Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02802544 2012-12-12
WO 2012/013513 PCT/EP2011/062081
-1-
Composition and process for whitening paper
The present invention relates to a composition suitable for surface treatment
of
paper, in particular a size press liquor, and a process for whitening paper
using
said composition.
In the production of paper, a sizing step is usually carried out for achieving
good
writing and printing properties and strength. Such a sizing step can take
place, on
the one hand, before the sheet formation in the paper pulp (internal sizing)
and, on
the other hand, after the sheet formation in the size press. A combination of
both
processes is also possible. In one or both production stages of paper,
whitening of
the pulp or of the paper sheet is usually also carried out by means of a
fluorescent
whitening agent (FWA). Usually, the size and fluorescent whitening agent are
added separately to the paper pulp in the case of pulp application, whereas
the
fluorescent whitening agent is incorporated into the size press liquor and
applied
together with it to the paper sheet in the case of surface sizing.
The combination of surface sizing and whitening of papers is widely used in
the
paper-producing industry. This method is widely used particularly in the
printing
and writing paper segment (copy, inkjet, offset, etc.). There is a continuing
trend
towards surface-sized papers having high whiteness and improved printing per-
formance and consequently there is a demand for size press liquors which are
as
effective as possible. US 6,207,258 B 1 discloses a composition and process
for
improved inkjet printing performance using a salt of a bivalent metal, in
particular
calcium chloride. Therefore, in order to achieve more brilliant and sharper
print-
ings, especially inkjet printings, the paper production industry uses nowadays
cal-
cium chloride in size press liquors. However, the use of that salt affects
adversely
CA 02802544 2012-12-12
WO 2012/013513 PCT/EP2011/062081
-2-
the performance of the fluorescent whitening agents commonly used in size
press
liquors. In particular, the whitening effectiveness is decreased, the shade is
mov-
ing to the greenish-yellowish direction, and additionally a loss of
fluorescence is
observed.
WO 2009/150180 Al and EP 2 135 997 Al disclose aqueous compositions con-
taining specific bis-tri azinyl amino- stilb ene compounds containing
alkylsulfonic
acid groups, a salt of a bivalent cation, and a carrier.
Surprisingly, it has been found that further specific bis-tri azinylamino-
stilbene
compounds when used in combination with salts of bivalent cations, such as cal-
cium chloride, in compositions suitable for surface treating of paper, such as
size
press liquors, also overcome problems of the prior art.
Therefore, the present invention relates to a composition suitable for surface
treat-
ment of paper, wherein the composition contains
(a) at least one fluorescent whitening agent of formula (I)
n(MO3S) (S03M) m
~/ N -
N, N \ S N
N H N--~ N
N~
R1-N S03M H
\ N-R4
R2
R3
wherein n and m are, independently of each other, an integer of 1, 2, or 3;
R1, R2, R3, and R4 represent, independently of each other, hydrogen, CI-C4
alkyl, C2-C4 alkoxyalkyl, C2-C4 cyanoalkyl, or C2-C4 hydroxyalkyl; or Ri
and R2 or R3 and R4 independently of each other together with N atom form
morpholine, piperidine or pyrrolidine ring;
CA 02802544 2012-12-12
WO 2012/013513 PCT/EP2011/062081
-3-
wherein at least one of R1, R2, R3 and R4 contains at least 3 carbon atoms;
M represents hydrogen, or one equivalent of a cation, in particular Li, Na, K,
Ca, Mg, ammonium, or ammonium which is mono-, di-, tri- or tetra-
substituted by C1- C4 alkyl or C2 - C4 hydroxyalkyl;
(b) at least one salt of a bivalent cation;
(c) at least one carrier; and
(d) water.
The invention further relates to a process for whitening paper, wherein a
cellulose
sheet is brought into contact with the above defined composition, preferably
in the
size press. Preferred embodiments of the invention are described in the
description
hereinafter, the claims and the figure.
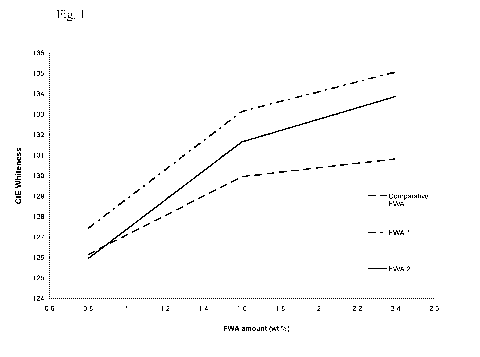
Fig. 1 is a diagram showing the influence of calcium chloride on the
performance
of different fluorescent whitening agents according to Example 1.
In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the composition suitable for
surface
treatment of paper is a size press liquor, and the process is a process for
whitening
paper in the size press, wherein a cellulose sheet is brought into contact
with the
size press liquor.
In the context of this invention, size press is understood as meaning a
surface ap-
plication unit, preferably of the paper machine, in which the cellulose sheet
formed is brought into contact with a size press liquor, and in which the
propor-
tion of the liquor which is to be taken up by the sheet (liquor absorption)
can pref-
erably be adjusted by means of the roll pressure.
CA 02802544 2012-12-12
WO 2012/013513 PCT/EP2011/062081
-4-
Recent developments of the size press or film press, namely of the Speedsizer
as
well as of the Symsizer as well as Gate-roll, are likewise understood as being
cov-
ered by the term size press.
According to the invention the composition contains at least one bis-
triazinylamino-stilbene compound of the above defined formula (I), wherein n,
m,
Ri to R4, and M are as defined above. In the context of this invention, in the
for-
mula (I) the alkyl group can be linear or branched, and the possible
substituents of
the alkyl group, which are alkoxy, hydroxyl and/or cyano groups, can be
attached
at any position of the alkyl chain. In the present invention, C2-C4
alkoxyalkyl
means C2-C4 alkyl substituted with C2-C4 alkoxy. In a preferred embodiment, n
and m are integers from 1 to 2, most preferred 2. In another preferred embodi-
ment, R1, R2, R3 and R4 represent, independently of each other, hydrogen, Ci -
C4
alkyl, C2-C4 cyanoalkyl, or C2-C4 hydroxyalkyl, in particular propyl,
cyanoethyl,
or hydroxypropyl. The -SO3M groups at the terminal aromatic rings can be in o-
,
m-, or p-position. The preferred positions depend on the number of the -SO3M
groups. If n or m is 1, p-position is preferred. If n or m is 2, the 2,5-
position is
preferred. In a preferred embodiment, at least one of R1, R2, R3 and R4 is
propyl,
cyanoethyl or hydroxypropyl. In another preferred embodiment, R1, R2, R3 and
R4
are propyl or hydroxypropyl, in particular all are either propyl or
hydroxypropyl,
wherein preferably n and m are 2. Most preferably, the hydroxypropyl group is
a
hydroxyisopropyl group. In another preferred embodiment, n and m are 2, and
the
two - SO3M groups are in 2,5-position. In a further preferred embodiment, n
and
m are 2, Rl and R3 are hydroxyisopropyl, and R2 and R4 are cyanoethyl.
In the compound of formula (I), at least one of R1, R2, R3 and R4 contains at
least
3 carbon atoms. Preferably, at least one of Ri and R2 and at least one of R3
and R4
contain at least 3 carbon atoms. In a further preferred embodiment, at least
one of
R1, R2, R3 and R4, in particular at least one of Ri and R2 and at least one of
R3 and
R4, represent(s) C3 - C4 alkyl, C3 - C4 alkoxyalkyl, C3-C4 cyanoalkyl, or C3-
C4
CA 02802544 2012-12-12
WO 2012/013513 PCT/EP2011/062081
-5-
hydroxyalkyl. In the present invention, C3-C4 alkoxyalkyl means C3 or C4 alkyl
substituted with C3 or C4 alkoxy.
Preferred embodiments of M are hydrogen, Na, K, Ca, Mg, in particular M is Na
or K, most preferred is Na.
The fluorescent whitening agents of formula (I) can be produced by known proce-
dures, and are used as free acids or as salts thereof, preferably alkali metal
salts.
Generally, the compounds are prepared by reacting cyanuric chloride with 4,4'-
diaminostilbene-2,2'-disulfonic acid or a salt thereof, and an appropriate
aniline
derivative containing a phenyl ring substituted with -SO3M group(s), and
substi-
tuted aliphatic amines or heterocyclic compounds. For example, EP 0 860 437 Al
describes the preparation of such compounds.
The composition of the invention can contain more than one, preferably two or
three, most preferred three, of the fluorescent whitening agents of formula
(I).
Component (a) of the composition can contain, in addition to the at least one
fluo-
rescent whitening agent of formula (I), one or more known bis-triazinylamino-
stilbene or distyryl-biphenyl based fluorescent whitening agents.
The salt of component (b) of the composition of the invention comprises
bivalent
cations, preferably cations of an earth alkaline metal, in particular calcium
or
magnesium. Preferably, the counterions of the bivalent cations are mono- or
mul-
tivalent anions, in particular halide, sulphate, hydrosulphate, phosphate,
hydro-
phosphate, dihydrophosphate, carbonate, hydrocarbonate, nitrate, acetate, or a
mixture thereof, preferably chloride or sulphate, most preferably chloride.
The
salts disclosed in US 6,207,258 B1 are also suitable. A preferred salt is
calcium
chloride, magnesium chloride, magnesium sulphate, or a mixture thereof, more
preferred is calcium chloride, magnesium chloride, or a mixture thereof, most
preferred is calcium chloride.
CA 02802544 2012-12-12
WO 2012/013513 PCT/EP2011/062081
-6-
The carrier of component (c) is any compound known in the art to be suitable
as a
carrier, in particular carriers suitable for size press liquors. Preferred
carriers are
carboxymethylcellulose (CMC), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), starch or mixtures
thereof, with starch being particularly preferred. Suitable carrier substances
are,
for example, hydrophilic polymers having the ability to form hydrogen bridge
bonds. Preferred carrier substances are starch, polyvinyl alcohols,
carboxymethyl-
celluloses and polyethylene glycols having a number average molecular weight
of
from 200 to 8000 g/mol, as well as any desired mixtures of these substances,
it
being possible for these polymers optionally to be modified. Preferred
polyvinyl
alcohols are those having a degree of hydrolysis >85%, preferred carboxymethyl-
celluloses are those having a degree of substitution DS of >0.5. Polyethylene
gly-
cols having a number average molecular weight Mn of from 200 to 8000 g/mol
are particularly preferred. Suitable starches are based e.g., but not
exclusively, on
potato starch, rice starch, wheat starch, maize starch or tapioca starch. In
particu-
lar, starches whose molecular weights have already been reduced by partial deg-
radation and/or which have been obtained by derivatization are preferably used
instead of natural starches. Furthermore, starches for which both modification
steps have been combined, i.e. which have been partially degraded and addition-
ally derivatized, are suitable. Typical methods for starch degradation are,
for ex-
ample, enzymatic, oxidative, thermal or hydrolytic treatment. Examples of suit-
able starch derivatives are hydroxyethyl starch or cationic starch.
The composition of the invention contains as component (d) water and, option-
ally, can contain sizing agents, such as alkenyl ketene dimer, alkyl ketene
dimer
(AKD), alkenyl succinic anhydride (ASA), rosin size, styrene maleic anhydride
copolymers, styrene acrylate, styrene acrylic acid copolymers, polyurethane or
ethylene acrylic acid copolymers, or other common paper chemicals, such as
styryl-acrylate copolymers, latex, pigments, defoamers, or salts, such as NaCl
or
NaHCO3, or mixtures of two or more thereof.
CA 02802544 2012-12-12
WO 2012/013513 PCT/EP2011/062081
-7-
The composition of the invention contains preferably component (a) in an
amount
of 0.02 to 3, more preferably 0.05 to 2, most preferably 0.1 to 1, weight-%
based
on 100 weight-% of the composition. If fluorescent whitening agents other than
those of formula (I) are used, their amount is 5 to 95 weight-% based on 100
weight-% of component (a). Component (b) is preferably contained in an amount
of 0.2 to 8, in particular 0.5 to 6, most preferably 1 to 5, weight-% based on
100
weight-% of the composition. Component (c) is preferably contained in an
amount
of 3 to 20, in particular 5 to 15, most preferably 6 to 12, weight-% based on
100
weight-% of the composition. The composition of the invention contains prefera-
bly water in an amount of 75 to 96.78, in particular 79 to 94.45, most
preferably
82.5 to 92.9, weight-% based on 100 weight-% of the composition.
Optionally, the composition contains a sizing agent, preferably in an amount
of 0
to 5, in particular 0 to 4, most preferably 0 to 3, in each case weight-%
based on
100 weight-% of the composition.
In addition, relatively small amounts, usually amounts of less than 5% by
weight,
of further auxiliaries, such as, for example, dispersants, thickeners,
antifreezes,
preservatives, complexing agents, etc., or organic byproducts from the
fluorescent
whitening agent synthesis which were not completely removed in the working-up,
may be contained in the composition of the invention.
Suitable compositions are also described in US 6,207,258 B1, wherein according
to the invention as component (a) at least one fluorescent whitening agent of
for-
mula (I) is used.
The production of the composition is effected by known methods and preferably
effected by combining an aqueous solution of the fluorescent whitening agent
used as component (a), which preferably has a suitable pH value, with the
other
components, such as carrier substances, sizing agents, binders, pigments,
salts or
standardizing agents. Preferably, an aqueous preparation of carrier component
(c)
CA 02802544 2012-12-12
WO 2012/013513 PCT/EP2011/062081
-8-
is prepared, to which preparation an aqueous preparation of salt component (b)
is
added, followed by the addition of an aqueous preparation of the fluorescent
whit-
ening agent component (a), preferably adjusted in pH value, and the other
compo-
nents.
The composition of the invention can be used for whitening paper, in
particular
for surface treatment of paper, e.g. in a size press.
The process of the invention for whitening paper is carried out according to
known processes, preferably using a size press, and is subject to no
restrictions.
The paper used is not critical and may be any cellulose sheet.
Paper obtained by the process of the invention exhibits, in addition to
improved
printing performance, improved whiteness, and is in particular suitable for
inkjet
printing applications.
The whiteness of the papers produced can be characterized by the CIE
whiteness.
Different fluorescent whitening agents can be compared to each other with
respect
to the saturation behavior when determined according to CIE whiteness. In
other
words, if a larger amount of fluorescent whitening agent is used and no
further
increase in whiteness is found, there is a saturation behavior and there may
even
be adverse effects on the whiteness when using higher amounts. The effect of
saturation is also referred to as greening. The greening limit, i.e. the point
at
which increasing amounts of fluorescent whitening agent used results in
virtually
no further increase in whiteness, can be derived, for example, from the a*-b*
dia-
gram, where a* and b* are the color coordinates in the CIE-L*a*b system.
The following example illustrates the invention and shows preferred embodi-
ments, without limiting the scope of protection.
CA 02802544 2012-12-12
WO 2012/013513 PCT/EP2011/062081
-9-
Example
The whitening performance of different fluorescent whitening agents in the
pres-
ence of calcium chloride was studied using the following test procedure for
size
press application.
First, a 15% starch solution of neutral oxidatively degraded potato starch
(Perfec-
tamyl 4692) and a 50% calcium chloride solution were prepared. The paper used
was a 80 g/m2 basepaper, which was a machine paper, internally sized (Cobb
equals to 110 g/m2) and slightly whitened with fluorescent whitening agent to
have the following optical characteristics: CIE -104.89; L* = 93.92; a* =
1.21; b*
-4.34.
The fluorescent whitening agent was weighed in a glass, and 13.33 g of 15%
starch solution was added. Then, 50% calcium chloride solution was weighed in,
and the solution was filled up with water to 20 g, so that the tests were
carried out
in a 10% starch solution. After stirring for a short time the solution was
applied on
one side of the basepaper by a semiautomatic lab coater with a Rakel (No. 2)
which should simulate a film press application. 1.7 g/m2 of dry starch was
applied
on that basepaper. After the drawing the paper was directly dried on a drying
cyl-
inder at about 100 C. After climatization over night the prepared side of the
pa-
pers were measured with a Datacolor spectrometer (IS02469) by determining
CIE, L*, a* and b*, the light source used based on IS02469 standard.
The amounts used of fluorescent whitening agent per 100g starch preparation
were as indicated in Table 1 below. The amount of calcium chloride was 2g for
each fluorescent whitening agent. The following fluorescent whitening agents
were used:
CA 02802544 2012-12-12
WO 2012/013513 PCT/EP2011/062081
-10-
SO3Na NaO3S
N NaO3S N o
N N
NaO S N N - N N SO3Na
s
HO ~ \ N H SO3Na HN-
N HO N OH
Y
FWA 1
OH
SO3Na NaO3S
N NaO3S N o
N N~
NaO S N N N SONa
s \ N H SO3Na HN- 3
~
N N
j
FWA 2
SO3Na NaO3S
N NaO3S N /
NaO S N N N SO3Na
s \ N H SO3Na HN-
~
N N
HO~ OH
Comparative FWA
OH HO
The results obtained are summarized in Table 1.
CA 02802544 2012-12-12
WO 2012/013513 PCT/EP2011/062081
-11-
Table 1
FWA Amount (wt%) CIE L* a* b*
in starch prepara- whiteness
tion
FWA 1 0.8 127.41 93.92 2.14 -9.32
1.6 133.13 94.13 2.15 -10.50
2.4 135.06 94.27 1.98 -10.87
FWA 2 0.8 125.94 93.87 2.11 -9.01
1.6 131.64 94.03 2.20 -10.21
2.4 133.86 94.17 2.11 -10,65
Comparative 0.8 126.13 93.98 1.80 -9.01
FWA 1.6 129.95 94.19 1.54 -9.76
2.4 130.81 94.37 1.22 -9.87
As may be taken from Table 1, FWA 1 and FWA 2 containing certain aliphatic
amine groups, namely of diisopropanolamine or dipropylamine, in combination
with dimethanilic acid, showed for almost all concentrations of fluorescent
whit-
ening agent used an improvement in whiteness in the presence of calcium
chloride
compared to the comparative FWA which does not contain that specific combina-
tion of groups. For further illustration, the results of Table 1 are also
shown in Fig.
1.
The above experimental data show that the use of bis-triazinylamino-stilbene
fluo-
rescent whitening agent compounds with a specific combination of terminal
groups according to the invention results in paper of improved whiteness in
the
presence of a salt of a bivalent cation, such as calcium chloride.