Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02832235 2013-10-03
Dispenser with table clamp
Technical Field
The present invention is directed to a dispenser for
disposable hygienic articles such as wipes or towels, soap,
or the like.
The hygienic articles may form a stack inside the dispenser
and be grasped by a user from the lower end of the stack
through a dispensing aperture. Some hygienic articles may be
provided on a roll, e.g. paper which at a free end may
protrude from a dispenser. Others may be provided in liquid
form, e.g. soaps or disinfectants.
Prior art
Such dispensers for hygienic articles are, for example,
mounted in restrooms or close to hand washbasins or sinks in
public establishments, industrial or kitchen premises. They
may be arranged standing on a horizontal surface such as a
tabletop. In general, however, they are mounted to a vertical
fastening surface such as a wall. Conventionally, the
dispensers are fastened to the wall by means of screws or
bolts, and they are provided with attachment holes in their
rear walls to this extent. WO-Al-2007/035139 discloses an
example.
In order to fasten the screws or bolts to the wall,
corresponding bore holes have to be prepared, which is
cumbersome and time consuming. Furthermore, in washrooms or
other areas exposed to high moisture, the fastening surfaces
are often covered with tiles or other water-tight layers.
Forming bore holes in this kind of surface is particularly
difficult and could, moreover, result in moisture intruding
into the holes. The bore holes also leave visible marks if
CA 02832235 2013-10-03
the screws or bolts are removed, e.g. because it is desired
to mount the dispenser at another location.
Furthermore, dispensers of the above' mentioned kind are also
Used in indu8try, for example in fabrication halls, where
they dispense paper for cleaning at workbenches or, wiping
spills of any kind. In this case, difficulties have occurred
in practice when the dispensers are only provided at a few
locations in a large fabrication hall, because the workmen
have to walk a relatively long distance every time they wish
to use an article from the dispenser. The workmen tend to get
a supply of paper and stack it on their workbenches, so that
it often gets dirty or moist before it is even used. In case
the dispensers are in the form of floor stands, they also
easily stand in the way, also when the floor is to be
cleaned.
On the other hand, there have been attempts to install such
dispensers where they are actually needed, e.g. on or close
to the workbenches as such. For example, magnets have been
used in order to fasten the dispensers to table tops or table
legs made from metal.
GB-A-2,443, 183 discloses a dispenser according to the
preamble of claim 1. Related devices are known from US-A-
6,119,992; US-A-5,297,749; US-A-1,793,682; and US-A-
4,004,687.
Disclosure of the invention
It is the object underlying the invention to provide a
dispenser which can be firmly but reversibly fastened to a
supporting structure such as the edge of a table or shelf.
The dispenser should remain securely attached when the
articles are grasped from the dispenser. The relatively large
weight of the dispensers, which may be in the order of
several kg, must also be taken into account.
CA 02832235 2013-10-03
In order to achieve this object, the present invention
provides a dispenser for hygienic articles comprising the
features of claim 1. The dispenser comprises a clamp suitable
for securing the dispenser to a supporting structure such as
the edge of a shelf or a table. The clamp includes a
stationary clamping part for engaging one side of the
supporting structure, a movable clamping part for engaging an
opposite side of the supporting structure, and means for
urging the clamping parts towards each other so as to tighten
the clamp about the supporting structure. Both the stationary
and the movable clamping parts each have a clamping face, and
a spacing between the clamping faces of the stationary
clamping part and the movable clamping part is variable so as
to adapt the clamp to supporting structures of different
thicknesses. The dispenser includes a dispenser housing for
accommodating the hygienic articles, and either the
stationary clamping part or the movable clamping part is
formed integral with the dispenser housing.
By means of its table clamp, which is an integral part of the
dispenser, the dispenser of the present invention can be
firmly but reversibly fastened to the supporting structure,
which can be the edge of a table or shelf or any other
supporting structure which may be gripped between the
clamping faces. The dispenser may be quickly affixed and also
easily detached from the supporting structure and relocated
if needed.
When the dispenser has been attached to the supporting
structure by means of the table clamp, it remains securely
attached. In this regard it is to be noted that there may be
rather considerable forces acting onto the dispenser, these
forces originating from the weight of the dispenser and the
articles contained therein on the one hand, and from the
actions carried out by the user on the other hand. For
example, the user may pull tissues out of the dispenser or
press an operating lever or the like in order to release a
portion of soap from the dispenser. The dispenser must be
CA 02832235 2013-10-03
attached so that it is not loosened also in the presence of
these considerable forces.
Optional features are recited in the dependent claims.
The clamping faces of the stationary clamping part on the one
hand and of the movable clamping part on the other hand are
preferably arranged in a spaced parallel relationship, and
the spacing between the clamping faces of the stationary
clamping part and the movable clamping part is preferably
variable in a direction which is essentially perpendicular to
the clamping faces. The spacing between the clamping faces of
the stationary clamping part and the movable clamping part
may then easily be varied so as to adapt the clamp to
supporting structures of different thicknesses.
The clamping faces may at least partly covered by protective
layers. These protective layers may for example be made from
a thermoplastic elastomer (TPE). They may be made as extra
parts which are then attached, e.g. glued, to the clamping
faces. The clamping faces and the protective layers could,
however, also be produced in a single process step, e.g. if a
2K injection molding process is employed.
As regards the table clamp as such, there are several
possibilities of how the clamp is designed. On the one hand,
the clamp may be a so-called C-/G-clamp, i.e. it may be
essentially C- or G-shaped and include a slot for being
disposed about the supporting structure. In this case, one
leg of the slot constitutes the stationary clamping part, and
the movable clamping part is supported on the opposite leg of
the slot so as to face the stationary clamping part.
In one embodiment, the movable clamping part is a threaded
rod having a head, and a rotation of the threaded rod results
in a translation of the head for tightening the clamp.
CA 02832235 2013-10-03
As an alternative, the movable clamping part includes a cam
surface and a lever, and the clamp is tightened by pivoting
the cam surface by means of the lever.
Furthermore, in one embodiment, the position of the movable
clamping part is also adjustable in the direction parallel to
the clamping faces, providing an additional degree of freedom
to the movable clamping part.
on the other hand, the table clamp could also be constructed
so that the movable clamping part is slidably supported
relative to the stationary clamping part by means of a rod,
and the spacing between the clamping parts is variable in the
longitudinal direction of the rod. In this case, at least a
part of the rod extends essentially at right angles with
respect to the clamping faces of the clamping parts. A first
end of the rod is attached to one of the clamping parts, a
second end of the rod extends through the other one of the
clamping parts, and a nut is in threaded engagement with the
second end of the rod and operable for urging the clamping
parts towards each other.
As an alternative, the means for urging the clamping parts
towards each other may include a spring biasing the movable
clamping part towards the stationary clamping part. The
spring biased table clamp would then correspond to a clamp
commonly known as a "quick clamp".
The movable clamping part of the table clamp could, for
example, provided in the form of a clamping block. In this
case the dispenser may further comprise means for guiding the
movable clamping block in its sliding movement towards and
away from the stationary clamping part.
The movable clamping part may be so arranged and constructed
as to be located at a certain distance from the edge of the
supporting structure in the mounted state of the table clamp.
CA 02832235 2013-10-03
This provides, on the one hand, for a favourable application
and distribution of the clamping forces provided by the
movable clamping part and the stationary clamping part. On
the other hand, as the head of the threaded rod is tightened
against the table plate at a point spaced from the table
edge, the head may also be located behind a frame or other
structure which may possibly be provided about the edge of
the table plate.
The distance is suitably chosen depending on the dimensions
of the dispenser to be clamped to the table edge. In
particular, the distance least one
third and more
preferably at least half of the width of the dispenser
housing, measured along the said edge and between the
farthest contact points between the dispenser housing and the
edge. Other parameters such as the height of the dispenser
housing may also be taken into account when determining the
distance.
Brief description of the Figures
The various aspects of the invention, including its
particular features and advantages, will be readily
understood from the following detailed description and the
accompanying drawings, in which:
Fig. 1 illustrates a dispenser,
Figs. 2a and 2b are perspective views of a bracket of the
dispenser,
Fig. 3 is a perspective view of a clamping block of the
dispenser, and
Figs. 4 to 6 show three alternative configurations of the
bracket and table clamp.
CA 02832235 2013-10-03
Detailed description of dispensers
The dispensers illustrated in Figures 1 to 6 are not in
accordance with the present invention, but are useful for
understanding the invention.
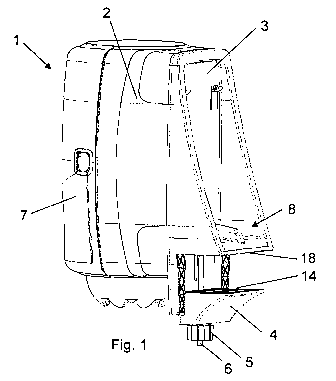
Fig. 1 illustrates a dispenser 1. The dispenser 1 is adapted
to contain a roll of paper towels. The dispenser 1 includes a
dispenser housing 2 in which the paper roll is to be
accommodated. The dispenser housing 2 is releasably fastened
to a bracket 3 in a manner described further below.
In order to firmly but reversibly attach the dispenser 1 to a
supporting structure such as the edge of a table, the
dispenser 1 includes a table clamp. In the present dispenser
1 this table clamp includes a stationary clamping part 8
which is formed integral with the bracket 3 and includes a
clamping face 18, and a movable clamping part which is
provided in the form of a clamping block 4 and includes a
clamping face 14. The clamping block 4 is movable insofar as
it can be slid towards and away from the stationary clamping
face 18. To this extent a rod 6 is provided which connects
the clamping block 4 with the bracket 3. The clamping faces
18, 14 are arranged in a spaced parallel relationship.
A cover 7 for closing the dispenser housing 2 is also
illustrated. The cover 7 may be pivoted about an essentially
vertical axis from the illustrated closed position to an open
position, in which an access opening provides access to an
interior of the housing 2. The cover 7 has a function of
protecting the paper roll inside the dispenser housing 2 from
humidity and dirt, and it may also be provided with a locking
mechanism. If desired, the locking mechanism may comprise a
removable key so that the cover 7 may be locked to the
housing 2 to prevent access to the access opening.
CA 02832235 2013-10-03
From Figure 1 it becomes also clear how a screw nut 5 is
provided in threaded engagement with the rod 6 so that by
turning the screw nut 5, the clamping block 4 may be urged
towards the stationary clamping face 18 of the bracket 3: In
order to fasten the dispenser 1 to a table edge, the
stationary clamping face 18 of the bracket 3 is engaged with
one side of the table plate, the movable clamping face 14 of
the block 4 is engaged with the opposite side of the table
plate, and the screw nut 5 is operated for urging the
clamping block 4 towards the stationary clamping face 18 of
the bracket 3 so as to tighten the table clamp about the
table edge.
Due to the sliding connection of the clamping block 4 via the
rod 6, the spacing between the clamping faces 18, 14 of the
bracket 3 and the clamping block 4 is easily variable in a
direction which is essentially perpendicular to the clamping
faces 18, 14, and in the longitudinal direction of the rod 6,
so as to adapt the table clamp to table plates of different
thicknesses. The dispenser 1 is mainly intended to be used
with workbenches or worktables, and therefore, the spacing
between the clamping faces is adjustable between 15 and 60
mm, which corresponds to the table thicknesses commonly
encountered in workbenches or worktables.
The rod 6 in and of itself is essentially L-shaped. The
longer part thereof extends essentially at right angles with
respect to the clamping faces 18, 14 of the clamping parts.
The shorter part extends parallel with the clamping face 18
of the stationary clamping part or bracket 3, respectively.
Turning now to Figures 2a and 2b, the structure of the
bracket 3 will be explained in more detail. Note that Figure
2a shows the bracket 3 only, whereas Figure 2b also
illustrates the movable clamping block 4, screw nut 5 and rod
6.
CA 02832235 2013-10-03
The bracket 3 has a generally longitudinal shape and is
mainly constituted by a plate structure 12. Furthermore, as
already explained, the bracket 3 includes the stationary
clamping part 8 as an integral part thereof, which in the
present dispenser 1 is constituted by a wall extending at a
right angle from the rear side of the plate structure 12,
i.e. the side opposite the front side to which the dispenser
housing 2 is attached.
On both sides of the plate structure 12 there are stiffening
side walls 16 which are perpendicular to both the plate
structure 12 and the stationary clamping part 8. In the
present dispenser 1, the stiffening side walls 16 have a
slightly curved shape: the upper ends of the stiffening side
walls 16 at the very top of the plate structure 12 is rather
narrow, and the side walls 16 gradually become wider towards
the bottom ends thereof at which they are connected with the
stationary clamping part 8.
The stationary clamping part 8 is not provided at the very
bottom end of the plate structure 12, but the plate structure
further extends beyond the stationary clamping part 8; the
extension is designated 19 in Figure 2b. The extension 19 is
also formed with a guiding structure for guiding the movable
clamping block 4 in its movement towards and away from the
stationary clamping part 8: A shallow groove 9 is formed in
the extension 19 which is slightly wider than the clamping
block 4.
In the dispenser 1, the entire bracket 3 is injection moulded
from acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). The plate
structure 12 as such is a rigid element, whereas the
stationary clamping part 8 as well as the stiffening side
walls 16 are double walled, hollow structures. Consequently,
the double-walled stationary clamping part 8 has a bottom
wall 81 and a top wall 82, and the stiffening side walls 16
CA 02832235 2013-10-03
each have an inner wall 161 and an outer wall 162 (see Figure
2b).
In order to accommodate the shorter end of the L-shaped rod
6, the bracket 3 is further provided with an accommodating
channel 20. The channel 20 co-extends with the double walled
stationary clamping part 8 and has an open end at the front
side of the bracket 3 and a closed end at the rear side of
the bracket 3. The channel 20 is delimited by the bottom wall
81 of the double-walled stationary clamping part 8, by two
side walls extending at right angles thereto, and by a top
wall. As shown in Figure 2a, the side walls and the top wall
of the rod accommodating channel 20 protrude from the top
wall 82 of the stationary clamping part so as to form a
protuberance 90.
The shorter end of the L-shaped rod 6 is inserted into the
rod accommodating channel 20 from the front side of the
bracket 3. The longer end of the L-shaped rod 6 extends
through an opening within the bottom wall 81 of the double
walled stationary clamping part 8. In the present dispenser 1
this opening has the form of a slit 22 which extends not only
in the bottom wall 81 of the stationary clamping part 8 but
further into the extension 19 of the plate structure 12. In
any event the longer end of the L-shaped rod 6 co-extends
with the extension 19 on the rear side thereof, so that the
clamping block 4 can be supported on the rod 6 in a manner to
be described below.
For attaching the dispenser housing to the bracket, four
knobs 17 are provided protruding from the front face of the
bracket. Adjacent two of these knobs 17 there are also
release tabs 10 provided which can be operated from the rear
side of the bracket 3 so as to release the dispenser housing
2 from the bracket 3. The dispenser housing 2 may
alternatively be attached to the bracket 3 by other means
which are per se known in the art.
CA 02832235 2013-10-03
The movable clamping block 4 is further illustrated in Figure
3. The block 4 is also an injection moulded structure and may
be made from glass fibre reinforced material, e.g. polyamide
or polyoxymethylene (P0M), so as to provide the required
strength and stiffness. It has a flat front face 41 which, in
the mounted state, faces the guiding groove 9 formed in the
extension 19 of the bracket 3. The bottom face 42 is also
flat and extends at right angles with the front face 41. The
side faces 44 are slightly curved, similar as the stiffening
side faces 16 of the bracket 3, and they are narrow at their
bottom ends adjacent the bottom face 42 and wider at their
top ends adjacent the top surface of the block, which forms
the clamping face 14 of the movable clamping block 4. The
block 4 as such is essentially hollow, but stiffening walls
24 are provided therein which extend parallel with the side
walls 44 of the block 4. In the present dispenser 1 there are
three such stiffening walls 24 inside block 4, and they are
equally spaced, but of course other numbers and arrangements
are possible.
Adjacent its front surface 41, the block 4 further comprises
a through hole 26 for accommodating the longer end of L-
shaped rod 6. In the mounted state, the longer end of the rod
6 extends through this through hole 26, and the screw nut 5
(see for example Figure 1) is screwed onto the free end of
the rod 6. The screw nut 5 is in threaded engagement with the
longer end of the rod 6 and operable for urging the
stationary clamping part 8 of the bracket 3 and the movable
clamping block 4 towards each other. To this extent, at least
that part of the rod 6 which is to be in engagement with the
nut 5 is provided with an external thread. Although not
shown, a stop may be provided at the very end of the rod 6,
e.g. in the form of a rubber cap, so as to prevent the screw
nut 5 from becoming disengaged from the rod 6.
CA 02832235 2013-10-03
Connecting the movable clamping block 4 with the stationary
clamping part 8 via the L-shaped rod 6 in this manner results
in a proper distribution of the clamping forces about the
clamping faces 18, 14 of the bracket 3 on the one hand and
the block 4 on the other hand. The force distribution is
important in order to provide a reliable clamping force, in
particular also in view of the considerable weight of the
dispenser 1.
Although not shown, at least one of the stationary clamping
face 18 and the movable clamping face 14 may be partly or
entirely covered by a protective layer, so as to protect both
the clamping face 18, 14 and the surface of the supporting
structure to which the table clamp is attached. The
protective layer would preferably be made from a TPE.
In the dispenser 1 described above, the bracket 3 includes
the plate structure 12, the stationary clamping part 8 and
the extension 19 for guiding the movable clamping block 4.
This is, however, only one possibility for configuring the
dispenser. Various alternative configurations are shown in
Figures 4 to 6 and will be described in the following.
Turning first to Figures 4a and 4b, these Figures show a
dispenser in which the bracket 3 is constituted by a
;
framework rather than a plate structure. In the dispenser,
the framework is constituted by tubes 11 and also includes
tube ends 11' forming the stationary clamping part 8 which
consequently is integrated with the bracket 3 also in this
dispenser. Round tubes 11 are used in the dispenser, but the
tubes could also be oval or square. Beams having, for
example, an I or H type profile could also be used to form
the framework, as long as the necessary stiffness is
provided.
The movable clamping part 4 is in this case constituted by a
threaded rod 13 which is in threaded engagement with an
CA 02832235 2013-10-03
extension 15 of the framework. During use, the extension 15
extends on the side of the support structure or table plate T
opposite the stationary clamping part 8. In a way, therefore,
the stationary clamping part 8 and the extension 15 form the
two legs of a slot into which the support structure T is
inserted. For fastening the table clamp to the support
structure T, the distance between the stationary clamping
part 8 and a head 17 of the threaded rod 13 is first adjusted
to a spacing slightly larger than the thickness of the
support structure T, and the threaded rod 13 is then
tightened towards the support structure T.
As the threaded rod 13 is engaged near the free end of the
extension 15, the head of the rod 13 is located at a certain
distance d (see Fig. 4a) from the edge of the table plate T.
This provides, on the one hand, for a favourable application
and distribution of the clamping forces provided by the
movable clamping part 4 and the stationary clamping part 8.
On the other hand, as the head of the threaded rod is
tightened against the table plate T at a point spaced from
the table edge, the head may also be located behind a steel
frame F which may possibly be provided about the edge of the
table plate T. The possible location of such a steel frame F
is indicated in dotted lines in Figure 4a.
The distance d is suitably chosen depending on the dimensions
of the dispenser to be clamped to the table edge. In
particular, the distance d may be chosen depending on the
width w of the dispenser housing 2, the width w being
measured along the table edge and between the farthest
contact points between the dispenser housing 2 and the table
edge (see Figure 4b), so that the distance d equals at least
one third of the width w. Other parameters such as the height
of the dispenser housing 2 may also be taken into account
when determining the distance d.
_
CA 02832235 2013-10-03
The dispenser housing 2 in and of itself remains unchanged if
compared with the dispenser shown in Figures 1 to 3, apart
from the fact that the means for connecting the dispenser
housing 2 to the bracket 3 will of course differ dependent on
the structure of the bracket 3.
As another alternative to the dispensers described above, the
bracket and table clamp could also be constituted as shown in
Figure 5. In this case, the bracket 3 includes a plate
structure 12 similar as in the dispenser of Figures 1 to 3.
This time, however, the stationary clamping part 8 is present
in the form of two tube ends 31 attached to the plate
structure. The plate structure further includes, as an
integral part, an extension 32 which extends on the side of
the support structure T opposite the stationary clamping part
31 during use. The extension 32 is perpendicular to the
actual plate structure 12, and a threaded rod 33 is in
threaded engagement with the extension 32. The threaded rod
33 has a head (not visible) which is tightened against the
support structure T and provides the movable clamping part 4,
in a manner similar to the dispenser of Figure 4.
In the case of Figure 5, the movable clamping part 4 is also
adjustable in a direction parallel to the clamping faces: The
threaded rod 33 can be offset along a slot 37 formed in the
extension 32 so as to be located nearer to or further away
from the dispenser housing 2. This provides an additional
degree of freedom to the movable clamping part 4, by means of
which the table clamp could also be adjusted so that the
threaded rod is tightened against a table plate T at a point
located at a distance from the table edge, e.g. also at a
point located behind a frame, e.g. a steel frame, which may
possibly be provided about the edge of the table plate (as
indicated in dotted lines in Figure 4a). Depending on the
dimensions and location of the steel frame in individual
cases, the table clamp may then be fixed on either side of
CA 02832235 2013-10-03
the steel frame by suitably adjusting the location of the
movable clamping part 4 or threaded rod 33, respectively.
Finally, in the dispenser of Figure 6, the bracket 3 is
constituted by a continuation of the dispenser housing 2 in
the rear direction, wherein this continuation has essentially
the shape of a triangular prism. The stationary clamping part
8 of the table clamp is provided by the bottom surface of
this triangular prism. For providing the movable clamping
part 4, a first rod 23 extends from the dispenser housing in
the longitudinal direction thereof, and a second rod 25 is
attached thereto essentially at right angles and so as to be
slidable in the longitudinal direction of the first rod 23.
In the dispenser, both rods 23, 25 are square rods, but any
other shape is possible as long as rod 25 cannot rotate about
rod 23. Consequently, rod 23 could be square, rectangular,
oval, or triangular, etc., and rod 25 could have an arbitrary
cross section. In any event, by sliding the second rod 25
relative to the first one 23, the spacing between the
clamping faces can be adjusted also in this case. The actual
clamping force is provided by a camshaft and lever action: to
the free end of the second rod 25, a cam 27 is fixed so as to
be pivotable about an axis perpendicular to both the first 23
and the second rod 25. The cam 27 is eccentric and can be
operated or pivoted, respectively, by means of a lever 29. In
the rotational position of the lever 29 shown in Figure 6,
the table clamp is fixed. By actuating the lever 29 in the
counter clockwise direction, the cam 27 would be pivoted so
as to loosen the table clamp from the support structure T.
Note that also in the dispenser of Figure 6, the movable
clamping part is located at a distance d from the edge of the
table plate T. In fact, in all the dispensers of Figures 4 to
6, the clamping face of the movable clamping part is
tightened against a point of the support structure which is
offset from the edge of the table plate. This provides for a
A =/,11,,,f,
CA 02832235 2013-10-03
more favourable application and distribution of the clamping
forces.
It is to be noted that the above dispensers use particular
combinations of brackets and table clamps. It would, however,
as well be possible to use further combinations of any of the
brackets disclosed above with an arbitrary table clamp, or
any of the table clamps disclosed above with an arbitrary
bracket. For example, a bracket as shown in Figure 4, using a
framework, could also be used together with a table clamp as
shown in Figure 6, employing the cam and lever principle.
All the dispensers described above can be firmly but
reversibly fastened to workbenches as they are commonly used
in larger heavy industries, or to worktables as they are more
commonly used in other types of industries such as electronic
packaging. The dispensers can be firmly but reversibly
attached to various locations of such workbenches or
worktables, in particular to the edge of the respective table
top but also to the legs of the tables. Using the table
clamp, the dispenser may as well be mounted upside down, or
mounted sideways to a table leg.
The dispensers described above are dispensers for dispensing
rolled paper towels. However, the contents of the dispenser
is not important for the invention, and the invention can be
used for many other types of dispensers for disposable
hygienic articles.
The brackets 3 of the above dispensers are for use with a
single type of dispenser housing 2. However, the bracket 3
could also be so arranged and constructed that dispenser
housings of different sizes and/or different types can be
releasably secured thereto. This is preferably achieved by
providing the bracket 3 with suitable fastening means,
without having to modify the dispenser housings as such. For
CA 02832235 2013-10-03
example, the knobs 17 and release tabs 10 provided in the
first one of the above described dispensers would have to be
suitably modified or replaced by more versatile means for
attaching the dispenser housing 2.
Furthermore, in order to mount the dispenser so supporting
structures which are not plate-shaped, e.g. round legs of a
table or chair, the clamping faces 18, 14 could be modified
or supplemented with suitable clamping inserts.
Finally, although the bracket 3 is releasably attached to the
rear of the dispenser housing 2 in the above dispensers, it
could generally also be attached to any other side of the
dispenser housing 2.
The dispenser according to the invention does not have a
mounting bracket, but either the stationary clamping part or
the movable clamping part is formed integral with the
dispenser housing as such. In all other respects, however,
the dispenser of the invention is in accordance with the
dispensers described above.