or
points by shock cords 88, or other type of force absorbing material which
permits
the bumper 84 and hence the trolley 11 to absorb all or some of the forces
developed by the trolley 11 along the zip line and bring the trolley 11 to a
safe
stop. The braking system 12 provides additional safety and control to the
rider to
slow their descent and safely reach the ground or tower. The trolley braking
system 12 and bumper 84 also provide control to the rider to ease the zip line
system 10 to a stop in preference to bumping into the ground or an object and
causing injury.
[065] The invention has been described in detail with particular reference
to
certain preferred embodiments thereof, but it will be understood that
variations
and modifications can be effected within the spirit and scope of the
invention.
19