Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02816061 2013-05-16
=
PUMPABLE SEAT ASSEMBLY AND USE FOR WELL COMPLETION
INVENTORS: TSCHETTER, Sam and JAHANGIRI, Armin
ASSIGNEE: ENCANA CORPORATION
Field of the Invention
[0001] The present invention relates generally to the field of vertical and
horizontal well
completion, and, more particularly, to a process for fracturing, stimulating
and producing a
wellbore without having to mill out and remove fracturing/bridge plugs and to
a pumpable seat
assembly for use with said process.
Background of the Invention
[0002] Oil and gas well are drilled to a depth in order to intersect a
series of formations or
zones which produce hydrocarbons. Often the drilled wells are cased with steel
casing pipe and
cemented to secure the casing in place. Hence, it is necessary to create a
flow path from these
cased producing zones to the surface of the wellbore. This is generally
accomplished by
stimulation processes such as fracturing using water, various chemicals and/or
proppants.
However, the steel and cement barrier needs to be first perforated with shaped
explosive charges
prior to fracturing the surrounding oil or gas reservoir.
[0003] Depending on the number of producing zones in a particular reservoir,
usually several
elevation levels and/or lateral intervals will need to be fractured. Thus, it
is common in the
industry to use a temporary well completion plug which is generally set in the
bore of the steel
well casing with a setting tool just below the level or interval where the
perforation of the steel
and cement barrier and fracturing occurs. It is understood that these bridge
or "frac plugs" can
also be pumped down the well on an electric wireline, either by itself or in
combination with the
perforating gun assemblies. When the barrier is perforated, "frac fluids"
and/or sand are pumped
down to the perforations and into the reservoir to stimulate movement of the
oil or gas. Use of
the temporary plug prevents contamination of the already fractured levels
below.
WSLega1\049798\00313 \ 9126098v1
CA 02816061 2013-05-16
[0004] Interval isolation and fracturing or stimulation can be performed on
both vertical and
horizontal wells with multiple planned intervals, often with multiple
intervals and sometimes
greater than 25 intervals per well at varying depths including sometimes
greater than 6000
Meters Below Kelly Bushing (MKB). Bridge/frac plug technology for interval
isolation for frac
stimulation purposes is proven, effective, predictable and repeatable.
[0005] Unfortunately, once all of the zones have been stimulated, these
temporary plugs may
prevent the flow of oil or gas to the surface. Thus, traditionally, these
plugs need to be milled or
drilled out using a drill bit using jointed pipe or coiled tubing. However,
there are operational
risks associated with this process and, further, this is a time consuming and
costly procedure.
Furthermore, it has been found that frac plugs having even a minimal amount of
steel are
difficult to drill during removal and can damage the drill bit.
10006] Coil tubing or jointed pipe intervention to mill out and remove the
plugs on extended
reach wells, e.g. lateral length exceeding 2500 m, is extremely costly,
unpredictable and
sometimes impossible due to metal to metal friction encountered sliding in the
casing, creating
what is known as coil tubing lock-up. In some cases, frac plugs that are not
reachable due to
friction lock up issues are left in the well (i.e., not milled out) and
intervals left behind these frac
plugs are expected to flow through a3/4 inch hole in the center of the frac
plugs. Flow can
sometimes be restricted by the number of frac plugs which were not accessible
for mill-out due
to the friction lock encountered. In some cases operations are exposed to such
risks as sticking
the coil tubing or bottom-hole assembly (BHA) in the well, resulting in
fishing operations for
pipe recovery. Fishing operations can cost an operating company millions of
dollars depending
on difficulty and risk, in extreme cases wellbore have been lost due to
fishing operations and
associated costs.
[0007] Accordingly, there is a need in the art for a well completion process
and plug which
will allow the plug to behave like a frac plug for a temporary period of time
and then allow the
flow of gas and or oil from the reservoir up to the well head without the need
for drilling the plug
out.
Summary of the Invention
[0008] The present invention relates generally to a process and apparatus
for multiple interval
isolation of a horizontal or vertical well, where intervention such as
drilling out frac plugs is not
WaegA049798\00313\ 9126098v1 2
CA 02816061 2013-05-16
necessary for well completions. Generally, a frac plug is provided, which is a
seat and slip
assembly that would be applicable to more than 80% of vertical and horizontal
completions
activity within the industry and that can be configured to fit all casing
sizes and casing weights.
In one embodiment, the pumpable seat assembly would be deployed or pumped on
electric
wireline down the well by itself or in combination with the perforating guns
to a desired depth
within the well. A standard setting tool would set the pumpable seat assembly
in the casing and
the wireline would then log on depth the guns and perforate the interval at
desired depth and pull
to surface.
[0009] In one aspect, a dissolvable ball is supplied which would be dropped by
the service
provider into the well from surface and then pumped downhole until the
dissolvable ball lands on
the pumpable seat assembly and provides isolation from the previous interval
for frac stimulation
purposes. The process can then be repeated a multiple number of times in the
same wellbore
using additional pumpable seat assemblies and dissolvable balls. Once the frac
or stimulation
services are completed, the dissolvable ball will dissolve and the well can be
flowed on
production, or equipped with production tubing, all without any wellbore
intervention.
[00010] In one aspect, the pumpable seat assembly has an inner diameter
that is greater
than about 1 inch. In one embodiment, the assembly has an inner diameter of
about 2 inches and
larger. By having a larger inner diameter than conventional frac plugs, once
the dissolvable ball
has dissolved, the flow would not be restricted.
(000111 In one aspect, the invention comprises a process for fracturing,
stimulating and
producing a wellbore having a plurality of oil or gas producing zones,
comprising:
introducing into the well a pumpable seat assembly comprising a generally
cylindrical
tube having an outer diameter and an inner diameter with an upper end forming
a ball seat;
setting the pumpable seat assembly below an oil or gas producing zone to be
produced;
introducing a dissolvable ball into the well, said dissolvable ball having a
sufficiently
large enough outer circumference so that it can sit on the ball seat and
temporarily restrict a flow
of fluids to the portion of the wellbore located below the pumpable seat
assembly;
fracturing the oil and gas producing zone to stimulate oil or gas production;
whereby the biodegradable ball is configured to dissolve within a
predetermined period of time
so that when it dissolves any oil or gas produced from zones below the
pumpable seat assembly
can flow through the cylindrical tube.
WSLega1\049798\00313\ 9126098v1 3
CA 02816061 2013-05-16
. ,
[00012] In one embodiment, the inner diameter of the cylindrical tube is
sufficient to
allow relatively unrestricted flow of oil or gas there through. In one
embodiment, the inner
diameter is greater than about 1 inch. In one embodiment, the inner diameter
is about 2 inches
and larger.
[00013] In another aspect, the pumpable seat assembly is provided for
temporarily sealing
a well casing, the pumpable seat assembly comprising:
a generally cylindrical tube having an outer diameter and an inner diameter
with an upper
end forming a ball seat;
a upper slip assembly and a lower slip assembly mounted on such cylindrical
tube and
adapted to selectively engage the well casing to anchor the pumpable seat
assembly;
an elastomeric packing element mounted on said cylindrical tube between the
upper slip
assembly and the lower slip assembly; and
a dissolvable ball having a sufficiently large enough outer circumference so
that it can sit
on the ball seat and temporarily restrict a flow of fluids to the portion of
the wellbore located
below the pumpable seat assembly.
[00014] In one embodiment, the inner diameter of the cylindrical tube is
greater than 1/4
inches. In another embodiment, the inner diameter of the cylindrical tube is
greater than 1 inch.
In another embodiment, the inner diameter of the cylindrical tube is greater
than 2 inches. In one
embodiment, the cylindrical tube has at least one flow port located at a lower
end of the
cylindrical tube.
[00015] Additional aspects and advantages of the present invention will be
apparent in
view of the description, which follows. It should be understood, however, that
the detailed
description and the specific examples, while indicating preferred embodiments
of the invention,
are given by way of illustration only, since various changes and modifications
within the spirit
and scope of the invention will become apparent to those skilled in the art
from this detailed
description.
Brief Description of the Drawings
[00016] The invention will now be described by way of an exemplary
embodiment with
reference to the accompanying simplified, diagrammatic, not-to-scale drawings:
WSLega1\049798\00313\ 9126098v1 4
CA 02816061 2013-05-16
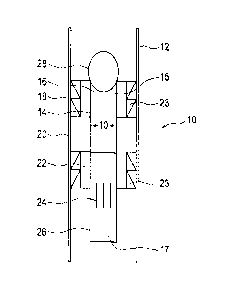
[00017] Figure 1 is a cross-sectional view of an exemplary embodiment of
the pumpable
seat assembly.
[000181 Figure 2 is a partial cross-sectional perspective of a plurality
of pumpable seat
assemblies set within a length of well casings.
Detailed Description of Preferred Embodiments
[000191 The detailed description set forth below in connection with the
appended
drawings is intended as a description of various embodiments of the present
invention and is not
intended to represent the only embodiments contemplated by the inventor. The
detailed
description includes specific details for the purpose of providing a
comprehensive understanding
of the present invention. However, it will be apparent to those skilled in the
art that the present
invention may be practised without these specific details.
[00020] The present invention relates generally to a process for
fracturing, stimulating and
producing a wellbore without having to mill out and remove fracturing/bridge
plugs and to a
pumpable seat assembly for use therein.
[00021] Figure 1 shows one embodiment of a pumpable seat assembly (10)
useful in the
present invention, which assembly (10) is shown being set within a wellbore
casing (12).
Pumpable seat assembly (10) comprises a generally cylindrical tube (14) having
an upper end
(15) and a lower end (17). Situated near the first end (15) of cylindrical
tube (14) is an upper slip
assembly (18) and situated near the lower end (17) of cylindrical tube (14) is
a lower slip
assembly (22). Both the upper and lower slip assemblies generally include a
plurality of
serrations (23) which engage the casing (12) and prevent longitudinal movement
of the slips (18)
and (22) once set.
[00022] An elastomeric packer element (20) is mounted on the cylindrical
tube (14)
between the upper slip ((18) and the lower slip (22). The packing element (20)
is adapted to be
deformed into sealing engagement with the casing (12) upon compression of
setting components
(not shown). Although the packing element (60) is shown and described as being
one-piece it is
to be understood that a packing element having multiple members is
contemplated under the
present invention. In either case, the packing element (20) is adapted to
provide a fluid-tight seal
between the cylindrical tube (14) and the casing (12).
WSLega1\049798\00313\ 9126098v1 5
CA 02816061 2013-05-16
[000231 The lower end (17) of the cylindrical tube (14) can further
comprise one or more
flow ports (24). The flow ports (24) facilitate the flow of oil or gas from
the region below the
pumpable seat assembly (10) through the cylindrical tube (14) to the wellhead
(not shown). The
upper end (15) further comprises a time-dissolvable ball (28), which ball (28)
is sized to
generally sit into and cover the seat (16) formed in the upper portion (15) of
the cylindrical tube
(14) to prevent the flow of fluids such as those used for fracturing,
stimulating and the like from
flowing through the cylindrical tube (14) to the formation below the pumpable
seat assembly
(10). The ball (28), however, is dissolvable within a predetermined passage of
time to then allow
the flow of oil and gas from the formation below to the surface. Thus, the
dissolvable ball (28)
functions to temporarily restrict the flow through the cylindrical tube (14)
until it is desirable to
do so. The inner diameter (ID) of the cylindrical tube must be large enough so
that unrestricted
flow can occur therethrough. In one embodiment, the ID is about 2 inches but
can be larger,
depending upon the ID of the varying casings and the tools are run in therein.
[00024] An example of biodegradable balls that may be used in the present
invention is
BioBalls soluble ball sealers available from Santrol of Texas. It is
understood that other oil field
service providers can also supply dissolvable products. Generally, dissolvable
balls can include
biodegradable balls that can degrade over a period of hours or days when
exposed to a set of
predetermined environmental conditions. For example, the environmental
conditions can include
normal wellbore operating conditions of temperature and pressure at a
particular depth or
elevation in the wellbore, as well as the normal chemistry for drilling mud or
pumping/frac fluids
used during completion operations.
[00025] Figure 2 shows an embodiment of a well completion process of the
present
invention using a plurality of pumpable seat assemblies (10) of the present
invention. In Figure
2, a horizontal portion of a well is shown which has been cased in with casing
(12), such as steel
pipe casing. The casing (12) may be cemented in place in the well. The
horizontal well portion
in Figure 2 comprises five separate producing zones, zone A, zone B, zone C,
zone D and zone
E. The end of the casing (12) is shown as element (130). The first zone to be
fractured/stimulated would be the zone closest to the casing end (130),
namely, zone A. A
perforating apparatus (not shown) can be used to form perforations 132 in the
casing (12) and
fracing/stimulating fluids can then be pumped down to complete the
fracing/stimulating process.
[00026] The next producing zone to be perforated/fractured/stimulated
would now be zone
B. However, it is desirable that any fracing/stimulating fluids that are used
to stimulate zone B
WSLega1\049798\00313\ 9126098v1 6
CA 02816061 2013-05-16
do not reach zone A in order to prevent re-stimulating or re-fracturing an
already
stimulated/fractured zone/interval. Thus, pumpable seat assembly (10a) is
pumped downhole
and set just below zone B but above zone A. Dissolvable ball (28a) is then
pumped down to
cover the open seat of pumpable seat assembly (10a). This will then prevent
any
fracing/stimulating fluid from reaching zone A. After zone B is stimulated,
the next zone to be
perforated/fractured/stimulated is zone C, using a second pumpable seat
assembly (10b)which is
pumped down the wellbore casing (12) followed by a second dissolvable ball
(28b). After zone
C is stimulated, zone D is the next producing zone to be
perforated/fractured/stimulated using
pumpable seat assembly (10c) and dissolvable ball (10c). Finally, pumpable
seat assembly (10d)
and dissolvable ball (10d) is used when zone E is
perforated/fractured/stimulated.
[000271 From the foregoing description, one skilled in the art can easily
ascertain the
essential characteristics of this invention, and without departing from the
spirit and scope
thereof, can make various changes and modifications of the invention to adapt
it to various
usages and conditions. Thus, the present invention is not intended to be
limited to the
embodiments shown herein, but is to be accorded the full scope consistent with
the claims,
wherein reference to an element in the singular, such as by use of the article
"a" or "an" is not
intended to mean "one and only one" unless specifically so stated, but rather
"one or more". All
structural and functional equivalents to the elements of the various
embodiments described
throughout the disclosure that are known or later come to be known to those of
ordinary skill in
the art are intended to be encompassed by the elements of the claims.
Moreover, nothing
disclosed herein is intended to be dedicated to the public regardless of
whether such disclosure is
explicitly recited in the claims.
WSLega1\049798\00313\ 9126098v1 7