Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02801628 2012-12-04
WO 2011/151984 PCT/JP2011/002767
Description
Title of Invention: DOCUMENT TRANSPORTER
Technical Field
[0001] This invention relates to a document transporter for transporting a
document such as
a bill along and in alignment with a passageway.
Background Art
[0002] One of known bill transporters comprises an aligning or a centering
device that may
automatically bring a bill into alignment with a passageway when the bill is
inserted
into the passageway in the deviated or inclined condition of the bill from a
longitudinal
central axis of the passageway. For example, Patent Document 1 below listed
discloses
a self aligning transport apparatus for variable media that comprises a
passageway and
a plurality of rotors aligned substantially parallel to side walls of the
passageway,
wherein at least one of the rotors has a surface shaped to drive the media in
an in-
termittent fashion in a direction longitudinal to the passageway so as to
align the media
substantially with the side walls when the media is free to rotate about each
rotor. In
this mechanism, the media is intermittently driven to intermittently bring the
surface of
the rotor into contact to the media, and at the point where the rotor becomes
disengaged from the media, the distorted media releases its strain energy
accumulated
upon contact to a side wall of the passageway to automatically bring the media
in
alignment with the passageway so that the media may be transported along the
passageway. However, the apparatus of Patent Document 1 naturally needs the
mechanism for intermittently bringing the rotor into contact to valuable media
while
resulting in increased abrasion in rotor which therefore must be exchanged for
new one
at fixed intervals.
[0003] Patent Document 2 undermentioned represents a banknote drive system
that
comprises a series of drive rollers located in a banknote guide channel and an
as-
sociated passive roller positioned opposite to drive rollers and having a
flattered or
notched portion to transport a banknote while gripping it between the drive
roller and
passive roller wherein flattered or notched potion defines a gap to pass the
banknote
through the gap during the stoppage of the passive roller's rotation so as to
allow
alignment of the banknote with a guide channel in the system. The banknote
drive
system shown in Patent Document 2 disadvantageously requires a stop mechanism
made up of a spiral cam surface formed with a stop face and a spring latch
with which
stop face of the cam surface is brought into engagement to stop rotation of
the passive
roller. This stop mechanism undesirably prevents continuous and smooth
rotation of
the passive roller and leads to complicated structure in the system.
2
WO 2011/151984 PCT/JP2011/002767
[0004] The following Patent Document 3 demonstrates a banknote centering
device that
comprises an enlarged slot for receiving a banknote longitudinally, side
engaging
members associated with the slot and movable from an open position either side
of the
slot to a narrow position defining a minimum position between the side
engaging
members, a banknote drive mechanism for driving a banknote from an insert
position
to a centering position where the banknote is freely centered within the slot,
a side
engaging member drive arrangement for moving the side engaging members in a
controlled manner towards one another and equally spaced either side of a
centerline of
the slot. The side engaging member drive arrangement includes a motor for ac-
celerating the side engaging members from the open position towards the narrow
position until further inward movement of the side engaging members is opposed
by
the sides of a banknote being parallel therewith and contacting the side
engaging
members over a substantial length thereof centering the banknote in the slot.
The drive
arrangement of the side engaging members includes a screw drive in drive
connection
with the side engaging members, and the screw drive includes a second shaft
parallel
to the common shaft to maintain the side engaging members appropriately spaced
by
the screw drive during movement between the open and narrow positions. The
banknote centering device of Patent Document 3 unfavorably demands the side
engaging members and the side engaging member drive arrangement for moving the
side engaging members towards one another.
[0005] Patent Document 4 below exhibits an aligning and reading apparatus for
a bill that
comprises first transporters for laterally conveying a bill along a passageway
when one
kind of bills having their different longitudinal length is supplied into the
passageway,
an alignment arrangement for centering the bill toward a longitudinal center
of the
passageway by urging inwardly the opposite ends of the bill conveyed by the
first
transporters, second transporters located on quarto lines of the bill for
further
conveying the centered bill, and a reading head located away from the quarto
lines of
the bill for detecting features of the bill. The apparatus shown in Patent
Document 4
disadvantageously has the increased number of assembled elements and cannot be
cut
down the cost for manufacture because it calls for the alignment arrangement
for
centering the bill toward a longitudinal center of the passageway by urging
inwardly
the opposite ends of the bill.
Citation List
Patent Literature
[0006] PTL 1: U.S. Patent No. 6,712,356
PTL 2: U.S. Patent No. 6,860,480
PTL 3: U. S. Patent No. 6,149,150
CA 02801628 2012-12-04
3
WO 2011/151984 PCT/JP2011/002767
PTL 4: Japanese Patent Disclosure No. 55-115891
Summary of Invention
Technical Problem
[0007] Thus, prior art apparatuses utilize an alignment or centering device of
its complicated
structure that undesirably leads to costly processes for manufacture with
limited
reduction in cost for manufacture. Accordingly, an object of the present
invention is to
provide a document transporter of the simplified structure capable of aligning
a
transported document with a passageway for the bill.
Solution to Problem
[0008] The document transporter according to the present invention comprises a
passageway
(2) and a conveyor (3) for transporting a document (1) along passageway (2).
Conveyor (3) comprises a frictional carrier (4) rotatably mounted in
passageway (2), a
drive device (5) for driving frictional carrier (4) and a weighting device (7)
for urging
document (1) against frictional carrier (4). Weighting device (7) comprises a
holder (8)
adjacent to passageway (2), and a sphere (6) rotatably maintained in holder
(8) to be in
contact to frictional carrier (4) to grip document (1) between sphere (6) and
frictional
carrier (4). When document (1) is inserted into passageway (2) with the
deviated or
inclined central axis of document (1) relative to a longitudinal central axis
of
passageway (2), document (1) is gripped between sphere (6) and frictional
carrier (4),
and at the time, either side edge (1 a) of document (1) comes into contact to
a side wall
(13) of passageway (2), and side wall (13) of passageway (2) causes flexible
document
(1) to elastically deform while emerging a restoring force in deformed
document (1) to
turn back to its original undeformed flat shape. This restoring force in
document (1)
may produce a reactive force that tends to separate the side edge (1 a) of
document (1)
off from side wall (13) of passageway (2) so as to move and bring document (1)
into
alignment with a longitudinal central axis of passageway (2). At that time, as
sphere
(6) in contact to moving document (1) rotates or makes a spherical motion
within
holder (8) depending on document (1) moving in any planar radial direction
from a
contact point with sphere (6) within passageway (2), a frictional force of
sphere (6) on
document (1) is very small, while the resultant reactive force is greater than
the
frictional force to sphere (6). Accordingly, document (1) can freely move
within a two-
directional plane containing the contact point with sphere (6) to release the
reactive
force so that document (1) moves to come into alignment with a longitudinal
central
axis of passageway (2) for automatic centering.
Advantageous Effects of Invention
[0009] The present invention can provide an inexpensive document transporter
of its
simplified structure capable of automatically aligning a transported document
with a
CA 02801628 2012-12-04
4
WO 2011/151984 PCT/JP2011/002767
passageway to certainly validate the aligned document by means of a
discrimination
sensor mounted in the back of the passageway.
Brief Description of Drawings
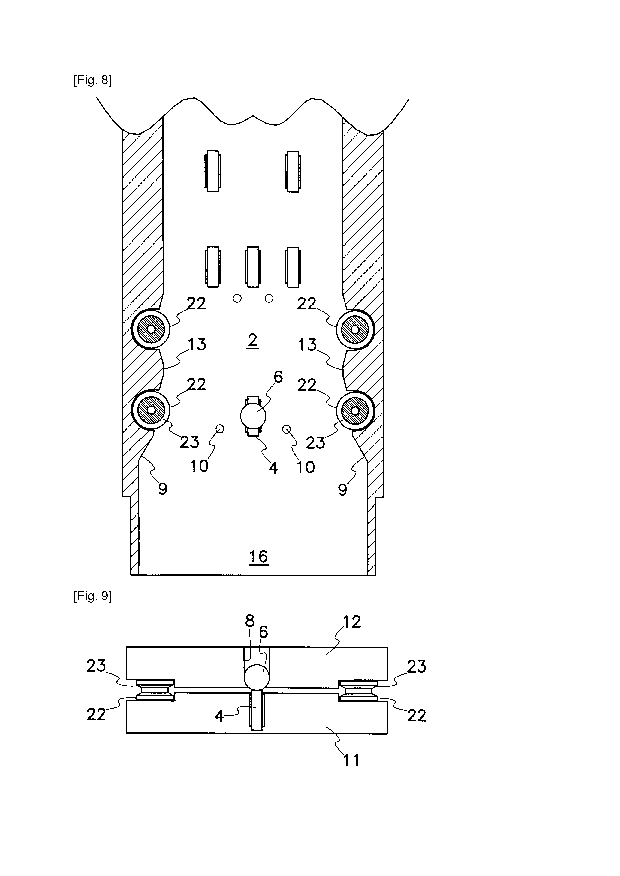
[0010] [fig. 1]A partial section view of a bill transporter as a first
embodiment according to the
present invention and a sectional view of a drive device for use in the bill
transporter
along a longitudinal direction of a passageway;
[fig.2]A plan view of the bill transporter shown in Figure 1;
[fig.3]A sectional view of the bill transporter along a transverse central
line of a ball
shown in Figure 1;
[fig.4]A sectional view showing a contact between the ball and frictional
carrier in
Figure 1;
[fig.5]A plan view of a passageway for receiving a bill inserted on the angle;
[fig.6]A plan view of the passageway wherein the bill of Figure 5 is moved
further
slightly inwardly of the passageway;
[fig.7]A sectional view showing a variation of the contact structure shown in
Figure 4;
[fig.8]A plan view of a first varied embodiment of a passageway in the bill
transporter
according to the present invention;
[fig.9]A sectional view of the bill transporter taken along a transverse
central line of a
ball shown in Figure 8;
[fig. 10]A sectional view of the bill transporter shown in Figure 8 taken
along its lon-
gitudinal central line;
[fig.11]A plan view of the passageway shown in Figure 8 for receiving a bill
on the
angle;
[fig.12]A plan view of the inclined bill further moved slightly inwardly of
the
passageway by a frictional carrier;
[fig. 13]A plan view of the bill slightly aligned with the passageway from the
condition
shown in Figure 12 during forward movement of the bill;
[fig. 14]A plan view of the bill slightly aligned with the passageway from the
condition
shown in Figure 13 during forward movement of the bill;
[fig. 15]A plan view of the bill perfectly aligned with the passageway during
forward
movement of the bill; and
[fig. 16]A plan view of the bill further moved inwardly of the passageway from
the
condition shown in Figure 15.
Description of Embodiments
[0011] Embodiments of the document transporter according to the present
invention will be
described hereinafter in connection with Figures 1 to 16 of the drawings. A
word
"document" used herein means a bill, a banknote, a coupon, a security, tender,
scrip of
CA 02801628 2012-12-04
5
WO 2011/151984 PCT/JP2011/002767
money equivalence or one of all economically valuable papers.
[0012] Figures 1 to 7 illustrate a first embodiment of the bill transporter
according to the
present invention. As shown in Figure 1, the bill transporter comprises a
passageway 2
and a conveyor 3 for transporting a bill 1 as a document inserted into
passageway 2.
Passageway 2 comprises a bottom wall 11, a top wall 12 and side walls 13 all
formed
of plastic or metallic materials. Conveyor 3 comprises a frictional carrier 4
rotatably
mounted in passageway 2, a drive device 5 for driving frictional carrier 4 and
a
weighting device 7 for urging or pressing bill 1 against a conveyor belt of
frictional
carrier 4. While the shown embodiments instantiate frictional carrier 4
utilizing a
conveyor belt, however, it may utilize a conveyor roller or conveyor rollers
accessible
to bill 1 in lieu of conveyor belt.
[0013] Weighting device 7 comprises a holder 8 formed adjacent to passageway
2, and a
sphere or ball 6 rotatably maintained in holder 8 to be accessible to or in
contact to
conveyor belt of frictional carrier 4 to grip bill 1 between ball 6 and
conveyor belt of
frictional carrier 4. As seen in Figures 1 and 3, frictional carrier 4 is
drivingly mounted
within a chamber 14 formed in a bottom wall of passageway 2. Drive device 5
comprises a drive motor 20 that is drivingly connected to frictional carrier 4
through a
power transmission device 21 of a desired reduction gear ratio. Power
transmission
device 21 may comprise a gear train, a belt transmission or their combination.
[0014] Holder 8 is formed in a top wall 12 of conveyor 3 for defining
passageway 2 to
arrange ball 6 in holder 8 that comprises a vertically formed cylindrical hole
8b, an
inner bearing surface 8a formed at a lower portion of cylindrical hole 8b into
a
partially spherical shape and an opening 8c formed at the bottom of holder 8
for com-
municating inner bearing surface 8a with passageway 2. Ball 6 is in contact to
inner
bearing surface 8a to freely rotate, roll, make a spherical motion or slide in
all or any
directions within inner bearing surface 8a when in contact to bill 1, and also
to
vertically move in holder 8 toward and away from passageway 2. When bill 1 is
inserted between ball 6 and conveyor belt of frictional carrier 4, it comes
into contact
to ball 6 urged downwardly by its own gravity, and ball 6 may freely rotate
within
inner bearing surface 8a in accordance with the moving direction of bill 1
that may be
easily and smoothly moved in any and all radial directions of 360 angular
degrees in a
planar surface from a contact point between ball 6 and bill 1 even though bill
1 is
gripped between ball 6 and conveyor belt of frictional carrier 4. Also, ball 6
may be in
contact to bill 1 at its any and all spherical outer surfaces to urge bill 1
on conveyor
belt of frictional carrier 4 under a constant pressure by its own gravity.
Ball 6 may
freely rotate and slide within holder 8 with an extremely less amount of
resultant
frictional force between ball 6 and bill 1 compared to a case of the sliding
contact only,
and also, ball 6 may upwardly move within holder 8 when any external force is
applied
CA 02801628 2012-12-04
6
WO 2011/151984 PCT/JP2011/002767
to ball 6 from the bottom.
[0015] Conveyor belt in frictional carrier 4 is formed of any plastic material
with its outer
surface covered with rubber materials of larger friction coefficient in
contact to moved
bill 1 and ball 6. Even where frictional carrier 4 comprises a conveyor roller
in place of
conveyor belt, such a conveyor roller may have its outer surface coated with a
rubber
material of larger friction coefficient. Ball 6 is made of a material selected
from the
group of corrosive-resistant materials such as stainless steel, iron or ferric
alloy, and in
a structure of ball 6 resiliently urged toward frictional carrier 4 by a
spring 15, ball 6
may be made of a relatively light metal such as copper, titanium, aluminum or
their
alloy or wear-resistant plastic materials.
[0016] An inner diameter of opening 8c in holder 8 is smaller than an outer
diameter of ball
6 to keep ball 6 within holder 8 without downward drop of ball 6 that however
can
move upwardly within holder 8. As shown in Figure 4, a bottom portion of ball
6
retained in holder 8 projects into passageway 2 through opening 8c of holder 8
and
makes contact to conveyor belt of frictional carrier 4 that upwardly projects
into
passageway 2 from bottom wall thereof so that bottom portion of ball 6 also
makes
contact to bill 1 in touch with conveyor belt of frictional carrier 4 while
bill 1 moves
between ball 6 and conveyor belt of frictional carrier 4 within passageway 2.
[0017] Opposite side walls 13 define passageway 2 and have inwardly tapered
surfaces 9 at
the front to form an inlet 16. A pair of inlet sensors 10 are arranged in
bottom and top
walls 11 and 12 in the vicinity of and on the opposite sides of conveyor belt
of
frictional carrier 4 to detect bill 1 inserted into passageway 2. Not shown in
the
drawings, but, each of inlet sensors 10 may have a photo-coupler of light
emitting and
receiving elements for detecting light-interruption between these elements by
bill 1
moving through passageway 2. When any inlet sensor 10 detects light-
interruption by
passage of bill 1, it produces a detection signal to a control device (not
shown) that in
turn effects a trigger signal to drive device 5 to activate drive device 5 and
thereby
drive frictional carrier 4. At that moment, ball 6 makes contact to rotating
conveyor
belt of frictional carrier 4 and thereby rotates within inner bearing surface
8a of holder
8, and when ball 6 makes spherical contact to bill 1 inserted into passageway
2, it may
freely rotate within inner bearing surface 8a of holder 8 in accordance with
movement
of bill 1 through passageway 2 if bill 1 moves in any planar direction in
passageway 2.
[0018] The embodiment shown in Figure 4 illustrates an example of the
structures wherein
ball 6 makes contact to conveyor belt of frictional carrier 4 or bill 1 under
its own
weight in other words at a given pressure, and this structure has the feature
capable of
maintaining a constant pressure on bill 1 by ball 6 without effecting any
change to
pressure by ball 6 on conveyor belt of frictional carrier 4 and on bill 1 even
though ball
6 rotates within inner bearing surface 8a of holder 8. If rotating ball 6 has
any frictional
CA 02801628 2012-12-04
7
WO 2011/151984 PCT/JP2011/002767
force on bill 1, it is smaller than a frictional force by bill 1 on frictional
carrier 4.
[0019] When bill 1 is inserted into passageway 2 with the deviated or inclined
central axis of
bill 1 relative to a longitudinal central axis of passageway 2 on a plane
surface as
shown in Figure 5, bill 1 is gripped between ball 6 and conveyor belt of
frictional
carrier 4, and at the time at least one or both of side edges la of bill 1
come into
contact to either or both side walls 13 of passageway 2, side wall or walls 13
cause
flexible bill 1 to elastically deform while inducing a restoring force in
deformed bill 1
to turn back to its original undeformed flat shape. This restoring force in
bill 1 may
produce a reactive force that tends to separate side edge or edges la of bill
1 off from
side wall or walls 13 of passageway 2 so as to move and bring bill 1 into
alignment
with a longitudinal central axis of passageway 2. At that time, as ball 6 in
contact to
moving bill 1 rotates or makes a spherical action within holder 8 depending on
bill 1
moving in any planar radial direction from a contact point with sphere 6
within
passageway 2, a frictional force of ball 6 on bill 1 is very small, while the
resultant
reactive force is greater than frictional force to ball 6. Accordingly, bill 1
can freely
move within a two-directional plane containing the contact point with ball 6
to release
the reactive force in bill 1 in contact to ball 6 so that bill 1 moves to come
into
alignment with a longitudinal central axis of passageway 2 for automatic
aligning or
centering of bill's attitude. In this way, this invention may provide an
inexpensive bill
transporter of its simplified structure capable of automatically aligning a
transported
bill with a passageway.
[0020] Figure 7 illustrates a variation from the embodiment in Figure 4 with
the vertically
inverted structure of ball 6 and frictional carrier 4 wherein frictional
carrier 4 is
rotatably arranged in chamber 14 of top wall 12 in conveyor 3; holder 8 is
formed in
bottom wall 11 of conveyor 3; and ball 6 is disposed in holder 8 to upwardly
and
elastically urge ball 6 toward conveyor belt of frictional carrier 4 by a
resilient force of
a spring 15 as an elastic material so that ball 6 makes contact to bill 1
moving between
ball 6 and frictional carrier 4. In the embodiment shown in Figure 7, as ball
6 is
arranged under conveyor belt of frictional carrier 4 without exerting ball's
own gravity
on bill 1, spring 15 is used to upwardly and elastically urge ball 6 to
produce a prede-
termined elastic force on bill 1 toward conveyor belt of frictional carrier 4.
However, if
any downward external force is applied to ball 6, it can downwardly move
against
resilient force of spring 15. Even this embodiment can produce its performance
and
effect equivalent to those of the structure shown in Figures 1 to 6 because
spring 15
may exert an unchanged pressing force of a constant level on bill 1 through
ball 6 at
any spherical outer surface of ball 6 in contact to bill 1.
[0021] Figures 8 to 16 represent a second embodiment of the invention wherein
two pairs of
guide rollers 22 are rotatably arranged face-to-face each other and attached
to opposite
CA 02801628 2012-12-04
8
WO 2011/151984 PCT/JP2011/002767
side walls 13 of passageway 2 shown in Figures 1 to 7. In the second
embodiment,
each guide roller 22 has an outer rim formed with a V- or U-shaped annular
groove 23
into which a side edge of bill 1 may be fit, and each of side walls 13 of
passageway 2
has an intermediate surface formed into an arcuate shape between anterior and
posterior guide rollers 22.
[0022] As shown in Figures 11 to 16, when bill 1 is inserted into passageway 2
with the
deviated bill's longitudinal axis from longitudinal central line of passageway
2, side
edges of bill 1 come into contact with guide rollers 22 which therefore are
rotated upon
contact with bill 1 so that guide rollers 22 may smoothly modify the moving
direction
of bill 1 to bring bill 1 into alignment with passageway 2. Then, as shown in
Figures
15 and 16, bill 1 is finally easily rendered aligned and coaxially with
passageway 2
during movement of bill 1.
Industrial Applicability
[0023] This invention is applicable to document transporters of various types
for
transporting documents in alignment with a passageway.
Reference Signs List
[0024] (1) a bill (a document), (la) side edges, (2) a passageway, (3) a
conveyor, (4) a
frictional carrier, (5) a drive device, (6) a ball (a sphere), (7) a weighting
device, (8) a
holder, (8a) an inner bearing surface, (8b) a cylindrical hole, (8c) an
opening, (9)
tapered surfaces, (10) inlet sensors, (11) a bottom wall, (12) a top wall,
(13) side walls,
(14) a chamber, (15) a spring, (16) an inlet, (20) a drive motor, (21) a power
transmission device, (22) guide rollers, (23) an annular groove,
CA 02801628 2012-12-04